1. cells and microscopy
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1
New cards
cell theory
where all living organisms are composed of one (unicellular) or more (multicellular) cells
2
New cards
cell
basic structural and physiological unit of all living organisms and is the smallest unit capable of surviving independently, they are the site of metabolic process and contain genetic information
3
New cards
field of view
circular area visible down a microscope
4
New cards
magnification
number of times large an object appears
5
New cards
resolution
ability to distinguish two distinct objects separately and see detail
6
New cards
eyepiece graticule
scale inserted to eyepiece which is calibrated with a state micrometer and then used to measure cells
7
New cards
stage micrometer
a slide with typically 1 mm ruler on it
8
New cards
light microscope
a cheap low magnification microscope with limited resolution that requires little training and maintains natural colours (1500x, 200nm)
9
New cards
transmission electron microscope
an electron microscope which produces a 2D black and white image at high resolution and magnification (500,000x, 0.1nm) expensive and requires training
10
New cards
scanning electron microcsope
an electron microscope which passes a beam of electrons back and forth over a sample to produce a black and white 3D image, expensive and requires training, low resolution and magnification (100,000x, 0.1nm typiclay 5-20µm tho)
11
New cards
confocal laser scanning microscope
light is scanned through an object and reflected or emitted light is detected, produces a 2D image or 3D image by stacking and requires less training than electron microscopes, lower magnification and low resolution (2000x, 200nm)
12
New cards
transmission electron microscope preparation
complex preparation where tissue is fixed, dehydrated embedded in resin then very thin sections cut and stained using heavy metal salts finally placed on a copper grip in a vacuum
13
New cards
scanning electron microscope preparation
variable ease of preparation, where samples surface is coated in gold atoms to scatter electrons
14
New cards
confocal laser scanning microscope preparation
variable ease of preparation where samples may be combined with fluorescent markers
15
New cards
methylene blue
stain which is able to be added to living cells without been fixed
16
New cards
fixing
process to attach stain to tissue using alcohol which makes proteins and nucleic acids insoluble and kills the cells
17
New cards
differential stain
a stain which stains different structures different colours to help identify them
18
New cards
magnification calculation
image size (mm) ÷ actual size (nm or µm)
19
New cards
1, 3, 2, 6, 5, 4
1. place the stage micrometer on microscope and focus onto it with 4x lens
2. workout length of 1 eye peice graticule division with the stage micrometer
3. rotate eyepiece graticule to align with stage micrometer
4. measure object with eyepiece graticule and calculate its length
5. remove stage micrometer and place object under
6. repeat with the each lens
20
New cards
calculate eye peice graticule length
stage micrometer measurement (µm) ÷ divisions on eyepiece graticule
21
New cards
1, 6, 2, 8, 5, 4, 7, 3, 9, 10
1. wear latex free gloves
2. a spreader at 45˚ is pushed along to spread blood by capillary action forming a smear
3. dilute with distilled water and leave for 5-7mins
4. fix with methanol
5. air dry slide
6. place a drop of blood on end of slide
7. flood with leishman’s stain for 2 mins
8. label slide
9. wash slide to remove excess stain till it appears pale pink
10. blot gently with filter paper and apply a coverslip
22
New cards
latex free gloves worn
prevent contamination, protect from pathogens, reduce allergies and skin reactions
23
New cards
leishman’s stain
a stain which contains methylene blue and eosin
stains different compounds different colours
methylene blue stains nucleic acids blue-purple
eosin stains cytoplasmic proteins pink-red
stains different compounds different colours
methylene blue stains nucleic acids blue-purple
eosin stains cytoplasmic proteins pink-red
24
New cards
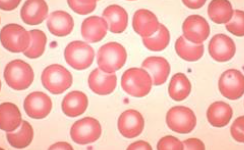
erythrocyte/red blood cell
biconcave discs (squeeze and SA) no nucleus or mitochondria, lifespan of 120 days, carry oxygen and some CO2
25
New cards
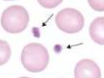
thrombocyte/platelet
biconcave discs of cytoplasm fragments form megakaryocytes (giant cells) life span of 6-7 days. contribute to blood clotting and clot formation
26
New cards
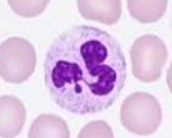
neutrophil
most numerous leucocyte, multilobed nucleus (squeeze) granular cytoplasm containing lysosomes, engulf bacteria in phagocytosis, non specific
27
New cards
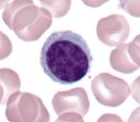
lymphocyte
smallest leukocyte, B and T versions, large darkly stained nucleus and clear cytoplasm with no granules, B produce immunoglobulins, helper T produce chemicals coordinating immune response and cytotoxic T destroy specific cells
28
New cards
monocyte
largest leucocyte, large kidney bean nucleus, clear cytoplasm, few granules, darl stained nucleus, carry out phagocytosis
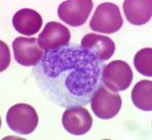
29
New cards
granulocytes
type of leucocytes with granules that is neutrophils
30
New cards
agranulocytes
type of leucocytes with little granules that is monocytes and lymphocytes
31
New cards
precautions when sampling own blood
swap wound with ethanol before and after and cover with dressing, don’t work with others blood, dispose of all materials in bleach, wash hands
32
New cards
haemocytometer
chamber used to count cells, contains a 1mm by 1mm grid, count in 0.2mm square, 0.1mm depth, repeat 5 times
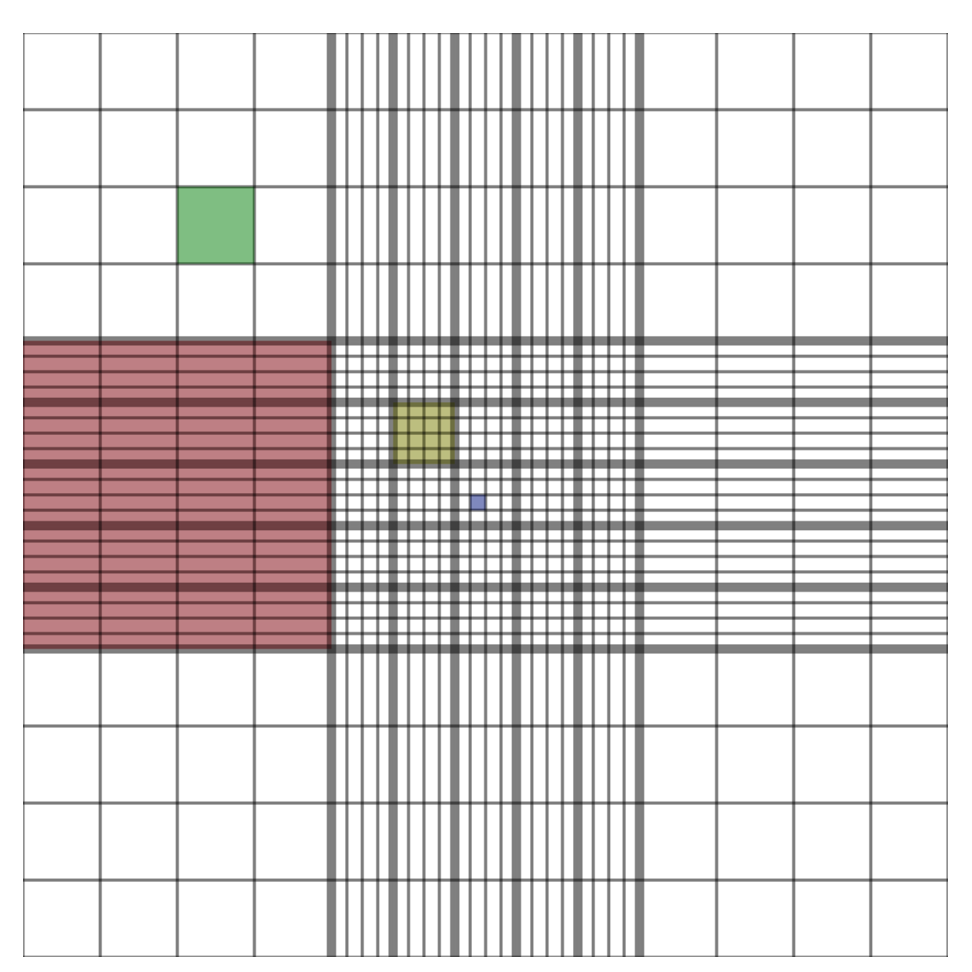
33
New cards
calculate cells in haemocytometer
1÷volume x number of cells x dilution factor
34
New cards
north west rule
count cells touching top and left but not right or bottom middle line
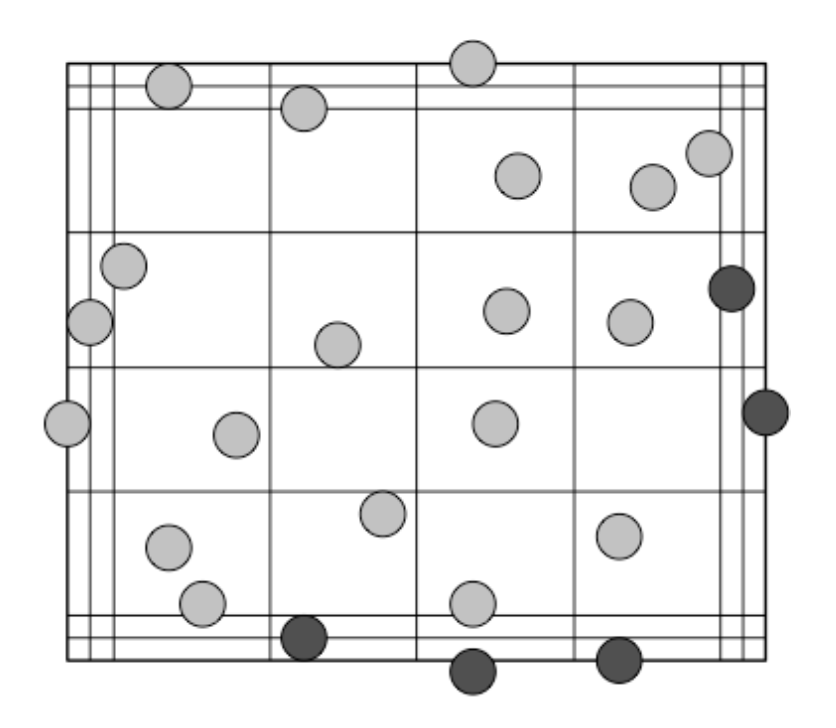
35
New cards
3, 1, 5, 2, 6, 4
1. apply a cover slip
2. count cells in one small central square
3. stir yeast cells in suspension and dilute using trypan blue to identify usable cells
4. calculate mean
5. introduce a sample under coverslip with a small pipette by capillary action
6. count in 4 other small squares
36
New cards
dacies fluid
used to dilute erythrocyte as it is isotonic preventing cells bursting or clumping
37
New cards
trypan blue
used to dilute yeast or mammalian cells as it is taken up by dead cells
38
New cards
flow cytometer
electronic counting apparatus to count and sort blood cells. By attaching fluorochromes to antigens which emit fluorescent light when a laser is shone
39
New cards
compartmentalisation
internal structures of cells are divided by membranes
40
New cards
organelles
intracellular structures with a specific function
41
New cards
eukaryotic cells
plant and animal cells with a nucleus
42
New cards
prokaryotic cells
bacteria cells with no nucleus
43
New cards
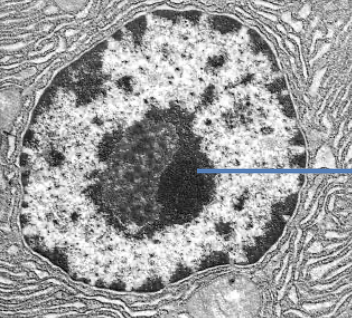
nucleus
largest organelle sounded by double envelope (nuclear envelope) with pores, contains chromatin( DNA coiled around histones), controls activities of the cells by mRNA
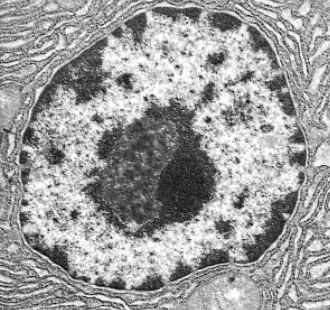
44
New cards
nucleolus
dark patch in nucleus which produces rRNA and assembles ribosomes
45
New cards
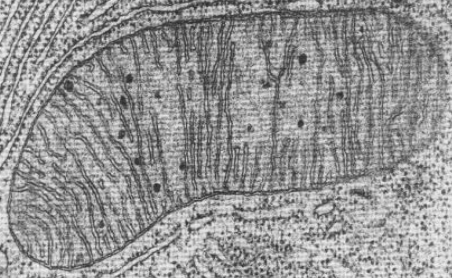
mitochondrion
spherical or sausage shaped, double membrane, inner is highly folded, site of aerobic respiration
46
New cards
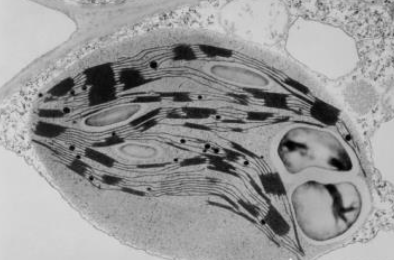
chloroplast
double membrane, contains stack of membrane bound compartments called thylakoids, site of photosynthesis, only in plants
47
New cards
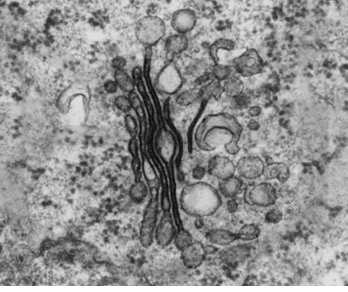
golgi body
stack of membrane bound flattened sacs, receives proteins vesicles from RER and modifies them, the repackaged to vesicles
48
New cards
vesicle
membrane bound sac moved within cells by cytoskeleton, transports materials around cells
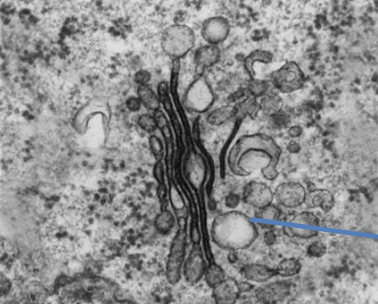
49
New cards
ribosome
tiny organelle bound to RER or free in cytoplasm, made of 2 subunits of rRNA and proteins, site of protein synthesis
50
New cards
rough endoplasmic reticulum RER
series of flattened membrane bound compartments called cisternae, continuous membrane with nuclear envelope, ribosomes on surface, packages proteins from ribosomes into vesicles
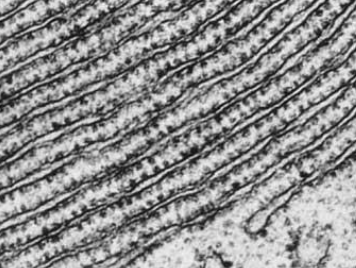
51
New cards
smooth endoplasmic reticulum SER
series of flattened membrane bound compartments with no ribosomes, carry out lipid synthesis, metabolism and membrane formation
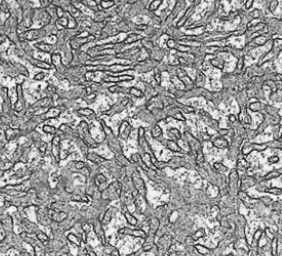
52
New cards
lysosome
spherical membrane bound vesicle produced by golgi body, contains hydrolytic enzymes, same function as vacuole, enzymes break down waste
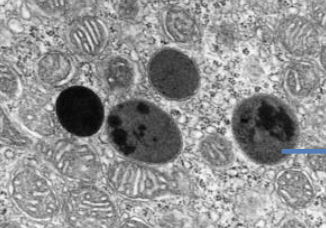
53
New cards
cytoskeleton
network of protein fibres, including microfilaments (actin), microtubules (tubulin), intermediate filaments (fibrous proteins), support cells and organelles, motor proteins use ATP to move organelles/molecules
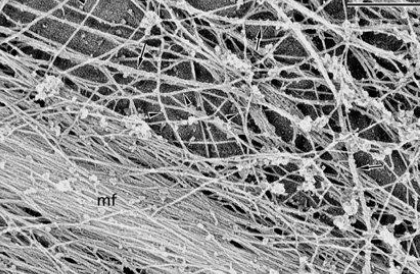
54
New cards
pair of centrioles
cylinder of 9 triplets of microtubules, 2 are arranged at right angles to form centrosome, organise spindle fibres in nuclear division
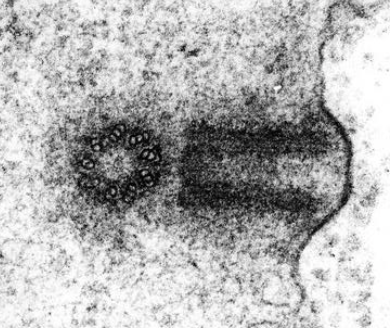
55
New cards
cillia
hair like extensions, 9+2 arrangement of microtubules, not really in plant cells, use ATP to beat and move fluids
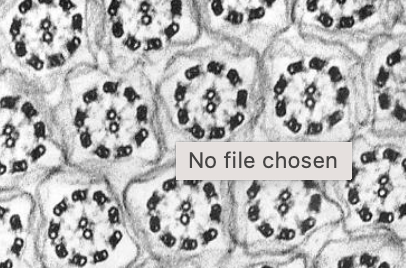
56
New cards
eukaryotic flagellum
few long hair like extensions, 9+2 arrangement of microtubules, not really in plant cells, use ATP to beat and whole cell
57
New cards
cell wall
made of cellulose, located outside plasma membrane, gives shape and support, stops bursting, only in plants
58
New cards
plasmodesmata
strands of cytoplasm that pass through channels in cell wall between adjacent cells, only in plants
59
New cards
large permanent vacuole
fluid filled organelle, filled with water and solutes, pushes cytoplasm against cell wall making it turgid, only in plants
60
New cards
tonoplast
membrane around vacuole which is selectively permeable
61
New cards
circular DNA
genetic material of prokaryotic cell, naked and located in cytoplasm
62
New cards
plasmid
small circular DNA in some prokaryotes, carry additional genes for a slective advantage
63
New cards
pili of fimbriae
specific attachment of prokaryotes to other cells
64
New cards
mesosome
infolded regions of cell surface of prokaryotes
65
New cards
capsule
polysaccharide outside layer, attachment to surfaces, resists desiccation (drying up), protection against been engulfed, prokaryotic cells
66
New cards
flagellum
long hair like extensions for movement
67
New cards
7, 1, 2, 4, 6, 5, 8, 3, 9
order production of proteins:
1. messenger RNA leaves by nuclear pore
2. messenger RNA assembles to ribosome attached to RER
3. vesicle fuses with plasma membrane
4. ribosome reads mRNA and synthesis protein which is transported through RER and packaged into transport vesicle
5. golgi apparatus modifies proteins and repackages them into secretory vesicle
6. proteins transported in vesicles along cytoskeleton by motor proteins from RER to golgi apparatus
7. a gene is transcribed into mRNA in nucleus
8. vesicles carrying modified proteins are transported along cytoskeleton by motor proteins to cell surface
9. membrane opens and modified proteins released
1. messenger RNA leaves by nuclear pore
2. messenger RNA assembles to ribosome attached to RER
3. vesicle fuses with plasma membrane
4. ribosome reads mRNA and synthesis protein which is transported through RER and packaged into transport vesicle
5. golgi apparatus modifies proteins and repackages them into secretory vesicle
6. proteins transported in vesicles along cytoskeleton by motor proteins from RER to golgi apparatus
7. a gene is transcribed into mRNA in nucleus
8. vesicles carrying modified proteins are transported along cytoskeleton by motor proteins to cell surface
9. membrane opens and modified proteins released