Biomechanics exam 3
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Mass
Amount of matter
Weight
The effect of gravity on mass
Inertia
Resisting change in motion
Center of gravity
The location of object in which all the mass is evenly distributed
Work
Force x distance

Power
Force x distance/time , force x velocity

Rectilinear motion
Straight line
Curvilinear motion
Curved line
What is linear motion measured by?
Linear displacement (feet, meters, etc)
Energy
Ability to do work
Nuclear, heat, chemical, electrical, mechanical are examples of
Energy
3 forms of mechanical energy
Kinetic, gravitation potential energy, elastic potential energy
Kinetic energy
Energy of motion, KE = ½ x mass x velocity 2
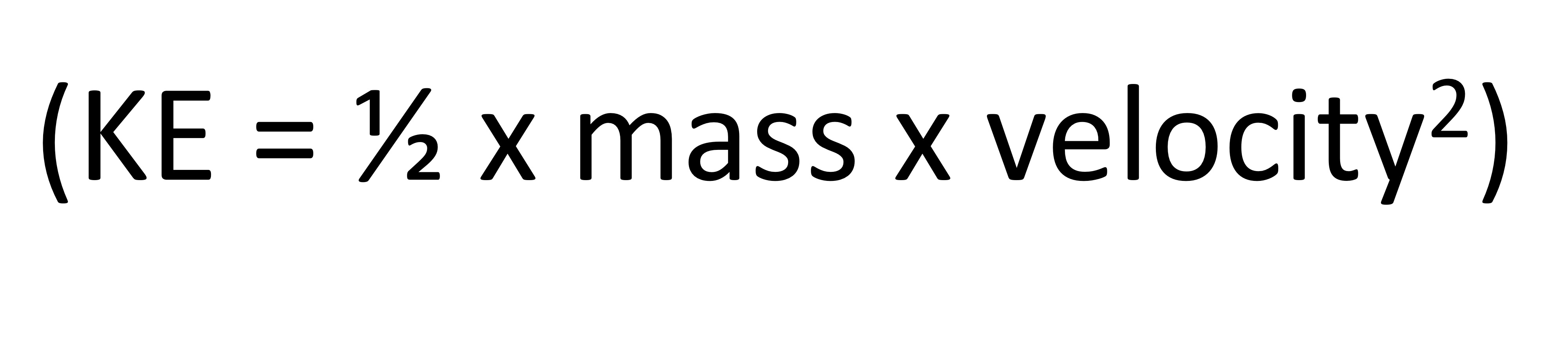
Gravitation potential energy
PE = weight x height above the ground

Elastic potential energy
Ability to do work while recoiling from being stretched/ compressed
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but it is constantly
Converted
There has be a- to have a change in motion
Net external force
The force you exert against the earth when walking is the
Internal force
The force of the earth pushing against you when walking is the
External force
The forces exchanged when walking is an example of the
Ground reaction force
What is the external force of bringing the fist up toward the shoulder
Force from bicep
4 properties of a force
Magnitude, direction, point of application, line of action
Rotary motion
When an object is restricted to moving around a fixed axes
Radius of rotation
Distance from axis to rotating object
What is rotary motion measured by?
Angular displacement (degrees)
Pressure
Force acting over a given area , force/ area

The environment will deliver a-- in response to the force the body exerts on the environment
Reaction force
Newtons 3rd law of Motion
For every force applied by one body on a second, the second body applies an equal and oppositely directed force on the first
If you're sprinting off a block, you are not moving into the ground meaning you are the - force?
Internal
When knee extension happens, the quads are the - force
External
The internal force and external force are - in magnitude
Equal
The arrow depicting force is called a
Force vector
Friction force
Normal force x coefficient of friction
Normal friction
Force pushing surfaces together
Coefficient of friction
The roughness of the surface
A high coefficient of friction means friction is
High
Centripetal force
Responsible for continually forcing the rotating object to follow circular path (inward)
Centrifugal force
Equal and opposite reaction force of centripetal force
Centripetal formula
Mass x speed 2 / radius of circle

Small radius of a turn needs- centripetal force; large radius needs-
More, less
Coefficient of elasticity (e)
Sq route of height of rebound/ height of drop

Vector quantities
Magnitude and direction - force
Scalar quantities
Magnitude only- mass, volume, area
Net effect is determined by __
Vector composition
Vector composition
More than one external force applied to a system (going from 2 to 1)
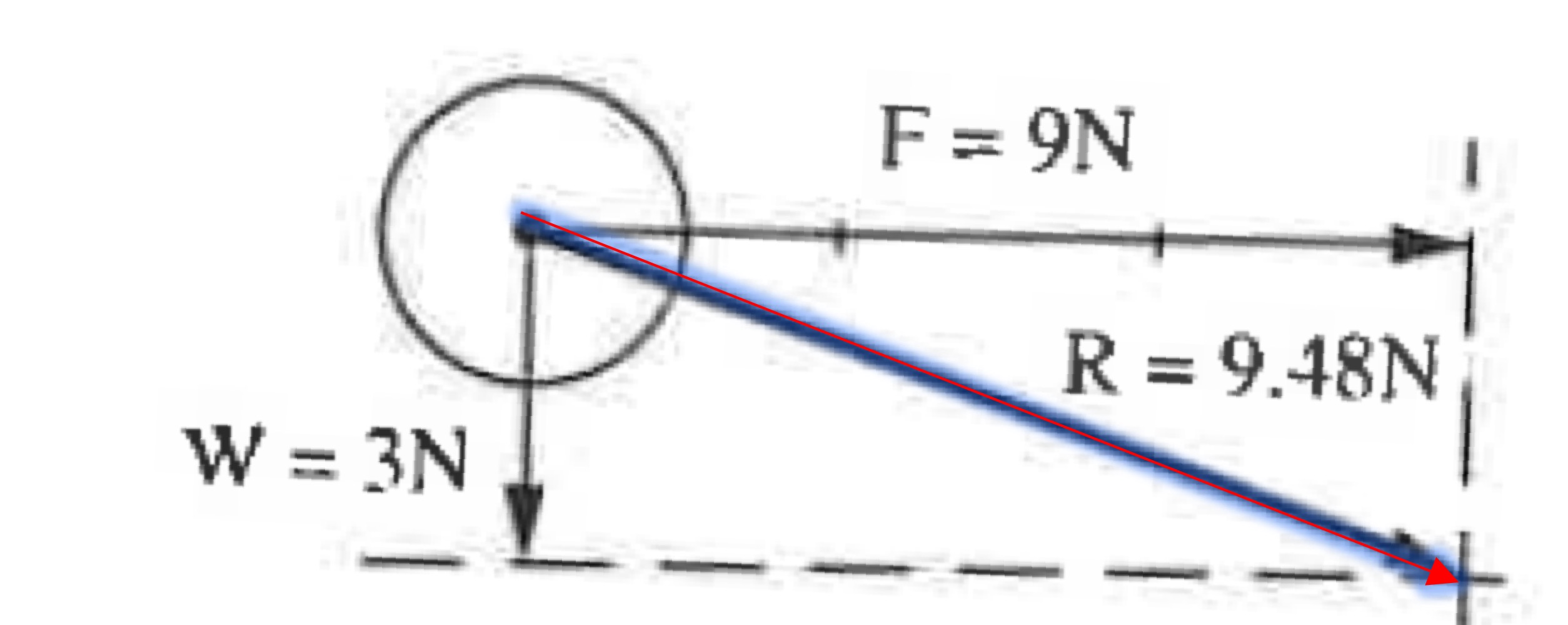
The - shows where the ball will go
Resultant vector
Colinear forces
Forces have the same line of action
Vector resolution is _ of the vector composition process
Reverse
Vector resolution
Taking a vector and breaking it into vertical and horizontal components (going from 1 to 2)
When performing a bicep curl, what are the 2 components
Stabilizing and rotary
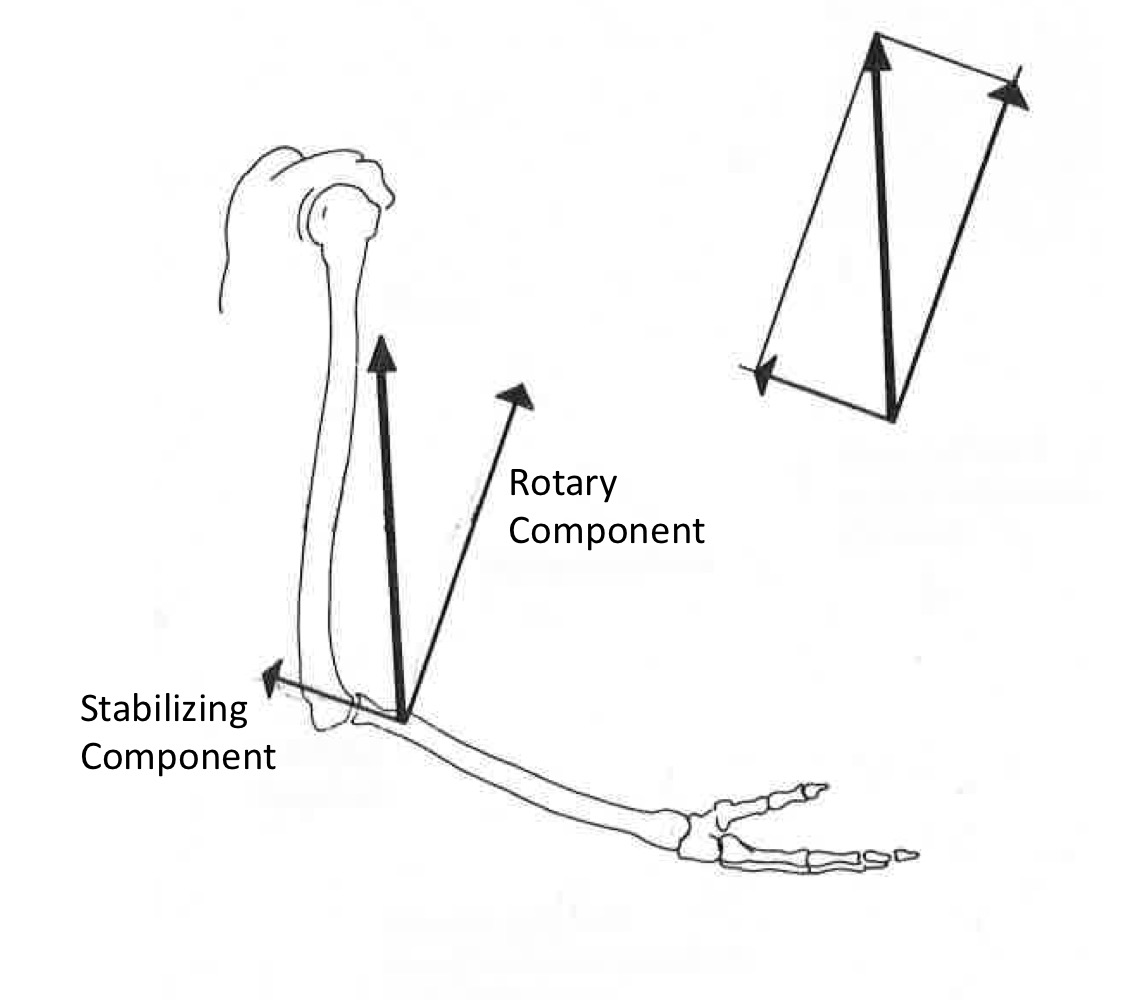
When an external force acts on a system which is restricted to moving around an axis, the result is
Rotary motion
2 rules for force to cause torque
Eccentric force, force must not pass through axis
Eccentric force
Away from axis (not in the center)
Torque formula
Force x force arm
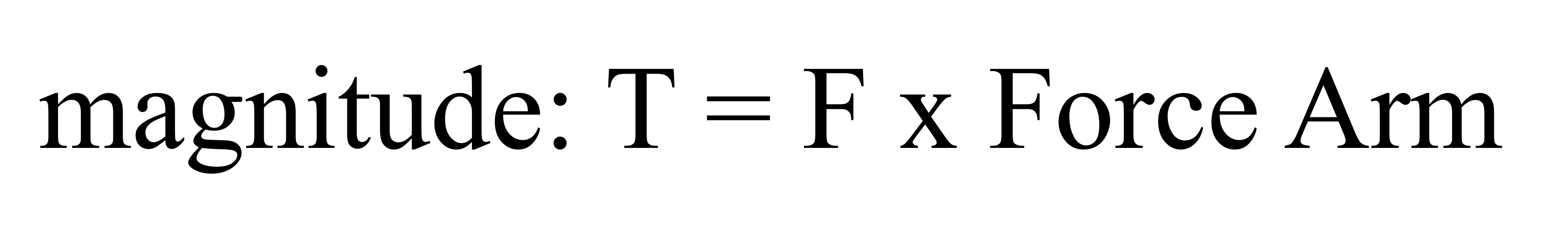
Force arm
Shortest distance from axis to the line of action of the force, only perpendicular distance
Clockwise -, counter clockwise _
-, +
Force is measured in newtons, force arm is measured in meters. What is torque expressed as?
Newton meters (Nm)
The rotary motion and response of a segment is determined by the-
Net torque
When would you want the torque of a weight to be stronger than the torque of your arm?
Eccentric training
4 functions of a machine
Balance forces, provide advantage in force, provide advantage in ROM and movement speed, and change force direction
3 machine-like structures used by the body
Lever, wheel -axle, and pulley
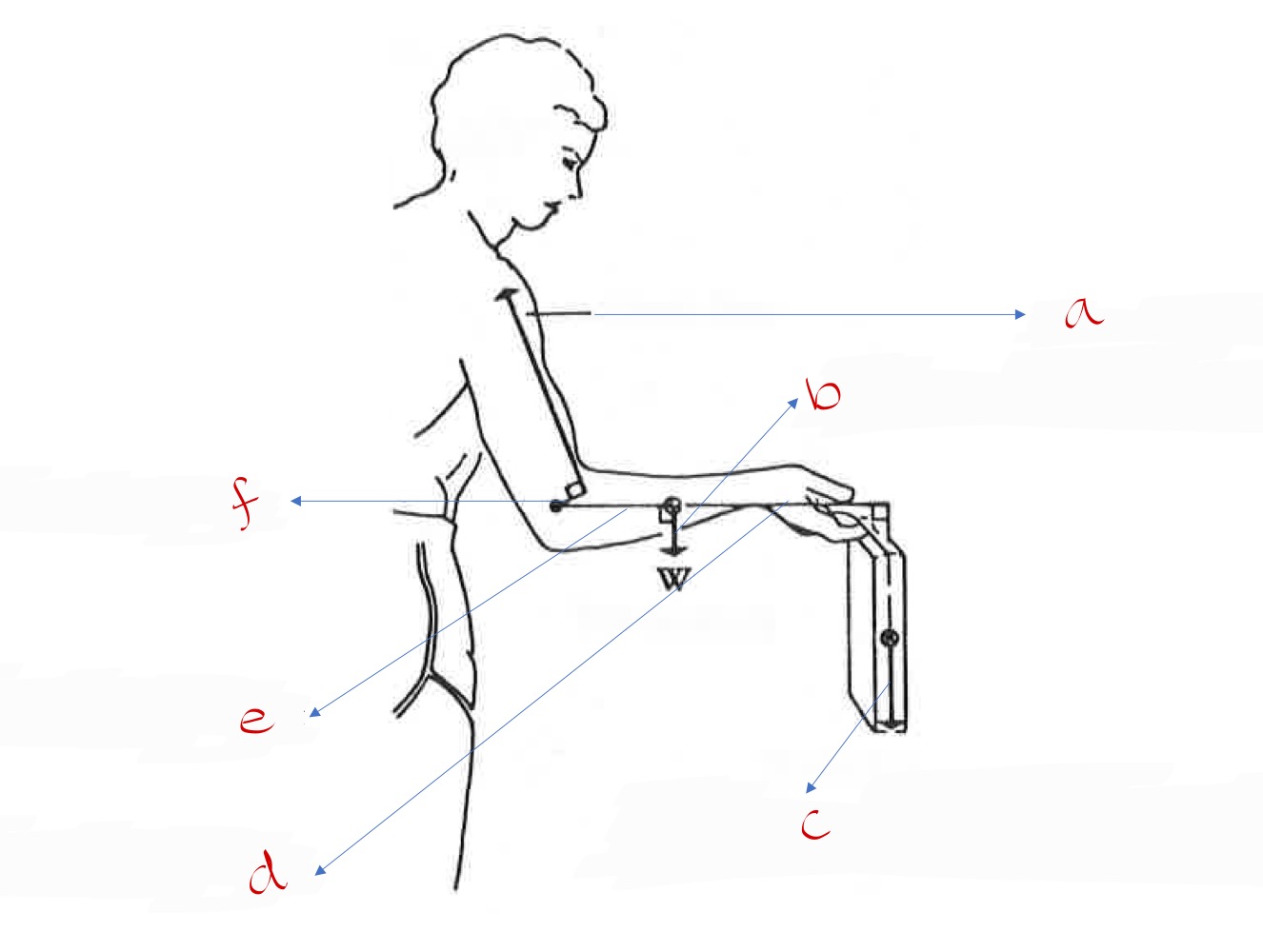
A: muscle force vector, B: weight of arm force vector, C: weight of briefcase force vector, D: weight of briefcase force arm E: weight of arm force arm, F: muscle force arm
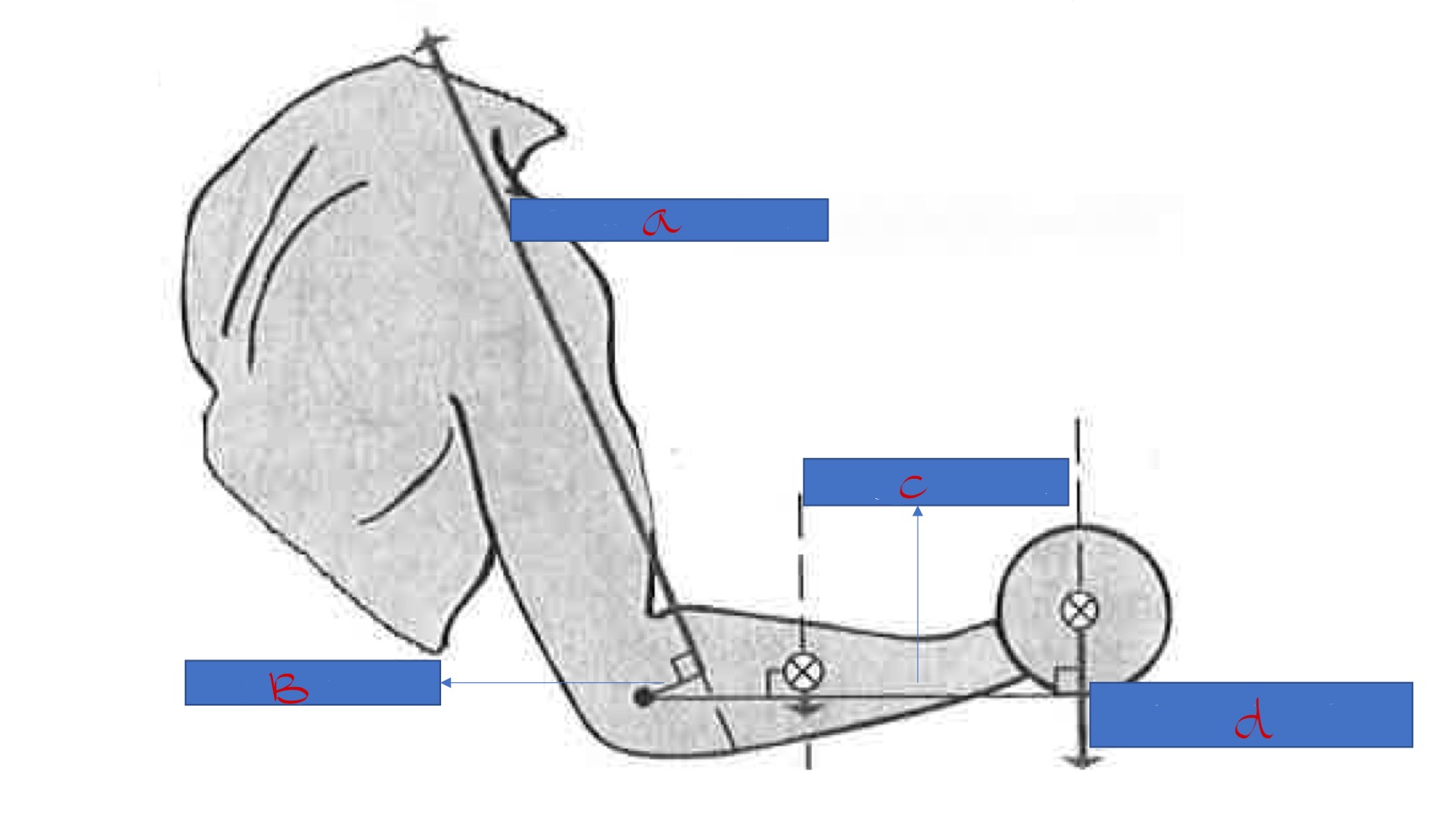
A: bicep force, B: bicep force arm, C: weight force arm , D: weight force
90 degree angle of pull- - force arm
Longest
Muscles of the body are at a biomechanical - when it comes to force
Disadvantage
Muscles of the body are at a biomechanical - when it comes to range of motion and speed of movement
Advantage
How are levers classified?
According to position of axis, motive force, and resistive force
First class lever
Axis is between the motive force and resistive force
What kind of levers are the triceps and calf muscles?
First class
Second class lever
The resistive force is between the motive force and axis
A nutcracker is an example of a - lever
Second class
Third class levers
The motive force is between the resistive force and axis
What kind of lever are most concentric body movements
Third class
What kind of lever is an eccentric body movement
Second class
Where is the motive force applied on the wheel axle machine of an automobile?
The axle
The medial and lateral malleoulus are examples of _
Pulleys