Triple Science Test
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What is speed?
Speed is how far something moves in a certain time.
What is the equation for speed?
Speed (m/s) = distance travelled (m) / time taken (s)
What is speed measured in?
Speed is measured in metres per second (m/s).
What is relative motion?
Relative motion compares how fast one object is moving to another.
How is relative speed measured?
If the 2 objects are moving with each other: Relative Speed = Object 1 - Object 2
If the 2 objects are moving towards each other: Relative Speed = Object 1 + Object 2
How to find the average speed from a distance-time graph?
To find the average speed from a distance-time graph: Average Speed (m/s) = Distance Covered (m/s) / Time Taken (s)
What is pressure?
Pressure is the force exerted on a surface due to weight.
What is pressure measured in?
Pressure is measured in:
Pascals (Pa) / N/m²
N/cm²
Why do studded boots grip on grass?
Studded boots grip on grass by concentrating force over a small area, increasing pressure to push the studs into the surface.
Why do snowshoes help walk in snow?
Snowshoes help walk in snow by spreading weight over a larger area, reducing pressure and preventing sinking.
What is the equation for pressure?
Pressure (N/m²) = force (N) / area (m²)
How is gas pressure produced?
Gas pressure is produced by the collision between gas molecules and their container.
What are the dependent variables of gas pressure?
Volume of container - as the size of the container decreases, the particles collide more with their container.
Temperature - as temperature increases, the particles gain more energy so they move faster and collide more.
Gas particle gradient - more gas molecules lead to more collisions.
What is atmospheric pressure?
Atmospheric pressure is the force exerted by the weight of the Earth's atmosphere on an area.
As altitude increases, how is atmospheric pressure affected and why?
As altitude increases, the air is less dense so there are less collisions between gas particles and there is less force exerted down on the object, so atmospheric pressure decreases.
As altitude decreases below sea level, how is atmospheric pressure affected and why?
As altitude decreases below sea level, there is more water exerting weight down on the object, so atmospheric pressure increases.
Why are solids and liquids incompressible?
Solids and liquids are incompressible as all the particles are in contact, so they transfer pressure without a change in volume.
Why do objects float?
Objects float when the upthrust caused by liquid pressure is greater than or equal to the object’s weight.
What is a moment?
A moment is the turning effect of a force around a pivot.
What is a moment measured in?
A moment is measured in newton metres (Nm).
What is the equation for a moment?
Moment (Nm) = force (N) × perpendicular distance from pivot (m)
What is the law of moments?
The law of moments is that during equilibrium, the total clockwise moments are equal to the total anticlockwise moments.
What is a habitat?
A habitat is where an organism lives.
What is a population?
A population is all the organisms of one species living in a habitat.
What is a community?
A community is all the populations of different species living in a habitat.
What are abiotic factors?
Abiotic factors are non-living factors of the environment.
What are examples of abiotic factors?
Moisture level
Light intensity
Temperature
CO₂ level
Wind direction and intensity
O₂ level
Soil pH and mineral content.
(My LIGHT Tiger COoked WIND On SOIL)
What are biotic factors?
Biotic factors are living factors of the environment.
What are examples of biotic factors?
New predators
Competition
New pathogens
Availability of food
(NEver COMe NEar Apples)
What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is the interaction of a community of biotic organisms with the abiotic aspects of their environment.
What is a niche?
A niche is the role of an organism in its habitat.
Why do organisms compete?
Organisms compete to survive and reproduce.
What do plants compete for?
Light
Space
Water from the soil.
Mineral ions from the soil.
What do animals compete for?
Territory
Food
Water
Mating Partners
What is interdependence?
Interdependence is species relying on other species for food, shelter, pollination, seed dispersal etc.
What is the disadvantage of interdependence?
The disadvantage of interdependence is that if one species is affected, it can disrupt the entire ecosystem, leading to population declines or extinctions.
Why may there be population declines or extinctions?
Population declines or extinctions may occur if there is less food or there are more animals being consumed.
What are stable communities?
Stable communities are communities where all the species and abiotic factors are in balance so the population sizes are roughly constant.
What are examples of stable communities?
Tropical Rainforests
Ancient Oak Woodlands
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process of plants transforming light energy into chemical energy for food.
Where does photosynthesis occur?
Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts containing chlorophyll that absorbs light.
How is energy transferred by photosynthesis?
Energy is transferred from the environment to the chloroplasts by light during photosynthesis.
What type of reaction is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction, which means that energy is transferred from the environment.
What is the word and balanced symbol equation for photosynthesis?
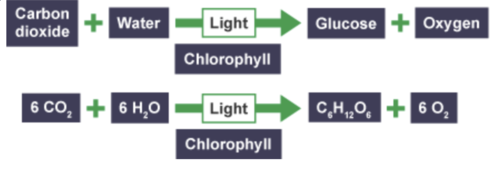
How do plants use glucose?
Respiration - transfers energy from glucose enabling the plants to convert the rest of the glucose into other useful substances.
Cellulose Production - glucose converts to cellulose to make strong cell walls.
Amino Acid Production - glucose combines with nitrate ions to make amino acids which are then made into proteins.
Oil and Fat Storage - glucose turns into lipids to store in seeds.
Starch Storage - glucose turns into starch and is stored in roots, stems and leaves for winter when photosynthesis pauses.
(Roaring Chickens Arrived On Scene)
How is the rate of photosynthesis affected?
Light intensity - provides the energy required for photosynthesis.
CO₂ concentration - a raw material required for photosynthesis.
Temperature - the energy of the enzymes required for photosynthesis.
Amount of chlorophyll - light must be absorbed for photosynthesis.
(LIGHT COuld TEar Apart)
How are leaves adapted for photosynthesis?
Lots of green chlorophyll - absorbs sunlight.
Thin - allows gases to diffuse in and out of the leaf.
Large surface area - absorbs as much light as possible.
Veins - xylem and phloem transport water and glucose.
(LOTS To Learn Vick!)
What are fertilisers?
Fertilisers are natural or artificial materials added to soil to provide essential nutrients and improve plant growth.
What are the minerals required for plant growth?
Nitrates - growth.
Phosphates - healthy roots.
Potassium - healthy leaves and flowers.
Magnesium - chlorophyll production.
What is a guard cell?
A guard cell is a kidney shape that opens and closes stomata in a leaf.
What are the adaptations of guard cells?
Fills with the plant when it has lots of water and goes plump and turgid, making the stomata open so gases can be exchanged for photosynthesis.
Loses water and become flaccid, making the stomata close when the plant is short on water, stopping water vapour from escaping.
Thin outer and thick inner walls make the opening and closing work.
Sensitive to light and closes at night to save water without losing out on photosynthesis.
Located on the undersides of leaves so less water is lost.
Where does most photosynthesis occur in a leaf and why?
The palisade layer is where most photosynthesis occurs as it contains the most chloroplasts and is closest to the light source.
What is the spongy mesophyll?
The spongy mesophyll is a layer in the leaf having spaces to allow gas exchange during photosynthesis.
What is the waxy cuticle?
The waxy cuticle is a waterproof layer reducing water loss by evaporation and acting as a barrier to the entry of pathogens in a leaf.
What is the upper epidermis?
The upper epidermis is a transparent layer on top of the leaf that lets light through and reduces water loss.
What is the lower epidermis?
The lower epidermis is the bottom layer of a leaf with stomata for gas exchange and guard cells controlling water loss.
What is respiration?
Respiration is the transfer of energy from glucose occurring in every cell.
What is aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is the release of energy using oxygen that always occurs in organisms.
Where does aerobic respiration mostly occur?
Aerobic respiration mostly occurs in the mitochondria.
What is the word and balanced symbol equation for aerobic respiration?
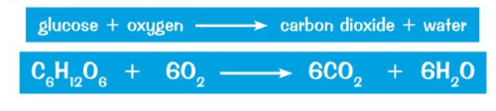
How is aerobic respiration performed?
Glucose is absorbed from the small intestine into the blood plasma and is transported to the cells where it diffuses in.
Oxygen is breathed in and diffuses into the bloodstream and is then carried by haemoglobin to the cells where it diffuses in.
Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the cells into the blood plasma and gets transported to the lungs where it diffuses into the air sacs and is exhaled.
What is anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration is the release of energy when the body lacks oxygen.
Why does aerobic respiration transfer more energy than anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration transfers more energy than anaerobic respiration because glucose isn’t fully oxidised in anaerobic respiration.
What is the word and balanced symbol equation for anaerobic respiration?
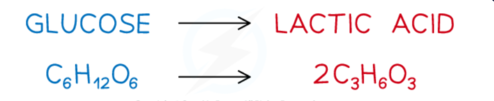
Where does lactic acid accumulate during anaerobic respiration and what does this lead to?
Lactic acid accumulates in the muscles during anaerobic respiration, leading to cramps.
How can lactic acid from anaerobic respiration be decomposed and why is this?
Lactic acid from anaerobic respiration be decomposed by increased inhalation as it will be decomposed to pyruvate by oxygen.
What is oxygen debt?
Oxygen debt is the amount of extra oxygen the body needs after exercise to decompose lactic acid from anaerobic respiration.
What is fermentation?
Fermentation is anaerobic respiration in yeast cells.
What is the word and balanced symbol equation for fermentation?

What can fermentation produce from yeast?
Bread
Beer
Wine
What makes bread rise during fermentation?
Carbon dioxide makes bread rise during fermentation.
What does a food chain represent?
A food chain represents the transfer of energy between organisms.
What do arrows in a food chain represent?
Arrows in a food chain represent the direction of energy transfer.
What does a food web represent?
A food web represents all connections of energy flow throughout all organisms in an ecosystem.
What is a consumer?
A consumer is an organism obtaining energy by feeding on other organisms.
What is a producer?
A producer is a plant at the start of a food chain that photosynthesises to produce food.
What is a herbivore?
A herbivore is a consumer of only producers.
What is a carnivore?
A carnivore is a consumer of only animals.
What is an omnivore?
An omnivore is a consumer of producers and animals.
What is a prey?
A prey is an organism eaten by a predator.
What is a predator?
A predator is an organism eating prey.
What is an apex predator?
An apex predator is the last link in a food chain.
What are pesticides?
Pesticides are chemicals intended to kill organisms that damage crops, which are poisonous to consumers.
What is bioaccumulation?
Bioaccumulation is the build-up of harmful or toxic materials - such as pesticides - in a food chain.
What is the trend of predator and prey populations and why?
When prey numbers increase, predators have more food, so their population grows.
As predator numbers rise, they eat more prey, causing the prey population to decrease.
With less prey available, predator numbers then decline.
This allows the prey population to recover, starting the cycle again.
Why is the predator-prey cycle out of phase with each other?
It takes a while for a population to respond to another e.g. when the rabbit population increases the fox population doesn't increase immediately as it takes time for them to reproduce.
What is chemosynthesis?
Chemosynthesis is bacteria producing chemical reactions to produce glucose for food.
How does chemosynthesis often use chemicals?
In chemosynthesis, chemicals are used as the source of energy and CO2 is often used as a reactant.
Where does chemosynthesis occur?
The bottom of the ocean via hydrothermal vents exerting chemicals.
The soil near volcanic vents.
What is a quadrat?
A quadrat is a square frame enclosing a known area that samples and shows the distribution of organisms that are not very stationary.
How is a quadrat used?
Divide your sample area into a grid.
Place a 1m² quadrat on the ground at a random point within the sample area.
Count all the organisms within the quadrat.
Repeat with random coordinates for several times.
Divide the total number of organisms by the number of quadrats to get the mean number of daisies per m².
What is a transect?
A transect is a line used to study the distribution of organisms across an area.
How is a transect used?
Mark out a line in the area being studied using a tape measure.
Count all the organisms touching the line or use quadrats at linear intervals.