Module 3 Erythocytes trapped in fibrin mesh (clot)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Clot Retractionand Fibrinolysis:
Fibrinolysis
pcocess of clots removed after repair is completed
Clot Retractionand Fibrinolysis:
Fibrinolysis: when does it begin?
what is plasminogen?
within 2 days and continues for several days unti lclot is dissovled
plasminogen: plasma protein trapped in clot, converted to plasmin
Disorders of Hemostasis: Thromboemboli
what is thrombus?
clot that developes and persists in unbroken blood vessel.
Disorders of Hemostasis: Thromboemboli
what is Embolus?
thrombus freely floating in bloodstream.
Disorders of Hemostasis: Thromboemboli
what is Embolism?
emolus obstructing a vessel
Disorders of Hemostasis: Thromboemboli
what are the 4 risk factors
atherosclerosis
inflammation
slow flowing blood
immobility
thromboelic conditions (continued)
anitcoagulants drugs for it?
aspirin
heparin
wafarin
bleeding disorders:
Thrombocytopenia
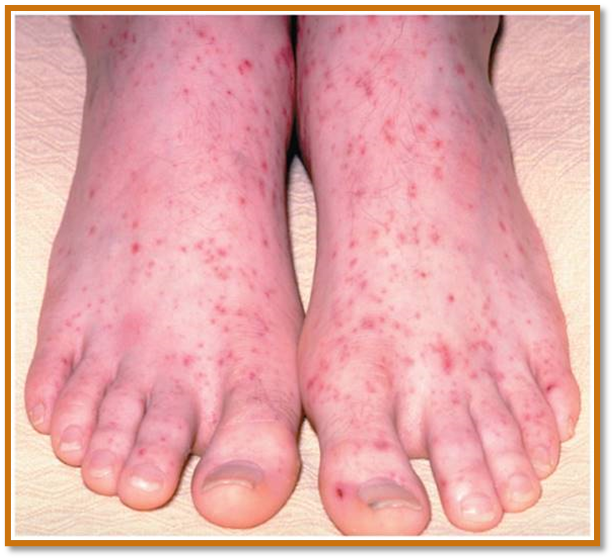
deficient number of circulating platelets
bleeding disorders:Thrombocytopenia
what is Petechia?
treatment?
appears as a resutls of spontanoeous widespread hemmorhage
treatment: platelet transfusion
Disorders of Hemostasis:
Bleeding disorders:
Impaired liver function
In severe liver disease, production of procoagulants (clotting factors) is decreased, resulting in diminished clotting capacity
Causes include vitamin K deficiency, hepatitis, or cirrhosis
liver disease prevents liver producing bile, which is needed to absorb fat and vitamin K
Disorders of Hemostasis:
Bleeding disorders:
Hemophillia
hereditary bleeding disorders affecting the intrinsic pathway
Disorders of Hemostasis:
Bleeding disorders:
hemophilia 3 different types
Hemophilia A
Hemophilia B
Hemophilia C
Symptoms: prolonged bleeding
Treament? injections of genetically engineered factors
Hemophilia A: X - linked inheritance, occurs mostly in males
Hemophilia B: X - linked inheritance, male dominant
Hemophilia C: Milder, occurs in both males and females
Disorders of Hemostasis:
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
has both widespread clotting and severe bleeding
widespread clotting occurs in intact blood bessels, blocking blood flow
Blood transfusion and Bloody typing:
Blood Transfusions:
Cardiovascular system minimizes effects of blood loss by?
reducing volume of affected blood vessels
stepping up production of RBC’s
Blood Transfusions:
loss of 15-30% causes what?
Pallor and weakness
Blood Transfusions:
loss of more than 30% results in?
fatal severe shock
Restoring blood volume:
Restoring low volume can be replaced with
normal saline or multiple electrolyte solution (ringer’s solution)
Replacement of volume restores adequate circulation but does not replace oxygen-carrying capacities of RBCs
Transfusing Red blood Cells:
what is used when blood loss is rapid and subtantial?
whole blood transfusions
Transfusing Red blood Cells:
infusision of ___ prefer to restore oxygen carrying capacity
packed red blood cells (PRBCs)
Transfusing Red blood Cells:
human blood groups:
antigen?
RBC antigens?
antigen: any as foreign can generate an immune response
RBC antigens: reffered to as agglutionogens, they promote agglutination
Blood typing:
antigens of what causes the most vigorous transfucsion reactions?
ABO and Rh blood groups
Transfusing Red blood cells:
ABO blood groups
Based on presence or absence of A and B agglutinogens on RBC surface
÷Type A blood has only A agglutinogen
÷Type B blood has only B agglutinogen
÷Type AB blood has both A and B agglutinogens
÷Type O blood has neither A nor B agglutinogens
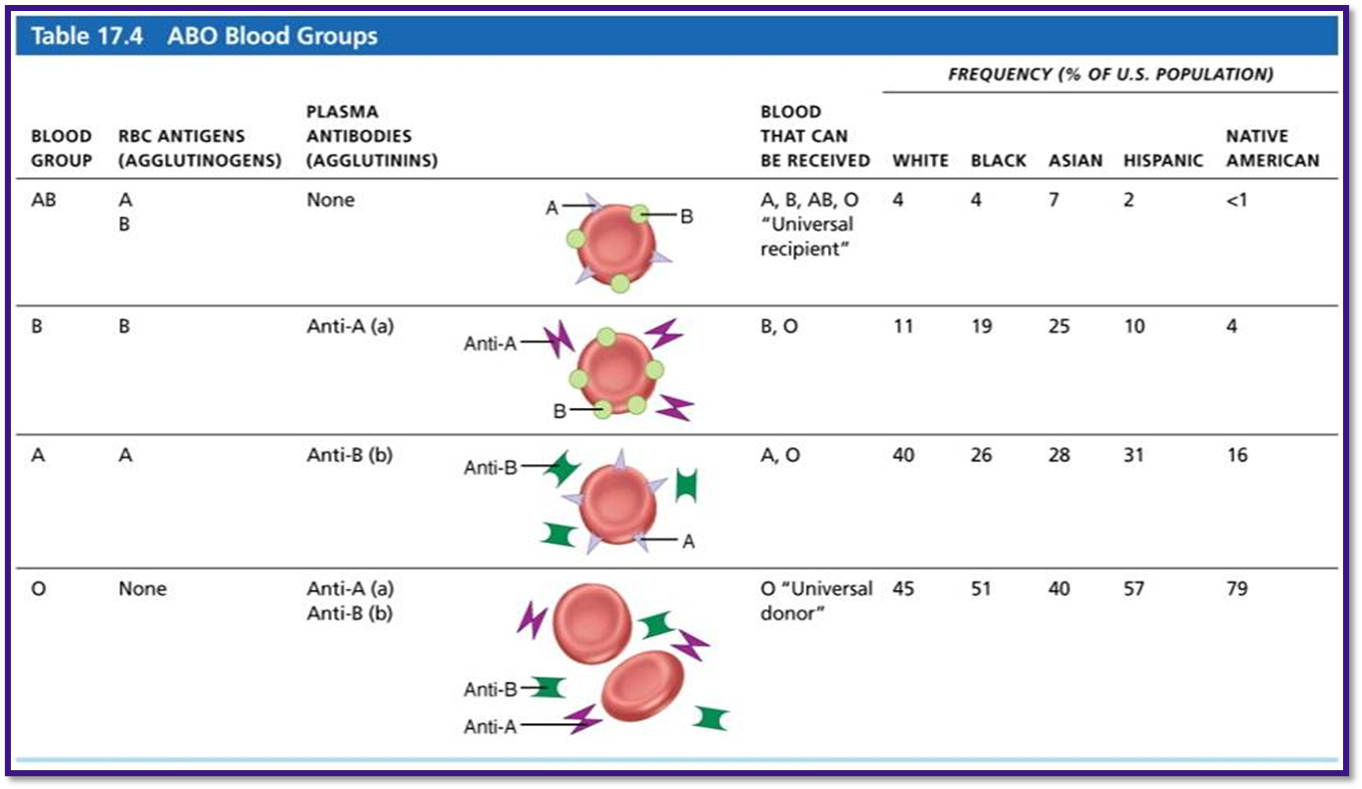
÷Anti-A or anti-B form in blood at about
2 months of age
RH blood groups:
how many named RH agglutinogens (Rh factors)
what 3 letters are most common?
52
C, D, and E
Anti - Rh anitbodies are ?
not spontaneously formed in Rh negative individuals
÷Anti-Rh antibodies form if
Rh negative individual receives Rh+ blood,
Rh negative mom is carrying Rh+ fetus
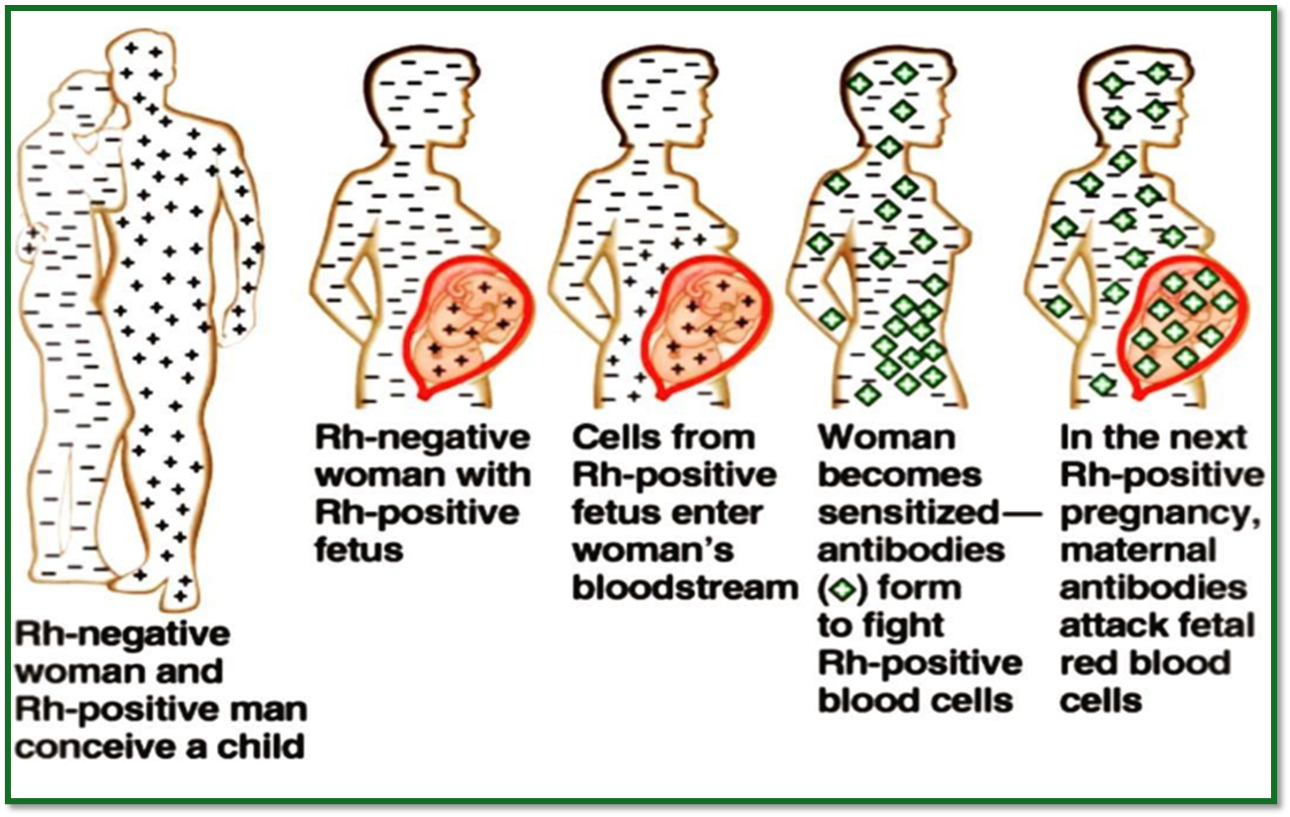
Hemolytic disease of newborn (aka erythroblastosis fetalis)
Only occurs in Rh negative mom with Rh+ fetus in?
First pregnancy:
÷Rh– mom exposed to Rh+ blood of fetus during delivery;
÷first baby born healthy
÷…but mother synthesizes anti-Rh antibodies
Second pregnancy:
÷Mom’s anti-Rh antibodies cross placenta and destroy RBCs of Rh+ baby
÷Baby treated with prebirth transfusions and exchange transfusions after birth
what prevents Rh negative mother from becoming sensitized
RhoGAM serum
what happens in a wrong transfusion reactions
if mismatched blood is infused
donor’s ccells are attacked by recipietns plasma agglutinins
what is the result of wrong transfusion reactions
÷Diminished oxygen-carrying capacity
÷Decreased blood flow beyond blocked vessel
÷Hemoglobin in kidney tubules can lead to renal failure
transfusion reactions
symptoms?
treament?
symptoms: fevers, chills, low blood pressure, rapid hearbeat, nausea, vomitting
treatment: preventing kidney damage with fluids and diuretics to wash out hemogloblin
what is the universal donor?
type O - no A or B antigens. O negative blood
what is the universal recipient?
type AB no anti A or anti B anitbodies
what is Autologous transfusions
you predonate your own blood that is stored and available when needed
what is cross matching:
mixing receipents serum with donor RBC’s to see if they are compatible
vice versa mix recipients RBCs with donor serum
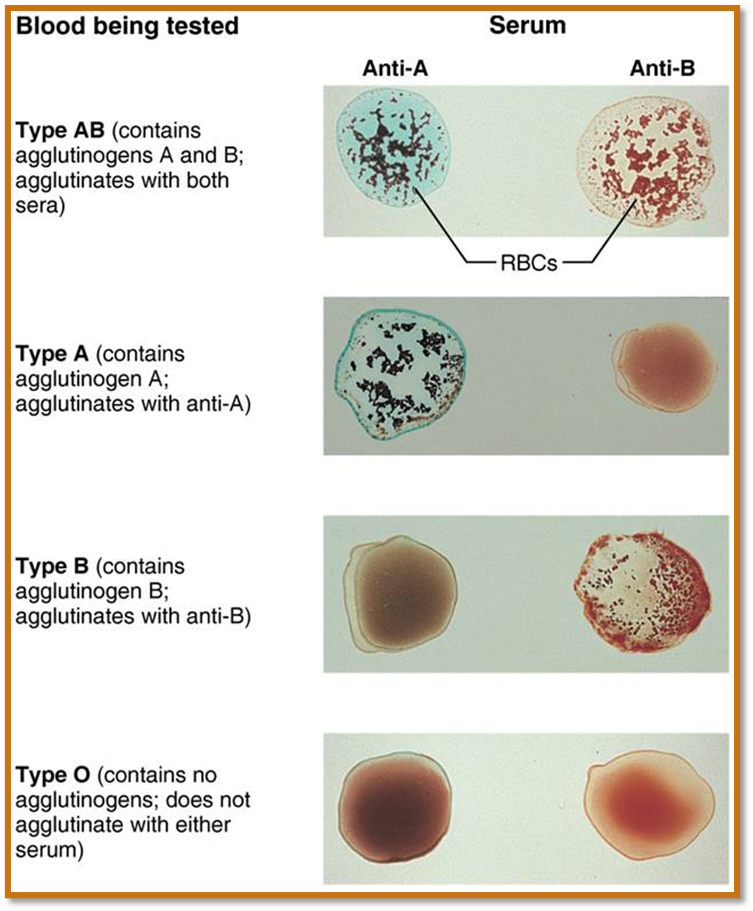
clump of RBCs will occur if?
agglutinogen is present
diagnostic blood test:
what is differential WBC count?
looks at proportions of each WBC
diagnostic blood test:
Prothrombin time and platelet counts
it assess hemostasis
diagnostic blood test:
CMP (comprehensive medical panel)
blood chemistry profile checks various blood chemical levels
Complete blood count (CBC)
checks formed elemts, hematocrit, hemoglobin
read slide 115