chemistry - separate chemistry 2: alcohols & carboxylic acids (9.26 - 9.34)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
9.26 methanol formula
CH3OH
9.26 methanol structure
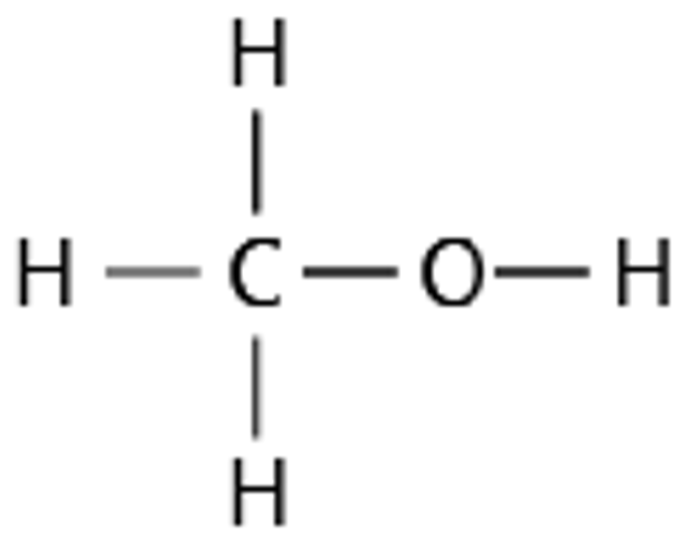
9.26 ethanol formula
C2H5OH
9.26 ethanol structure
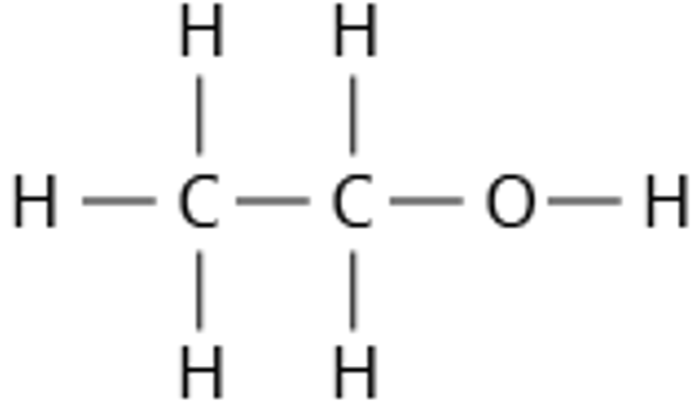
9.26 propanol (propan-1-ol) formula
C3H7OH
9.26 propanol (propan-1-ol) structure
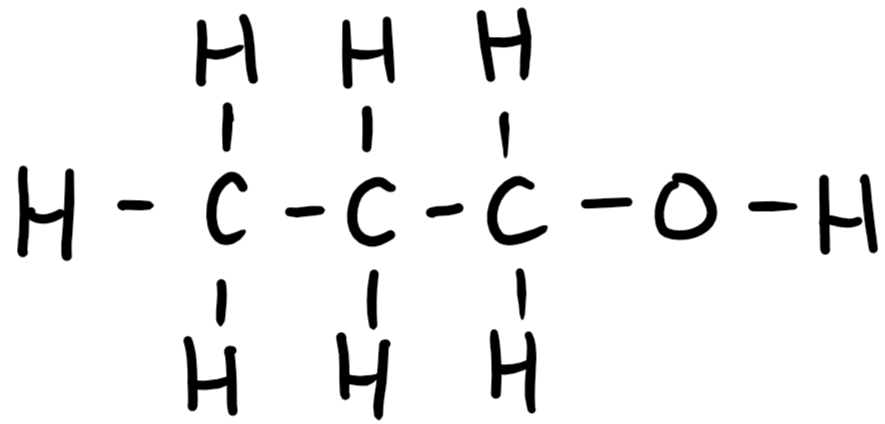
9.26 butanol (butan-1-ol) formula
C4H9OH
9.26 butanol (butan-1-ol) structure
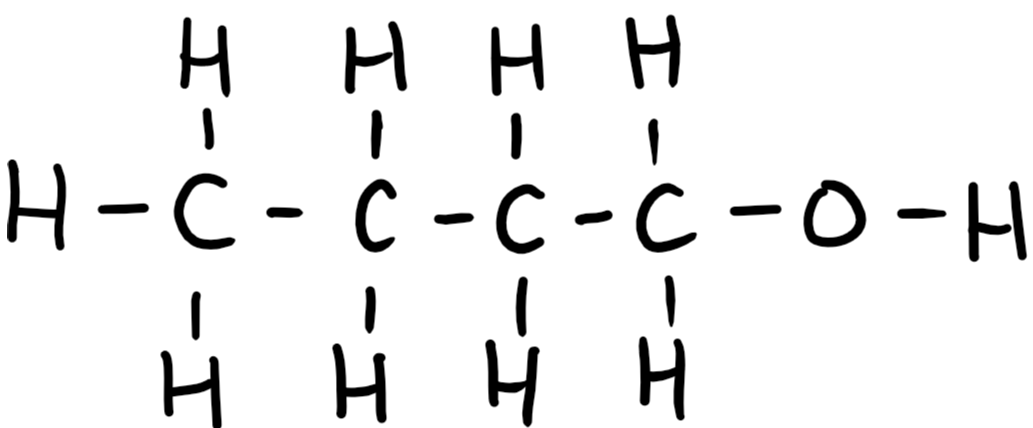
9.27 alcohols functional group
-OH
9.27 what happens when alcohols are dehydrated?
alcohols dehydrated to form alkenes
9.28 core practical: investigate temp. rise produced in known mass of water by combustion of alcohols ethanol, propanol, butanol & pentanol
measure mass of alcohol burner & cap
record mass & name of alcohol
place alcohol burner in centre of heat-resistant mat
use measuring cylinder to add 100cm3 cold water to conical flask
measure & record initial temp. of water
clamp flask above alcohol burner
light wick of burner & allow water to heat up by about 40°C
replace cap on burner & measure & record final temp. of water
measure mass of alcohol burner & cap again & record mass
calculate mass of alcohol burned to produce 1°C rise in temp.
repeat steps 1-10 using fresh, cold water & diff. alcohol
9.29 methanoic acid formula
HCOOH
9.29 methanoic acid structure
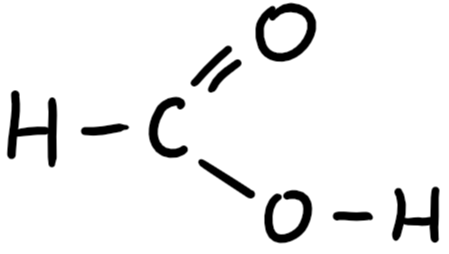
9.29 ethanoic acid formula
CH3COOH
9.29 ethanoic acid structure
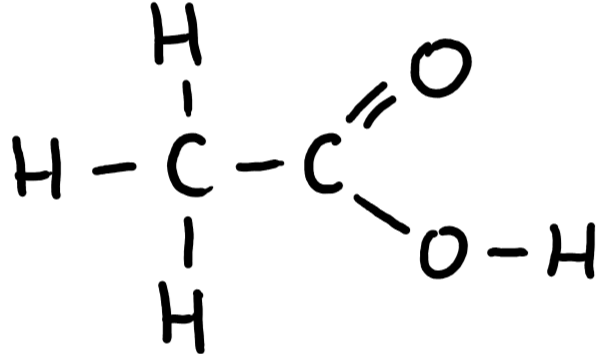
9.29 propanoic acid formula
C2H5COOH
9.29 propanoic acid structure
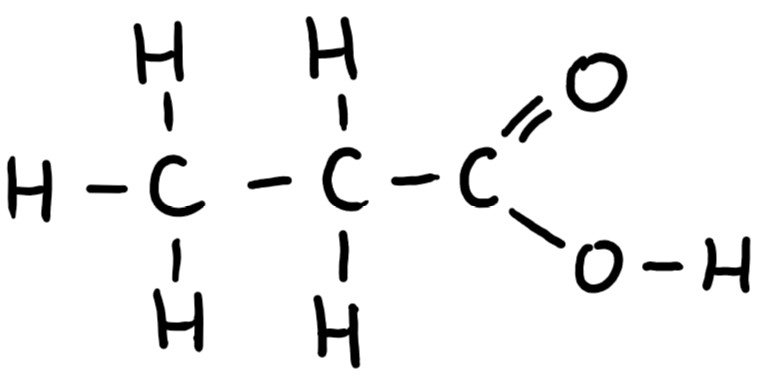
9.29 butanoic acid formula
C3H7COOH
9.29 butanoic acid structure
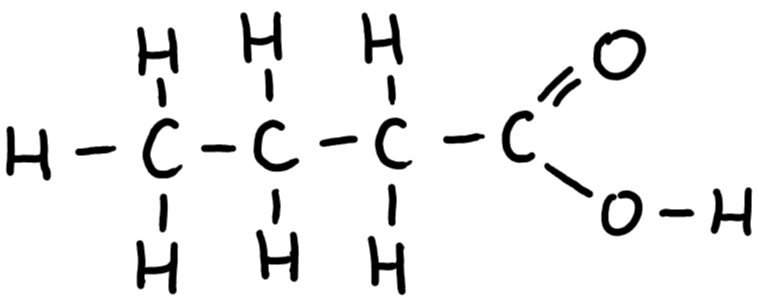
9.30 carboxylic acids functional group
-COOH
9.30 what properties do solutions of carboxylic acids have?
solutions of carboxylic acids have typical acidic properties
9.31 what happens when ethanol is oxidised?
ethanol oxidised to produce ethanoic acid (+ water)
9.31 what happens when alcohols are oxidised?
produce carboxylic acids (+ water)
9.32 what do members of given homologous series have in common?
similar reactions
9.32 what do members of given homologous series have similar reactions?
molecules contain same functional group
what do alcohols produce when completely combusted?
carbon dioxide + water
9.33 production of ethanol
carbohydrate starch broken down into sugars
plant material containing sugars mixed with water & yeast
enzymes in yeast turn sugars → ethanol & CO2 in fermentation
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
what type of respiration is yeast fermentation?
anaerobic respiration
9.34 how to obtain concentrated solution of ethanol?
fermentation only produces alcohol concs. up to 15% - higher concs. kill yeast cells
more concentrated solutions of ethanol formed by fractional distillation
b.p of ethanol < b.p. of water
heated liquids evaporate
vapours cool as rise up fractionating column
ethanol has lower b.p. - remains gas for longer, separates from water
first fraction/distillate collected contains higher % of ethanol