Community Ecology: Species Interactions, Competition, Predation, and Succession
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What is a community in ecology?
A community is a group of species that occur at any particular locality.
What characterizes a biological community?
Species richness and primary productivity.
What does species richness refer to?
The number of species present in a community.
What is primary productivity?
The amount of energy produced in a community.
How does community composition change?
It changes continually along environmental gradients, such as moisture.
What is an ecological niche?
The total of all the ways an organism uses the resources of its environment.
What are the components of an ecological niche?
Space utilization, food consumption, temperature range, mating conditions, and moisture requirements.
What is interspecific competition?
Competition that occurs when two species attempt to use the same resource and there is not enough to satisfy both.
What is interference competition?
Physical interactions over access to resources between species.
What is exploitative competition?
Competition that occurs when species consume the same resources.
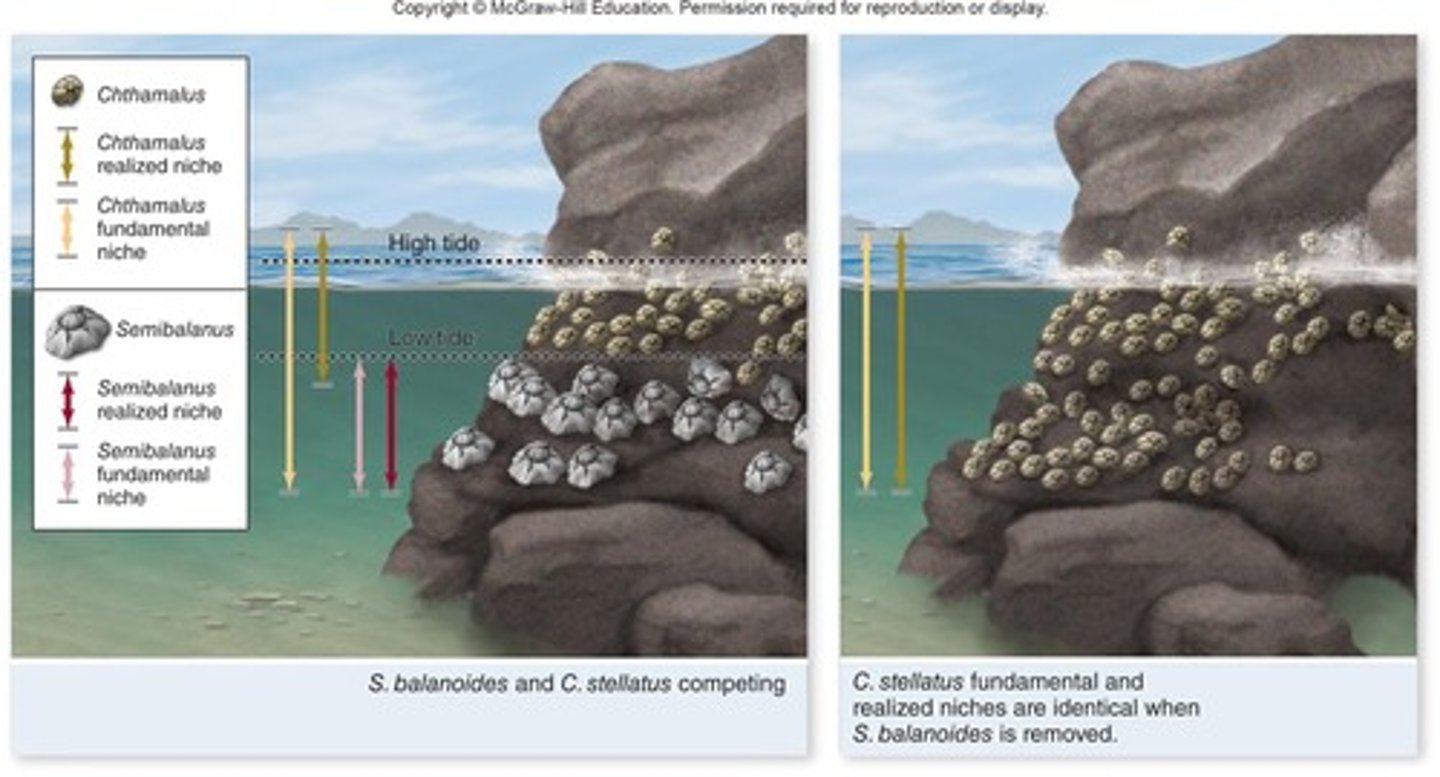
What is a fundamental niche?
The entire niche that a species is capable of using based on its physiological tolerance limits and resource needs.
What is a realized niche?
The actual set of environmental conditions and presence of other species in which a species can establish a stable population.
What is the competitive exclusion principle?
Species with the same requirements cannot coexist in the same place with the same resources.
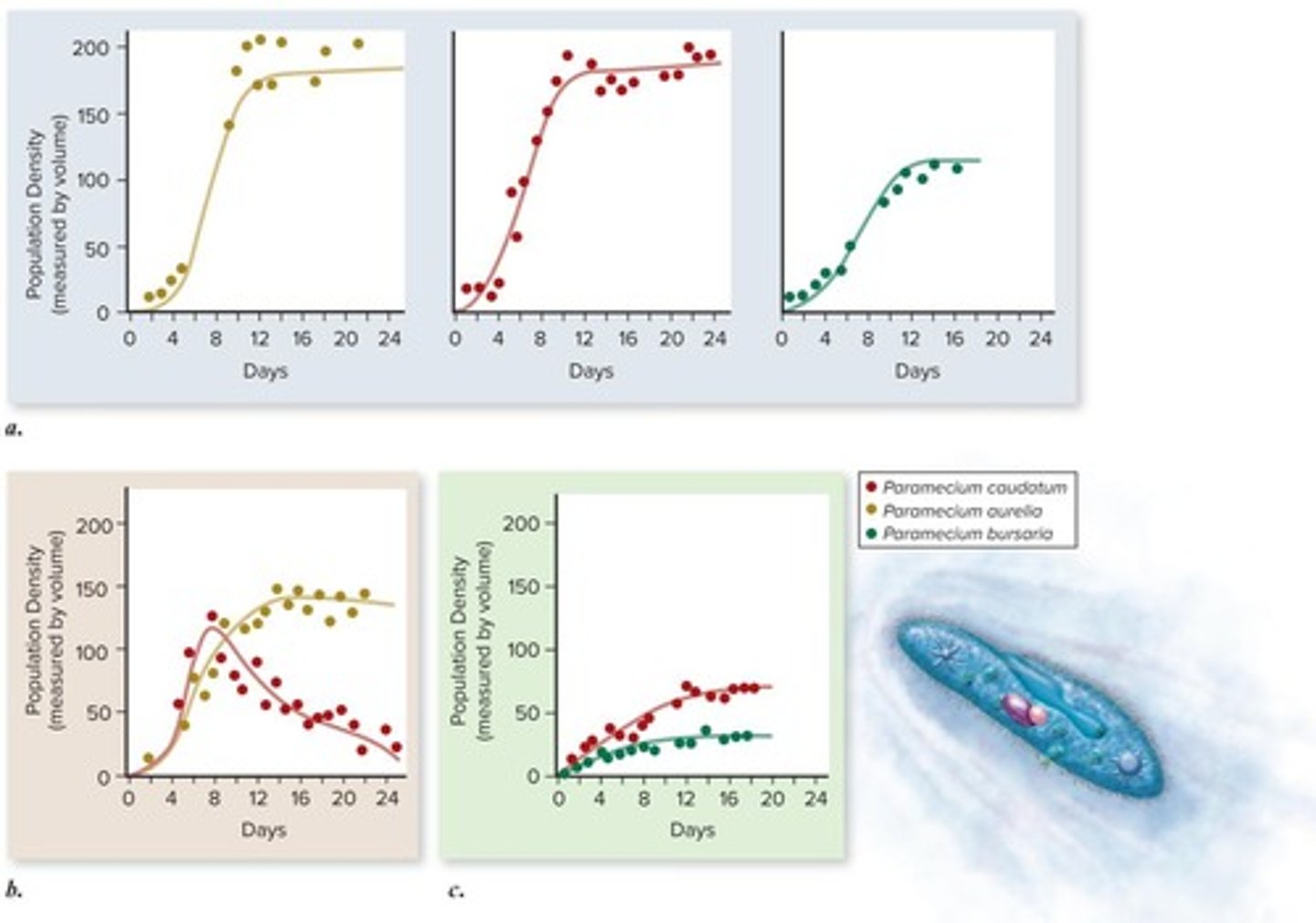
What did G.F. Gause's experiment demonstrate?
It demonstrated the competitive exclusion principle using three Paramecium species.
What is resource partitioning?
The division of resources among similar species to avoid direct competition.
What is character displacement?
Differences in morphology evident between sympatric species, often resulting from natural selection.
What is predation?
The consuming of one organism by another.
How does predation affect prey populations?
Predation strongly influences prey populations, often leading to declines.
What is an example of an invasive species affecting local wildlife?
The Burmese python in the Florida Everglades, which caused major declines in native wildlife populations.
What percentage decline did raccoons experience due to the Burmese python?
99.3% decline.
What percentage decline did white-tailed deer experience due to the Burmese python?
94.1% decline.
What is the significance of studying ecological niches?
Understanding ecological niches helps explain species interactions and community dynamics.
What role does natural selection play in resource partitioning?
Natural selection can lead to resource partitioning among similar species occupying the same geographic area.
What is the relationship between niche restriction and species presence?
Niche restriction can occur due to the presence or absence of predators and pollinators.
What is the impact of competitive exclusion on biodiversity?
Competitive exclusion can reduce biodiversity by preventing similar species from coexisting.
How can ecological niches be affected by environmental changes?
Changes in environmental conditions can alter the availability of resources and affect species interactions.
What can happen to prey populations?
They can experience explosions and crashes.
What is an example of a prey population crash?
The extinction of the Stephen Island wren in New Zealand due to a single cat.
What is coevolution in the context of predation?
A race where prey evolve defenses against predators while predators evolve better hunting strategies.
How do plants adapt to herbivory?
Plants evolve mechanisms such as chemical defenses to protect themselves from herbivores.
What are secondary compounds in plants?
Chemical defenses that include oils and toxins to deter herbivores.
What is the role of monarch butterfly caterpillars in chemical defense?
They incorporate cardiac glycosides from milkweed for protection against predation.
What do poison dart frogs produce for defense?
Toxic alkaloids in the mucus covering their brightly colored skin.
What is aposematism?
A warning coloration used by poisonous insects and animals to signal danger to predators.
What is cryptic coloration?
A form of camouflage that allows animals to blend in with their surroundings.
What is mimicry in ecological terms?
When one species resembles another to gain an advantage, often for protection.
What is Batesian mimicry?
When a palatable mimic resembles an unpalatable model to avoid predation.

What is Müllerian mimicry?
When several unrelated but poisonous species evolve to resemble one another.

What are the three major types of symbiosis?
Commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism.
What is mutualism?
A symbiotic relationship that benefits both species involved.
How do ants and acacias demonstrate mutualism?
Acacias provide shelter and food for ants, while ants protect acacias from herbivores.
What is parasitism?
A relationship where one species benefits at the expense of another.
What are ectoparasites?
Parasites that feed on the exterior surface of a host organism.
What are parasitoids?
Insects that lay eggs on living hosts, with larvae feeding on the host's body.
What is the potential for coevolution in symbiotic relationships?
Symbiotic relationships can lead to adaptations in both species involved.
What is an example of a parasitic relationship between ants and acacias?
Some ants clip acacia branches to prevent other ants from living in the tree, harming the acacia.
How does predation affect ecological processes?
Predation can influence the dynamics of prey populations and the overall ecosystem.
What is the significance of chemical defenses in animals?
They help protect animals from predation by making them unpalatable or toxic.
What is the relationship between herbivores and plant defenses?
Herbivores may coevolve with plants, developing adaptations to overcome plant defenses.
What ecological process can affect the outcome of another process?
The occurrence of predation can influence competition and mutualistic interactions.
What is an external parasite?
An organism that obtains its food from a host plant, such as the flowering plant dodder.
What are endoparasites?
Parasites that live inside their host.
What is a characteristic of endoparasites?
They exhibit extreme specialization for the host they invade.
What is a complex life cycle in parasites?
A life cycle involving more than one host.
What is Dicrocoelium dendriticum?
A flatworm that uses ants as an intermediate host and cattle as its definitive host.
How does Dicrocoelium dendriticum affect ants?
It changes the behavior of ants, causing them to climb to the top of a blade of grass to be eaten by cows.
What is commensalism?
A relationship where one species benefits and the other is neutral.
Give an example of commensalism.
Spanish moss hanging from trees.
How do oxpeckers interact with grazing animals?
Oxpeckers eat parasites off grazers but may also pick scabs and drink blood.
What is the role of predation in competition?
Predation, such as starfish eating barnacles, allows other species to thrive by reducing competition.
What defines a keystone species?
A species whose impact on the community is greater than expected based on its abundance.
How do sea stars act as a keystone species?
Their predation on barnacles increases species richness in the marine community.
What role do beavers play as a keystone species?
Beavers create dams that transform streams into ponds, creating new habitats.
What is primary succession?
The process of community development on bare, lifeless substrates.
Where does primary succession occur?
On surfaces like open water, rocks, and areas behind retreating glaciers.
What is secondary succession?
Succession that occurs in areas where an existing community has been disturbed but some organisms remain.
What are the three dynamic concepts in succession?
Establishment, facilitation, and inhibition.
What characterizes early successional species?
They are often r-selected species that are tolerant of harsh conditions.
What is the role of facilitation in succession?
Early species introduce changes that favor the establishment of later species.
What does the inhibition concept in succession imply?
Changes caused by one species inhibit the growth of the original species.
How can animal communities change during succession?
Animal species can change in synchrony with vegetation, affecting pollination and dispersion.
What factors cause communities to change?
Climatic changes, species invasions, and disturbance events.
What is the Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis?
Communities with moderate disturbance levels have higher species richness than those with little or great disturbance.
Why is understanding disturbance important in ecology?
Disturbance is common and plays a crucial role in structuring communities.