Movement Through Cell Membranes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Define Diffusion
The spreading out of molecules from a region of high to low concentration
Define Osmosis
The movement of molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from a region of high to low concentration
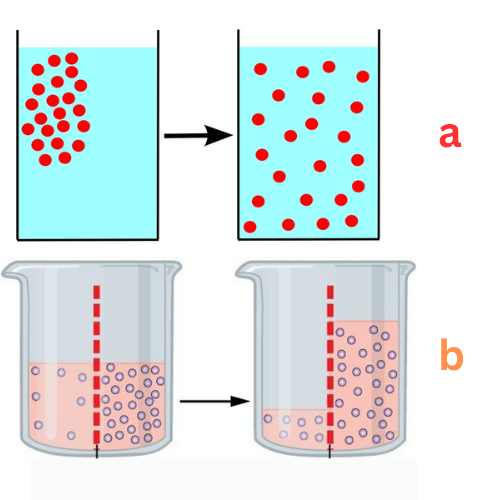
Label This Diagram
a - diffusion
b - osmosis
Define Passive
Does not require energy
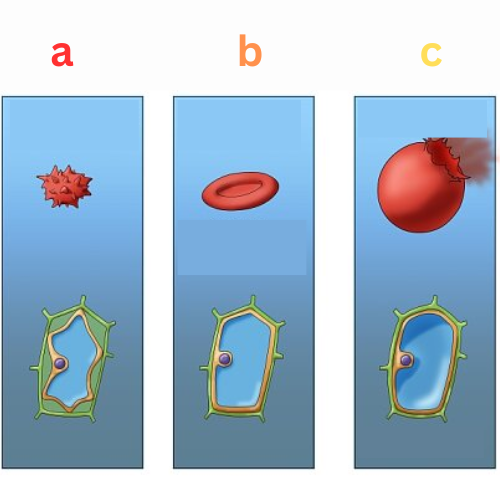
Label This Diagram
Osmosis in Cells
a - hypertonic
b - isotonic
c - hypotonic
Define Hypertonic
In Animal Cells
Water moves out the cell due to a more concentrated solution outside
What happens to Hypertonic Animal Cells
Cell shrivels and dies
Define Isotonic
In Animal Cells
Water equally moves in and out the cell due to an equally concentrated solution outside
What happens to Isotonic Animal Cells
Cell volume stays the same
Define Hypotonic
In Animal Cells
Water moves into the cell due to a less concentrated solution outside
What happens to Hypotonic Animal Cells
Cell enlarges and bursts
Define Turgor
The force of the cell contents against the cell wall
Define Isotonic
In Plant Cells
Water equally moves in and out the cell due to an equal concentrated solution outside
What happens to Isotonic Plant Cells
Cell volume stays the same
Define Hypotonic
In Plant Cells
Water moves into the cytoplasm due to a less concentrated solution outside
What happens to Hypotonic Plant Cells
Turgor Pressure
Define Hypertonic
In Plant Cells
Water moves out the cytoplasm using osmosis due to a more concentrated solution outside
What happens to Hypertonic Plant Cells
Plasmolysis
Define Plasmolysis
Loss of turgor pressure in plant cells due to loss of water
Define Permeable
Substances can pass through
Define Imperable
Substances are not allowed to pass through
Define Semi-Permeable
Some substances are allowed to pass through
Define Food Preservation
Salting food results in the water being removed from harmful micro-organisms and not spoiling the food