Competition Policy
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Who enacts competition policy
CMA Competition and Markets Authority
What are the aims of competition policy
To protect public interests
What would competition policy achieve
Prevents excessive pricing and exploitation of consumers
Promotes competition within the market
Ensures standards, quality and choice
Natural monopolies are regulated particularly with essential products
Promotes technological innovation - ensuring some profits are invested
When will the CMA intervene
To break up cartels and punish those involved with cartel agreements
Investigating mergers - if a merger results in a market share of over 25 percent they may intervene to prevent this
Liberalise concentrated markets
Monitor state aid control - Subsidies given to farmers for example do not harm competition between firms , industries and countries basically ensuring the subsidy is distributed fairly
What are the types of price regulations used
RPI - relatively fair - firms are allowed to raise their prices proportional to rate of inflation
RPI - X - Restrict price below rate of inflation by ‘X’ percent - promotes efficiency and cost cutting
RPI ± K - This measure accounts for capital investment - if profit is not enough for a firm to invest into capital improvements then they will be allowed to rise their prices by K and vice versa
Draw a diagram of monopoly price regulation
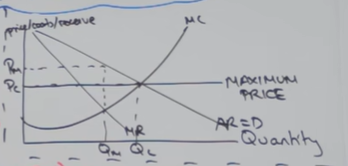
Evaluation of price regulations
Imperfect information - could lead to x or k being set inaccurately
Cost of implementing this regulation opportunity cost
When using RPI ± k there is no incentive to cut costs as it will simply adjust to allow for capital investment
Regulatory capture - Regulations may be too lax as investigators end up sympathising with firms in the industry due to previous experience with these firms
What are the other regulation methods used
Quality control/ performance targets
Windfall taxes on profit
Profit control covering costs and adding percentage return on capital employed
Merger policy
Privatisation
Deregulation
Reducing trade barriers
Evaluate usage of all monopoly regulation
Level of information that the individual has access to when making the decision so that it is accurate
Costs of regulations are very high (Not worth it for all the benefits) gov failure
Regulatory capture
Benefits of monopoly - if monopolies are regulated too harshly then it will result in benefits of monopoly being removed (Dynamic efficiency) but also promoting competition in a natural monopoly results in a wasteful duplication of resources