weak acids and bases
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what is a proton acceptor
a base
what is a proton donor
an acid
what is a definiton of an acid
it donates H+ to its environment
what is the ionisation or dissociation constant
Ka
if numerator > denominator what does this mean regarding the ka and acid and base
Ka is large and acid is strong
if denominator > denominator what happens regarding the ka and acid or base
Ka is small and acid is weak
what is the Ka equation
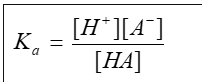
what is the ionisation or dissociation constant
Kb
if numerator > denominator what happens in regards to the kb and acid/base
Kb is large and base is strong
if denominator > numerator what happens in regards to kb and acid/base
Kb is small and base is weak
whar is the equation for Kb
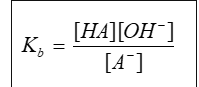
how to calculate pH for weak acids
set up an equilibrium equation and determine the H+ using Ka equation
then use Ph = -log (h+)
what is a bronsted acid
a proton donor
In an equilibrium equation, if HA is an acid, indicate what the resulting A- is called.
conjugate base
True or false.
A base with a low pKa value is classed as a weak base.
TRUE
True or false.
When comparing two acids, the acid with the higher pKa is the strongest acid.
FALSE
the acid with the lower pka is the strongest
Indicate what the resulting pH of a solution with a strong acid and a weak base will be.
acidic with a pH less than 7