Unit 4 - Memory - AP Psychology
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Automatic Encoding
Requires no effort (What did you have for breakfast?)
Effortful Encoding
Requires work (School)
Structural Encoding
(Shallow) Emphasis on physical structural
Phonemic Encoding
Emphasis on what words sound like
Semantic Encoding
(Deep) Emphasis on the meaning of words themselves
Elaborative Rehearsal - Imagery
Attaching images to information makes it easier to remember
Elaborative Rehearsal - Dual Encoding
Using multiple methods of processing to remember (Word + photo)
Elaborative Rehearsal - Chunking
Break info into smaller units to aid in memory (Such as a phone #)
Elaborative Rehearsal - Mnemonics
Shortcuts to help us remember info (Acronyms, Method of Loci (imaginary location in your mind))
Context Dependent Memory
Where you learn the info is where you best remember the info
State Dependent Memory
Physical state you were in when learning is the way you should be when testing (study drunk, test drunk.)
Mood Congruent Memory
Remember happy events when happy, or sad when sad
Forgetting curve
Recall decreases rapidly at first, and then eventually reaches a plateau.
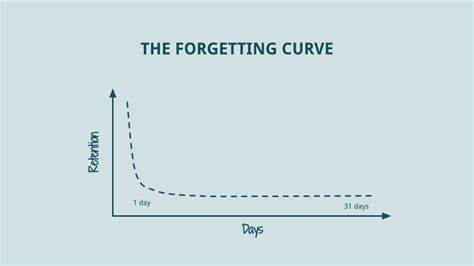
Distributed Practice (Spacing effect)
Review a little every night (resets forgetting curve)
Massed Practice
Cramming info into one session
Testing effect
Testing over material perodically
Sensory Memory
Stores all incoming stimuli that you receive
Iconic Memory
Visual memory, lasts for less than a second.
Echoic Memory
Auditory memory, lasts 2-3 seconds.
Short Term Memory
Info passes from sensory memory to STM — lasts 30 secs, and can remember 7 items
Maintenance Rehearsal
Repeating the info — resets the clock
Explicit Memory
Requires conscious effort to recall, Amygdala & Hippocampus
Implicit Memory
Automatic, no effort needed, in the Cerebellum
Episodic
Explicit - Memories of events, life experiences
Semantic
Explicit - Facts and general knowledge
Priming
Implicit - info that is seen earlier “primes” you to remember something later on or perceive something a certain way
Procedural
Implicit - info of skills and muscle memory
Working Memory
Splits STM into 2 - visual spatial memory (Iconic) & phonological loop (Echoic).
Prospective Memory
Remembering you need to do something (Pick up milk).
Autobiographical Memory
Memory for your own personal history — combo of episodic and semantic
Tip of the tongue phenomenon
Feel as if you know information but cannot directly recall it
Schemas
Frameworks that organize information
Assimilation
Incorporate new info into existing scheme (Cat is a dog b/c 4 legs)
Accommodation
Adjusts existing schemas to incorporate new information (Cat and dogs = different)
Long-term potentiation
Neural basis of memory — connections are strengthened over time with repeated stimulation
Serial Position Effect
Tendency to remember the beginning (primacy), and the end (recency) of the list best.
Recall
Remember what you’ve been told w/o cues (Essays)
Recognition
Remember what you’ve been told w/ cues (MCQ)
Repressed Memories
Unconsciously buried memories due to trauma or as a defense mechanism
Encoding failure
Forgetting info because you never encoded it/paid careful attention to it in the first place
PROactive Interference
OLD info blocking NEW info
RETROactive Interference
NEW info blocking OLD info
Constructive Memory
THe way we update memories w/ new memories, associations, feelings — memory is unreliable
Source Amnesia
You remember the information, but not where it comes from
Misinformation Effect
Distortion of memory by suggestion or misinformation
Framing
The way a question is framed impacts how information is recalled/perceived
Imagination Inflation
People are more confident an event happened after repetitively imagining it
Anterograde Amnesia
Amnesia moves forwards, therefore you forget new information.
Retrograde Amnesia
Amnesia moves backwards, therefore you forget old information.
Infantile Amnesia
Memories before age 3 are unreliable — hippocampus still forming
Where are implicit/procedural processed?
Cerebellum
Where are emotional memories processed?
Amygdala
Where is encoding and retrieval processed?
Frontal Lobe
Memory consolidation
Memories are strengthened and made more stable with time