Ch. 2 - The Chemistry of Biology
5.0(4)Studied by 32 people
Card Sorting
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:25 PM on 2/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
1
New cards
Matter
all materials that occupy space and have mass
2
New cards
What is matter composed of?
atoms
3
New cards
Atom
simplest form of matter not divisible into simpler substances
4
New cards
Protons
(+) subatomic particles
5
New cards
Neutrons
neutral subatomic particles
6
New cards
Electrons
(-) subatomic particles
7
New cards
4 Fundamental Forces
1. Gravity
2. Electromagnetism
3. Strong nuclear force
4. Weak Force
8
New cards
Electromagnetism
like charges repel, unlike attract
9
New cards
Strong nuclear force
Holds nucleus together
10
New cards
Weak force
Radioactivity (neutron)
11
New cards
What do all atoms share?
The same fundamental structure
12
New cards
Element
pure substances w/ a characteristic number of protons, neutrons, and electrons and predictable chemical behaviors
13
New cards
Atomic number
number of protons
14
New cards
Atomic mass
number of protons **and** neutrons
15
New cards
Isotopes
variant forms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons
16
New cards
Atomic weight
average mass numbers of all isotopic forms
17
New cards
Electron orbitals
volumes of space surrounding the atomic nucleus where electrons are likely to be found
18
New cards
Molecule
a chemical substance that results from the combination of two or more **atoms**
19
New cards
Compounds
molecules that are combinations of two or more different **elements**
20
New cards
Formula/Mass Weight
sum of all of the atomic masses of the atoms a molecule contains
21
New cards
Chemical bonds
when 2 or more atoms share, donate, or accept electrons to form molecules and compounds
22
New cards
What are the three different types of chemical bonds?
1. Covalent bonds
2. Ionic bonds
3. Hydrogen bonds
23
New cards
Covalent bonds
* electrons are shared among atoms
* strongest
* strongest
24
New cards
Polar covalent bonds
* unequal sharing (negative and positive pole)
25
New cards
Nonpolar covalent bonds
equal sharing
26
New cards
Ionic bonds
* one or more electrons from one atom are removed and attached to another atom which forms **positively charge cations** and **negatively charged anions**
* least important
* least important
27
New cards
Hydrogen bonds
**weak** bonds between hydrogen and other atoms
* electrons are not shared, lost, or gained
* electrons are not shared, lost, or gained
28
New cards
Organic chemicals
compounds containing carbon bonded to hydrogens
29
New cards
Ionization
aqueous dissociation of an electrolyte into ions
30
New cards
Functional group
a particular molecular combination that reacts in predictable ways and confers particular properties on a compound
31
New cards
What can functional groups help define?
The chemical class of certain groups of organic compounds
32
New cards
C Hopkins Cafe Mg NaCl
* Carbon
* Hydrogen
* Oxygen
* Phosphate
* Potassium
* Iodine
* Nitrogen
* Sulfer
* Calcium
* Iron
* Magnesium
* Sodium
* Chlorine
* Hydrogen
* Oxygen
* Phosphate
* Potassium
* Iodine
* Nitrogen
* Sulfer
* Calcium
* Iron
* Magnesium
* Sodium
* Chlorine
33
New cards
Functional Groups of Organic Compounds
* accessory molecules that bind to organic compounds
* confer unique reactive properties on the whole molecule
* confer unique reactive properties on the whole molecule
34
New cards
Hydroxyl Formula
R-OH
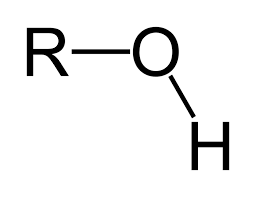
35
New cards
Where can hydroxyl be found?
Alcohols and carbohydrates
36
New cards
Carboxyl formula
R−COOH
37
New cards
Where can carboxyl be found?
Fatty acids, proteins, organic acids
38
New cards
Amino formula
R-CH(NH2)-COOH
39
New cards
Where can amino be found?
Proteins, nucleic acids
40
New cards
Ester formula
R-COO-R
41
New cards
Where can ester be found?
Lipids
42
New cards
Phosphate formula
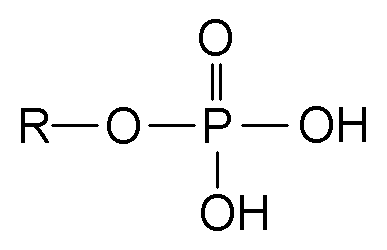
43
New cards
Where can phosphate be found?
DNA, RNA, ATP
44
New cards
Carbohydrate
A compound containing primarily carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio
45
New cards
What is the general formula for Carbohydrates?
(CH2O)n
46
New cards
Dehydration synthesis
loss of water in a polymerization reaction
47
New cards
What is the function of carbohydrates?
polysaccharides provide cell structure, adhesion and metabolism
48
New cards
How does cellulose affect cell walls?
Cellulose provides the strength and rigidity of the cell wall
49
New cards
Chitin
* Polysaccharide similar to cellulose in chemical structure
* Major compound in the cell walls of fungi and the exoskeletons of insects
* Major compound in the cell walls of fungi and the exoskeletons of insects
50
New cards
Peptidoglycan
* When polysaccharides are linked to peptide fragments
* Provides the main source of structural support to the bacterial cell wall
* Provides the main source of structural support to the bacterial cell wall
51
New cards
Gram-negative bacteria’s cell wall contains what?
Lipopolysaccharide
52
New cards
Lipopolysaccharide
LPS of gram-negative bacteria is an endotoxin w/ generalized pathologic effects such as fever
53
New cards
Glycocalyx
* attachment to other cells
* site for receptors
* carbohydrate-rich molecule
* site for receptors
* carbohydrate-rich molecule
54
New cards
Glycosidic bonds
link of subunits of disaccharides and polysaccharides
55
New cards
Peptide
Molecule composed of short chains of amino acids, such as a dipeptide, tripeptide, and a tetrapeptide
56
New cards
Phosphodiester bond
Forms when **two hydroxyl groups** **in phosphoric acid** react w/ a **hydroxyl group** on other molecules, forming **ester bonds**
57
New cards
Disulfide bonds
Occurs between sulfur atoms on the amino acid cysteine
58
New cards
Lipids (what are they? created by? classification?)
* long hydrophobic, C-H chains attached to a glycerol molecule
* created by **dehydration synthesis**
* triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids and waxes
* created by **dehydration synthesis**
* triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids and waxes
59
New cards
Triglycerides
* 3 fatty acids bound to glycerol
* Saturated/unsaturated
* Energy storage
* Saturated/unsaturated
* Energy storage
60
New cards
Saturated fatty acid
has all carbons in the chain bonded to hydrogen w/ single bonds
61
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acids
Has at least one carbon-carbon double bond
62
New cards
Give an example of a more saturated fat?
Solid fats (butter)
63
New cards
Example of unsaturated fats
Oils (liquid fats)
64
New cards
Name some bad things **saturated fats** can do to you
* Raise your cholesterol levels
* Increase risk of heart disease
* low density lipoproteins
* Increase risk of heart disease
* low density lipoproteins
65
New cards
Name good things **unsaturated fats** can do to you
* Lower cholesterol levels
66
New cards
Structure of phospholipids
* Glycerol w/ 2 fatty acids + a phosphate group
* Bilayers of phospholipids form membranes
* Bilayers of phospholipids form membranes
67
New cards
What does the structure of phospholipids provide?
Impenetrable barrier that accounts for the selective permeability and transport of molecules
68
New cards
How are amino acids attached in order to form proteins?
Through peptide bonds
69
New cards
Functions of proteins
support, enzymes, defense, transport, movement
70
New cards
Primary structure of a protein
* Series of amino acids bound in a chain
* Amino acids display small charged functional groups
* Amino acids display small charged functional groups
71
New cards
Secondary structure of a protein
* Develops when CO- and NH- groups on adjacent amino acids form **hydrogen bonds**
* then folds the chain forming an alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
* then folds the chain forming an alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
72
New cards
Tertiary structure of a protein
* forms when parts of the secondary structure interact by forming **covalent disulfide bonds** and other interactions
* creates a 3-D mass
* creates a 3-D mass
73
New cards
Quartenary structure of a protein
* exists only in proteins that consist of more than 1 polypeptide chain
* typical of antibodies and some enzymes that act in cell synthesis
* typical of antibodies and some enzymes that act in cell synthesis
74
New cards
Structure of DNA
* adenine & thymine, cytosine & guanine
* Double Helix
* formed by **2 very long polynucleotide strands** linked along their length by **hydrogen bonds** between the **nitrogenous bases**
* Double Helix
* formed by **2 very long polynucleotide strands** linked along their length by **hydrogen bonds** between the **nitrogenous bases**
75
New cards
Structure of RNA
* polynucleotide that consists of a long chain of nucleotides
* **single strand** that contains **ribose sugar** instead of **deoxyribose**
* **uracil** instead of thymine
* **single strand** that contains **ribose sugar** instead of **deoxyribose**
* **uracil** instead of thymine
76
New cards
Three types of RNA
mRNA: messenger RNA
tRNA: transfer RNA
rRNA: ribosomal RNA
tRNA: transfer RNA
rRNA: ribosomal RNA
77
New cards
Purines
* two rings
* 2 types: adenine & guanine
* 2 types: adenine & guanine
78
New cards
Pyrimidines
* one ring
* 3 types: thymine, cytosine, and uracil
* 3 types: thymine, cytosine, and uracil
79
New cards
ATP
* adenosine triphosphate
* nucleotide: adenine, ribose, 3 phosphates
* nucleotide: adenine, ribose, 3 phosphates
80
New cards
Function of ATP
transfer and storage of energy