HWS2-U4-Industrial Revolution & Market Economy
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Economy
the way goods and services are produced and consumed

consumer
someone who acquires goods and services for his or her own personal use.

producer
A person, company, or country that makes, grows, or supplies goods or commodities for others

market
the entire activity of buying and selling goods and services

profit
the financial gain received by selling something for more than it cost to make it.

incentive
a thing that motivates someone - producers are motivated by the profits they expect to gain from the goods and services they offer

competition
When producers offer the same goods and services - producers that compete to gain consumers and make the most profit.

innovation
the process of developing newer, better things

supply
the amount of something that is available

demand
the number of consumers who want a good or service.
market forces
the interaction of supply and demand that shapes a market economy

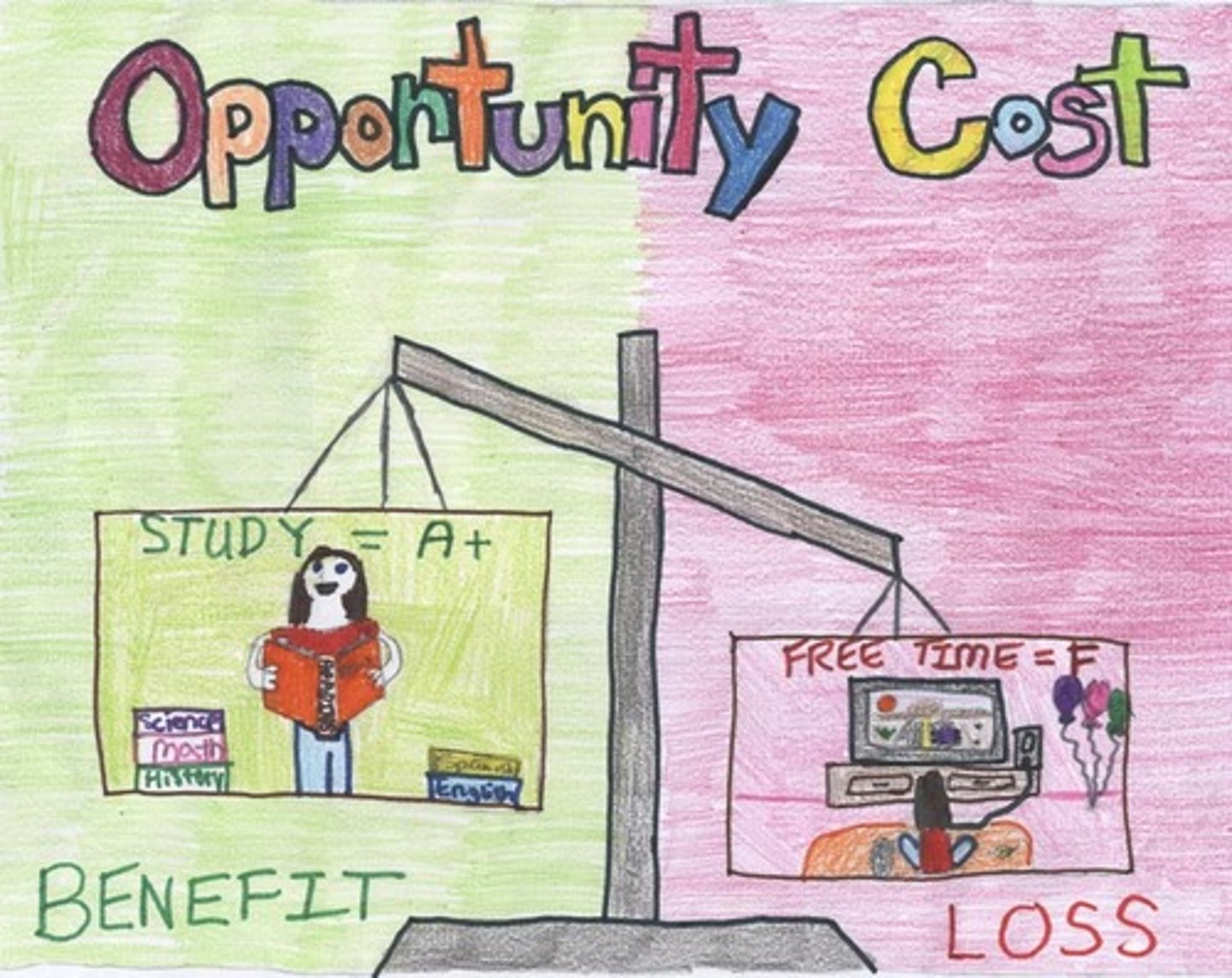
opportunity cost
the benefit you give up by choosing to one thing instead of another

scarcity
the limited amount of resources available

Command Economy
An economic system in which the government controls a country's economy - it decides what will be produced, how much will be produced, and how much goods and services will cost.
Market Economy
an economy where producers are free to decide what to produce, and consumers are free to buy whatever they need and want.
Mixed Economy
market-based economic system with some government involvement
Scarcity
the condition that exists because there are limited resources & unlimited wants & needs.
Economics
the study of human behavior under conditions of scarcity (essentially how do they make choices).
Cost-benefit principle
When making a choice, evaluate the full sets of costs and benefits. Pursue that choice only if the benefits are at least as large as the costs.
Interdependence principle
Your best choice depends on your other choices, external developments, and expectations about the future.
Marginal Principle
If something is worth doing, keep doing it as long as MB (Marginal Benefit) > MC (Marginal Cost).
Opportunity Cost Principle
When faced with a choice, your decision should reflect the opportunity cost, rather than just the out-of-pocket financial cost. (What is opportunity cost?)
Opportunity cost
the most desirable alternative given up as the result of a decision. (Cost = singular)
PACED
a decision making model that is used for many purposes in rational decision making. It considers the problem, alternatives, criteria, evaluation, & decision.
NIL deals
Name - Image - Likeness
Supply & demand
an economic concept that states that the price of a good rises and falls depending on how many people want it (demand) and depending on how much of the good is available (supply)
Factors of Production
Land, Labor, Capital (financial, physical, &/or human), & Entrepreneurship
incentives
An outcome (positive or negative) that can influence the decision making of individuals, governments, firms, etc.
FoP: LAND
Natural resources available for production - these are "gifts of nature" and not made by humans.
FoP: LABOR
Work that is performed by paid workers.
FoP: CAPITAL (Financial)
$$ - cash - funding
FoP: CAPITAL (physical)
Human made goods used to produce/make other goods.
FoP: CAPITAL (human)
Education & Training
FoP: Entrepreneurship
"Brains behind the operation"
** Presence of someone willing to incur risk to attain profit.
Market Economy: Who owns the Factors of Production?
Individuals & Businesses (firms)
Market Economy: What decisions do individuals and businesses have to make?
- What to produce?
- How to produce?
To whom should the goods/services be allocated?
Market Economy: What is the main incentive?
PROFIT
💸💵💰💲
In a market economy, what determines prices?
The supply & demand market.
Other terms to describe a market economy?
Capitalism, free-enterprise, free-market
Command Economy: Who owns the Factors of Production?
An authority (usually the government
Command Economy: What decisions do the authorities have to make?
- What to produce?
- How to produce?
To whom should the goods/services be allocated?
Command Economy- other names:
Socialism, Communism
Mixed Economy
Economic system that combines attributes of both the market economy and a command economy.
Industrial Revolution resulted in:
rise of urban populations, mass quantities of consumer goods, and the transformation of society
The spark for the Industrial Revolution in Britain was:
SHEEP! 🐑🐑
New textile material that revolutionized the industry:
COTTON!
Drawbacks of earlier textile production;
it was done by hand and took a very long time
Invention of John Kay
Flying shuttle that quickly moved the thread back and forth and pounded the thread into place
Unintended consequence of John Kay's invention
cotton shortage
What happens tot he price of materials when there is limited supply?
Price will go up.
In Europe, land =
wealth, power, and influence
Pre- mechanized machinery, the sources of power were:
human power, wind, water
How did Eli Whitney's invention actually increase slavery?
because the cotton gin increased cotton production tremendously and made it more profitable
The Industrial Revolution "arrived" in part due to:
innovation & enslaved peoples
Luddites
workers that were afraid of losing their jobs and turned to violence smashing and damaging machines to demonstrate their frustration
As textile manufacturing grew and led to factories, what resources were also in demand
iron and coal.