01.AB BIO, HN Characteristics of Living Things, & Hierarchy of Life (PARTS A & B)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Biology
The study of life

Cell
Basic unit of life
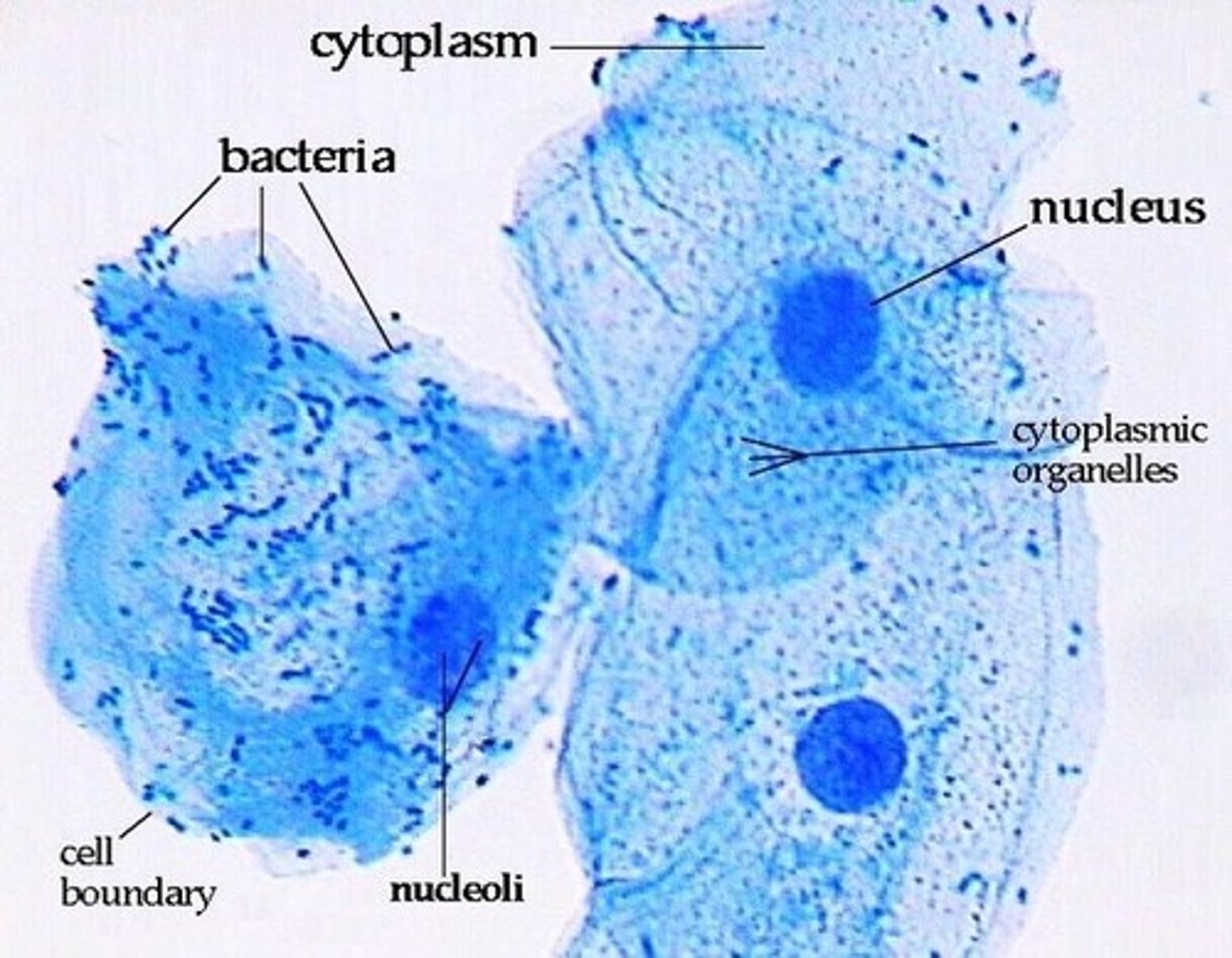
Unicellular
Made of a single cell
Multicellular
Made up of more than one cell
Organism
A living thing
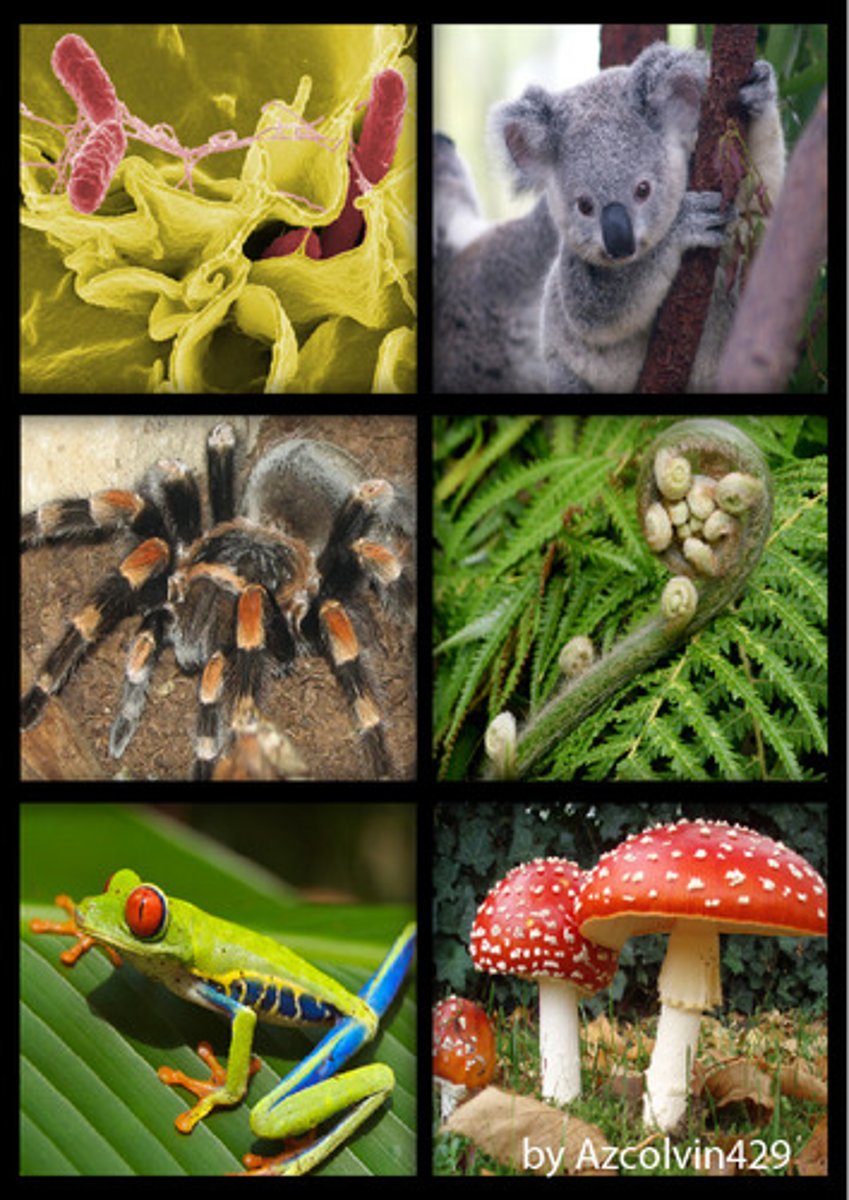

Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
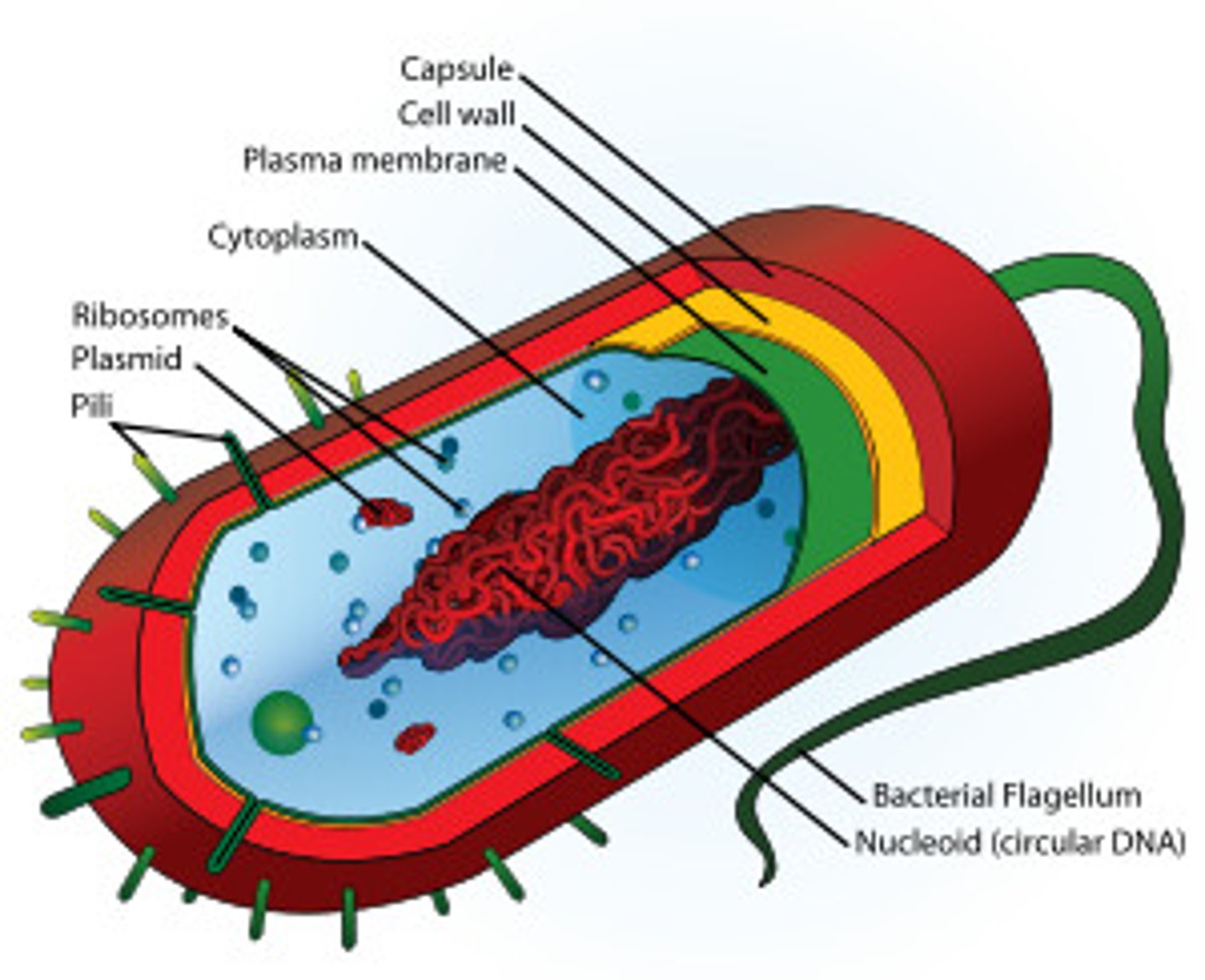
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
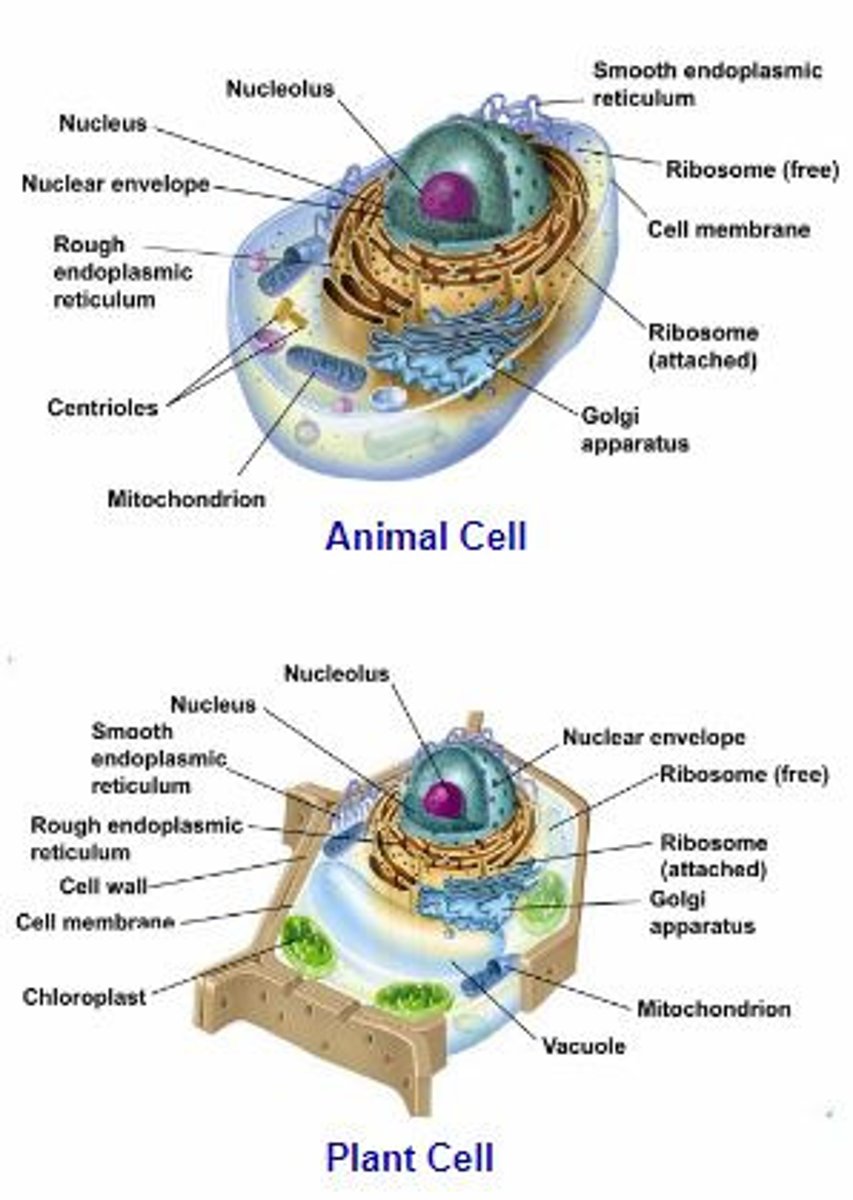
Reproduction
Create new cells or a new individual
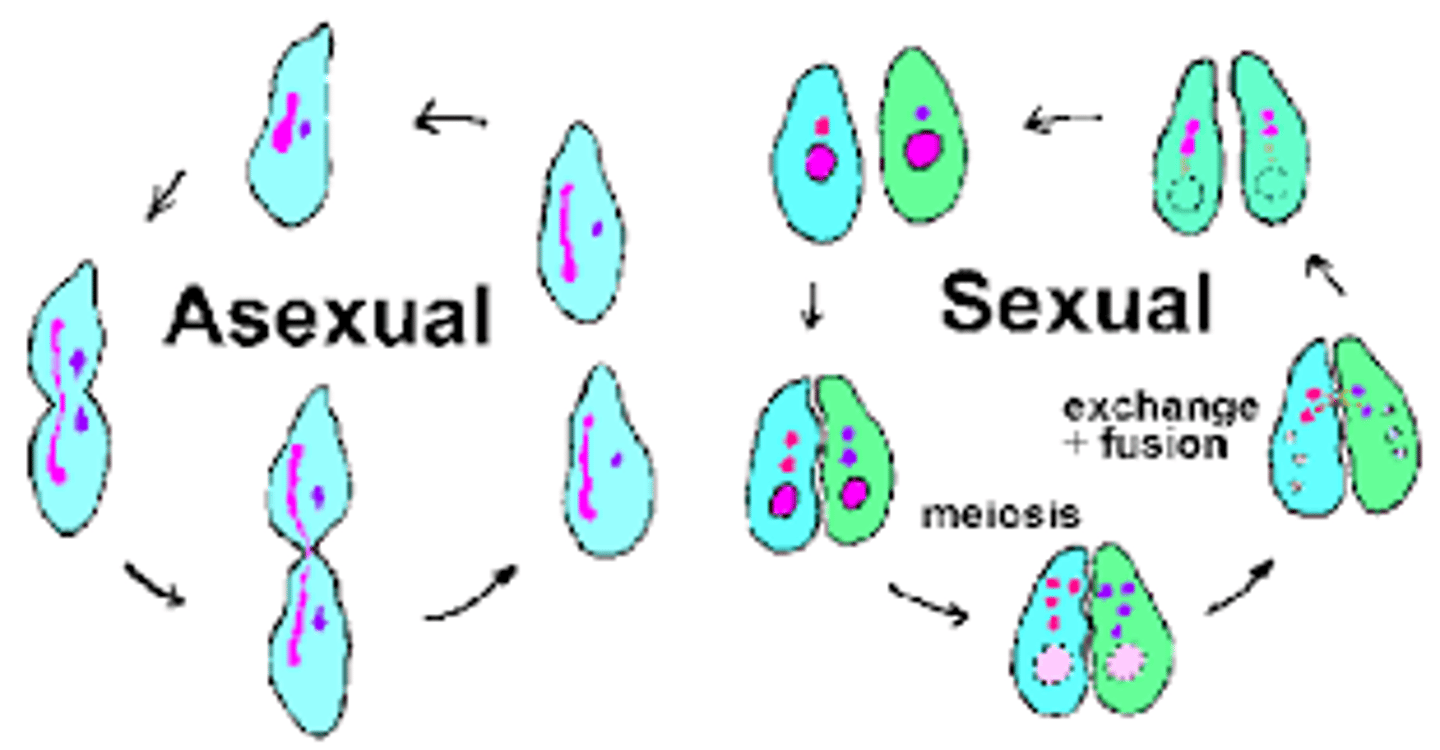
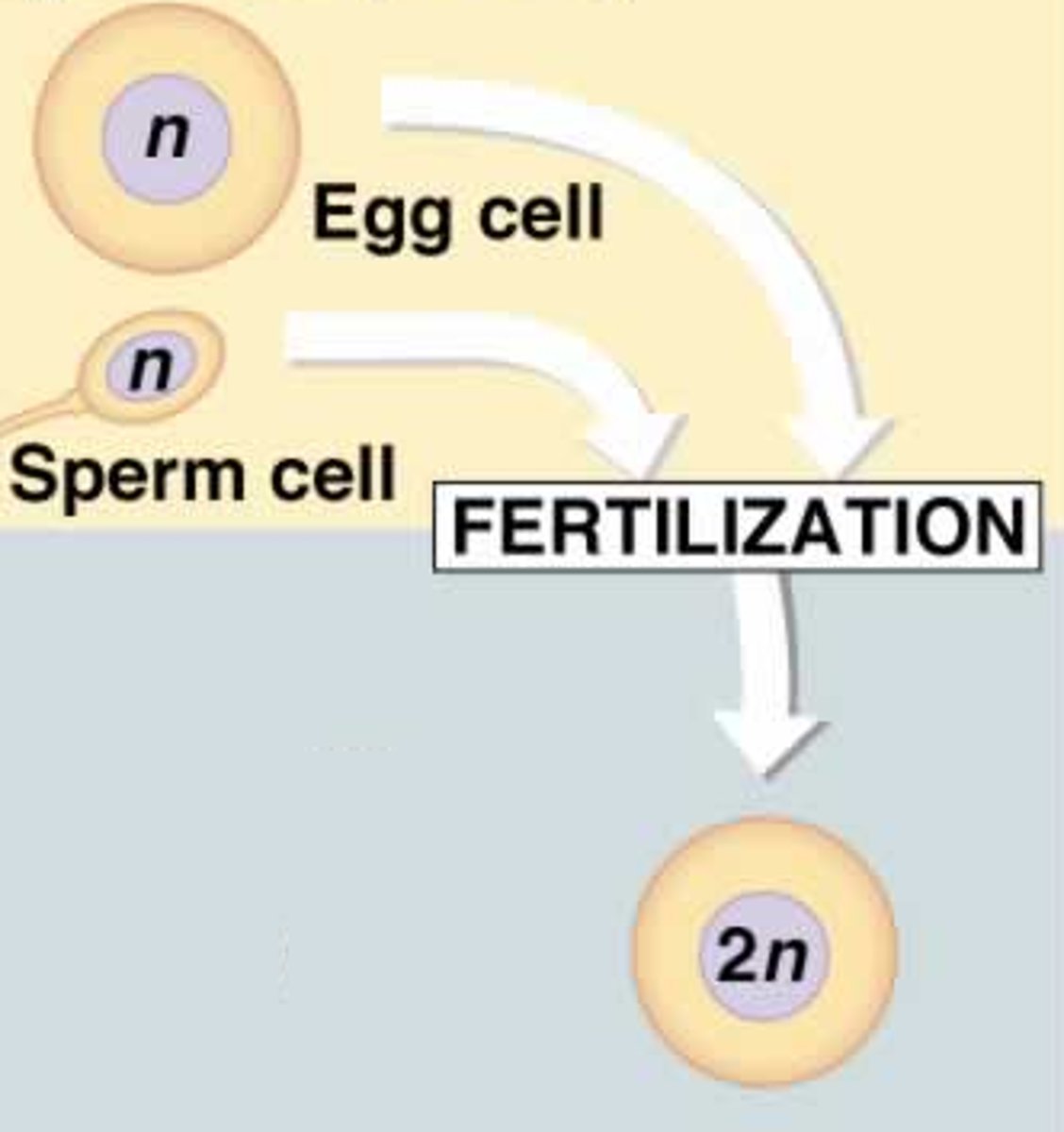
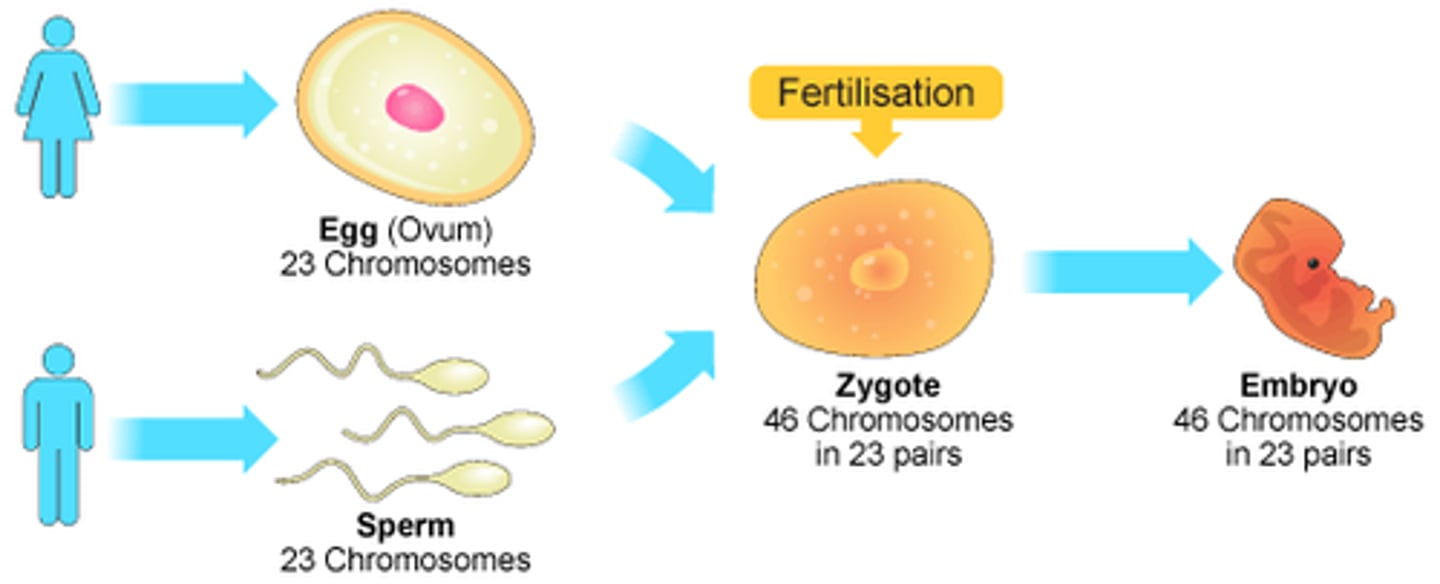
Sexual reproduction (Description)
A process in which cells or DNA from two different parents join to form a genetically unique organism
Sexual reproduction (Examples)
Examples include conjugation, fertilization and pollination
Asexual reproduction (Description)
A process in which a single parent reproduces by itself to make an identical copy of itself
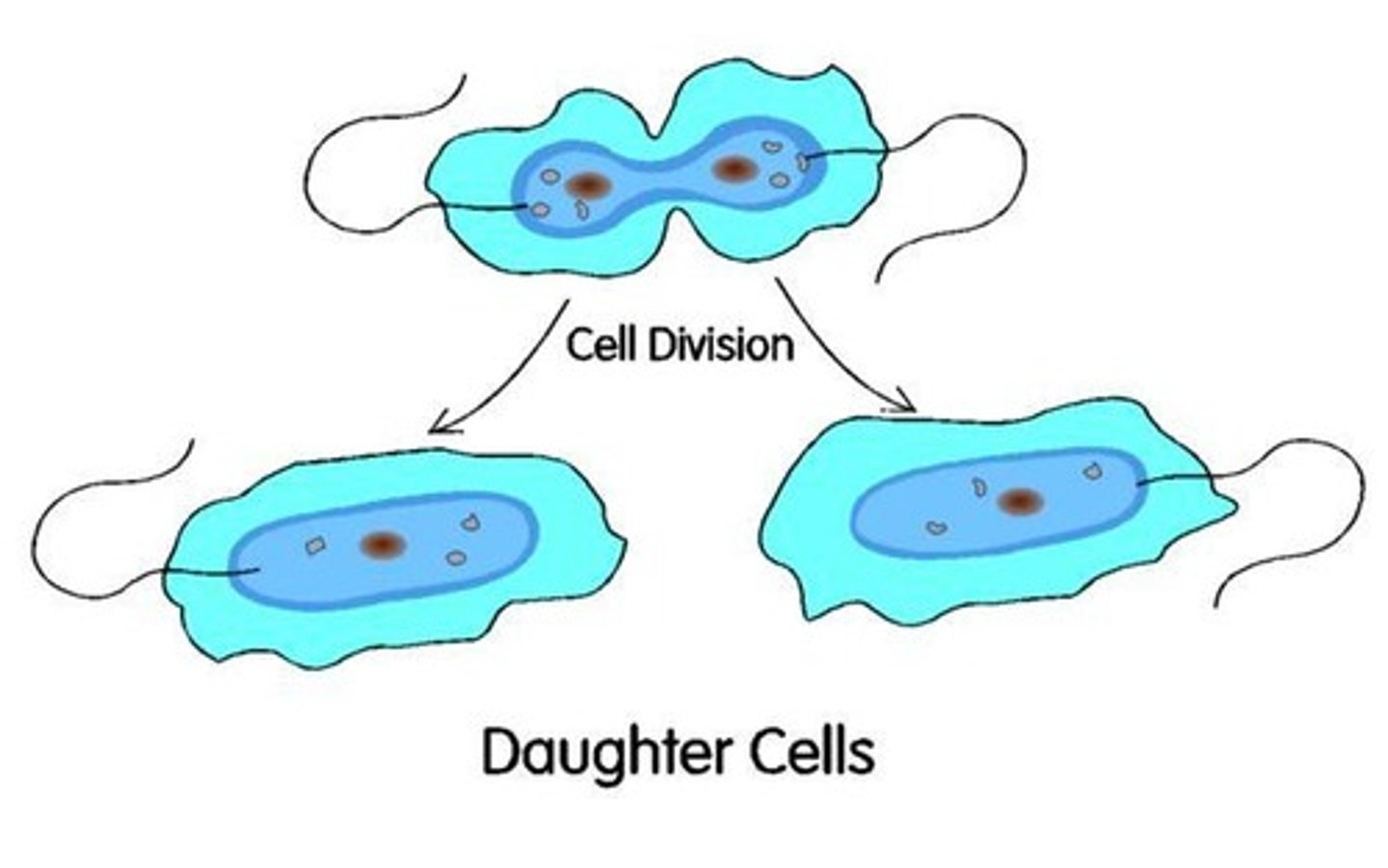
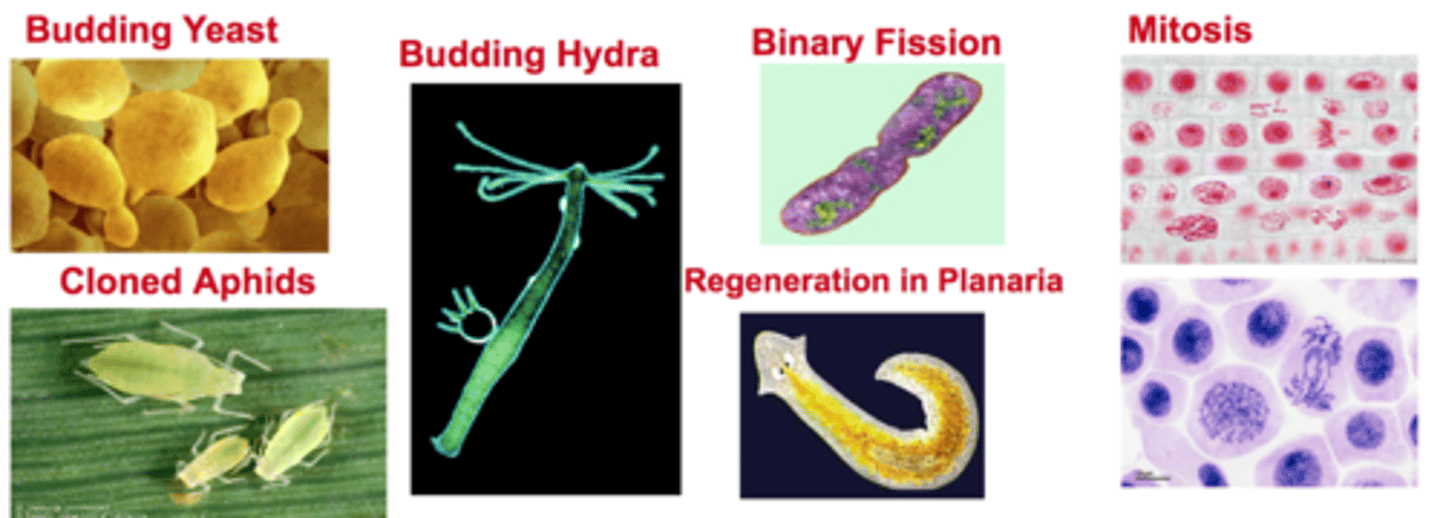
Asexual reproduction (Examples)
Examples include binary fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration and mitosis
Evolve
The process in which species change over time
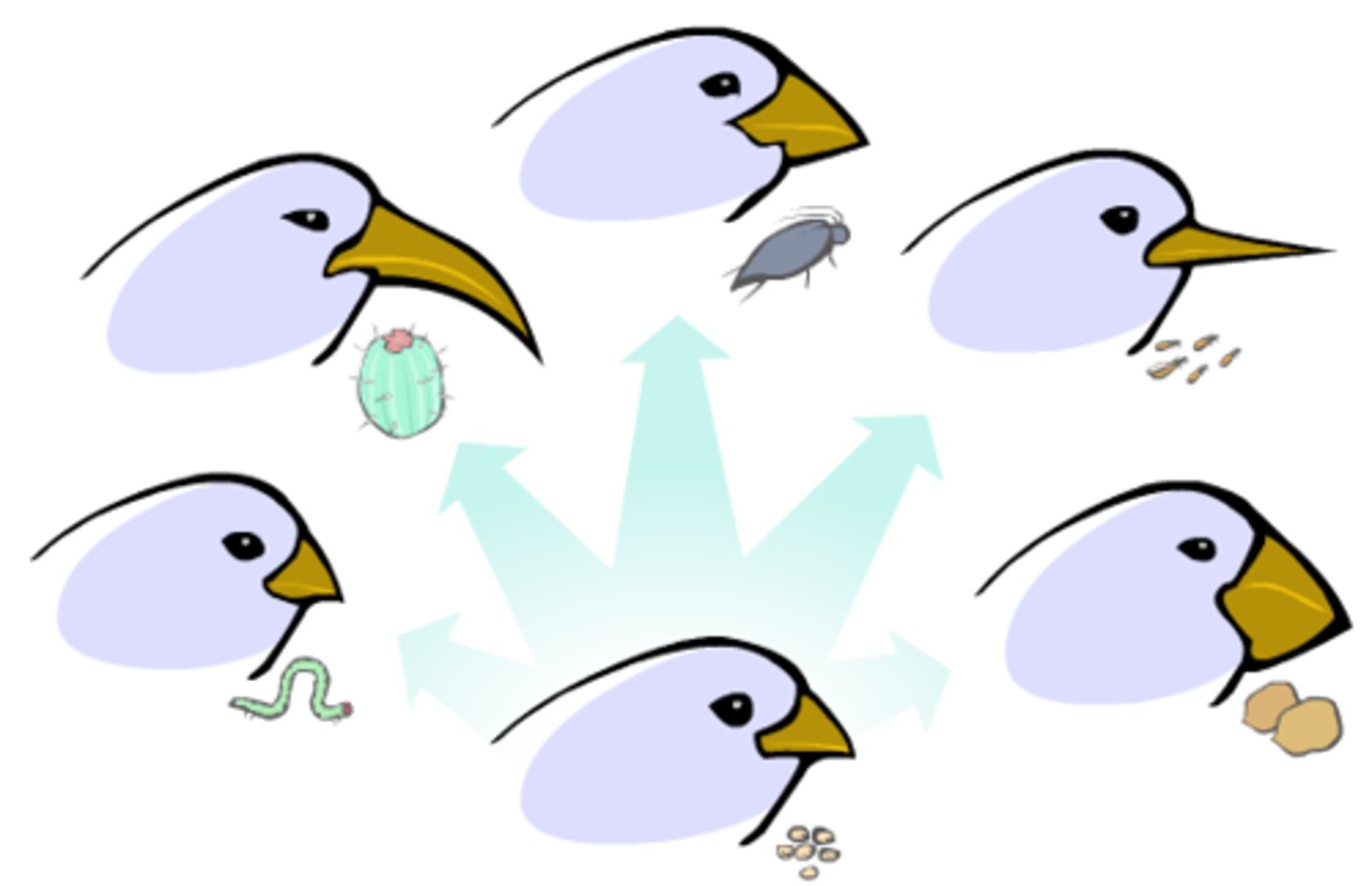
Adaptation
A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce
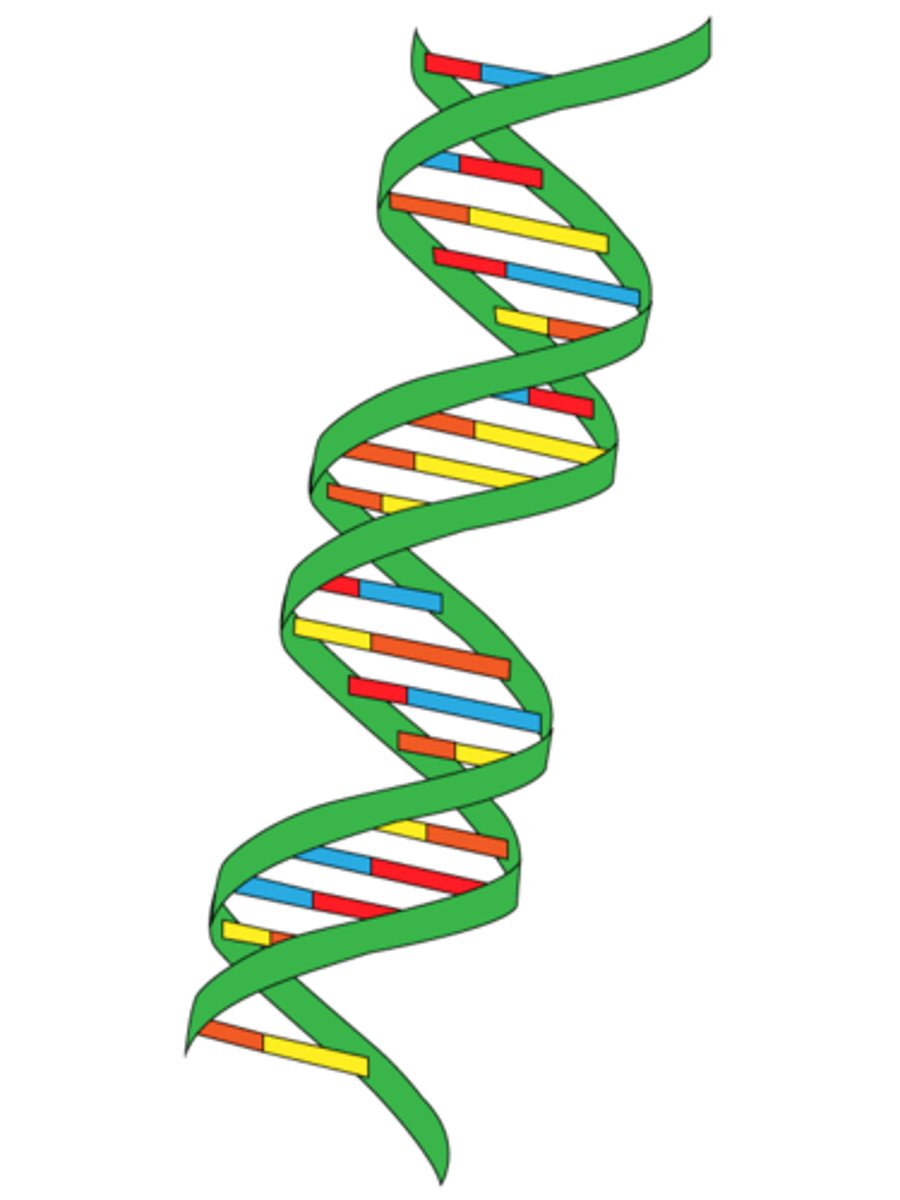
DNA
A nucleic acid found in the nucleus of all living cells, which carries the organism's hereditary information
Homeostasis (Description)
Maintaining a constant internal environment
Homeostasis (Examples)
Examples include the ability of humans to maintain a body temperature of 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit or the ability to maintain blood sugar levels
Energy
The ability to do work
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food

Heterotroph
An organism that obtain food by eating other organisms or their by-products

Growth (Description)
An increase in the size of an organism

Growth (Examples)
Examples includes a plant getting bigger or a cell getting bigger

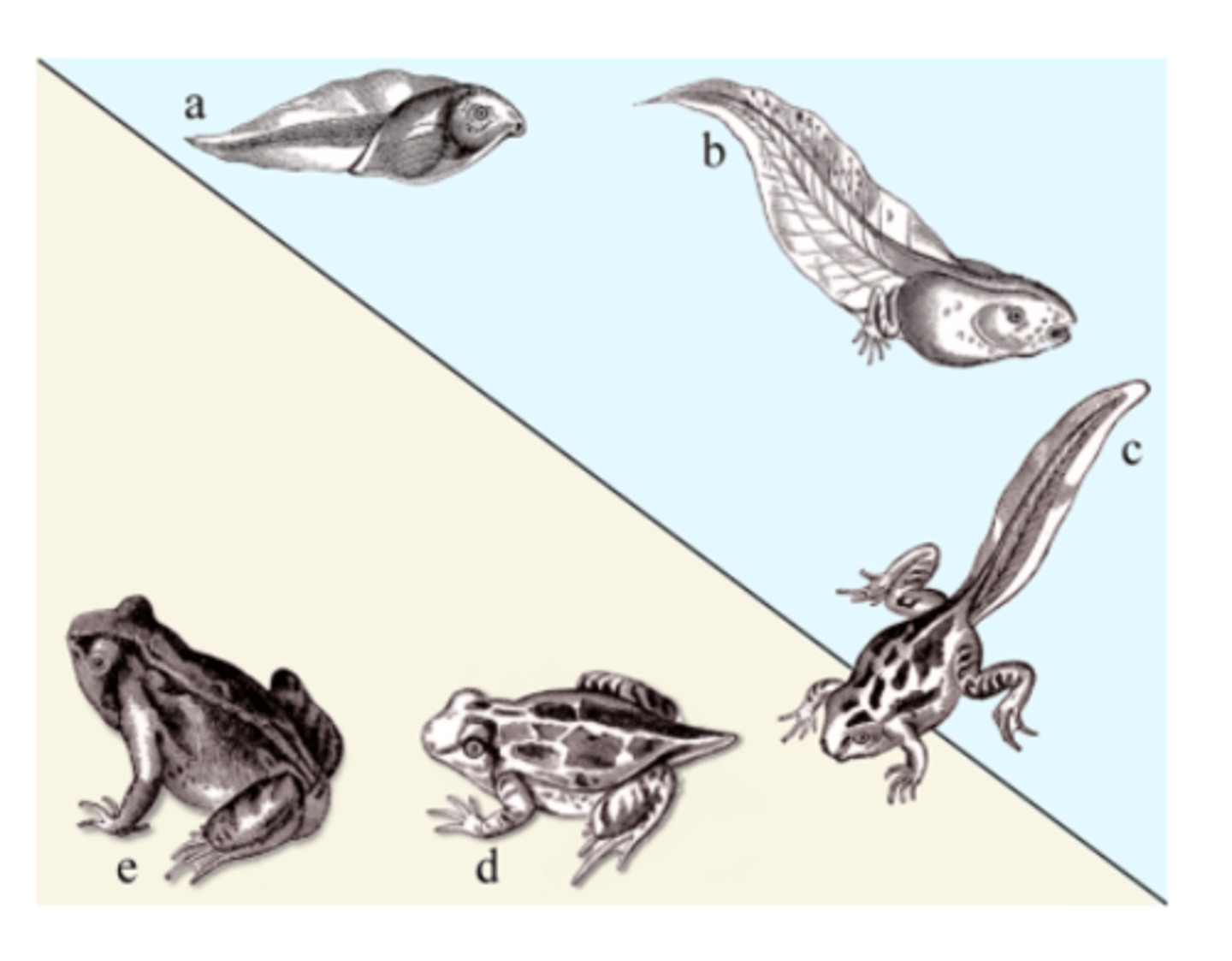
Development (Description)
The process of change that occurs during an organism's life to produce a more complex organism
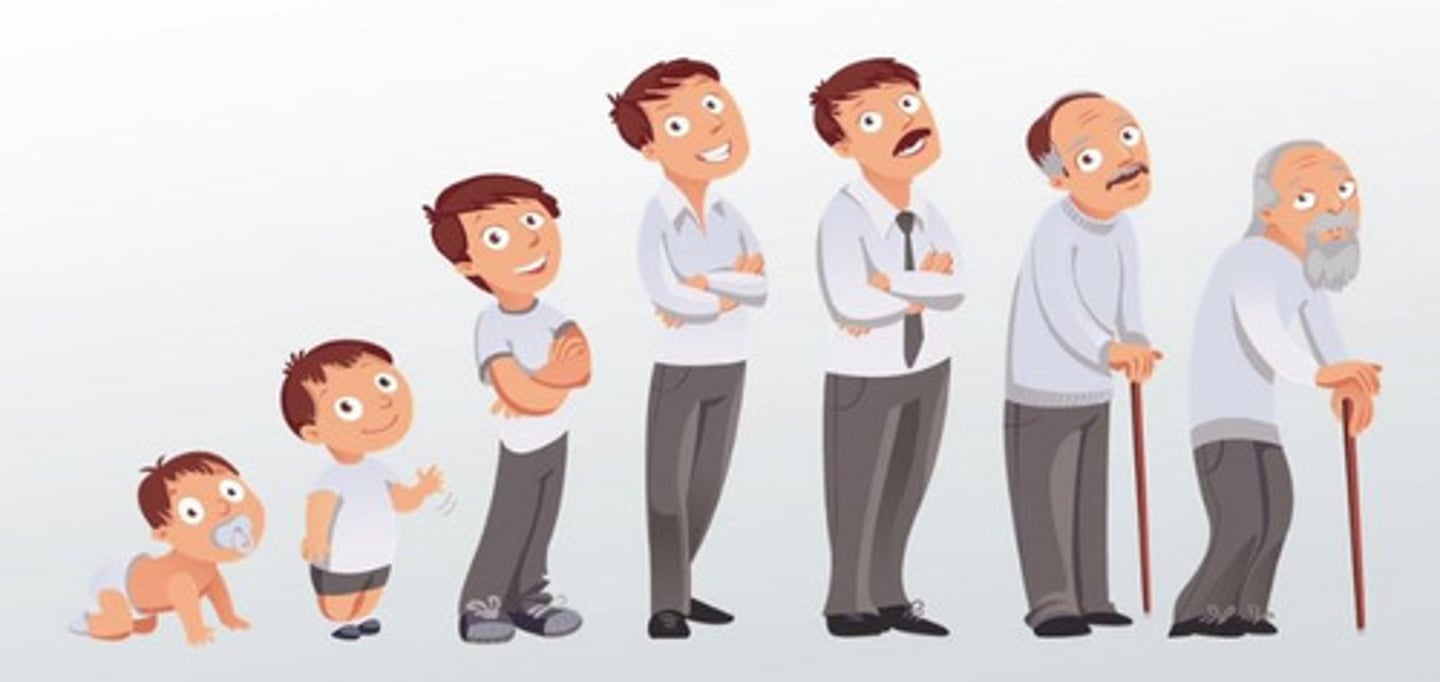

Development (Examples)
Examples include a tadpole becoming a frog or a fetus becoming an adult
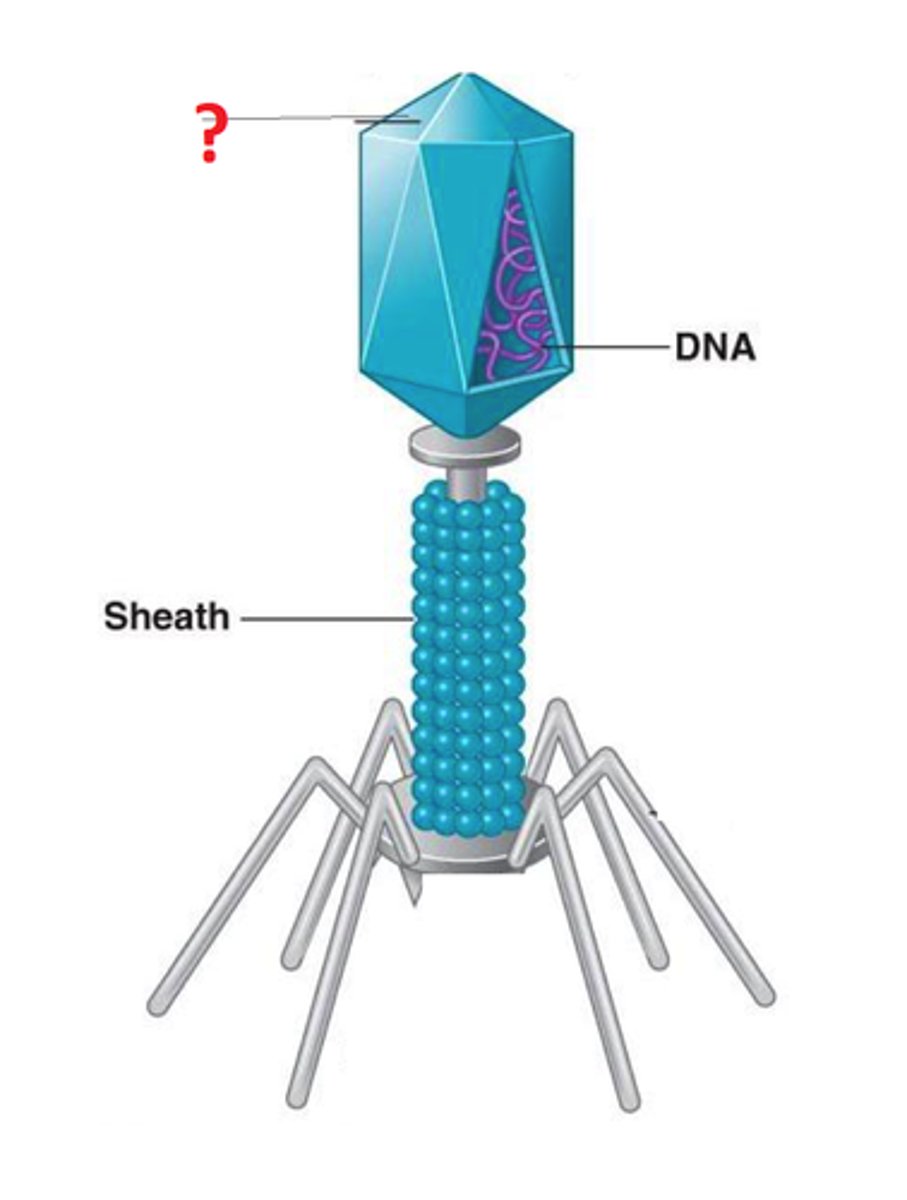
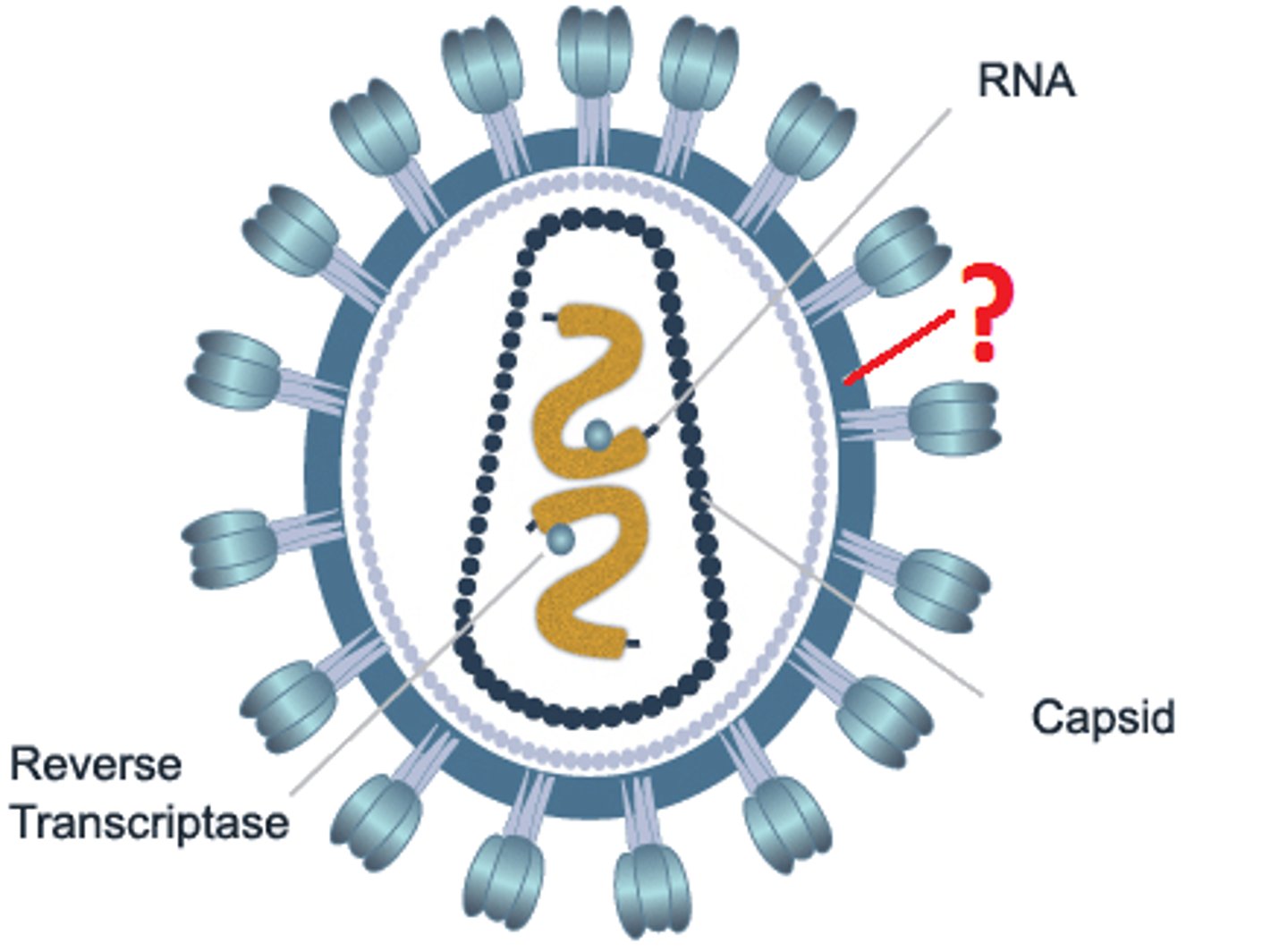
Virus
A tiny, nonliving particle that typically contain a protein coat surrounding an RNA or DNA core of genetic material but no semipermeable membrane, that are capable of growth and multiplication only in living cells, and that cause various important diseases in humans, animals, or plants.
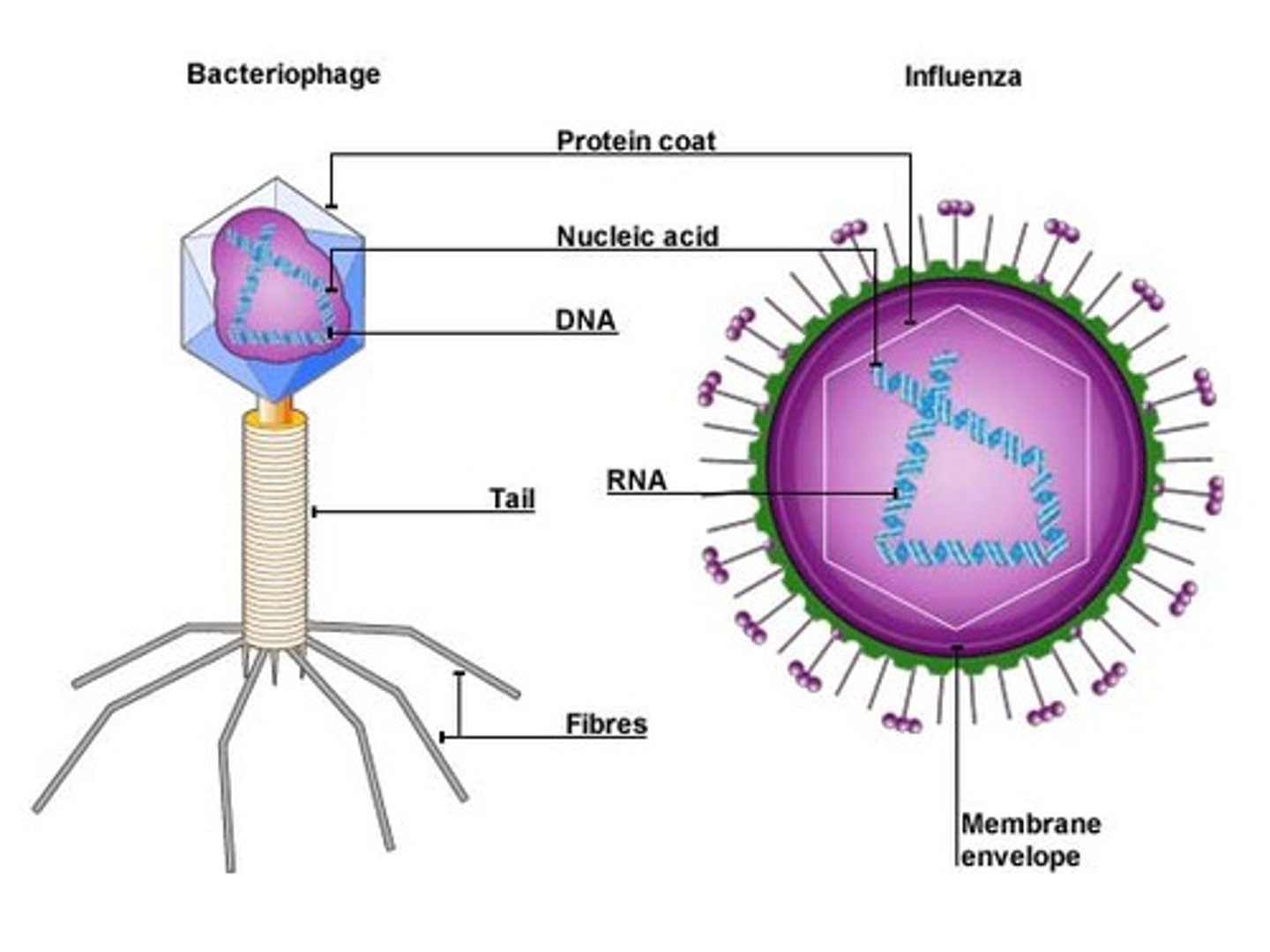
Capsid
Outer protein coat of a virus
Envelope
a membranelike layer that covers the capsids of some viruses
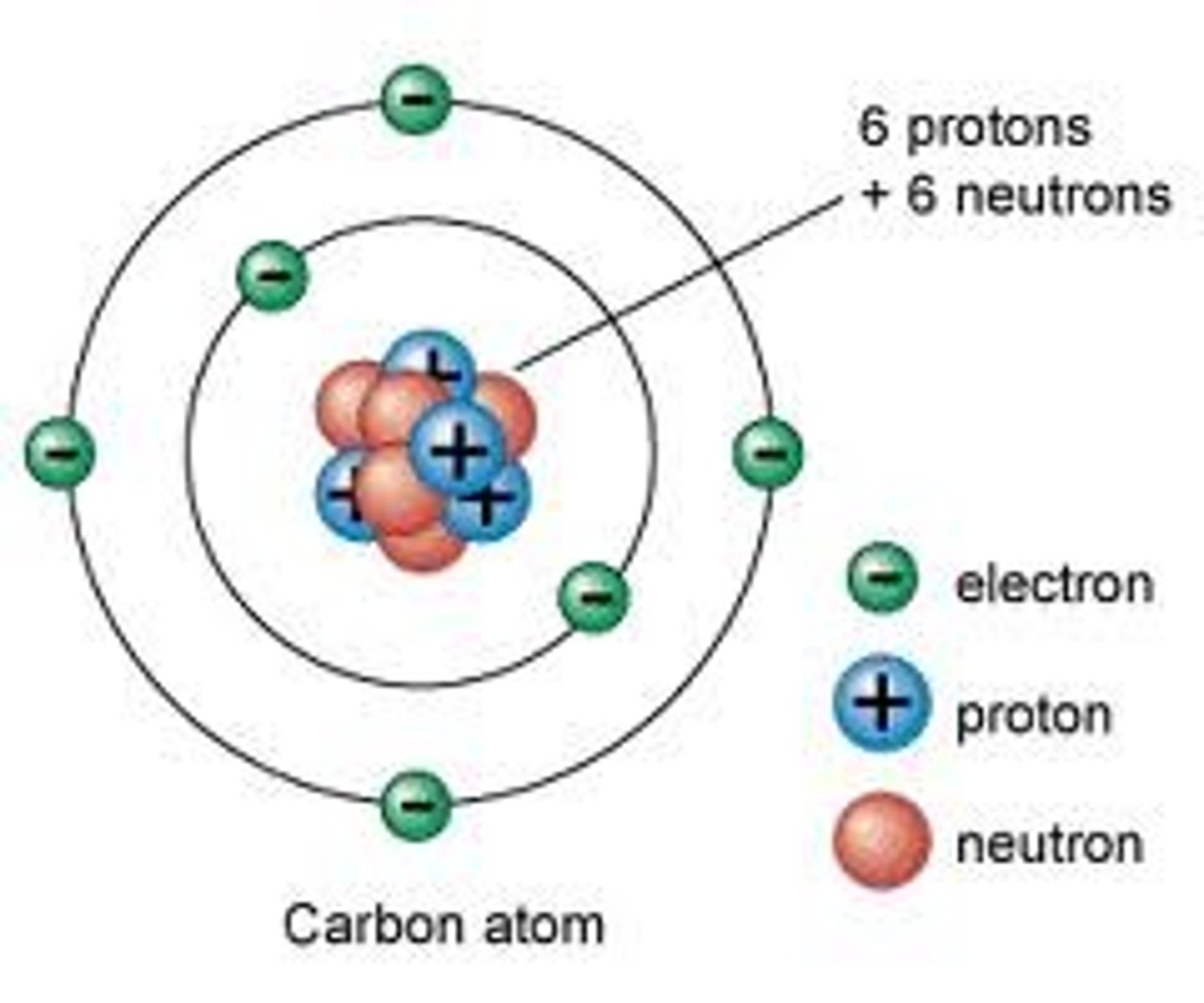
Atom
Smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element
Molecules
Groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
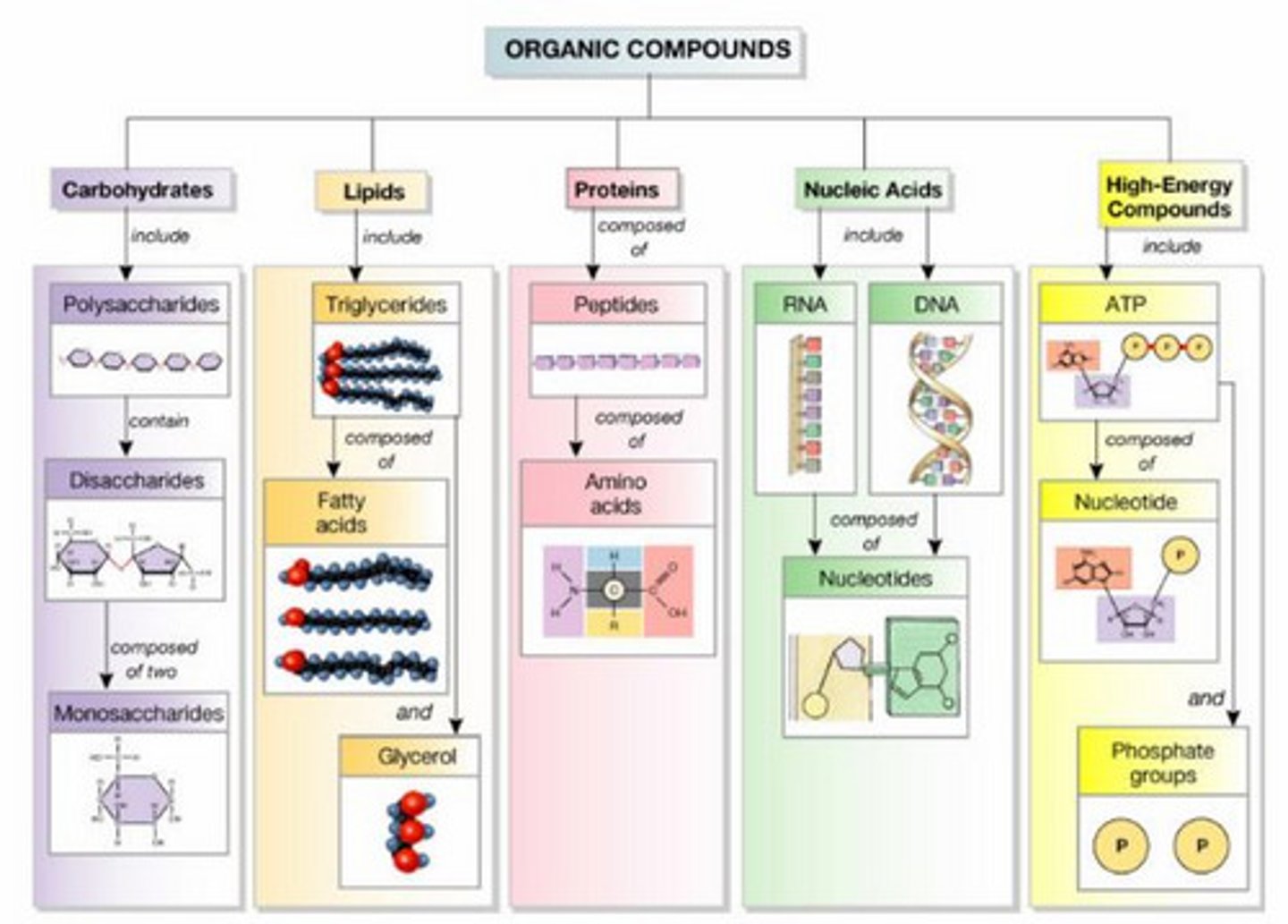
Macromolecules
Four main classes of large biological molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids)
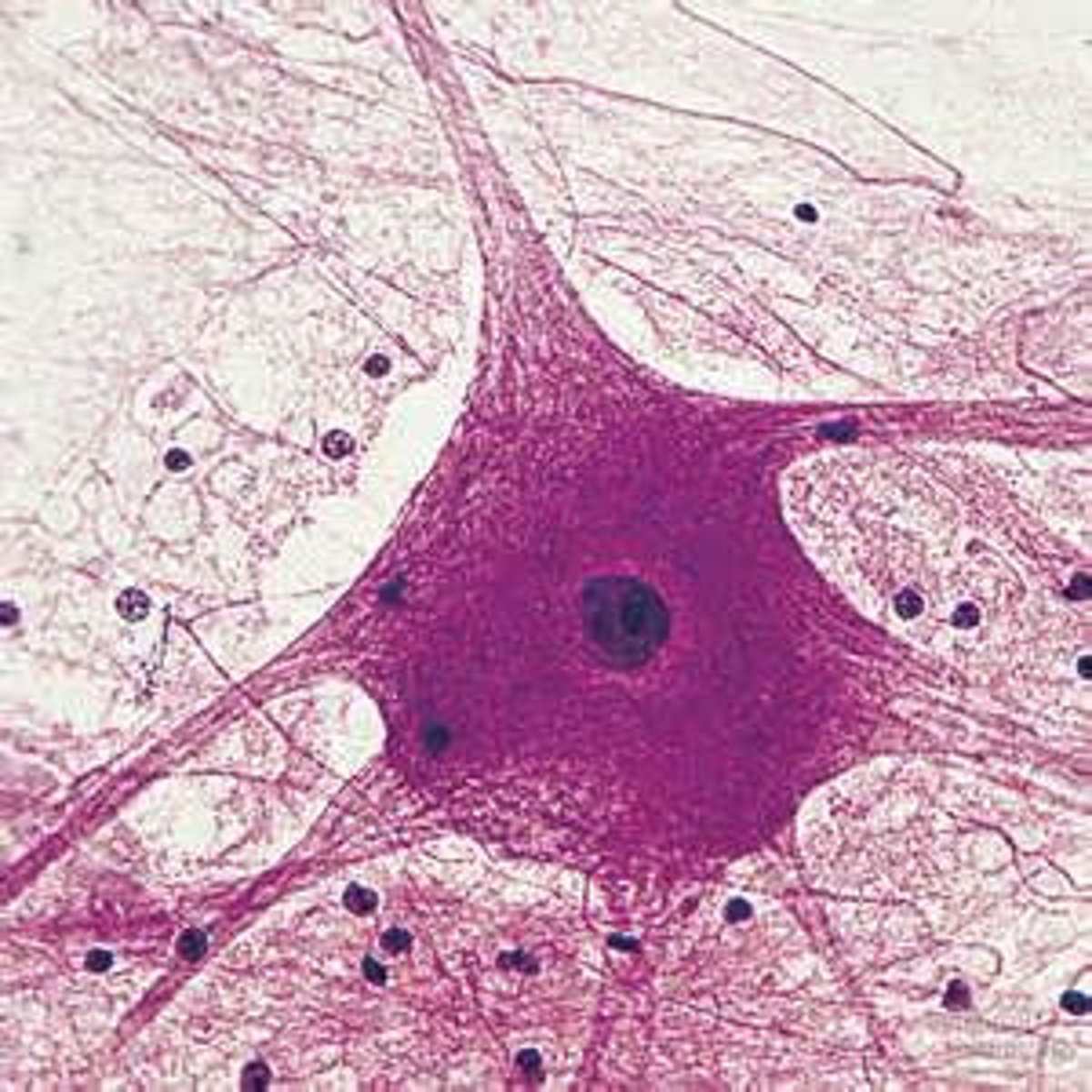
Cell
Basic unit of life
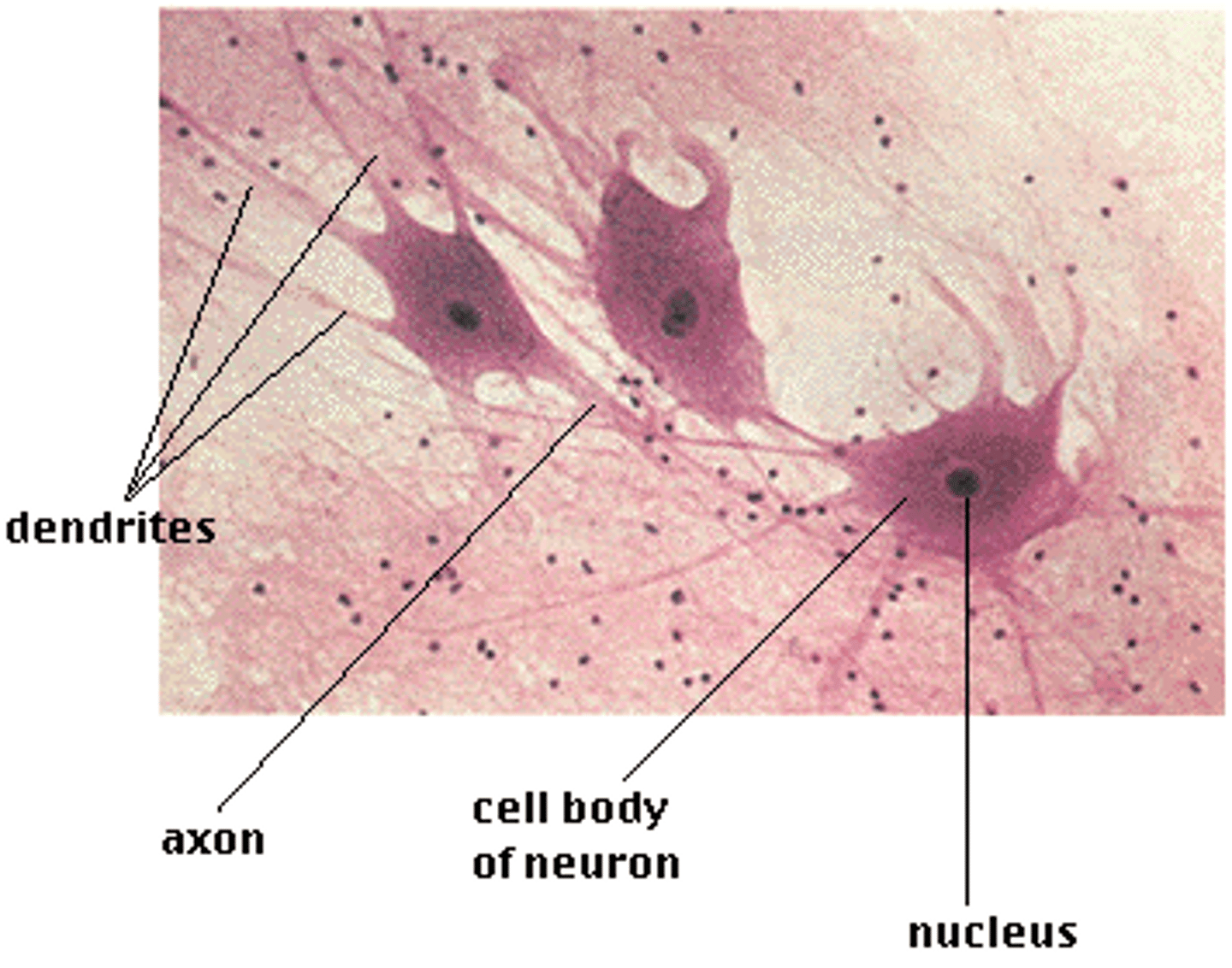
Tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
Organ
A collection of tissues that carry out a specialized function of the body
Organ system
Group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
Organism
A living thing

Population
A group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area.

Community
A group of interdependent organisms inhabiting the same region and interacting with each other

Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.

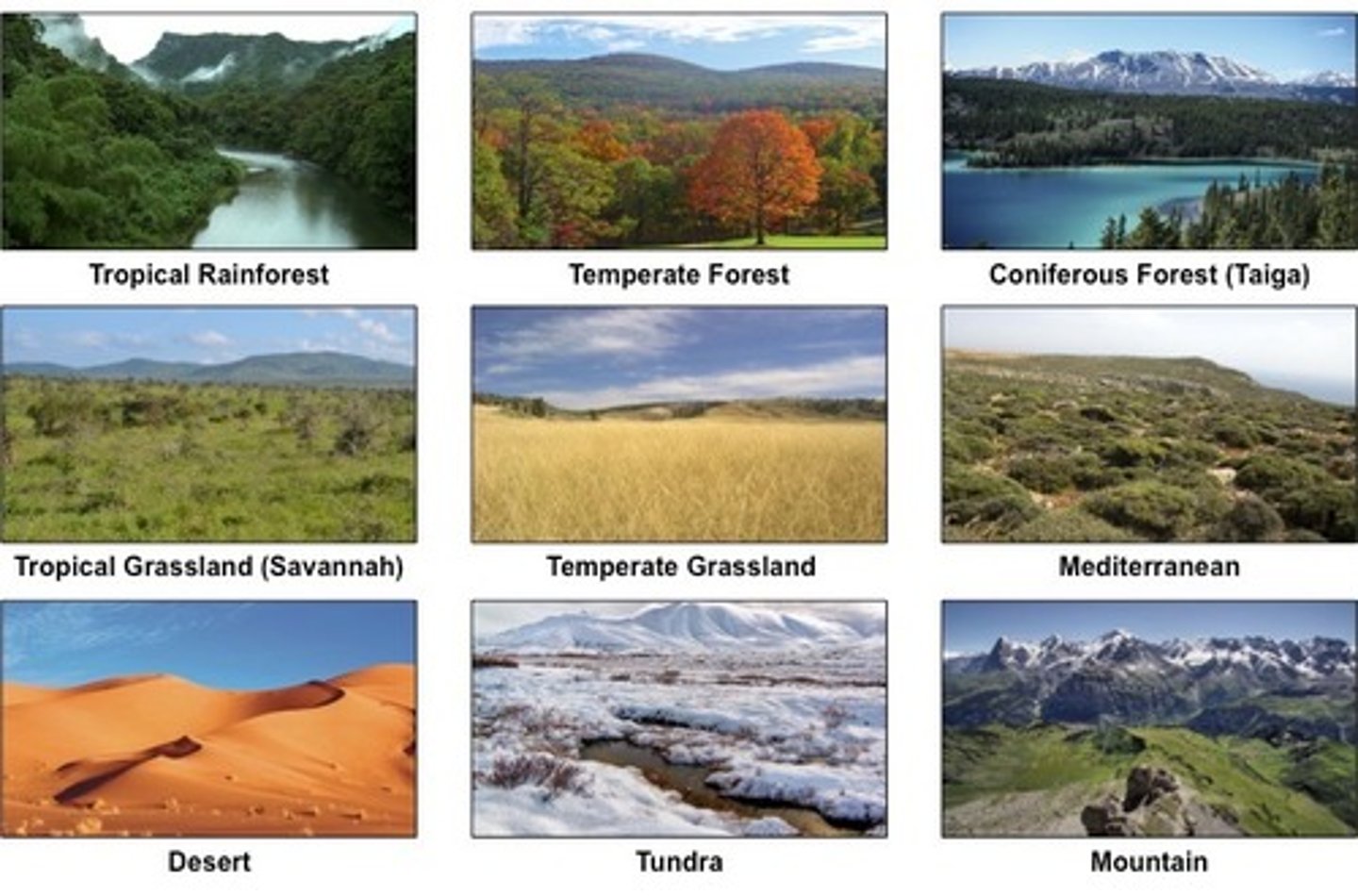
Biome
A group of ecosystems with similar climates and organisms

Biosphere
Earth
