Georgia Odyssey 2nd Edition Study Guide
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
The Spanish
Who made first contact with the state of Georgia (two centuries before Georgia was chartered as a British colony)?
Hernando De Soto
Who led the first expedition into Georgia interior?
1540
When did Hernando De Soto lead the first expedition into Georgia's Interior?
1732
When did Georgia receive its charter?
James Edward Oglethorpe
Who is Georgia's founder?
- James Edward Oglethorpe
- Repulsed the Spanish at the Battle of Bloody Marsh on St. Simon's Island
How did Georgia become part of the British Empire (battle?)?
- Free passage
- Fifty acres of land
- Supplies and foodstuffs for a year
What did the georgia colony's initial settlers receive?
So carefully that they were probably the most selectively chosen colonists to come to British North America
How careful were the first settlers screened?
Welcoming Jews and other persecuted religious minorities
- Established a settlement at Ebenezer (i.e. later known as Effingham county)
How did Oglethorpe and the trustees bend colonial policy?
George Whitefield
Who was the colony's leading minister of the gospel?
1750
When did slavery begin in Georgia?
1752
When did Georgia become a royal colony? (i.e. trustees returned their charter to the crown)
1760
What year did James Wright become royal governor?
What did James Wright do?
- He led the way to the Carolina-ization of Georgia by growing rice and indigo
- Played a key role in physical growth as well (negotiated treaties with nearby indians): Increased the land area approximately fivefold
Rice and Indigo (1750s - 1760s)
What spurred the colony's economic upturn (colonial ga)?
- Own land
- Hold office
- Profit from the colony in any way
What were trustees forbidden to do? 3
- 60
- 25
- 50
By 1773, ________ people owned owned at least ________ hundred acres each, and together they held more than ________ percent of the colony's slaves.
Who is James Habersham?
The Colonial Council President
The stamp act
Georgia was the only colony to comply with what act?
The Stamp Act said that the colonists had to pay a tax on printed papers (1765)
What is the Stamp Act?
Savannah
The British showed up and occupied __________ in 1778.
1795 Yazoo Land Fraud
in which four land companies bribed legislators to approve their acquisition of 35 million acres (nearly 60 percent of the land area that now constitutes Alabama and Mississippi) at the cost of only five hundred thousand dollars.
Trail of Tears
- One of the most shameful chapters in the state's history
In 1838, the last sizable contingent of cherokees were marched along the __________ to Oklahoma.
Yes
- Including women in theory (not practice)
Were all taxpayers entitled to vote by 1789?
Five
- Contributed to the speed of slavery in upcountry
How many slaves were deemed the equivalent of three white constituents, according to the new constitution of 1798?
- inventor of the cotton gin on a plantation Washington, GA (1793)
Who is Eli Whitney?
Removed seeds from cotton, making it feasible to grow hardier varieties than was possible when separating by hand.
What did the cotton gin do?
What was Georgia soon leading the world in?
Cotton production (increased about 10% a year from 1825 - 1860)
Largely in response to expanding English textile industry
Remained a key player in national & international economy
What revitalized slavery?
The cotton boom (the more cotton planters grew, the more slaves they needed)
from under 30 thousand in 1790 --> over 100 thousand by 1810
75% in black belt
Ran across middle third of Georgia
Where is the black belt in Georgia? (i.e. slavery)
A series of anti-black laws & a way of life (1865)
- An institutionalize, rigid system of racial segregation
What is the Jim Crow system?
Slavery
What drove Georgia from the Union and into the War Between the States?
$900
- Slaves represented a source of wealth far more important than the cotton cultivated or land it grew on
What was the average per capita of slave in 1860?
Five
The average slave holder in GA was _________ times more wealthier than the average northerner.
As much as half
How much of Georgia's total wealth was invested in slaves?
Why was Georgia's decision crucial to the success of the disunionist movement?
- Georgia was the second largest state east of the Mississippi
- It had the largest population
- The most slaves
- And the most slaveholders of any deep south state
Milledgeville
What was the capital city of Georgia at the time of Civil War Cesession talks?
November 1860
When did the legislature meet in the capital city to talk Secession?
A lawyer & judge, Henry L. Benning
Who became the namesake of Fort Benning?
What was Henry L. Benning known for?
- Stood before legislature Nov. 18, 1860
- Made case for secession
- Did not want Abraham Lincoln elected because he planned to abolish slavery
- A bare 51% majority vote for delegates favoring secession
- January 19th: convention voted 166-130 in favor of secession
The legislature approved a bill authorizing a convention to be elected by statewide vote on January 2, 1861. What did this vote yield? secession
Alexander H. Stephans
Who was the vice president of the Confederate States of America?
General William Tecumseh Sherman
Who was in the conquest of Atlanta (1864) and March to the Sea?
From Atlanta, to Macon, to Savannah
- Leaving the country barren in its tracks
Where did General William Tecumseh Sherman's columns go?
- Many escaped
- Made their way to the union lines to enlist in the fight for freedom
When union troops drew near & Sherman's troops began making their way to Atlanta, what did the slaves do?
- Lost some 40 thousand men to war
- Economy destroyed (cotton not produced -- slaves at war)
What happened to the state of Georgia in the Civil war? 📉
Under leadership of provisional governor James Johnson, what did the new postwar constitution acknowledge?
- Supremacy of U.S. Constitution
- Abolition of slavery
- Repealed ordinance of secession
- Repudiated the state's war debt (in excess of 18 million dollars)
- Extended the vote to "free white male citizens"
- Authorized public schools for whites (not blacks)
- blacks also excluded from service on juries
- Rejected 14th amendment to extend due process to blacks
What did the GA legislature do post civil war?
- Former confederate vice president Alexander H. Stephens
- Former confederate Herschel V. Johnson
Who were elected to the Senate, proving that Georgia was still stuck in its pre-civil war ways?
Radical republicans fully in control of Congress, divided the south into five military districts.
What was the military reconstruction of 1867? (affected whole south)
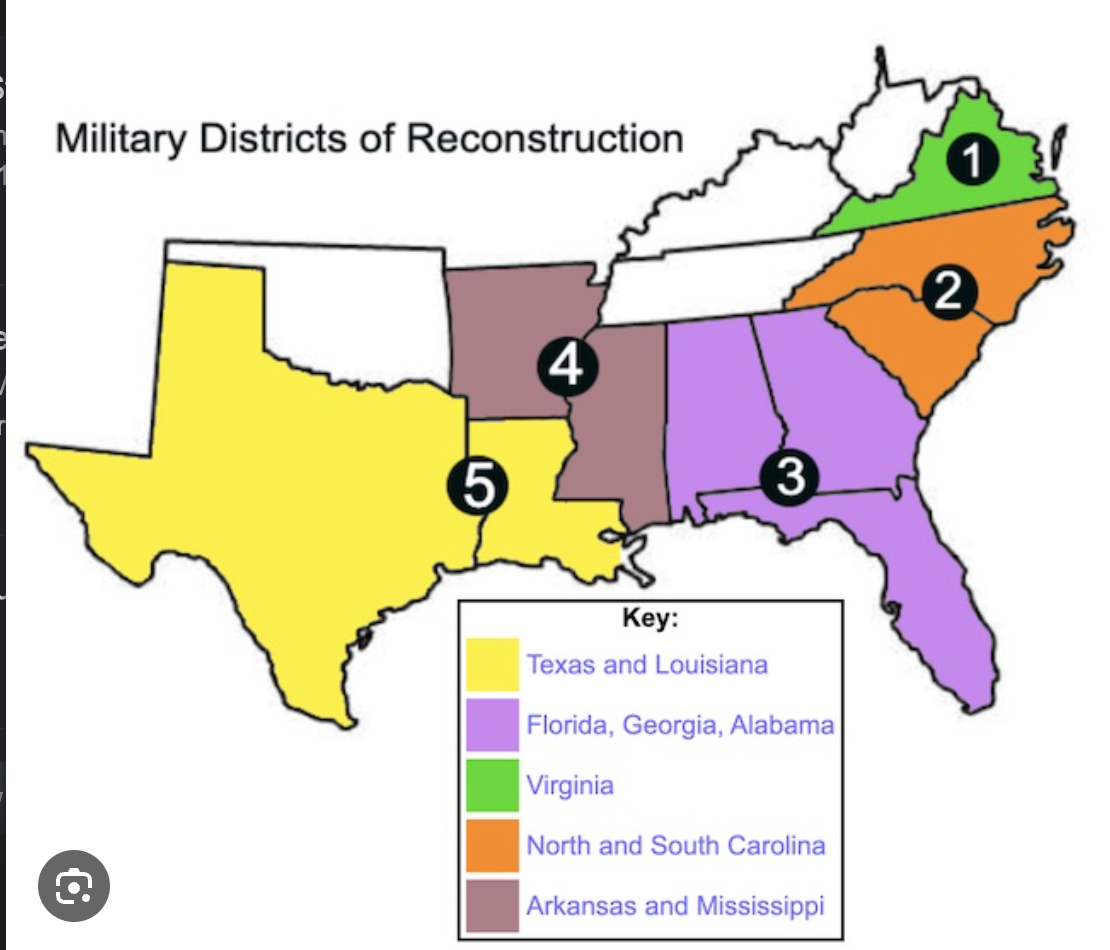
- Right of citizenship
- Right to vote
- Ostensible guarantee of equal protection the law
A new constitutional convention gave blacks what rights (military reconstruction of 1867)?
What happened in the April 1868 election?
- Republicans secured a solid majority in both houses (thanks to support from black voters)
- Republican Rufus Bullock = governorship
What did Rufus Bullock do in his administration?
The work of _____ _______ (1868 election)
-Ratified the 14th amendment, extending due process to blacks
- Dismissed the issue of white supremacy
On grounds that the constitution did not provide for black office holding
On what grounds did the democrats succeed in ousting all but four of the thirty-two blacks elected?
What is the "Camilla Massacre"? (1868)
Violence and intimidation where Republican officers at severe risk of injury or death when in public
At least nine black republicans were killed
What happened to governor Rufus Bullock?
In the election of December 1870, he fled the state to avoid impeachment
James M. Smith
- Ended radical reconstruction (i.e. less blacks elected)
In 1871, who succeeded Bullock?
- Poll tax
- Threat of violence
What kept blacks away from the polls? (2)
Scarce -- and refused to make loans when land was the only available collateral
What were banks like in postbellum (post-civil war) Georgia?
It allowed farmers to receive food, supplies, or seeds on credit and pay back the loan after their crop was harvested and sold.
What was the crop lien system?
Yes; crippling, and destructive debt was a way of life amongst GA farmers
Did the size of the lien often exceed the market value of the crop?
Forced sales & foreclosures
How did those who supplied credit gain land (crop-lien)?
Renting of land to former slaves
What is sharecropping?
Crop-lien
What brought the demise of safety-first agriculture?
"Bourbon Triumvirate"
- Joesph E. Brown
- John B. Gordon
- A. H. Colquitt
Who helped overthrow the reconstruction in 1870 and 1871?
Thomas E. Watson
(Post Civil War Banks Scarce)
Who was the most dynamic figure in the agrarian uprising? (and Georgia's most prominent populist)— turned racist later in his life
Stressed cooperative action
What is the Farmers' Alliance?
What did the Atlanta Farmers' Alliance do?
Successful in establishing a state cooperative farm exchange in Atlanta; Bought fertilizer and other supplies in high volume and made them available at lower prices.
What did the Atlanta Alliance seek the assistance of Washington for?
The "subtreasury plan" -- Farmers would store their crops at strategically located warehouses and receive loans of up to 80% of their value.
Not economic but racial, for the agrarian insurgency reached out to blacks and called on them to join in a counterattack.
To most Georgians, what was the most radical aspect of the Farmers Alliance?
Expand the money supply by printing new currency -- to fund the loans
What did the Atlanta Farmers' Alliance spokesman call on the Federal Government to do?
Who is Henry Woodfin Grady?
Led the "New South" Crusade
- Editor of the Atlanta Constitution (Atlanta's biggest booster)
Sought to promote prosperity through economic diversification, especially the rapid expansion of industry
What did the "New South" crusade seek to do?
What is sectional reconciliation?
"Every dollar of Northern money reinvested in the South gives us a new friend in that section" - Grady
Grady
Who was the souths most eloquent spokesmen for economic change?
Lynchings
What did Georgia lead the nation in between 1899 - 1918?
Aimed at reaffirming white supremacy and reminding blacks that any wrongs might bring horrible retribution
What was the purpose of lynching?
Codified well established practices
- The emergence of segregation by law made people more inclined to discriminate
What did Jim Crow laws do?
Only to Georgians with white skin
The 1900 democratic party primary rules had what stipulation?
Required potential registrants to pass a literacy test
In 1908 what constitutional amendment was passed? 📖
a message of accommodation, black self-help and economic self-sufficiency
What was Booker T. Washington's message in his "Atlanta Compromise" speech?
The 19th (womens rights)
Georgia was the first state to reject which amendment?
Rebecca Lattimer Felton
In 1922, who became the first woman to serve in the U.S. senate? (at age 87)
Rebecca Lattimer Felton 👯♀
Who was the state's foremost feminist and leading reform advocate? (but also agreed with lynchings of lustful black men)?
atop Georgia's Stone Mountain
In 1915, the Klu Klux Klan was reborn where
(because of Tom Watson)?
Who was Leo Frank?
the Jewish manager of a pencil factory plant in Atlanta, falsely accused of murder mary phagan.
The murdur of Mary Phagan, a 14 year old factory worker (April 27, 1913)
What was Leo Frank accused of?
What happened to Leo Frank?
He was hanged by 25 men in Marietta
Watson
What important person contributed to the death of Leo Frank? (he kept pushing even tho Leo was innocent.)
Why did Georgia get rid of the County Unit System? What effect did this have on the political system?
Gray v. Sanders, the US Supreme Court declared the county-unit system unconstitutional. gubernatorial election was held on the basis of popular vote
What was the purpose of the County Unit System?
Ensured that rural counties would be able to control the General Assembly in spite of urban population growth.
What did Talmadge do to end the Textile Strike in 1934?
Declared martial law, using National Guard to break up the strike
The New Deal
What did Talmadge oppose?
(fact: talmadge son, Herman, follow his dads steps as a staunch defender of the southern way of life.)
The white primary, clearing the way for blacks to vote in the 1946 election
In 1944 what did the U.S. Supreme Court invalidate?
Boll Weevils
What caused cotton production to fall between 1918 - 1922?
Allowing local tax exemptions for factories
In 1930s, due to Georgia farm economy headed towards collapse (boll weevil plague), voters approved a constitutional amendment allowing what?
Introduced a program of subsidized acreage reduction
- Georgia lost 40% of its sharecroppers
What was the New Deal Agricultural Adjustment Administration (AAA)?
World War II (1939-1945)
What was the pivotal event in Georgia's economic transformation?
Massive federal spending (war stuff)
What did World War II bring to Georgia?
Economic, political, and social modernization
At the end of world war II, Georgia stood in an era of what?