DNA translation
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
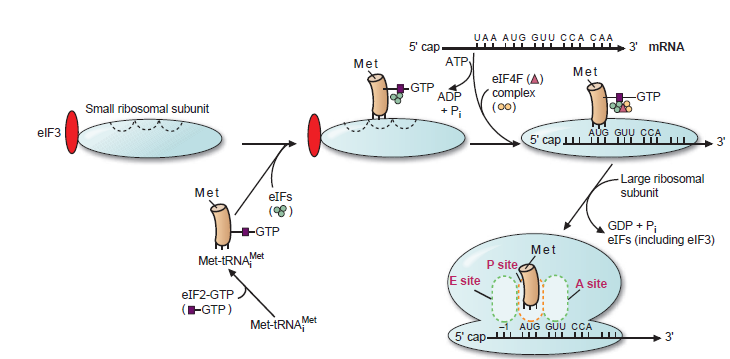
What is the initiation process in translation?
Formation ▪ of initiation complex
- tRNA binds to the small (40S) ribosomal subunit
- Requires hydrolysis of ATP
▪ The cap of 5’-end of mRNA binds to CBP that contains initiation factors.
- Other IF join the initiation complex
▪mRNA then binds to the initiation complex
- The complex start to scans the mRNA for the AUG start codon
▪ At the start codon:
- GTP is hydrolysed, IFs are released & the large ribosomal (60S) subunit join the complex
▪ The ribosome is now complete. It has 3 binding sites for tRNA:
- P (peptidyl), A (aminosyl), E (ejection) sites
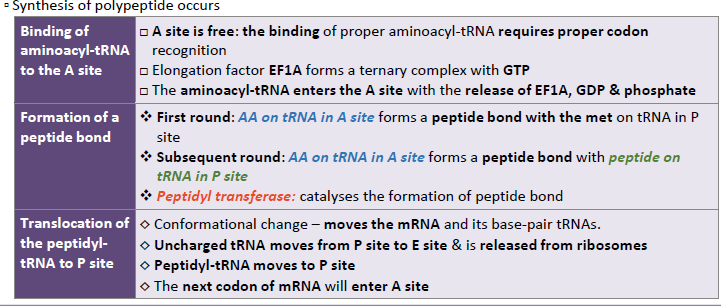
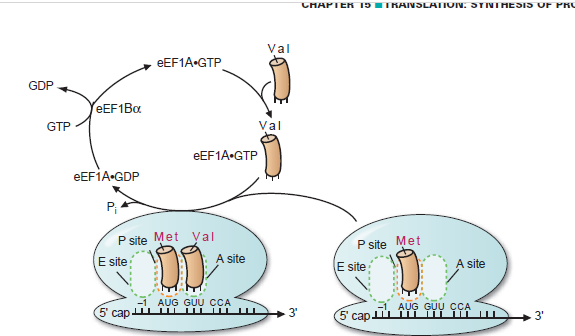
Describe the elongation steps in translation.
What happens in the termination phase of translation?
▪ Occurs when a stop codon enters A site
▪ Cytoplasmic release factors bind to the stop codon
- It catalyse the cleavage of the bond between polypeptide & tRNA
- It alters peptidyl transferase & adds H2O instead of an AA
▪ Protein is released & the ribosome breaks into 2 subunits to move on to another mRNA translation
How is the genetic code interpreted in translation?
Codons: Each group of three mRNA nucleotides (codon) codes for a specific amino acid.
Start and Stop Codons: Translation always begins at an AUG (methionine) start codon and stops at one of the three stop codons