ch 3 biomolecules practice questions
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
What other atoms aside from hydrogen can carbon covalently bond to?
Oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur
What is the major characteristic responsible for the complexity and variety of organic compounds?
The chemical versatility of carbon
The category of organic molecule to which enzymes belong that speeds up chemical reaction is
protein
The organic compound that is a component of cell membrane is
lipids
The organic compound that stores and passes the genetic information from parents to offspring is
nucleic acid
The _______ organic compound is broken down into glucose to provide energy for the body.
carbohydrate
Experiments from Miller and Urey were completed under biotic conditions. T/F
F
Chemical evolution resulted in the first forms of life on Earth after formation of organic molecules. T/F
T
What samples were specifically obtained from the experiment?
Protein
What external source specifically formed organic molecules from abiogenic material
Ultraviolet radiation
Aldehyde
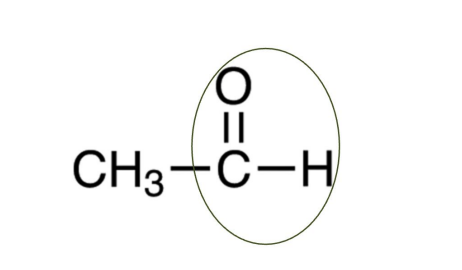
Hydrolysis
Addition of water
Methyl
Stereoisomers
Same molecular constitution, but different spatial arrangement
Dehydration Synthesis
Removal of water
Structural Isomers
Same chemical formula, but different arranged differently
Define dehydration vs hydrolysis.
Dehydration joins be removing water; Hydrolysis breaks by adding water
List the monomer and the bond type for carbohydrate, proteins, and nucleic acids
Carbohydrates - monosaccharides - glycosidic bonds; Proteins - amino acids - peptide; Nucleic acids - nucleotides - phosphodiester.
Lipids are macromolecules in the same sense as others are. TRUE or FALSE
false
Select all that apply:
a. Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are considered macromolecules here because they are polymers of repeating monomers.
b. Lipids are excluded from macromolecules in this framework because they are not true polymers
c. Hydrolysis removes components of water to join monomers
d. Dehydration joins monomers by removing components of water
a. Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are considered macromolecules here because they are polymers of repeating monomers.
b. Lipids are excluded from macromolecules in this framework because they are not true polymers
d. Dehydration joins monomers by removing components of water
Most five or six carbon sugars are rings in aqueous solutions. TRUE or FALSE
True
The bond joining two sugars is
Glycosidic
Linkage in maltose is:
a. Alpha 1 to 4
b. Beta 1 to 4
c. Alpha 1 to 6
d. Beta 1 to 6
a. Alpha 1 to 4
Lactose monosaccharides are
Galactose and Glucose
Which disaccharide is glucose plus fructose?
Sucrose
List where the OH is in the ring plane for the following (above or below):
a. Alpha glucose →
b. Beta glucose →
a. Alpha glucose → OH below
b. Beta glucose → OH above
Select all that are TRUE.
a. Polysaccharides may be linear or branched
b. Chitin is assembled from glucose units modified with nitrogen-containing groups
c. Cellulose has α 1→4 linkages
d. Plants store starch as granules in plastids called amyloplasts
e. Glycogen is more extensively branched than amylopectin
a. Polysaccharides may be linear or branched
b. Chitin is assembled from glucose units modified with nitrogen-containing groups
d. Plants store starch as granules in plastids called amyloplasts
e. Glycogen is more extensively branched than amylopectin
Name the storage polysaccharides in plants and animals:
Starch and Glycogen
Bacteria can break down cellulose and chitin, but human can not. Perhaps humans lack an enzyme that:
a. Breaks down complex carbohydrates
b. Breaks polysaccharides that contain galactose
c. Breaks polysaccharides in which every other residue is flipped in orientation
d. Breaks polysaccharides that originate from plants
c. Breaks polysaccharides in which every other residue is flipped in orientation
The two structural polysaccharides that are important in our world are
cellulose and chitin
Which of the following are true? Select all that apply
a. Glycogen is a disaccharide
b. Carbohydrates serve as fuel for the cell/body
c. Neutral lipids serve as hormones that regulate activities within the cell
d. Lipids are hydrophilic
e. Fats are semisolid
b. Carbohydrates serve as fuel for the cell/body
e. Fats are semisolid
Cellulose is a polymer of glucose with what type of linkages?
beta 1-4 glycosidic linkages
True or False: Saturated fatty acids bind the maximum number of hydrogen atoms to the carbon chain?
True
Fats are constructed from two types of molecules:
Glycerol and Fatty Acids
Choose the following false statements, select all that apply
a. Saturated fats are healthier for humans than unsaturated fats
b. Hydrogenation adds hydroxyl groups to the carbons in an unsaturated fat to make saturated fats
c. Waxes are formed through a long chain fatty acid and ester oxygen to an alcohol
d. All unsaturated fatty acids will only have one double bond
e. Saturated fatty acids only have single bonds
a. Saturated fats are healthier for humans than unsaturated fats
b. Hydrogenation adds hydroxyl groups to the carbons in an unsaturated fat to make saturated fats
d. All unsaturated fatty acids will only have one double bond
Glycerol structure is
3 carbon alcohol with a hydroxl group attached to each carbon
If fatty acid chains in phospholipid bilayer contains saturated and long chains, they exhibit high permeability. True or False?
False
All of these affect the permeability of molecule through the phospholipids except:
a. Polarity
b. Size
c. Charge
d. Temperature
d. Temperature
What makes the phospholipids tails hydrophobic?
Anything related to the nonpolar hydrocarbon tails
What category of lipids do steroid hormones such as testosterone and estrogens belong to?
a. Cholesterol
b. Steroids
c. Amino Acids
d. Peptide
b. Steroids
Why is cholesterol important in animal cells?
It helps with fluidity and stability of the cell membrane
What structural feature defines steroids as a type of lipid?
The 4 carbon rings framework
Acidic amino acids
Aspartic acid (Asp), Glutamic acid
Basic amino acids
Lysine (Lys), Arginine (Arg), Histidine (His)
Disulfide bonds are formed between amino acids containing ______ R group
Sulfur-containing
What are the four components bonded to the central carbon atom in most amino acids?
The R-variable, Carboxyl group, Hydrogen atom, and amino group
How can amino acids act as both acids and bases?
Because they contain both a carboxyl group (acidic) and an amino group (basic), amino acids can donate or accept protons, allowing them to act as both acids and bases (amphoteric)
Denaturation destroys a protein’s primary structure. (T/F)
F
Protein folding is influenced by temperature, pH, and salt concentration. (T/F)
T
The protein helpers that assist folding into the correct tertiary structure are called ____
Chaperonins
Anfinsen’s experiment with ribonuclease demonstrated that protein shape is determined by its __________.
amino acid sequence / primary structure
Which bonds are most responsible for stabilizing tertiary protein structure?
a) Hydrogen bonds
b) Hydrophobic interactions and van der Waals forces
c) Peptide bonds
d) Glycosidic bonds
b) Hydrophobic interactions and van der Waals forces
Which statement about denaturation is TRUE?
a) It always destroys primary structure.
b) It only affects hydrogen bonds in alpha helices.
c) It can be caused by heat, pH changes, or chemicals.
d) It has no effect on protein function.
c) It can be caused by heat, pH changes, or chemicals.
DNA uses uracil instead of thymine. T/F
F
Purines contain two carbon–nitrogen rings. T/F
T
A–T base pairs are held together by three hydrogen bonds. T/F
F
ATATT is more stable than CGCGG T/F
F
Adenine and Guanine are purines T/F
T
Which of the following correctly distinguishes a nucleoside from a nucleotide? a) A nucleoside has a base, sugar, and phosphate group, while a nucleotide has only a base and sugar.
b) A nucleoside has only a nitrogenous base and sugar, while a nucleotide also includes one or more phosphate groups.
c) A nucleoside is found only in DNA, while nucleotides are found only in RNA.
b) A nucleoside has only a nitrogenous base and sugar, while a nucleotide also includes one or more phosphate groups.
During nucleotide polymerization, what type of bond forms between nucleotides?
a) Glycosidic bond between phosphate and sugar
b) Hydrogen bond between phosphate groups
c) Phosphodiester bond between the 5′ phosphate of one nucleotide and the 3′ OH of another
c) Phosphodiester bond between the 5′ phosphate of one nucleotide and the 3′ OH of another
Why does nucleotide polymerization require an input of energy?
a) The reaction increases entropy and is spontaneous.
b) The phosphate groups carry repelling negative charges, requiring energy to link.
c) The nitrogenous bases must be converted to amino acids first.
b) The phosphate groups carry repelling negative charges, requiring energy to link.
Matching Practice
1. DNA
2. Phosphodiester bond
3. Purine
4. Nucleotide
5. RNA
6. ATP
A. Usually single-stranded, can be involved in protein synthesis.
B. Nitrogenous base with a double-ring structure (A, G).
C. High-energy molecule with three phosphate groups.
D. Double-stranded helix with complementary base pairing.
E. Base + sugar + phosphate group.
F. Links nucleotides together in a polynucleotide chain
1 - D
2- F
3- B
4 - E
5 - A
6 - C
Which of these hydrocarbons has a double bond in its structure?
| a. | C3H8 |
| b. | C2H6 |
| c. | CH4 |
| d. | C2H4 |
| e. | C2H2 |
d. C2H4
Which functional group forms the highly reactive part of aldehydes and ketones?
| a. | carbonyl |
| b. | hydroxyl |
| c. | phosphate |
| d. | amino |
| e. | carboxyl |
carbonyl
Which functional group is polar and a key component of alcohols?
| a. | carbonyl |
| b. | hydroxyl |
| c. | phosphate |
| d. | amino |
| e. | carboxyl |
b. hydroxyl
Which functional group acts as an organic base?
| a. | carbonyl |
| b. | hydroxyl |
| c. | phosphate |
| d. | amino |
| e. | carboxyl |
d. amino
Isomers are two or more molecules with ____ chemical formula and ____ molecular structures.
| a. | a different; different |
| b. | the same; different |
| c. | a different; the same |
| d. | the same; the same |
| e. | a structural; theoretical |
b. the same; different
Structural isomers differ from each other ____.
| a. | in the arrangement of their covalent bonds |
| b. | in their molecular formulas |
| c. | by being mirror images that cannot be superimposed on each other |
| d. | by having double covalent bonds instead of single bonds |
| e. | by having different atomic isotopes in their molecules |
a. in the arrangement of their covalent bonds
When molecules are referred to as D- or L- (for example D-forms of sugars and L-forms of amino acids), the D- and L- designations refer to the specific ____.
| a. | functional group |
| b. | structural isomer |
| c. | covalent bond |
| d. | secondary structure |
| e. | stereoisomer |
e. stereoisomer
Reactions that use the equivalent of a water molecule to break a molecule into smaller subunits are called ____ reactions.
| a. | equilibrium |
| b. | hydration |
| c. | hydrolysis |
| d. | redox |
| e. | dehydration synthesis |
c. hydrolysis
Reactions that remove the equivalent of a water molecule when subunits are joined to make a larger molecule are called ____ reactions.
| a. | equilibrium |
| b. | hydration |
| c. | hydrolysis |
| d. | redox |
| e. | dehydration synthesis |
e. dehydration synthesis
Monosaccharides and disaccharides are types of ____.
| a. | proteins |
| b. | lipids |
| c. | nucleic acids |
| d. | carbohydrates |
| e. | amino acids |
d. carbohydrates
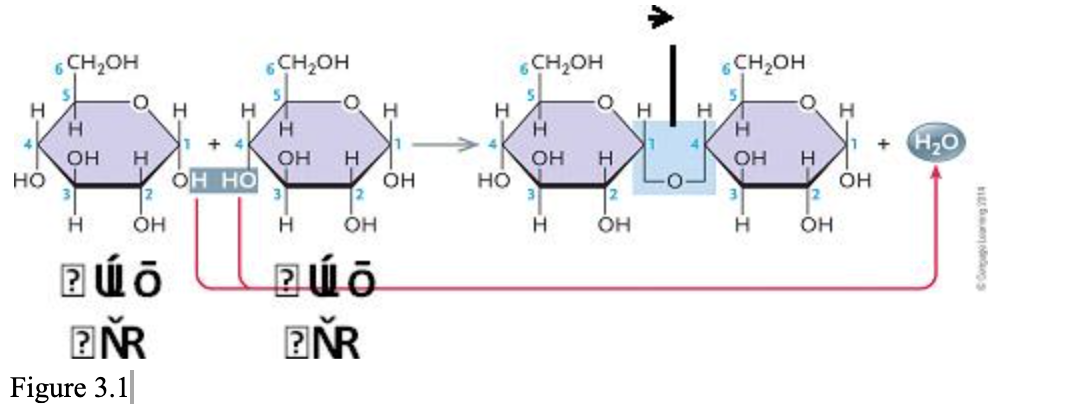
The accompanying figure illustrates the synthesis of ____.
| a. | sucrose |
| b. | maltose |
| c. | lactose |
| d. | cellulose |
| e. | fructose |
b. maltose
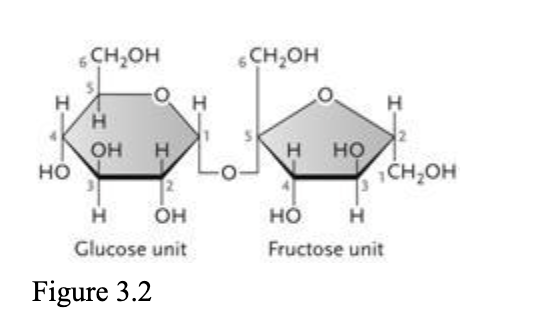
The disaccharide in the accompanying figure is ____.
| a. | cellulose |
| b. | galactose |
| c. | maltose |
| d. | sucrose |
| e. | lactose |
d. sucrose
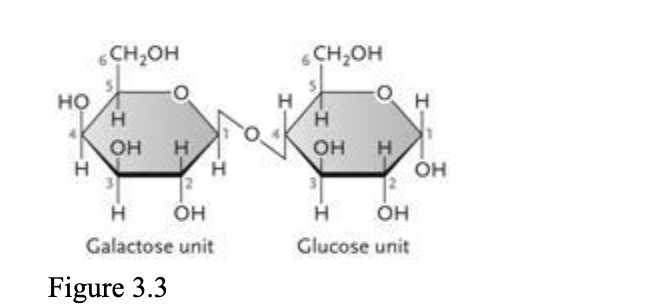
The disaccharide in the accompanying figure is ____.
| a. | lactose |
| b. | fructose |
| c. | maltose |
| d. | cellulose |
| e. | sucrose |
a. lactose
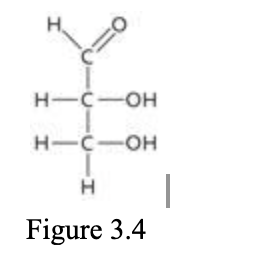
The molecule in the accompanying figure is glyceraldehyde, an example of a ____ sugar.
| a. | triose |
| b. | hexose |
| c. | pentose |
| d. | heptose |
| e. | tetrose |
a. triose
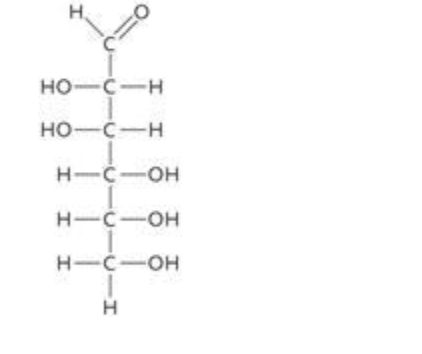
The molecule in the accompanying figure is mannose, an example of a ____ sugar.
| a. | triose |
| b. | hexose |
| c. | pentose |
| d. | heptose |
| e. | tetrose |
b. hexose
Amylose is a polymer made up of glucose monomers joined by ____.
| a. | b(1-4) linkages |
| b. | b(1-6) linkages |
| c. | a(1-4) linkages |
| d. | a(1-6) linkages |
| e. | both b(1-4) and a(1-6) linkages |
c. alpha 1-4 linkages
The linkage commonly found between subunits in a chain of monosaccharides is called a ____ bond.
| a. | phosphodiester |
| b. | disulfide |
| c. | glycosidic |
| d. | hydrogen |
| e. | peptide |
c. glycosidic
Probably the most abundant carbohydrate on Earth, which unbranched chain of b-glucose subunits is the primary structural fiber in plant cell walls?
| a. | chitin |
| b. | amylopectin |
| c. | cellulose |
| d. | glycogen |
| e. | amylose |
c. cellulose
Which polysaccharide is a chain of glucose units that are modified by having nitrogen-containing groups, is the main structural fiber in the external skeletons of arthropods, and also a structural material in the cell walls of fungi?
| a. | chitin |
| b. | amylopectin |
| c. | cellulose |
| d. | glycogen |
| e. | amylose |
a. chitin
Suppose that an equal amount of each polysaccharide was placed in a landfill. Which polysaccharide should last the longest before it is decomposed?
| a. | chitin |
| b. | amylopectin |
| c. | cellulose |
| d. | glycogen |
| e. | amylose |
c. cellulose
In many animals, this polysaccharide is found in large quantities in liver and muscle cells. It is highly branched, with many a(1-4) and a(1-6) linkages.
| a. | chitin |
| b. | amylopectin |
| c. | cellulose |
| d. | glycogen |
| e. | amylose |
d. glycogen
A fatty acid has a(n)____ group at the end of a hydrocarbon chain.
| a. | carbonyl group |
| b. | hydroxyl group |
| c. | phosphate group |
| d. | amino group |
| e. | carboxyl group |
e. carboxyl group
If three molecules of a fatty acid having the formula C16H22O2 are each joined to a molecule of glycerol (C3H8O3) by a dehydration synthesis reaction, what will be the formula of the resulting neutral fat molecule?
| a. | C48H66O6. |
| b. | C48H72O8. |
| c. | C51H68O6. |
| d. | C51H72O8. |
| e. | C51H74O9. |
c. C51H68O6
Glycerol forms the backbone of ____.
| a. | triglycerides only |
| b. | polysaccharides and nucleic acids |
| c. | nucleic acids only |
| d. | polypeptides only |
| e. | triglycerides and phospholipids |
e. triglycerides and phospholipids
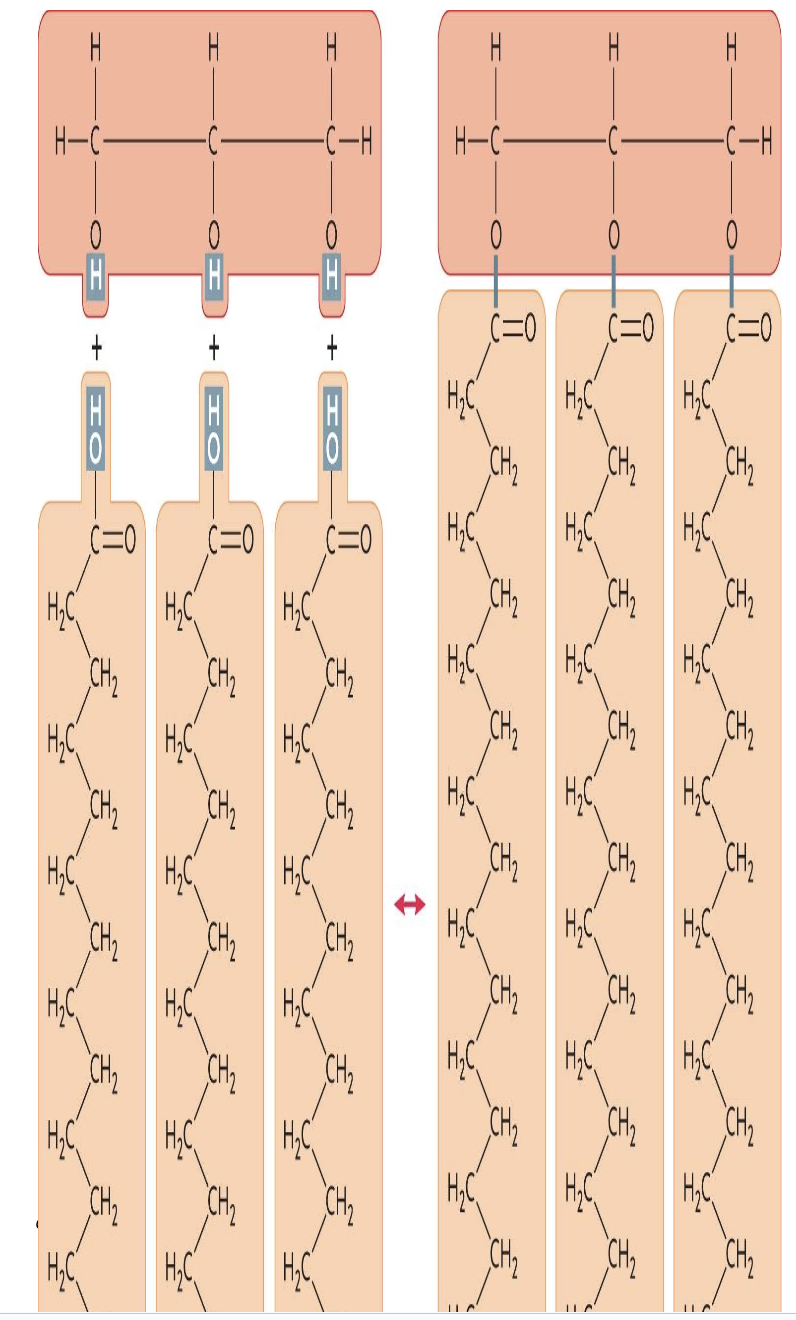
The molecule in the accompanying figure is a(n) ____.
| a. | triglyceride |
| b. | amino acid |
| c. | steroid |
| d. | polysaccharide |
| e. | phospholipid |
a. triglyceride
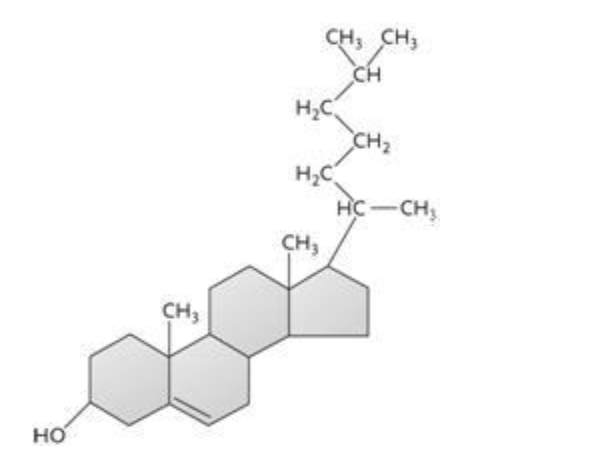
The molecule shown above is a(n) ____.
| a. | triglyceride |
| b. | amino acid |
| c. | steroid |
| d. | polysaccharide |
| e. | phospholipid |
c. steroid
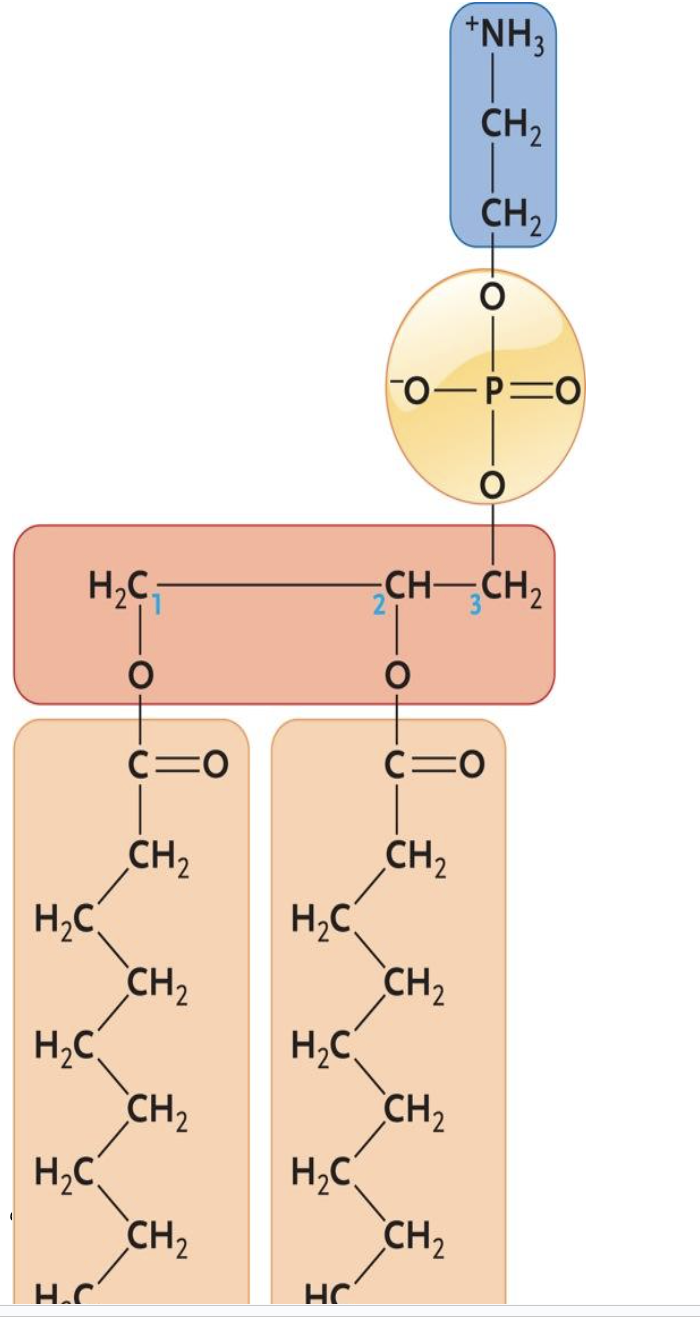
The molecule shown above is a(n) ____.
| a. | triglyceride |
| b. | amino acid |
| c. | steroid |
| d. | polysaccharide |
| e. | phospholipid |
e. phospholipid
Sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) are involved in regulating the synthesis of ____.
| a. | proteins |
| b. | lipids |
| c. | nucleic acids |
| d. | carbohydrates |
| e. | amino acids |
b. lipids
We would expect to find fatty acids with ____ carbons in living organisms.
| a. | 8 |
| b. | 13 |
| c. | 16 |
| d. | 19 |
| e. | 26 |
c. 16
Waxy coatings, such as those found on skin, hair, and feathers of some animals and the cuticle of some plants, are commonly used by living organisms for protection against water loss and for lubrication. Such waxes are considered to be a type of ____.
| a. | triglyceride |
| b. | steroid |
| c. | neutral lipid |
| d. | phospholipid |
| e. | fatty acid |
c. neutral lipid

The molecule in the accompanying figure is ____, and has ____.
| a. | unsaturated; a carbon-carbon double bond |
| b. | saturated; a carbon-carbon double bond |
| c. | unsaturated; no carbon-carbon double bonds |
| d. | saturated; no carbon-carbon double bonds |
| e. | saturated; a carbon-carbon triple bond |
d. saturated; no carbon-carbon double bonds
Why are trans fats more harmful for consumption than saturated fats?
| a. | Trans fats increase LDL cholesterol levels more than saturated fats. |
| b. | Trans fats decrease HDL cholesterol levels more than saturated fats. |
| c. | Saturated fats prevent LDL transport more than trans fats. |
| d. | Trans fats are often consumed with other food additives that increase fat absorption in the gut. |
| e. | Saturated fats are more natural, and better digested in the gut. |
b. Trans fats decrease HDL cholesterol levels more than saturated fats.
Which molecule is the main structural component of biological membranes?
| a. | starch |
| b. | triglyceride |
| c. | protein |
| d. | phospholipid |
| e. | steroid |
d. phospholipid
HDL cholesterol is considered "good" cholesterol. What role does HDL play in preventing coronary heart disease?
| a. | HDL cholesterol inhibits LDL cholesterol synthesis |
| b. | HDL cholesterol prevents transport of LDL cholesterol in blood |
| c. | HDL cholesterol activates LDL cholesterol breakdown |
| d. | HDL cholesterol prevents free radical formation in plaques |
| e. | HDL cholesterol removes excess cholesterol from plaques |
e. HDL cholesterol removes excess cholesterol from plaques
Testosterone has important regulatory functions in humans and many other animals. Molecules with regulatory functions like testosterone are called ____.
| a. | phytosterols |
| b. | enzymes |
| c. | lipoproteins |
| d. | hormones |
| e. | receptors |
d. hormones
The sex hormones of many animals are lipid molecules known as ____.
| a. | fatty acids |
| b. | phospholipids |
| c. | carotenoids |
| d. | steroids |
| e. | lipoproteins |
d. steroids
Which class of molecule is the most diverse in terms of structure and roles played in cells?
| a. | proteins |
| b. | lipids |
| c. | nucleic acids |
| d. | carbohydrates |
| e. | amino acids |
a. proteins
Proteins are polymers of ____.
| a. | amino acids |
| b. | monosaccharides |
| c. | steroids |
| d. | nucleotides |
| e. | phospholipids |
a. amino acids