Nursing Fundamentals
1/329
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
330 Terms
Asepsis
Asepsis is the absence of pathogenic (disease-producing) microorganisms.
Medical asepsis
Medical asepsis (clean technique) reduces organisms and prevents transfer.
Surgical asepsis
Surgical asepsis (sterile technique) destroys microorganisms and their spores.
4 Moments of hand hygiene
The specific times when hand hygiene should be performed to prevent infection.
Soap-based disinfectant
A method of hand hygiene appropriate when hands are visibly dirty.
Soap
Removes visible soiling but is ineffective at killing microorganisms.
Trendelenburg position
Bedframe tilted with head of bed down.
Reverse Trendelenburg position
Bedframe tilted with foot of bed down.
Supine position
Bed horizontal with floor.
Semi-fowler's position
Head of bed (HOB) elevated 30-45 degrees.
Fowler's position
Head of bed (HOB) elevated 45-90 degrees.
Bathing Safety Guidelines
Adapt to level of dependence, personal hygiene accessibility, contact with bodily fluids, and evaluate before and after care.
Risk Factors For Skin Breakdown
Includes immobilization, reduced sensation, nutrition and hydration alterations, secretions and excretions on the skin, vascular insufficiency, external devices, and age.
High Fowlers Position
Position where the patient is seated upright to assist with oral nutrition.
Aspiration precautions
Place a patient in a position that minimizes the risk of aspiration.
Patient diet orders
Includes clear fluids, full liquid, pureed, mechanical/dental soft, soft, and regular diets.
Body mechanics
Keep back, neck, pelvis, and feet in alignment; tighten stomach muscles; face direction of movement.
Bed making importance
Important for safety, comfort, and emotional well-being.
Evaluation after care
Assess the patient's condition before and after providing care.
Correctly position patient
Maintain body alignment, comfort, circulation, and balance.
Aids for patient positioning
Pillows, trochanter rolls, rolled towels, splints, various foam boots/wedges/hand splints.
Range of Motion (ROM)
ROM can be active, passive or active assisted.
Posterior
Dorsal.
Anterior
Ventral.
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment.
Distal
Farther from the point of attachment.
Medial
Closer to the midline of the body.
Lateral
Farther from the midline of the body.
Superior
Above or higher than another part of the body.
Inferior
Below or lower than another part of the body.
Flexion
Decreasing the angle between two body parts.
Extension
Increasing the angle between two body parts.
Hyperextension
Movement of a body part beyond its normal resting position.
Dorsiflexion
Movement of the foot upwards.
Plantar flexion
Movement of the foot downwards.
Abduction
Movement of a limb away from the body.
Adduction
Movement of a limb towards the body.
Eversion
Turning the sole of the foot outward.
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward.
Circumduction
Circular movement of a limb.
Stage 1 Pressure Ulcer
Non-blanchable erythema of intact skin; skin is intact.
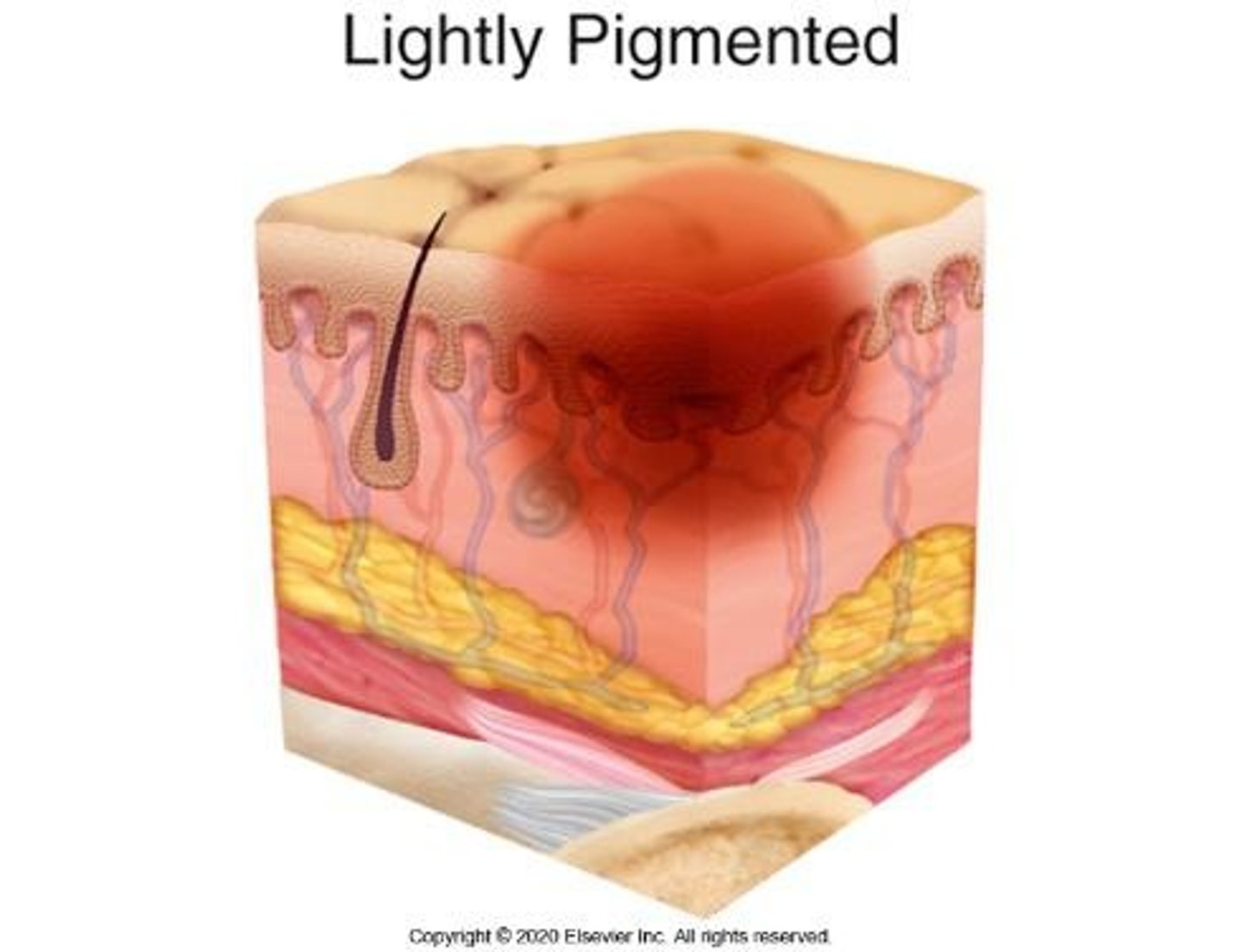
Stage 2 Pressure Ulcer
Partial-thickness skin loss with exposed dermis; wound bed is viable, pink or red and moist.
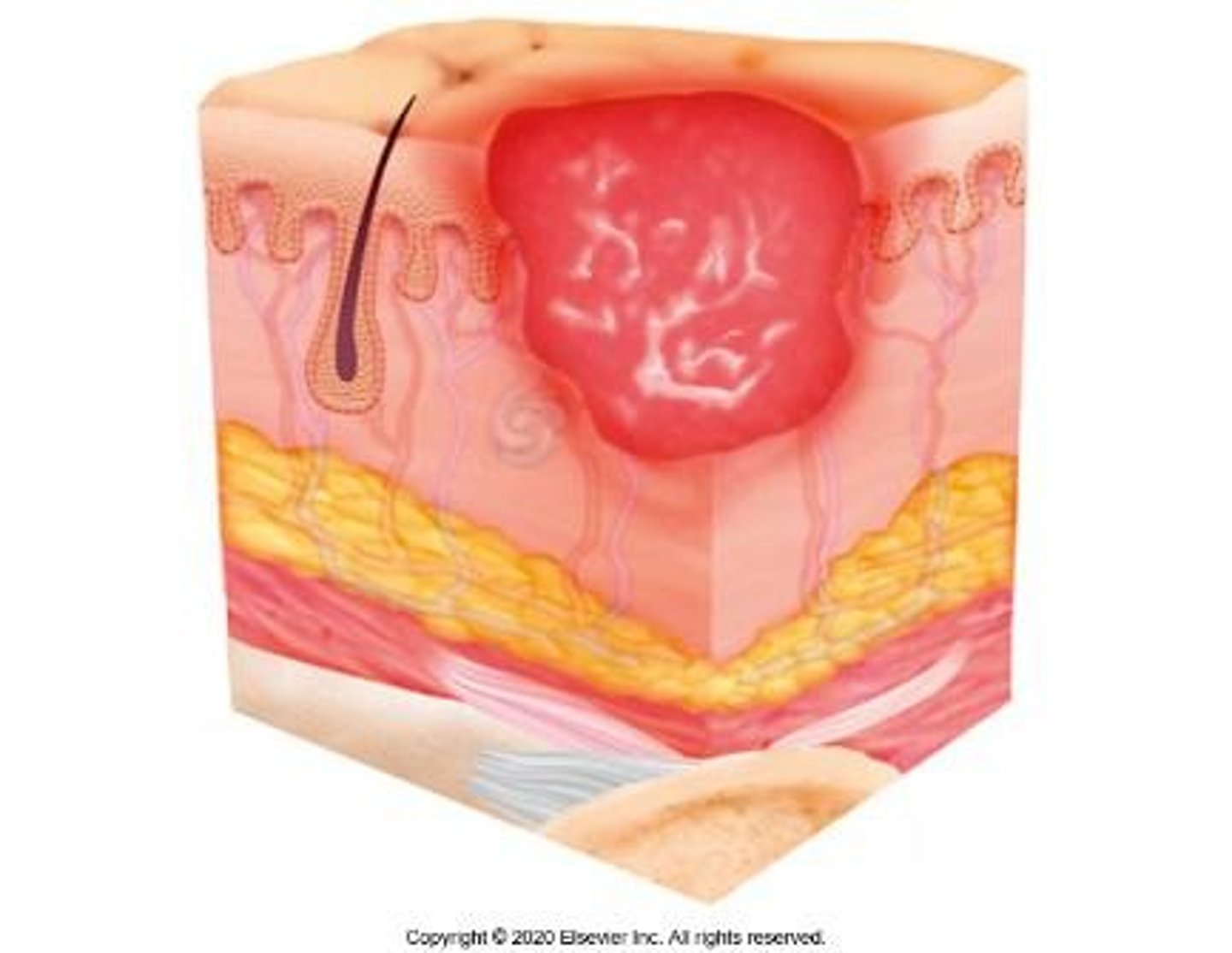
Stage 3 Pressure Ulcer
Full-thickness skin loss; adipose tissue is visible.
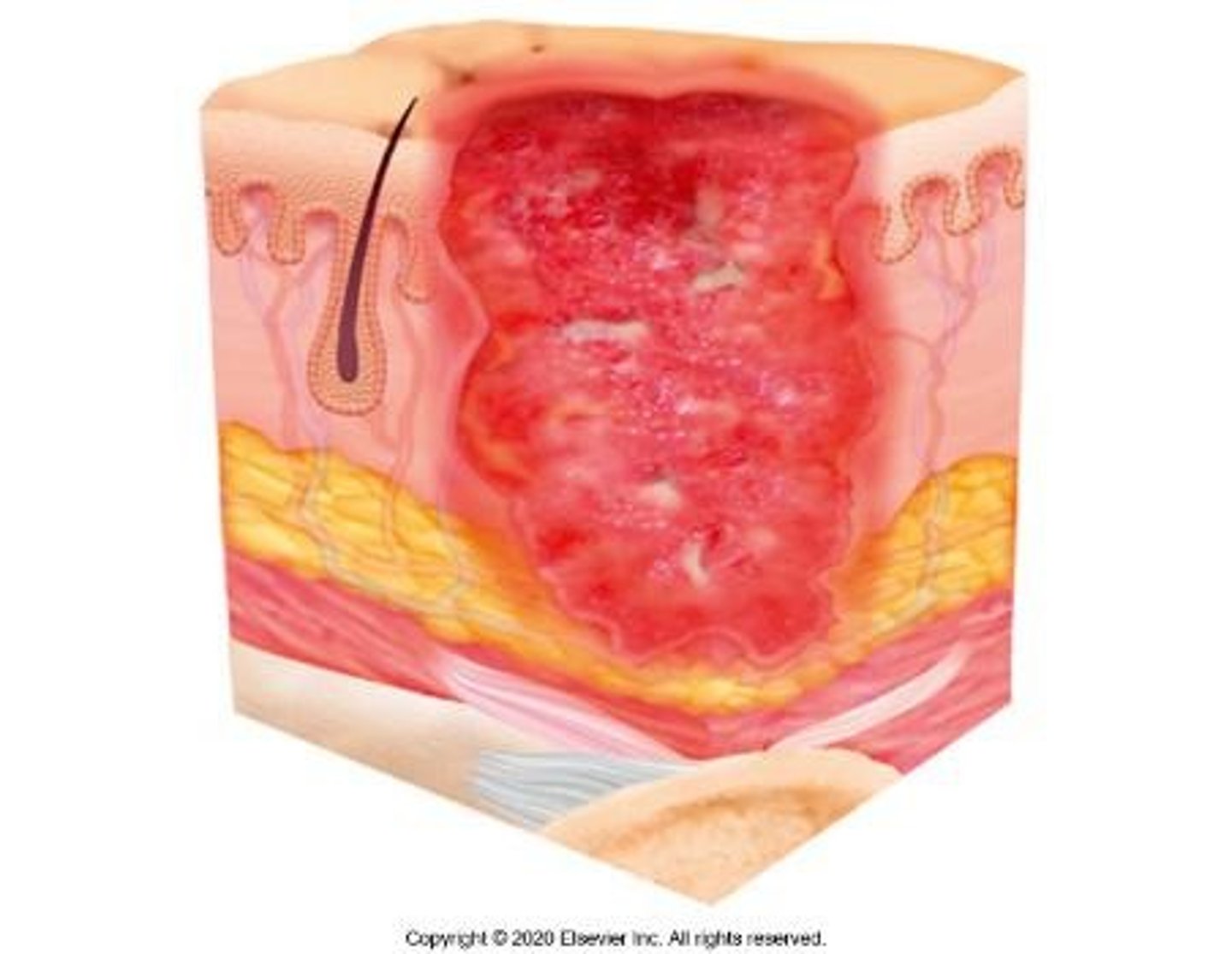
Stage 4 Pressure Ulcer
Full-thickness skin and tissue loss; deep injury with exposed or palpable fascia, muscle, tendon, ligament or cartilage, or bone; slough of eschar may be visible.
Orthostatic hypotension
BP drop >20mm Hg systolic or >10mm Hg diastolic with dizziness, light-headedness, tachycardia, pallor, feeling faint.
Applying Physical Restraints
Use restraints only as a last resort; employed as a temporary measure; associated with serious complications; requires a physician's order.
What is the primary purpose of hygiene in nursing?
To promote and preserve health, ensuring comfort, safety, and a sense of well-being.
What factors can influence a patient's hygiene practices?
Personal, social, and cultural factors, as well as illness or disability.
What should a nurse convey while performing hygiene tasks?
Respect and cultural sensitivity, while ensuring privacy and discussing patient concerns.
What are the functions of the skin?
Protection from heat, injury, and infection; secretion; excretion; temperature regulation; sensation.
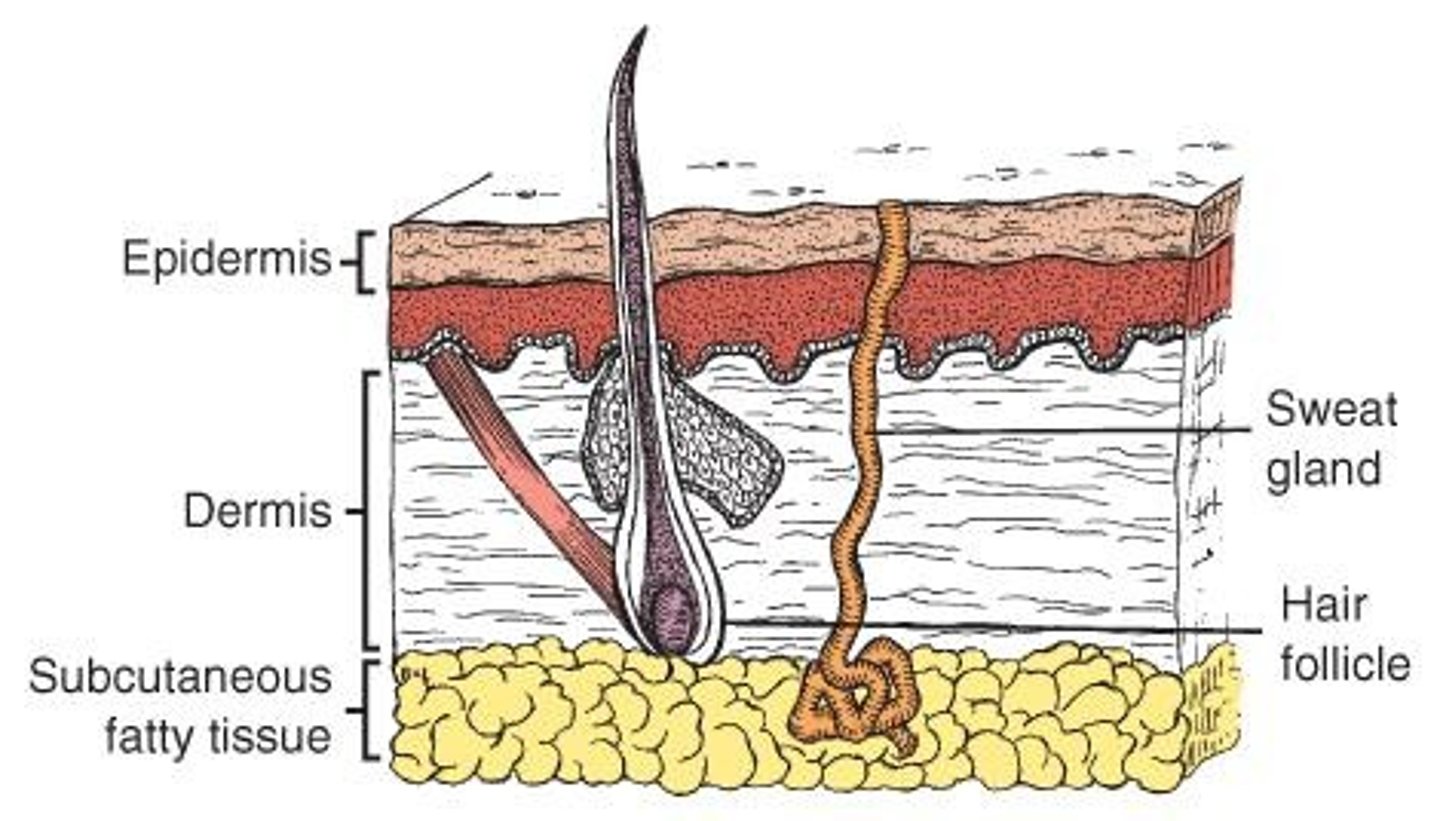
What are common skin problems that nurses should be aware of?
Dryness, acne, rashes, contact dermatitis, psoriasis, and abrasions.
What are risk factors for skin impairment?
Immobilization, reduced sensation, nutrition and hydration alterations, secretions on the skin, vascular insufficiency, external devices, and age.
How should a nurse accommodate cultural considerations during hygiene care?
By maintaining privacy, providing gender-congruent caregivers, and respecting cultural rituals.
What are the principles of bathing a patient?
Clean skin regularly, avoid extreme water temperatures, maintain ideal room temperature, and assess the patient during the bath.
What is the proper technique for perineal care?
Clean from front to back, maintain privacy, and wear gloves.
What factors influence hair care in patients?
Condition of the hair, daily routines, and cultural preferences.
What is the recommended method for washing the eyes?
Wash from inner to outer canthus using different sections of the washcloth for each eye.
Why is daily oral hygiene important?
It prevents and controls plaque-associated oral disease, promoting health, comfort, nutrition, and verbal communication.
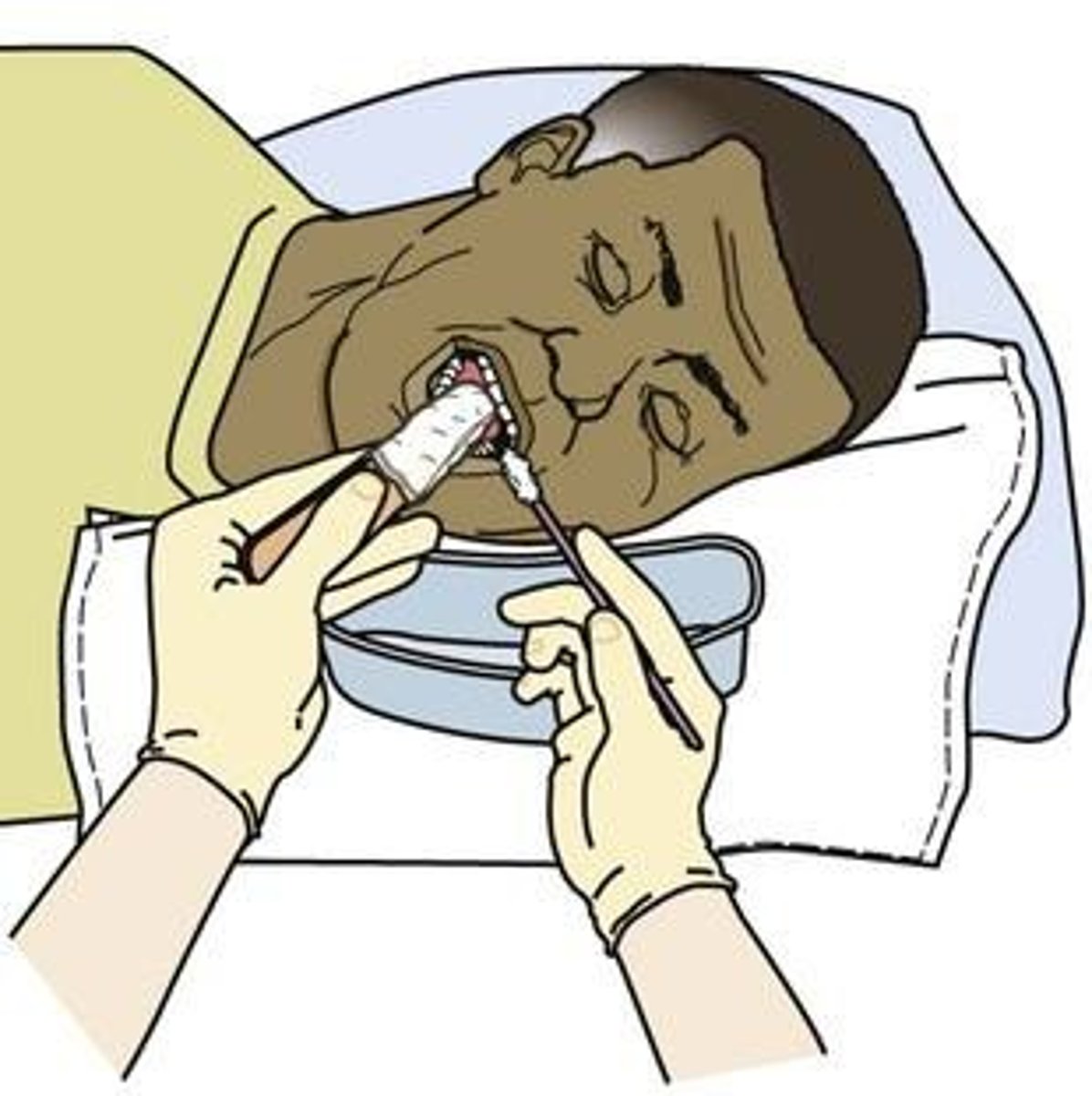
What steps should be followed when performing mouth care?
Inspect the oral cavity, brush teeth at a 45-degree angle, clean the tongue, rinse, and floss as appropriate.
What precautions should be taken when providing mouth care for unconscious patients?
Use two nurses for safety, inspect the oral cavity, and avoid inserting fingers into the mouth.
What are the International Dysphagia Diet Levels?
Guidelines for modifying food textures and liquid consistencies for patients with swallowing difficulties.
What is the significance of maintaining an upright position during feeding?
It helps prevent aspiration and ensures safe swallowing.
What should a nurse assess before performing a bed bath?
The patient's ability to assist, the environment, and any patient concerns or preferences.
What is the role of therapeutic communication in nursing hygiene care?
To discuss health-related concerns, provide education, and promote patient independence.
What should be done if a patient refuses assistance with hygiene care?
Seek the assistance of a caregiver of the same gender or respect the patient's wishes while ensuring their comfort.
What is the purpose of monitoring intake and output in nursing?
To assess the patient's hydration status and nutritional needs.
What are some common patient preferences regarding hygiene?
Preferred products, bathing routines, and times of day for hygiene activities.
What is the importance of patient-centered care in hygiene?
It accommodates the patient's preferences and cultural practices, enhancing their comfort and cooperation.
What should be included in the assessment during a patient's bath?
Physical assessment of the skin and range-of-motion exercises.
What is the recommended position for a patient during oral nutrition assistance?
High Fowler's position with the chin down to minimize aspiration risk.
What are some considerations for feeding patients with dysphagia?
Use thickened liquids, avoid mixing textures, minimize distractions, and provide verbal cues.
What is the significance of cultural sensitivity in nursing hygiene care?
It ensures respect for diverse practices and enhances patient comfort and trust.
What is the most important technique for infection control and prevention?
Hand hygiene

What are the five moments of hand hygiene?
1. Before patient contact 2. Before aseptic task 3. After body fluid exposure risk 4. After patient contact 5. After contact with patient surroundings
What is the definition of asepsis?
The absence of pathogenic microorganisms.
What are the two types of asepsis?
1. Medical asepsis (clean technique) 2. Surgical asepsis (sterile technique)
What is the nurse's role in infection control?
Role modeling, patient education, and breaking the chain of infection.
What items are included in personal protective equipment (PPE)?
Gloves, masks, gowns, and eye protection.
What are standard precautions?
Infection control practices used for all patients, regardless of infection status, including handling blood and body fluids.
What are transmission-based precautions?
Precautions used for patients known or suspected to be infected with pathogens that can be transmitted via contact, droplet, or airborne routes.
What should be done if hands are visibly soiled?
Wash hands with soap and water.
What is the purpose of bed making in patient care?
To provide comfort, maintain a clean environment, and allow for social interaction.
What are the key concepts in body mechanics?
1. Wide stance 2. Bend at the knees 3. Keep body alignment 4. Tighten stomach muscles 5. Keep weight close to body
What is the significance of using a comfortable working height for bed making?
It helps prevent musculoskeletal injuries.
What is the difference between an occupied bed and an unoccupied bed?
An occupied bed is made while the patient is in it, while an unoccupied bed is made when no patient is present.
What is the correct position for a semi-fowler's bed?
Head of the bed elevated at 30-45 degrees.
What is the purpose of mitered corners in bed making?
To secure the linens tightly and prevent them from coming loose.
What should be done with soiled linens?
Place them in the appropriate receptacle for disposal.
What is the recommended action for a nurse if they miss a nursing practice lab?
Contact the instructor, submit a learning activity, and provide a learning plan.
What is the role of self-directed learning in the BScN program?
It is an expectation for all courses, promoting independent study and engagement.
What should students do if masks are required in the laboratory?
Students and staff are responsible for providing their own supply.
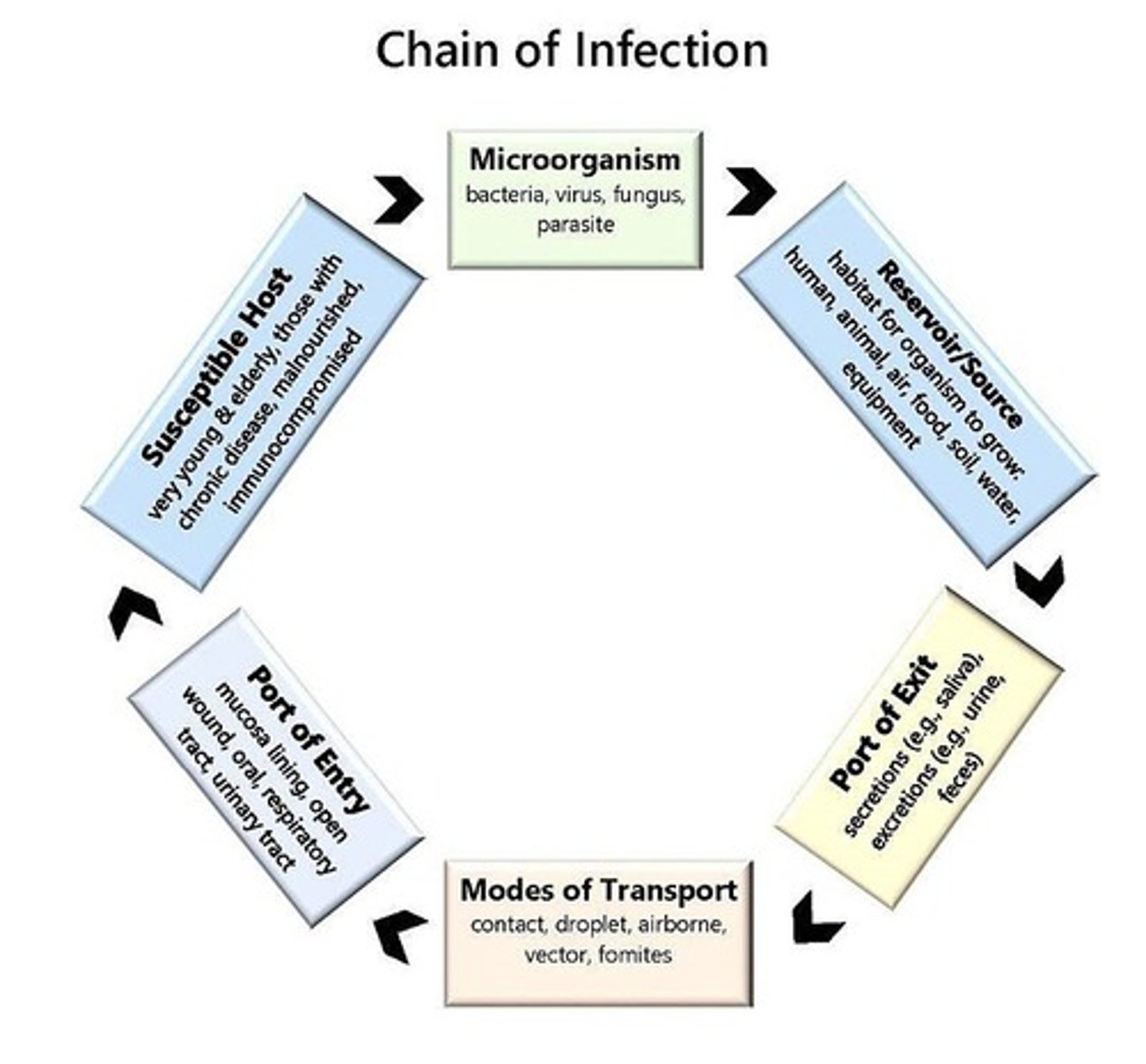
What is the chain of infection?
The process by which infections are transmitted from one host to another.
What are the safety guidelines for lab attendance?
Arrive on time, complete homework before lab, and actively participate in learning activities.
Why is it important to maintain privacy while making a bed?
To respect the patient's dignity and comfort.
What should be checked for safety in a patient's environment?
Bed height, furniture placement, slip hazards, and adequate lighting.
What is the significance of using safe handling techniques when making an occupied bed?
To conserve the patient's energy and ensure their safety.
What is the importance of hand hygiene in infection control?
It reduces the risk of transmitting infections to patients and healthcare workers.
What should be done before performing any clinical procedure?
Perform the appropriate safety checks and ensure proper hand hygiene.
What is the expected outcome of demonstrating correct hand hygiene practices?
To effectively reduce the risk of infection transmission.
What is the role of the nurse in patient education regarding infection control?
To inform patients about practices that prevent infection and promote safety.