BIO 1111 FInal Exam Study Guide
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Hydrophilic Substance
A substance that likes water (can interact with water molecules).
Is a catalyst (a protein that acts as a catalyst in biochemical reactions, lowering the activation energy).
Programmed cell death occurs when triggered by signals that activate a cascade of “Suicide” proteins for in the cells designated to die (a normal part of growth and development)
A type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically diverse gametes. (mix it up and split it up)
enables an organism to meet its nutrient and energy demands
Mutations
Permanent alterations in the DNA sequence (can lead to changes in protein function and contribute to genetic diversity).
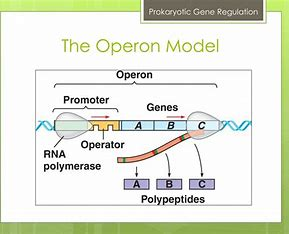
Operon
A unit of genetic expression in prokaryotes that consists of a promoter, operator, and one or more structural genes.
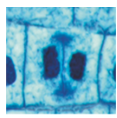
What phase is this?
Telophase/Cytokinesis

What phase is this?
Anaphase
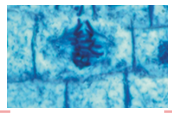
What phase is this?
Metaphase
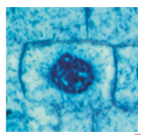
What phase is this?
Prometaphase
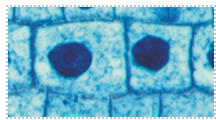
What phase is this?
Prophase
what does the G1 Phase do?
grow cell
What does the S Phase do?
synthesis DNA
What does the G2 Phase do?
Grow cell more and prep for M-phase
What happens in M-phase (Mitosis and Cytokinesis)?
form two identical daughter cells.
What are the phases in Interphase?
G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase
What are the 2 phases of M-phase?
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
What are the steps in MItosis
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase/cytokinesis
What is the acronym for the steps in Mitosis?
PPMAT
Somatic Cells
everything except egg or sperm
2n = 46
n = ?
23, number of different chromosomes
What is 2n called?
Diploid (sporophyte for plants by mitosis)
What is n called?
Haploid (gametophyte for plants by meiosis)
asexual reproduction
a single individual passes all of it's genes to its offspring (no variation), like creating a clone
sexual reproduction
two individuals passes half their genes to its offspring creating variations every time
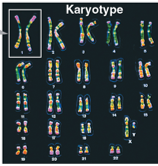
Karyotype
Ordered display of chromosome from cell
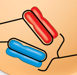
Homologous Chromosomes (homologs)
Chromosomes that have the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern
autosomes
all 22 chromosomes, except for the sex chromosome
Sex chromosomes
The last chromasome, X or Y
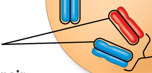
two nonsister chromatids
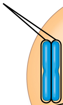
Sister Chromatids
What are the phases for Mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase/cytokinesis → identical daughter cells, Somatic Cells
What are the phases for Meiosis
prophase 1 (cross DNA), metaphase 1, anaphase 1, telophase/cytokinesis 1, prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, telophase/cytokinesis 2 → nonidentical daughter cells, Gametes
What is the cell cycle
Interphase, G1, S phase, G2, Mitosis prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase/cytokinesis Meiosis prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, telophase/cytokinesis 2
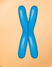
What is the name of this ‘X’ shape?
Chiasmata (chromosome)
What is synapsis?
Homologous chromosomes pair up for cross over
What are the nitrogenous bases?
A, T, G, C
Pairing a purine. What is a purine? (Pure As Gold)
Adenine and Guanine
Pairing a pyrimidine. What is a pyrimidine?
Cytosine and Thymine
Which is correct? Pairing:
pyrimidine with pyrimidine, or
purine with purine, or
pyrimidine with purine
pyrimidine with purine
Where does replication start?
origins of replication (where the two DNA strands are separate, opening up replication “bubble”)
Helicase (in DNA replication)
enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication fork
Single-strand Binding Proteins
they bind to and stabilize single-stranded DNA
Topoisomerase
relieves the strain that helicase might cause when unwinding them
DNA Polymerase
adds the other bases (ACTG) components of DNA (making the other side) by synthesizing it
Primase (primer)
is the starting point
Leading Strand
growing towards the replication fork, so can be made in one piece using only one primase
lagging strand
growing away from the replication fork, needs multiple primases, so made in pieces, also known as okazaki fragments
is DNA replication an anabolic or catabolic process (cat knocks down building)
anabolic
DNA Ligase
it seals gaps after DNA replication
DNA Pol I
cuts out Primase from 5’ end and replaces missing nucleotide pieces with other DNA nucleotides from 3’ end of adjacent fragment
DNA Pol III
Builds new sequence - synthesizes new DNA, adds nucleotides to RNA Primer (or pre-existing DNA strand)
What is the order of DNA replication?
Topoisomerase, Helicase, Single-Strand Binding Protein, Primase, DNA Pol III, DNA Pol I, DNA Ligase
In which direction does DNA replication occur? (3’ or 5’)
Always moves starting from 3’ end
Nuclease
cuts out damaged stretches of DNA
Telomeres
on tail ends of chromosomes after DNA replication, on the missing pieces that cannot be copied
the smallest unit of life that can exist on its own
cell
subatomic particle found in nucleus with pos. charge …
proton
if an atom has 13 protons and 15 neutrons, it’s atomic number is …
13