BSC 2085L midterm practical
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
What is the green arrow pointing to in the image?
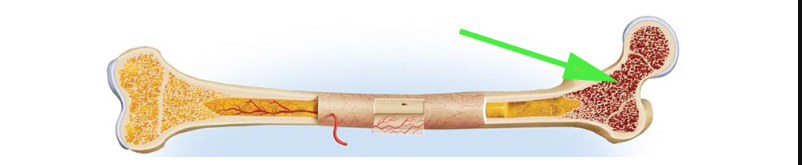
Red bone marrow
The red bone marrow is located in the spongy bone and is responsible for blood cell production.

What are the enlarged ends of a long bone called, as indicated by the green arrow?
Epiphyses
The epiphyses are the rounded ends of a long bone that participate in joint articulation and contain spongy bone with red marrow.
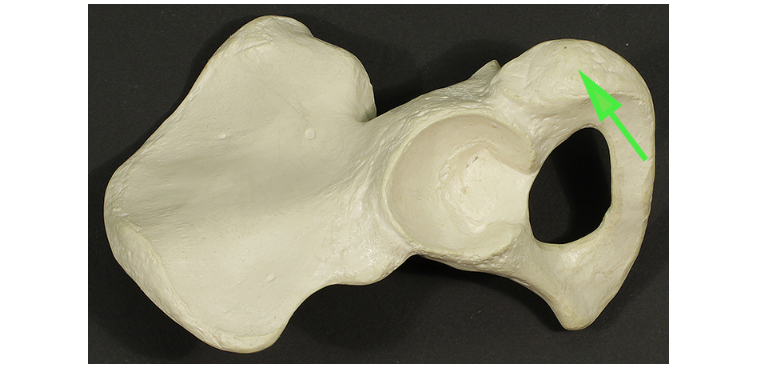
What is the roughened area of the ischium called, marked by the green arrow?
Tuberosity
A tuberosity is a large, rounded projection where muscles and ligaments attach.
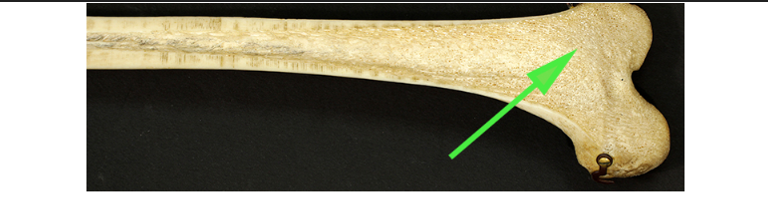
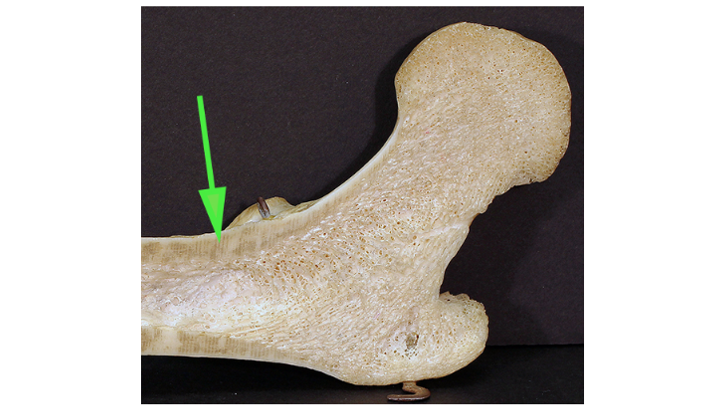
What type of bone is marked by the green arrow?
Spongy bone
Spongy (cancellous) bone has a porous structure that helps reduce weight while maintaining strength.
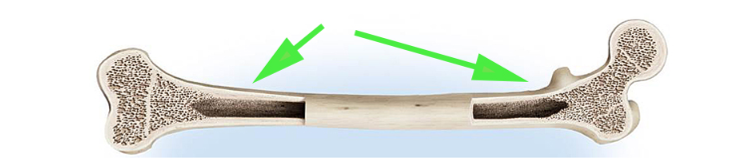
What is the shaft of a long bone called, indicated by the green arrows?
Diaphysis,
The diaphysis is the central, elongated shaft of a long bone that contains the medullary cavity.
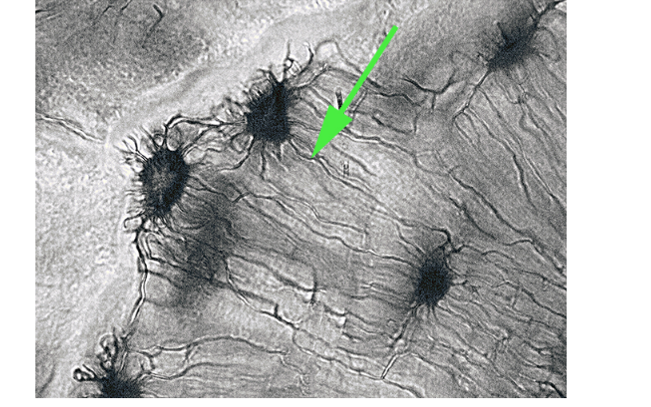
What are the tiny tunnels represented by the green arrow, which allow osteocytes to communicate?
Canaliculi
Canaliculi are microscopic canals between lacunae that allow nutrient and waste exchange among osteocytes.
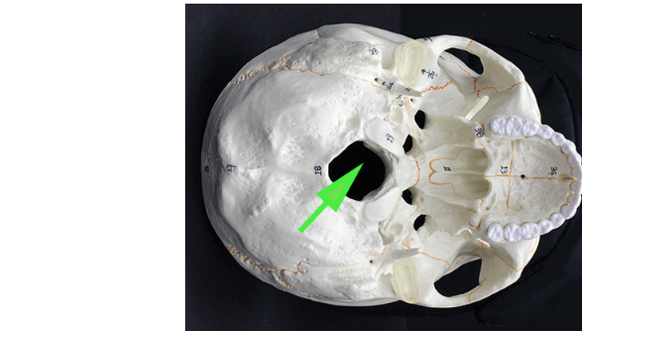
What is the hole in the occipital bone called, as shown by the green arrow?
Foramen
A foramen is an opening in the bone that allows the passage of nerves and blood vessels.
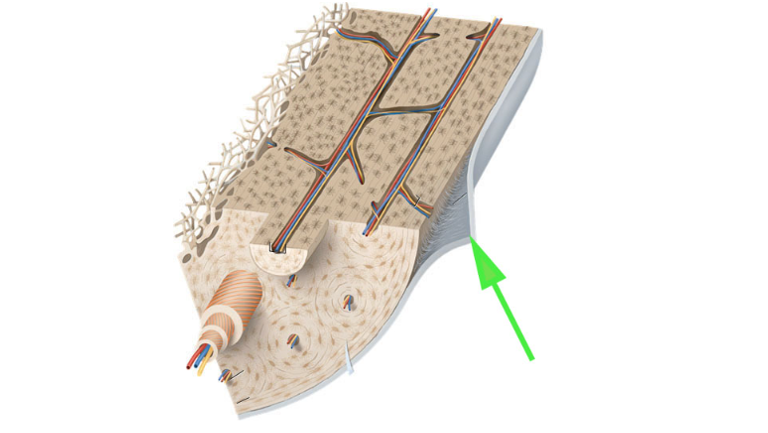
What is the membrane covering most of the bone surface, as indicated by the green arrow?
Periosteum
The periosteum is a dense layer of vascular connective tissue that envelops bones except at their joints.
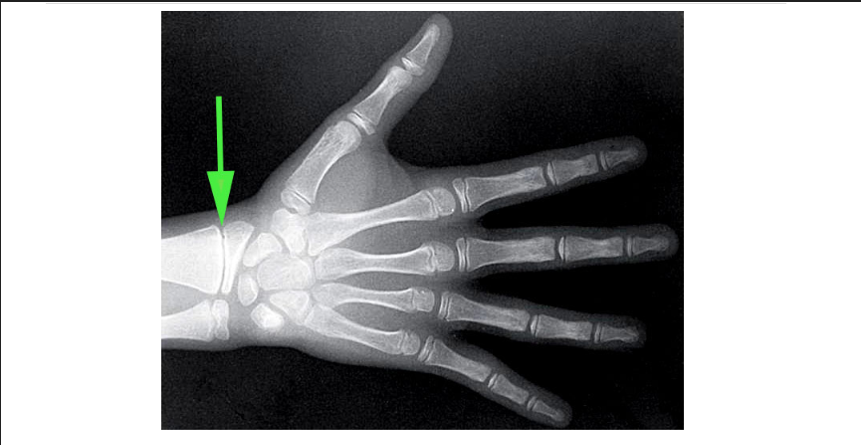
What is the growth plate in a child’s hand called, as marked by the green arrow?
Epiphyseal plate
The epiphyseal plate is a layer of cartilage that allows bones to grow during childhood.
What type of bone tissue is marked by the green arrow?
Compact bone
Compact bone is the dense, strong outer layer of bone that provides structural support.
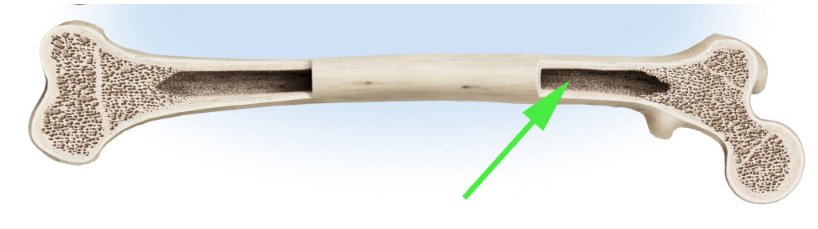
What is the cavity marked by the green arrow inside the long bone?
Medullary cavity
The medullary cavity is the central space inside long bones that contains bone marrow.

What is the shallow depression in the bone called, as shown by the green arrow?
Fossa
A fossa is a shallow depression in a bone, often serving as an articulation point.
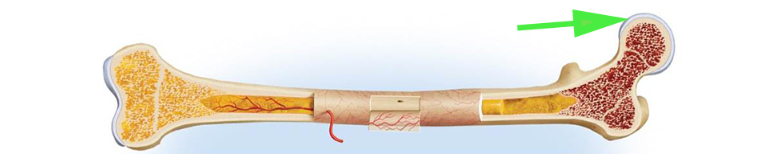
What is the tissue covering the articular surfaces of bones called?
Cartilage
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that reduces friction and cushions joints.

What is the material filling the bone space indicated by the green arrow?
Yellow marrow
Yellow marrow consists mainly of fat cells and is found in the medullary cavity of long bones.
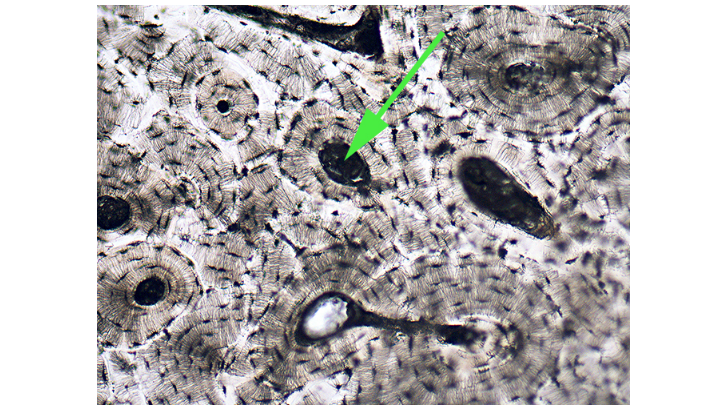
What is the dark area in the bone tissue marked by the green arrow called?
Haversian canal
The Haversian canal is a central channel in compact bone that contains blood vessels and nerves.

What is the hemispheric projection at the end of the humerus called, as shown by the green arrow?
Head
The head of the humerus articulates with the scapula at the shoulder joint.
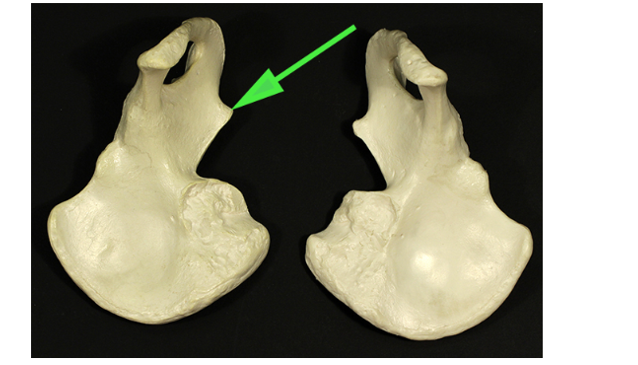
What is the short, sharp projection of the bone marked by the green arrow?
Spine
The spine is a thin, pointed projection from a bone, such as the ischial spine.
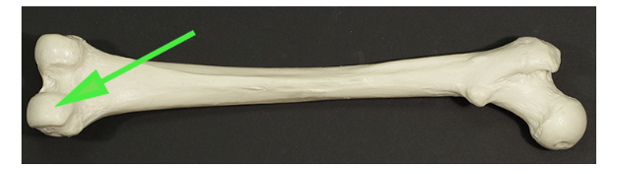
What is the irregularly shaped surface of the femur, shown by the green arrow?
Condyle
A condyle is a rounded protrusion at the end of some bones that articulates with another bone.
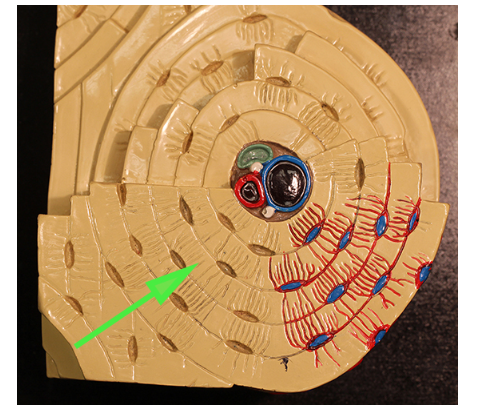
What is the green arrow pointing to in the osteon model?
Lamella
The lamellae are concentric rings of compact bone that make up the osteon structure.
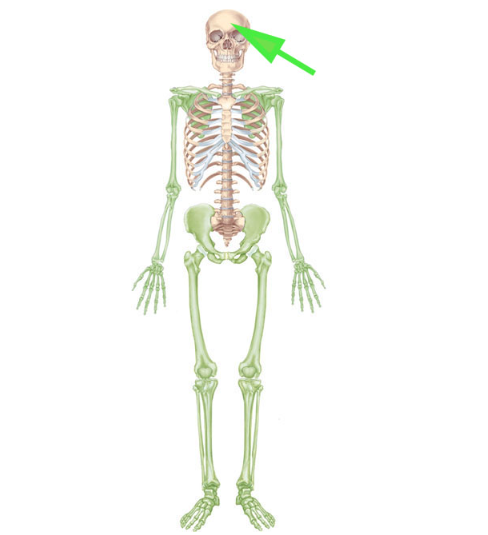
What part of the skeleton is not colored green and makes up the axial skeleton?
Skull (part of the axial skeleton)
The axial skeleton consists of the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage.
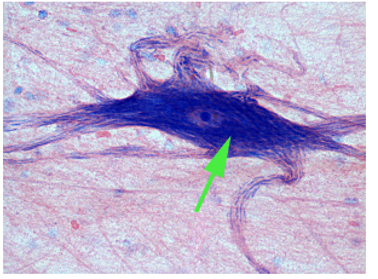
What is the green arrow pointing to in the image?
Neuron
A neuron is a specialized cell that transmits nerve impulses. It consists of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon.
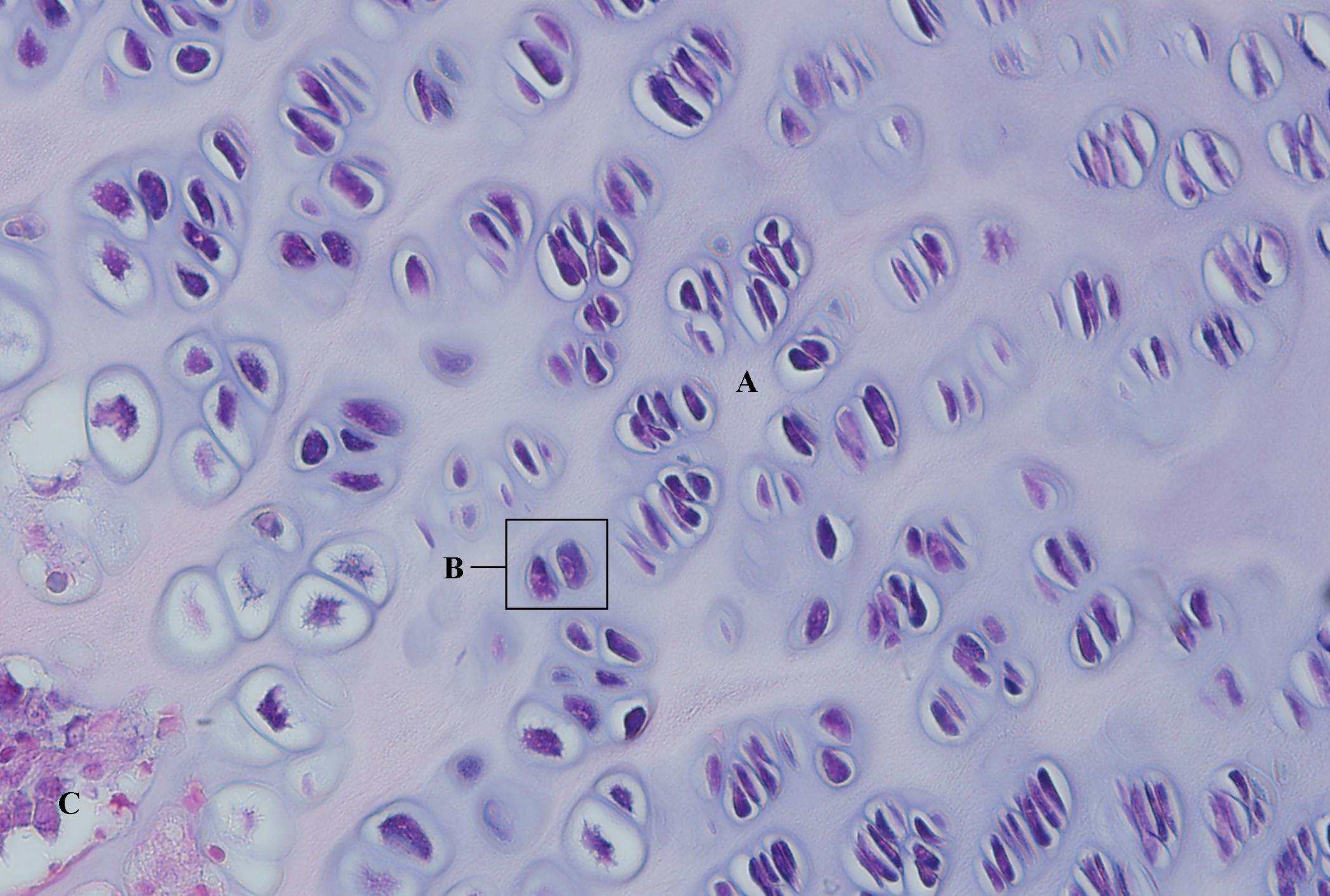
What type of cartilage is shown in the image?
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage provides support and flexibility. It is found in the nose, trachea, and at the ends of long bones.
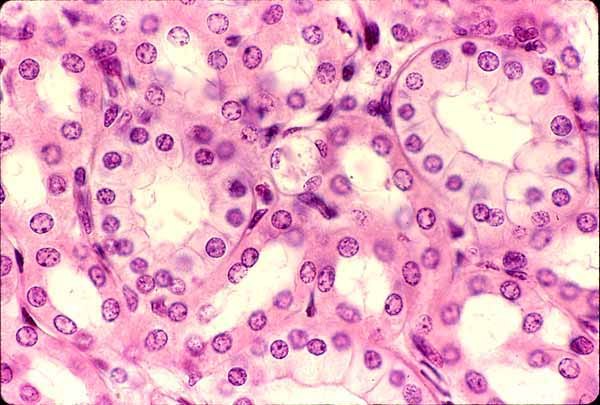
What type of epithelium is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Simple cuboidal epithelium
Explanation: Simple cuboidal epithelium consists of cube-shaped cells and is found in glands, ducts, and kidney tubules, where it functions in secretion and absorption.
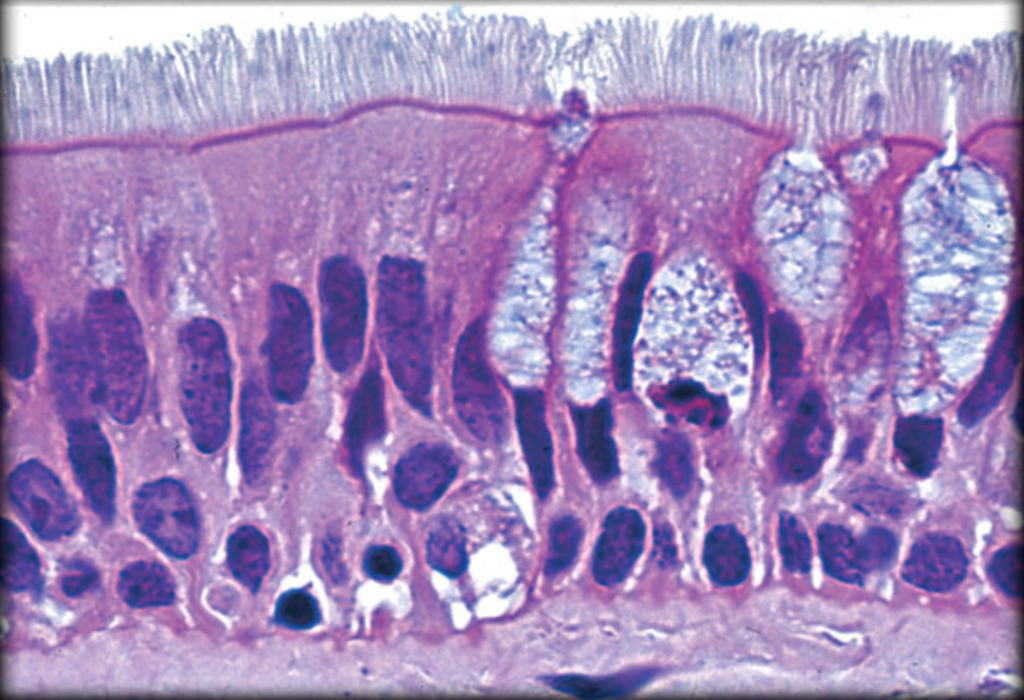
What type of epithelium is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Explanation: Pseudostratified columnar epithelium appears layered due to varying cell heights, but all cells touch the basement membrane. It is found in the respiratory tract.
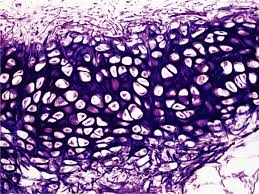
What type of connective tissue is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Elastic cartilage
Explanation: Elastic cartilage contains elastic fibers, allowing it to maintain shape and flexibility. It is found in the ear and epiglottis.
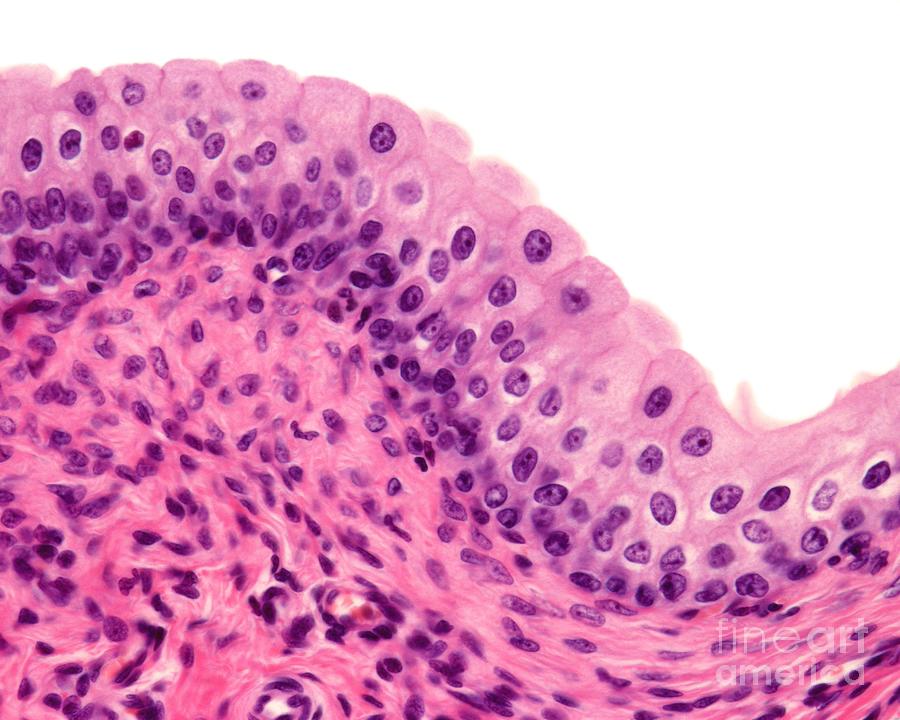
What type of epithelium is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Transitional epithelium
Explanation: Transitional epithelium allows for stretching and is found in the urinary bladder.
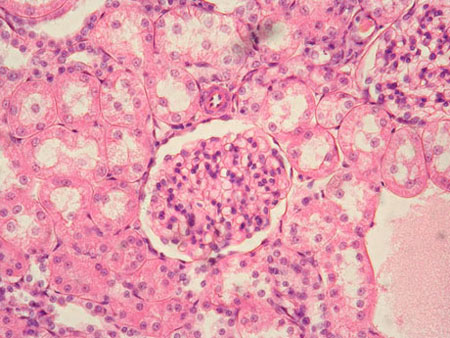
What type of epithelium is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Simple squamous epithelium
Explanation: Simple squamous epithelium consists of a single layer of flat cells and is found in the alveoli of the lungs and blood vessels.
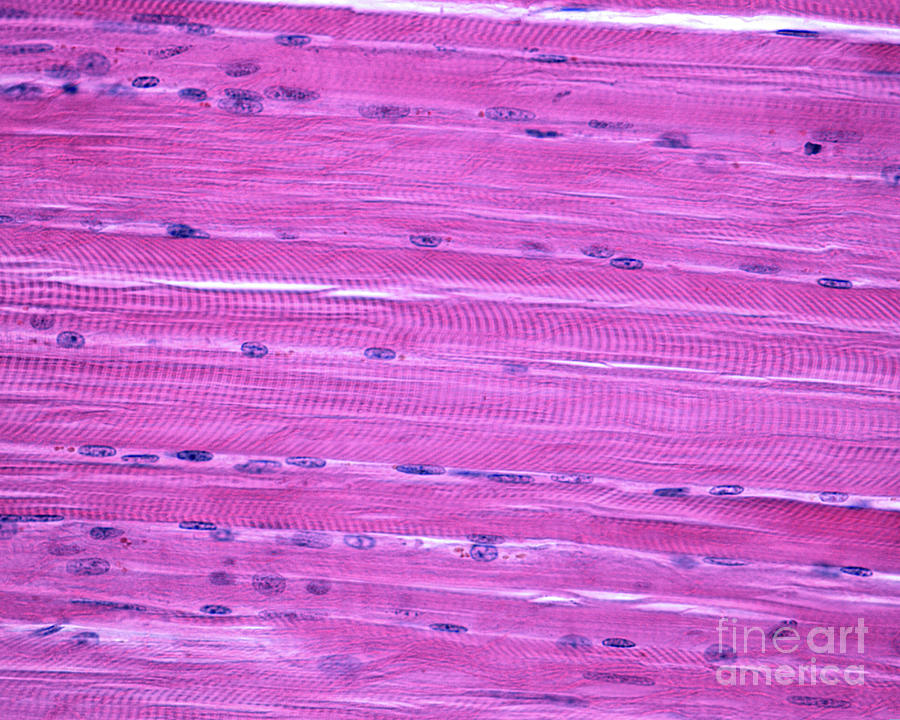
What are the marks indicated by the green arrow called?
Answer: Striations
Explanation: Striations are alternating light and dark bands in skeletal and cardiac muscle that result from the arrangement of actin and myosin filaments.
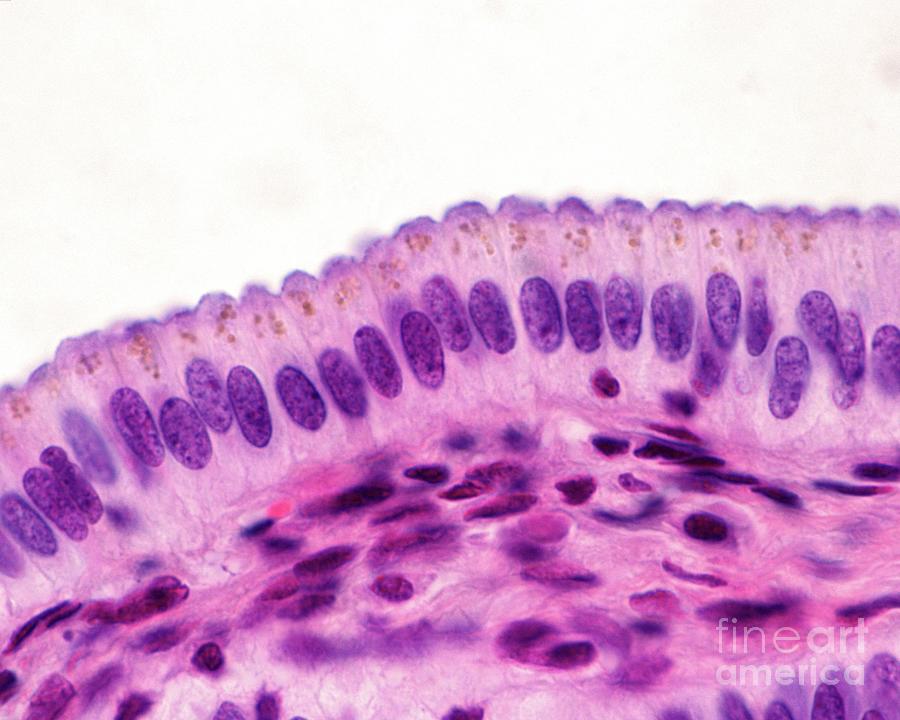
What type of epithelium is shown in the image?
Answer: Simple columnar epithelium
Explanation: Simple columnar epithelium consists of tall, column-like cells and is found in the digestive tract for absorption and secretion.
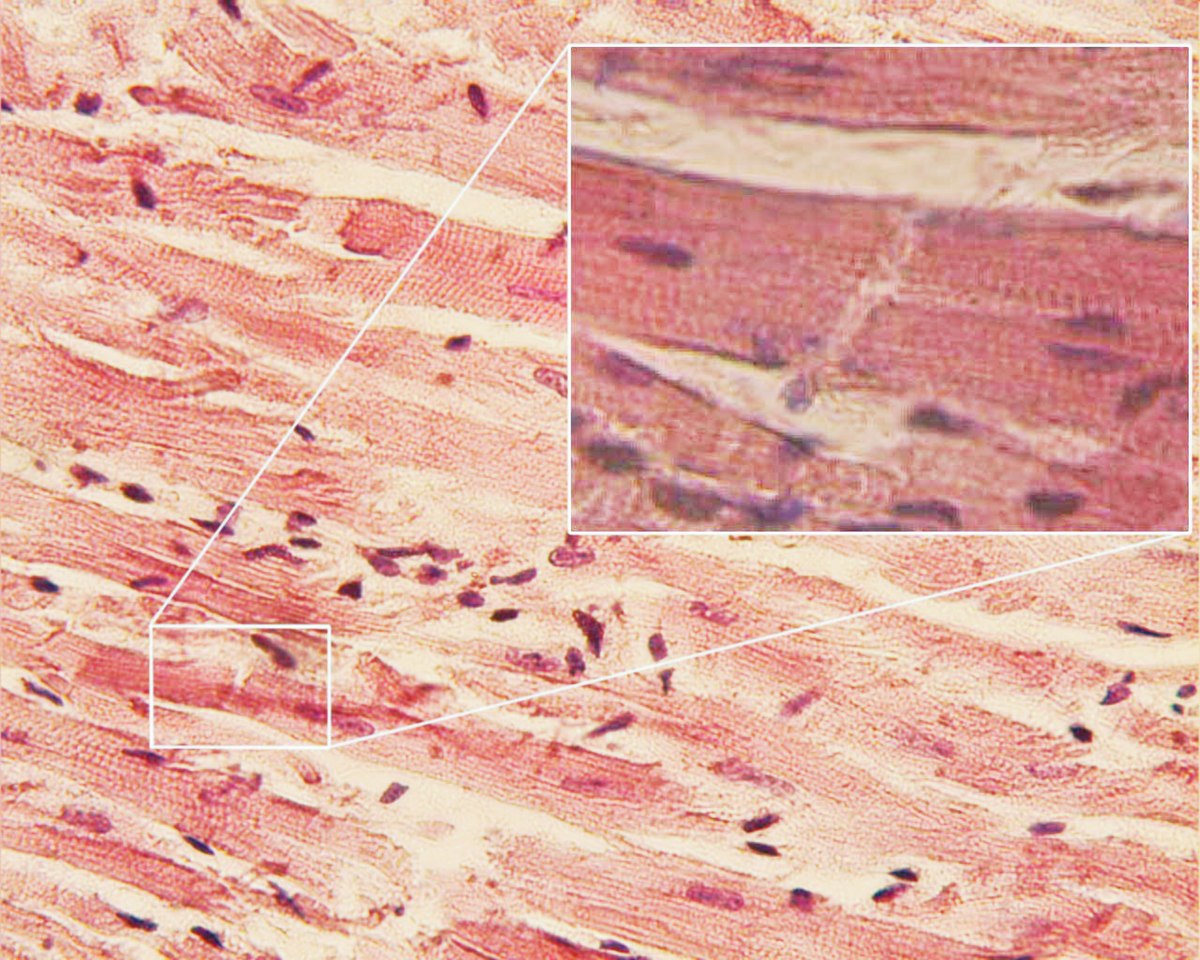
What is the structure indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Intercalated disc
Explanation: Intercalated discs are specialized junctions between cardiac muscle cells that allow rapid transmission of electrical impulses.
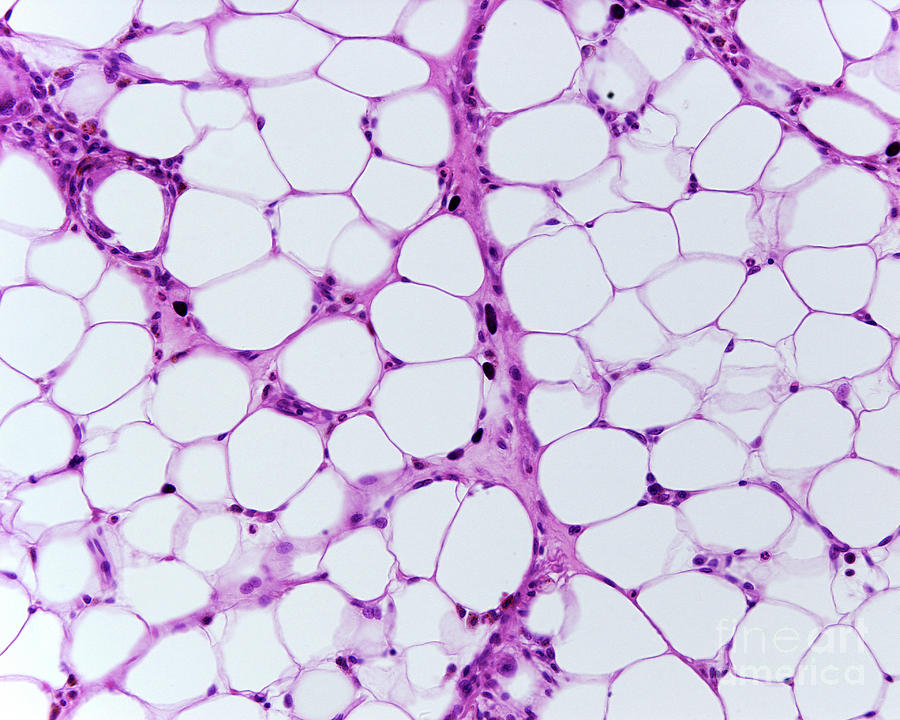
What type of connective tissue is shown in the image?
Answer: Adipose tissue
Explanation: Adipose tissue stores energy in the form of fat and provides insulation and cushioning.
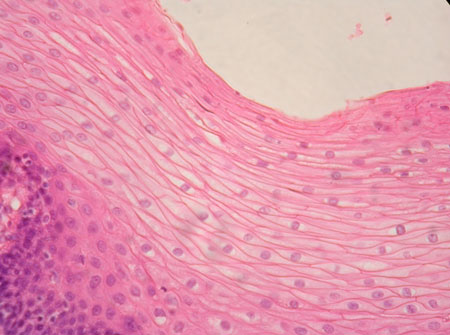
What type of epithelium is shown in the image?
Answer: Stratified squamous epithelium
Explanation: Stratified squamous epithelium consists of multiple layers of flat cells and is found in areas subject to friction, such as the skin and esophagus.
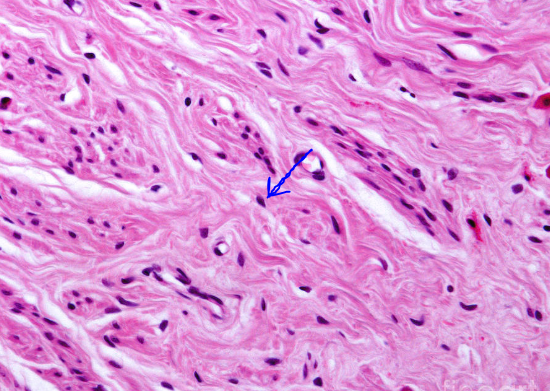
What type of connective tissue is shown in the image?
Answer: Blood
Explanation: Blood is a connective tissue composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, responsible for transport and immune response.
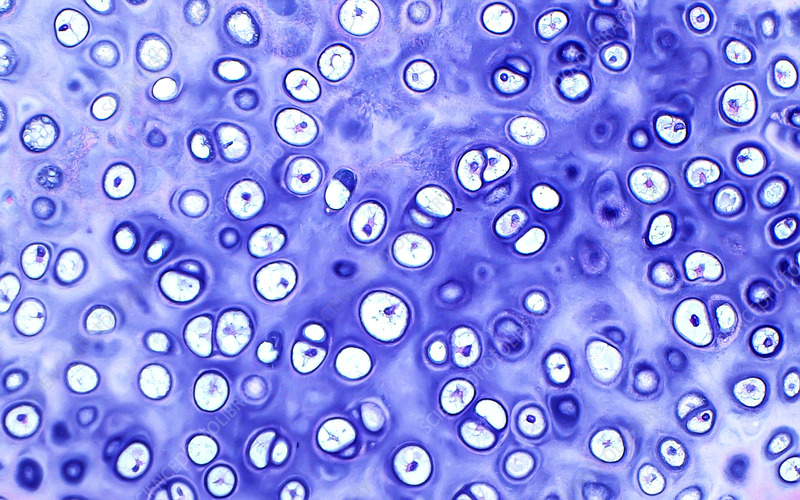
What type of connective tissue is shown in the image?
Answer: Hyaline cartilage
Explanation: Hyaline cartilage provides support with some flexibility and reduces friction in joints.
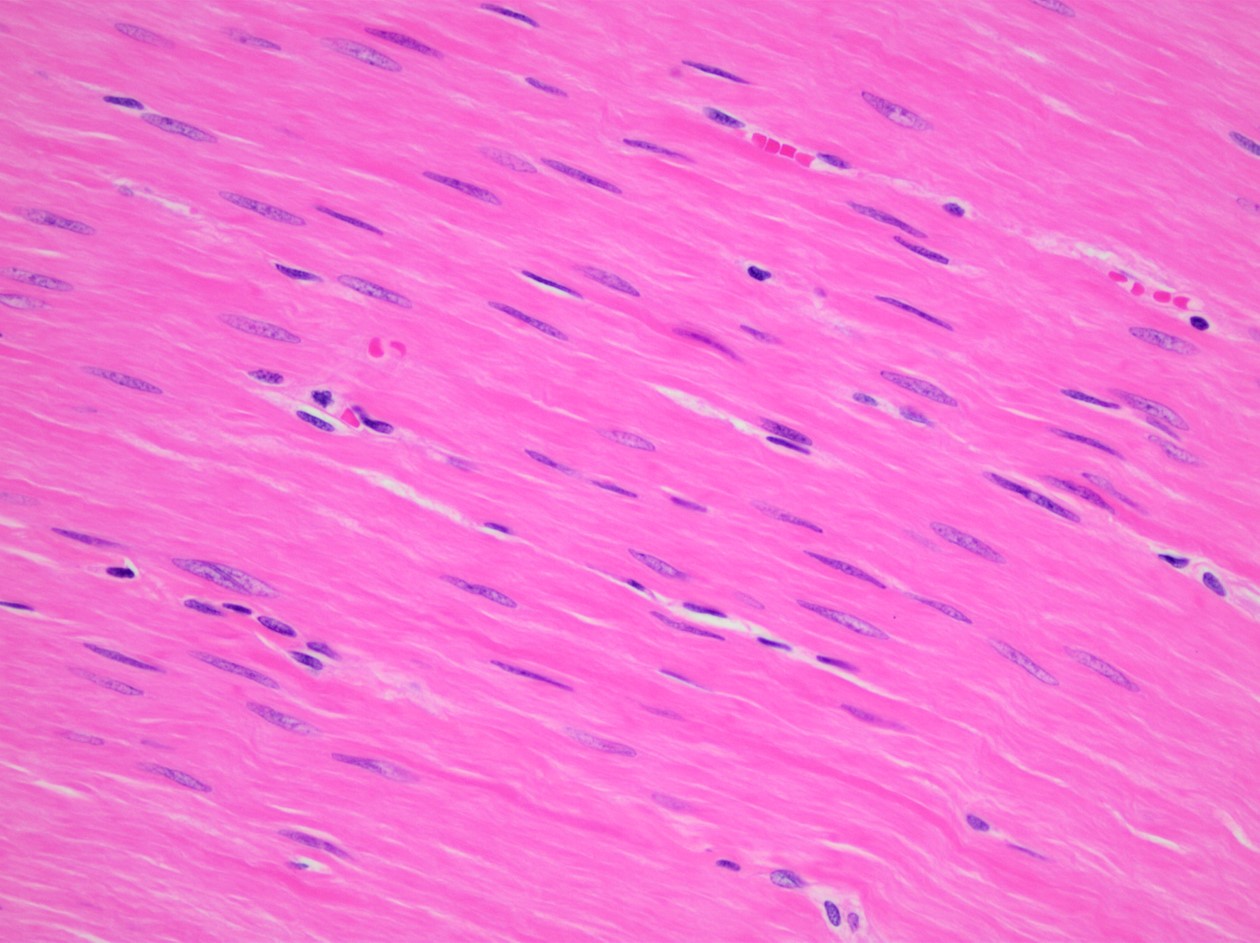
What type of muscle tissue is shown in the image?
Answer: Smooth muscle
Explanation: Smooth muscle is involuntary, non-striated muscle found in the walls of hollow organs such as the intestines and blood vessels.
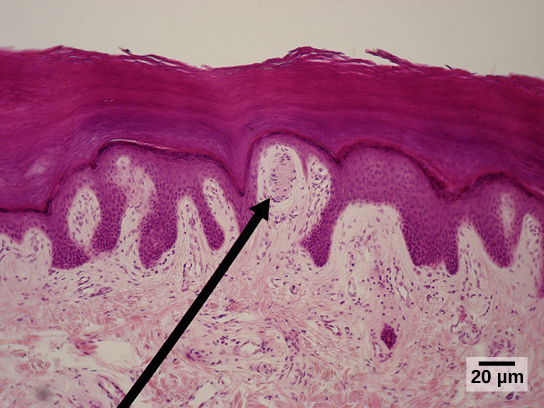
What is the sensory receptor indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Meissner’s corpuscle
Explanation: Meissner’s corpuscles are touch receptors found in the dermis, responsible for detecting light touch and texture.
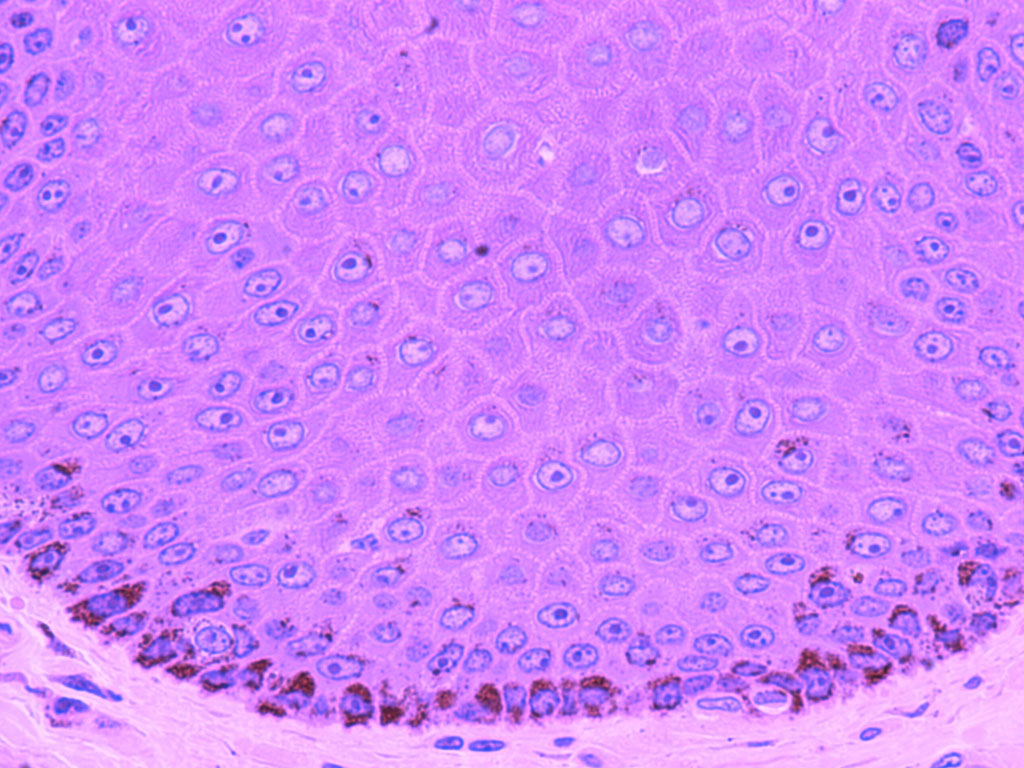
What is the stratum indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Stratum basale
Explanation: The stratum basale is the deepest layer of the epidermis, containing basal cells that divide and produce new skin cells.
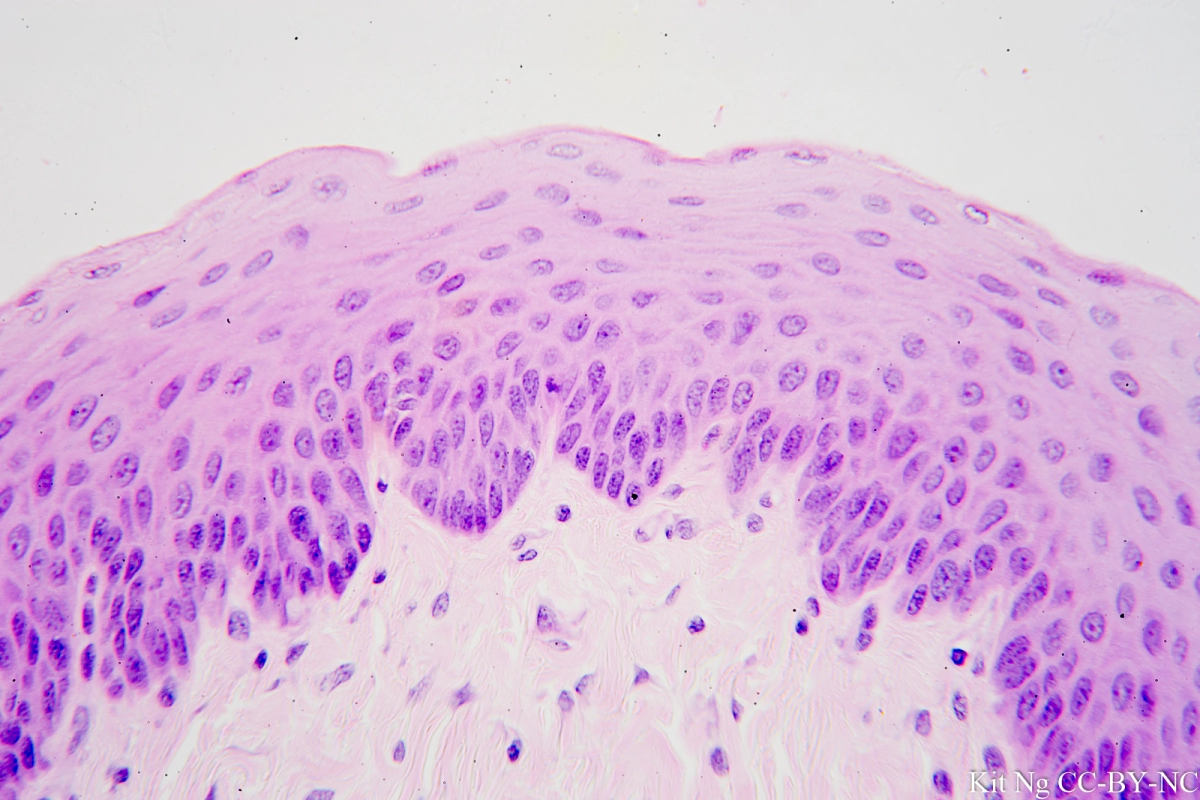
What tissue is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Stratified squamous epithelium
Explanation: Stratified squamous epithelium protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion, such as the skin and mouth.
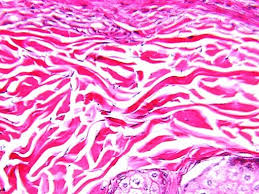
What type of connective tissue is shown in the image?
Answer: Dense irregular connective tissue
Explanation: Dense irregular connective tissue provides strength and support in multiple directions and is found in the dermis of the skin.
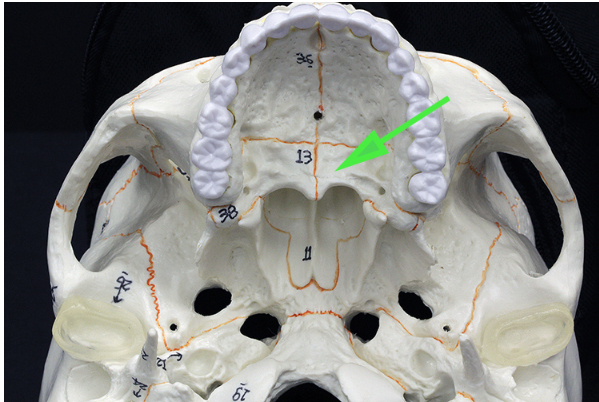
What bone is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Palatine bone
Explanation: The palatine bone is located at the back of the oral cavity and forms part of the hard palate, nasal cavity, and eye orbit.
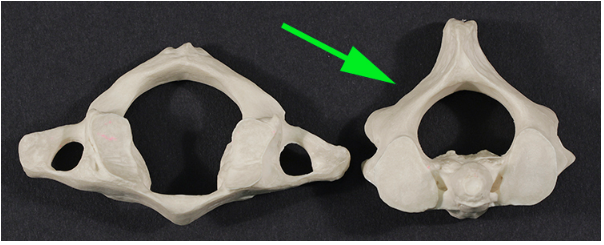
What cervical vertebra is marked by the green arrow?
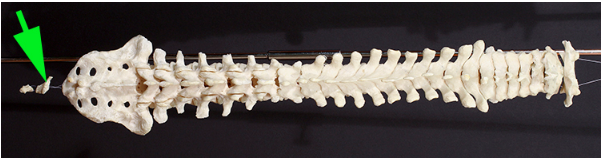
What structure is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Coccyx
Explanation: The coccyx, or tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column and consists of fused vertebrae that provide attachment for ligaments and muscles.
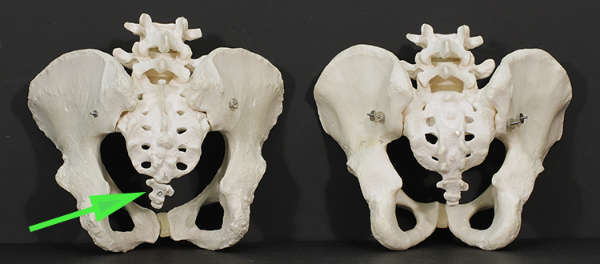
What structure is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Coccyx
Explanation: The coccyx is the small, triangular bone at the base of the spine, made up of fused vertebrae.
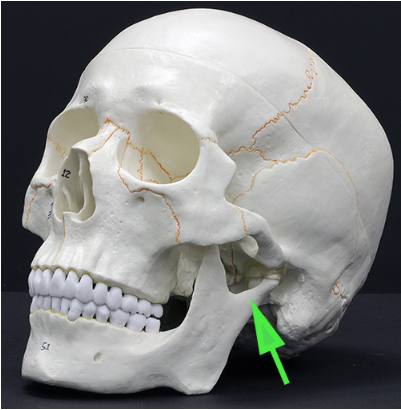
What structure is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Condyloid process
Explanation: The condyloid process is part of the mandible and forms the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) by articulating with the temporal bone.
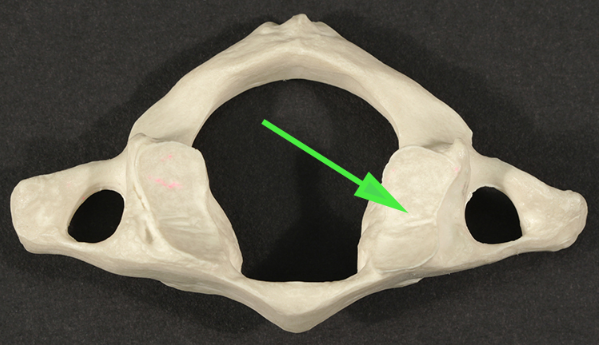
What part of the vertebra is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Superior articular facet
Explanation: The superior articular facet is a smooth surface on a vertebra that articulates with the inferior articular facet of the vertebra above it.
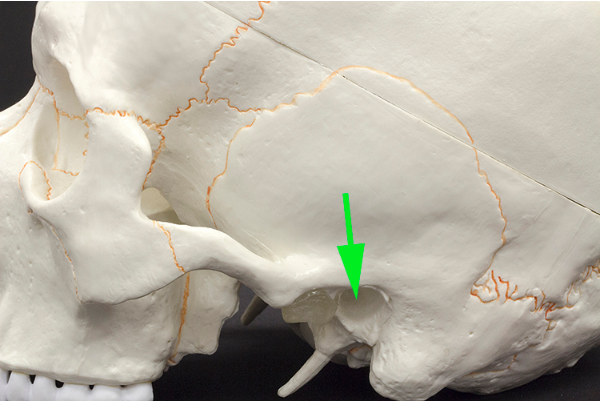
What opening is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: External acoustic meatus
Explanation: The external acoustic meatus is the canal that leads from the outer ear to the eardrum and middle ear.
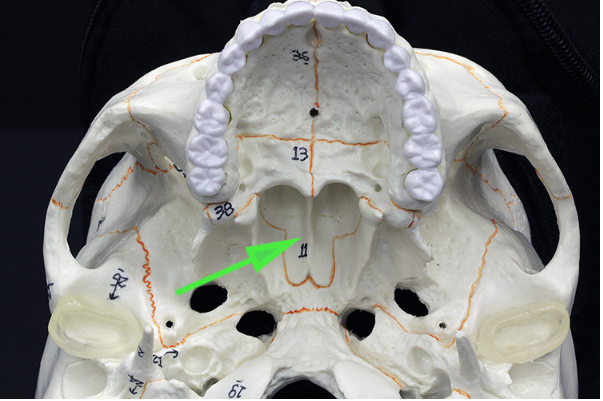
What bone is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Vomer bone
Explanation: The vomer bone forms part of the nasal septum and helps divide the nasal cavity into two passages.
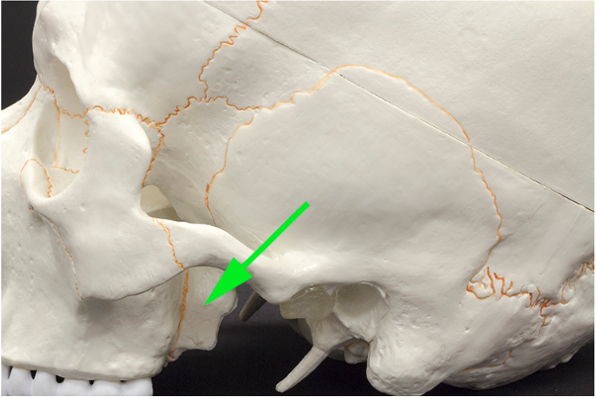
What part of the sphenoid bone is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Pterygoid process
Explanation: The pterygoid process extends from the sphenoid bone and serves as an attachment point for muscles of mastication.
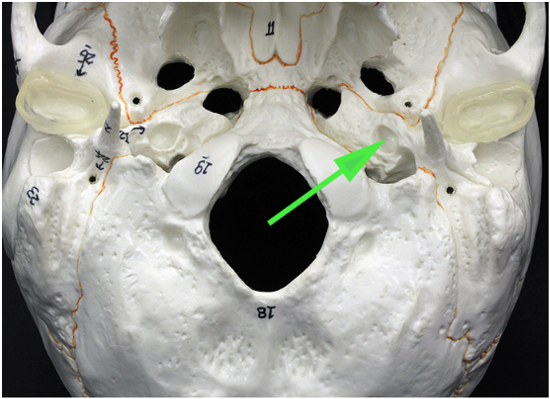
What opening is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Carotid canal
Explanation: The carotid canal is a passage in the temporal bone that allows the internal carotid artery to enter the skull and supply blood to the brain.
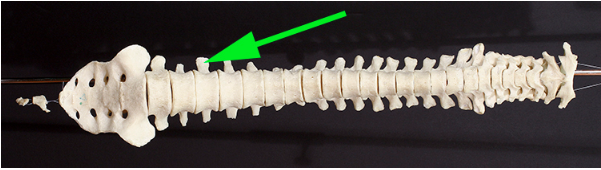
What process is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Transverse process
Explanation: The transverse process is a lateral projection from the vertebral arch that serves as an attachment site for muscles and ligaments.
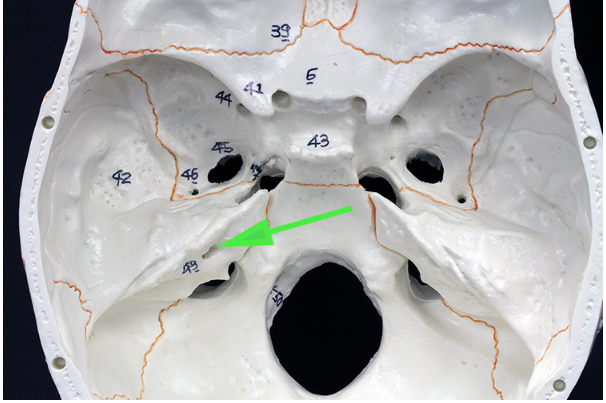
What opening is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Internal acoustic meatus
Explanation: The internal acoustic meatus is a canal in the temporal bone that transmits the facial and vestibulocochlear nerves.
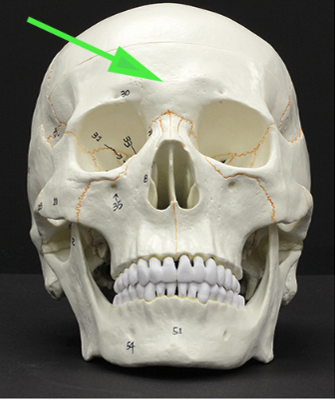
What bone is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Frontal bone
Explanation: The frontal bone forms the forehead, the superior part of the eye sockets, and the anterior cranial fossa.
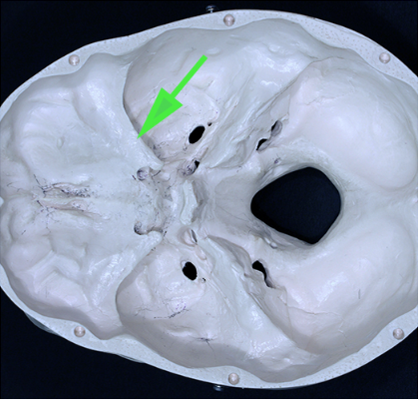
What part of the sphenoid bone is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Lesser wing
Explanation: The lesser wings of the sphenoid bone contribute to the formation of the anterior cranial fossa and the orbital cavity.
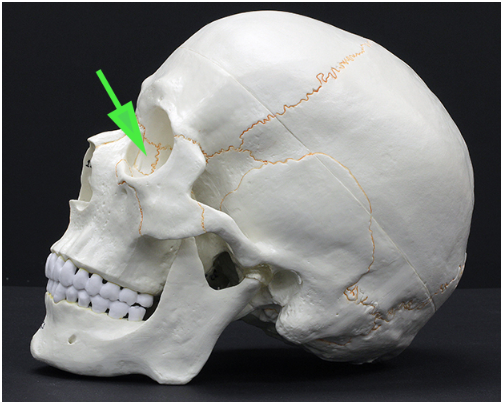
What bone is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Lacrimal bone
Explanation: The lacrimal bone is a small, thin bone forming part of the medial wall of the orbit and contains the lacrimal sac, which aids in tear drainage.
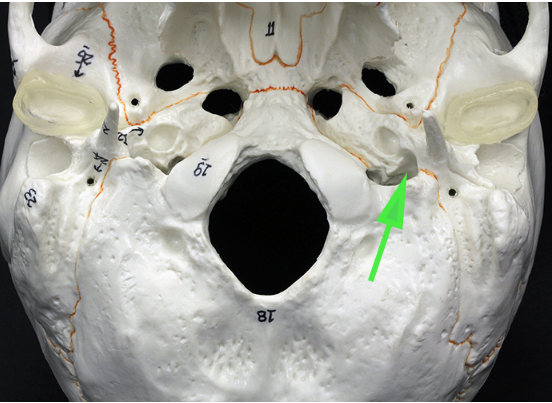
What opening is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Jugular foramen
Explanation: The jugular foramen is a large opening in the base of the skull that allows the internal jugular vein and several cranial nerves to pass through.
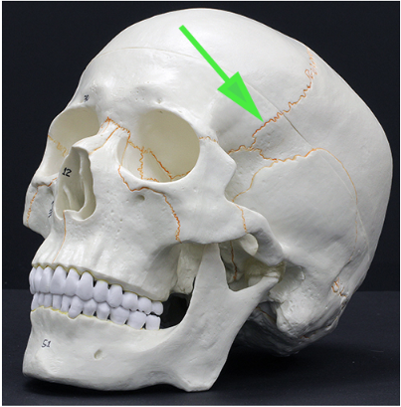
What suture is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Coronal suture
Explanation: The coronal suture is the fibrous joint that connects the frontal bone to the parietal bones.
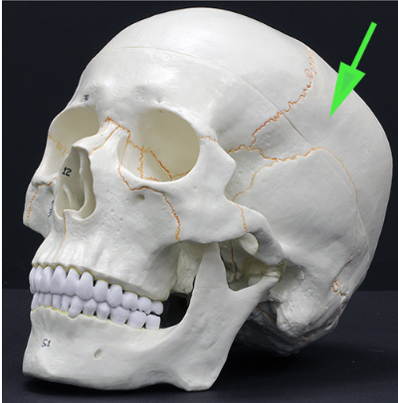
What bone is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Parietal bone
Explanation: The parietal bones form the sides and roof of the cranial cavity and articulate at the sagittal suture.
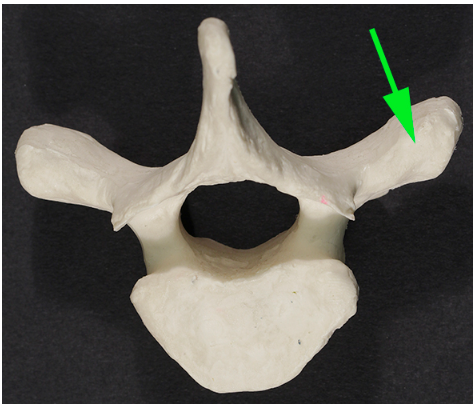
What part of the vertebra is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Transverse process
Explanation: The transverse process is a lateral bony projection from the vertebral arch that serves as an attachment site for muscles and ligaments.
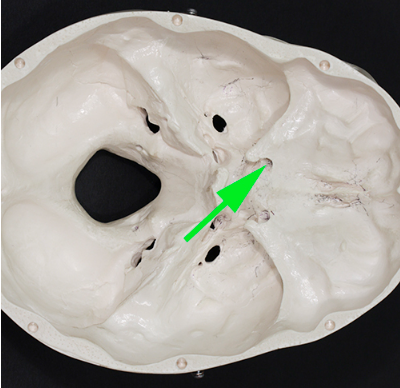
What opening is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Optic canal
Explanation: The optic canal is an opening in the sphenoid bone that transmits the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery to the eye.
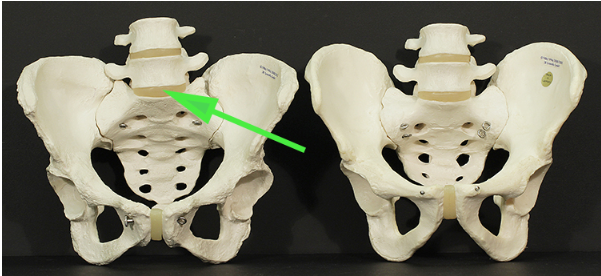
What is the structure indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Intervertebral disc
Explanation: The intervertebral disc is a fibrocartilaginous structure located between adjacent vertebrae. It provides cushioning and allows flexibility in the spinal column.
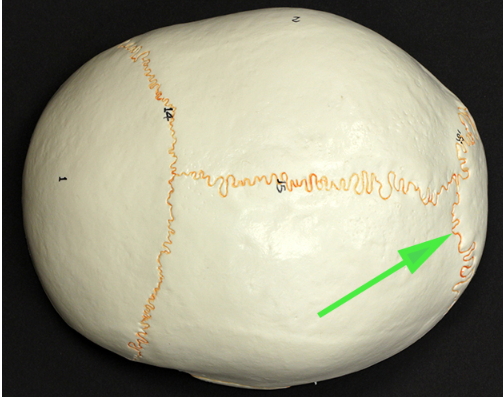
What is the suture marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Lambdoid suture
Explanation: The lambdoid suture is the fibrous joint that connects the parietal bones to the occipital bone in the skull. It is important for cranial flexibility and growth.
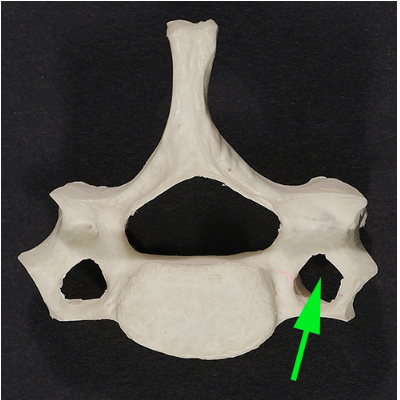
What is the opening marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Transverse foramen
Explanation: The transverse foramen is found in cervical vertebrae and allows the passage of the vertebral artery and vein, which supply blood to the brain.
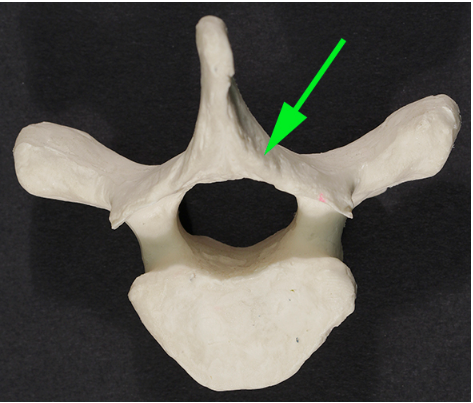
What part of the vertebra is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Spinous process
Explanation: The spinous process is a bony projection off the posterior of each vertebra. It serves as an attachment site for muscles and ligaments.
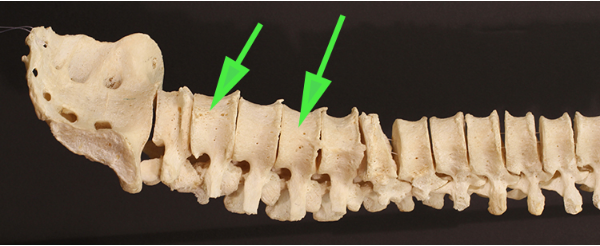
Which type of vertebra are the green arrows indicating?
Answer: Lumbar vertebrae
Explanation: The lumbar vertebrae are the largest and strongest in the spinal column, supporting most of the body's weight. They lack transverse foramina and have large bodies.
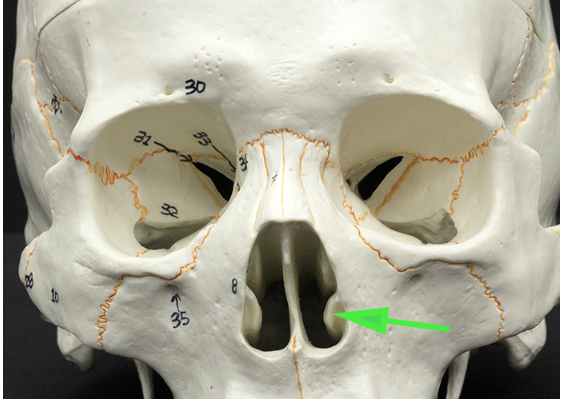
What is the bone marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Inferior nasal concha (turbinate bone)
Explanation: The inferior nasal concha is a separate facial bone that helps warm and humidify the air before it enters the respiratory tract.
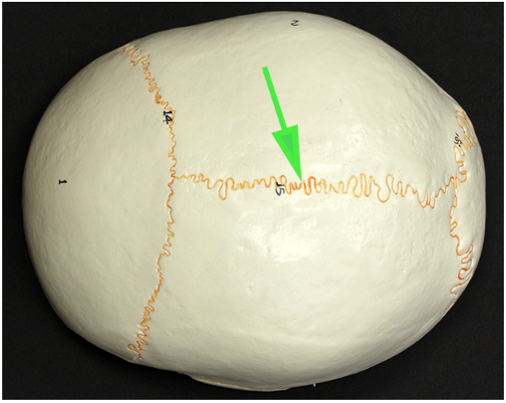
What is the suture marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Sagittal suture
Explanation: The sagittal suture runs along the midline of the skull, connecting the two parietal bones. It allows skull growth during infancy.
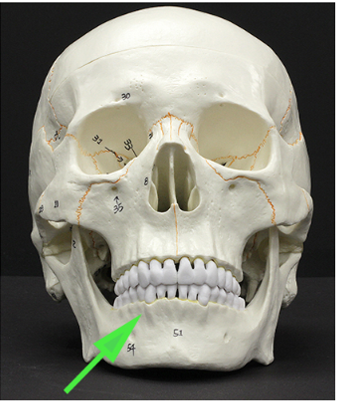
What are the skinny processes of bone found between teeth and marking the edges of the tooth sockets?
Answer: Alveolar processes
Explanation: The alveolar processes are extensions of the maxilla and mandible that house the tooth sockets and support the teeth.
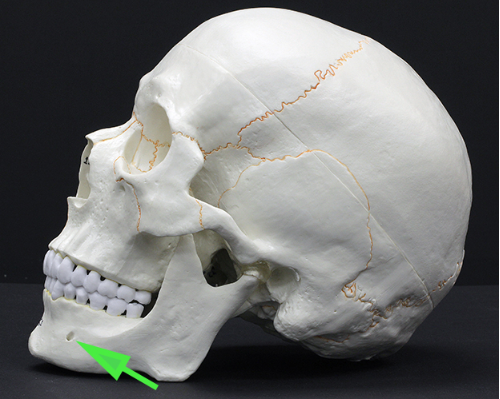
What is the opening marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Mental foramen
Explanation: The mental foramen is a small hole in the mandible that allows nerves and blood vessels to pass to the chin and lower lip.
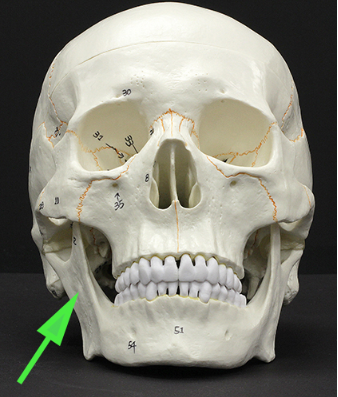
What is the structure marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Ramus of the mandible
Explanation: The ramus is the vertical portion of the mandible that connects the lower jaw to the skull via the temporomandibular joint.
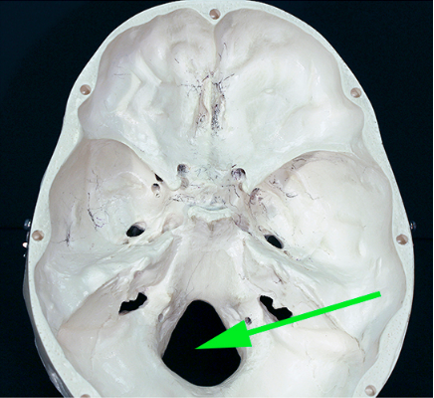
What is the bump marked by the green arrow on the occipital bone?
Answer: Occipital condyle
Explanation: The occipital condyles are rounded projections that articulate with the first cervical vertebra, allowing head movement.
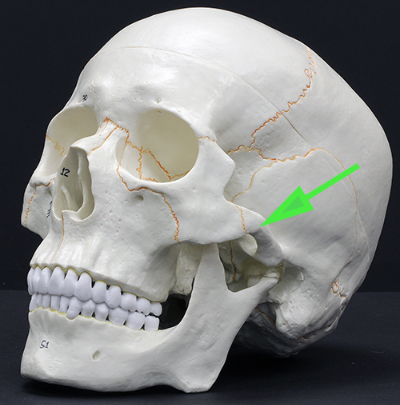
What is the process indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Zygomatic process of the temporal bone
Explanation: The zygomatic process extends from the temporal bone to form part of the zygomatic arch (cheekbone).
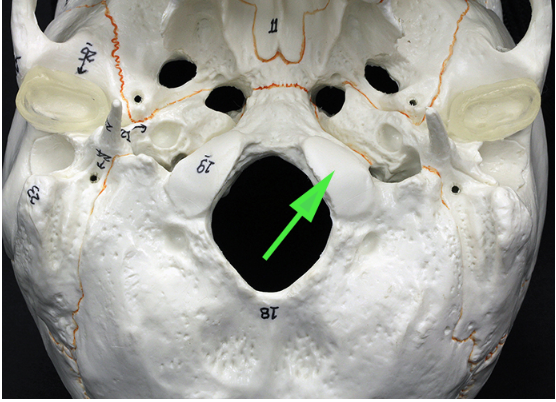
What is the opening marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Foramen magnum
Explanation: The foramen magnum is a large opening in the occipital bone through which the spinal cord passes to connect with the brain.
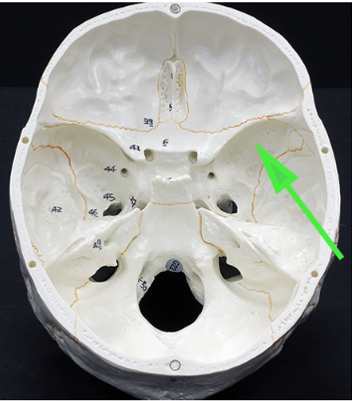
What area of the sphenoid bone is indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Greater wing
Explanation: The greater wings of the sphenoid bone extend laterally and form part of the base of the skull, providing attachment for muscles.
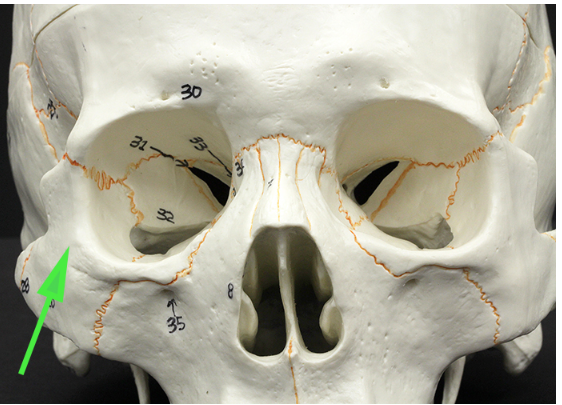
What is the bone indicated by the green arrow?
Answer: Zygomatic bone
Explanation: The zygomatic bone, or cheekbone, forms part of the lateral orbit and gives structure to the face.
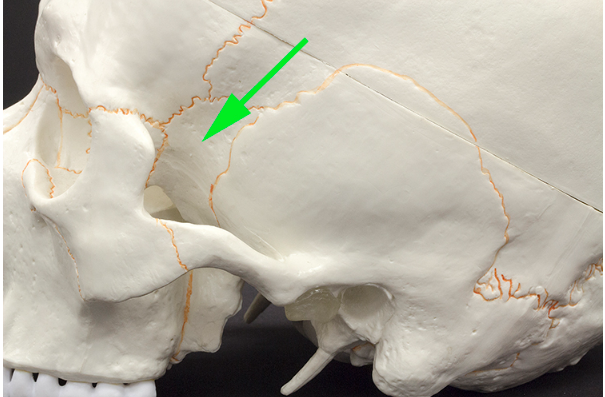
What area is marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Temporal bone
Explanation: The temporal bone forms the sides and base of the skull and houses the structures of the ear.
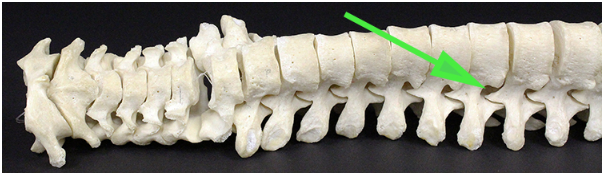
What is the opening marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Intervertebral foramen
Explanation: The intervertebral foramen is the opening between adjacent vertebrae through which spinal nerves exit the spinal cord.
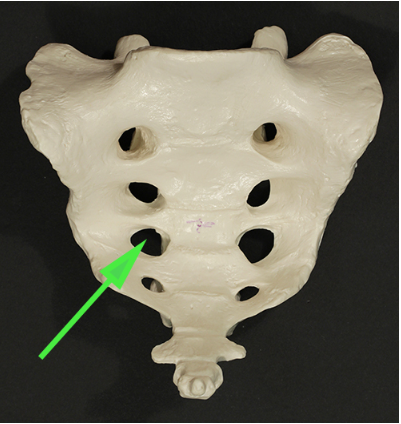
What is the opening marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Anterior sacral foramen
Explanation: The anterior sacral foramina allow for the passage of sacral nerves and blood vessels.
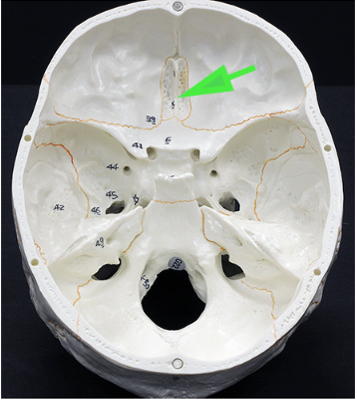
What is the bone marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Ethmoid bone
Explanation: The ethmoid bone forms part of the nasal cavity and the medial wall of the orbit, containing air cells that contribute to sinus function.
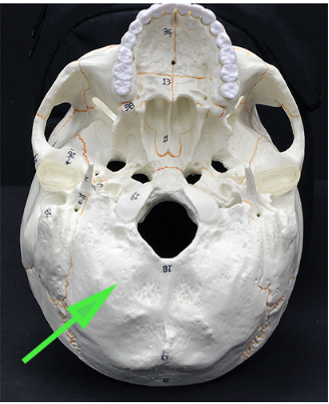
What is the bone marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Occipital bone
Explanation: The occipital bone forms the posterior and inferior part of the skull and contains the foramen magnum for spinal cord passage.
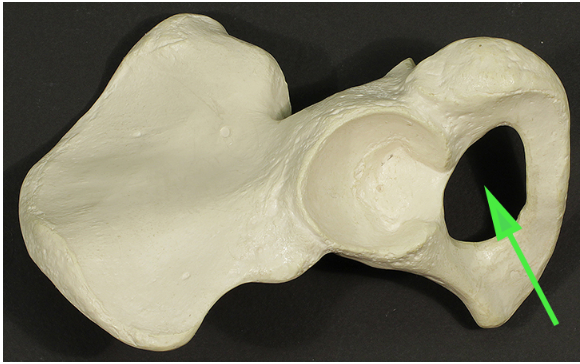
What is the opening marked by the green arrow?
Answer: Obturator foramen
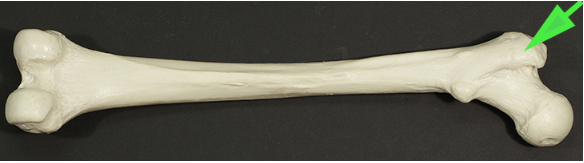
Identify the large process marked by the green arrow.
Answer: Greater trochanter

Name the part of the femur indicated by the green arrow.
Answer: Femoral neck
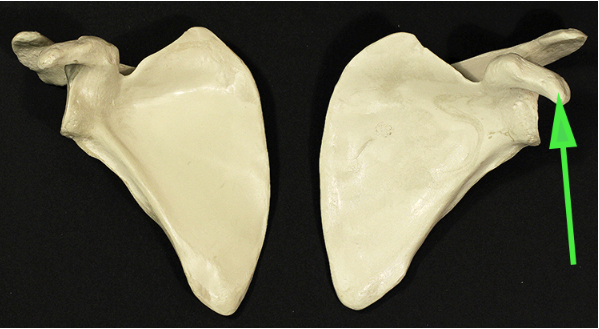
Name the process indicated by the green arrow.
Answer: Acromion

Identify the portion of the humerus marked by the green arrow.
Answer: Medial epicondyle
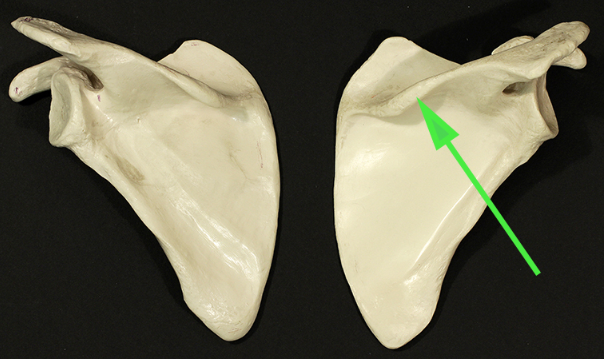
Name the part of the scapula indicated by the green arrow.
Answer: Scapular spine
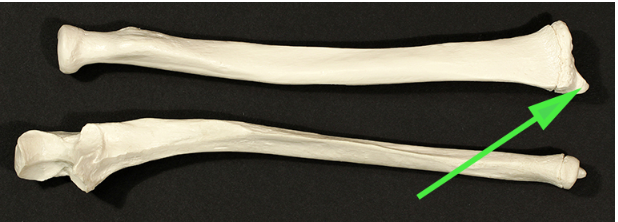
Name the process indicated by the green arrow.
Answer: Medial malleolus
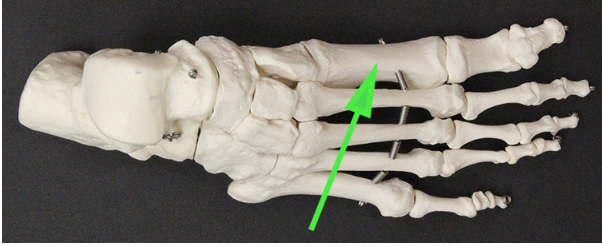
Name the bone indicated by the green arrow.
Answer: First metatarsal
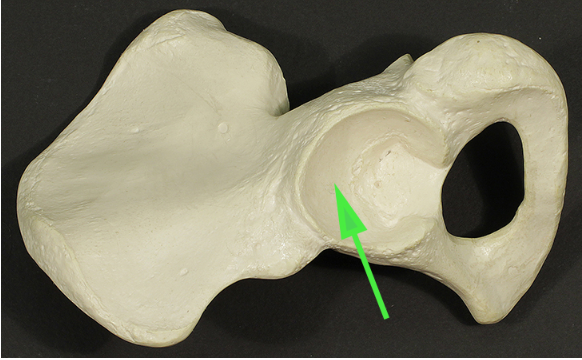
Name the structure marked by the green arrow.
Answer: Acetabulum
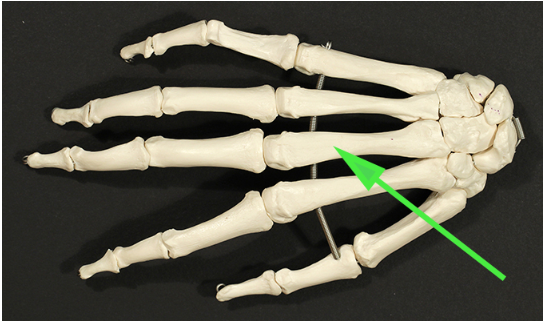
Name the bone found in the palm of the hand that is indicated by the green arrow.
Answer: Metacarpal bone
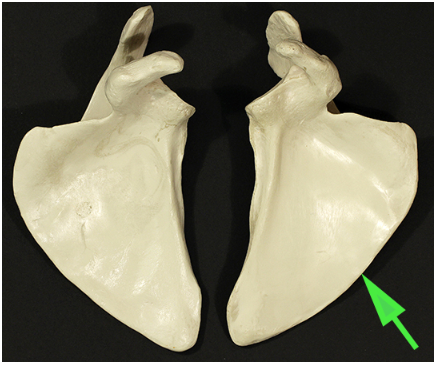
Name the border of the scapula being indicated by the green arrow.
Answer: Medial border
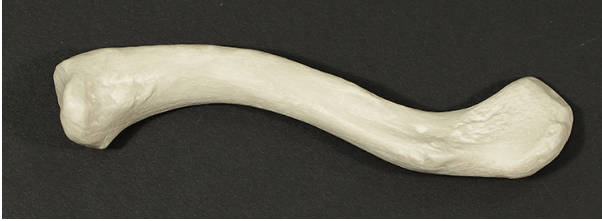
Is this the left or right clavicle?
Answer: Left

Is this the left or right tibia?
Answer: Right
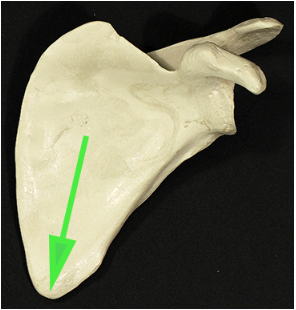
Name the pointed part of the scapula marked by the green arrow.
Answer: Inferior angle

Name the bump indicated by the green arrow.
Answer: Radial tuberosity
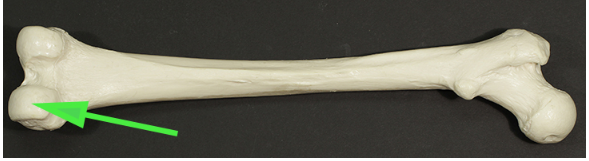
Name the portion of the femur indicated by the green arrow
Answer: Medial condyle
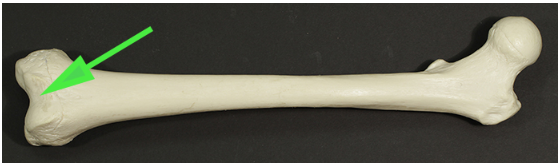
Name the area of the femur found at the spot indicated by the green arrow.
Answer: Patellar surface
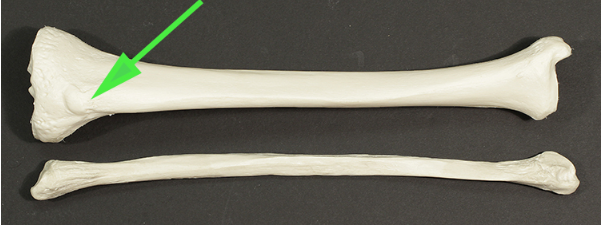
Name the bony process indicated by the green arrow.
Answer: Tibial tuberosity
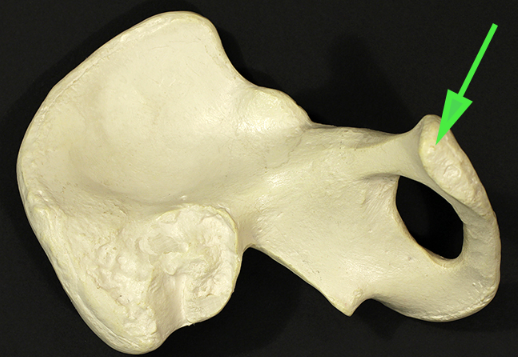
Name the bone marked by the green arrow.
Answer: Pubis
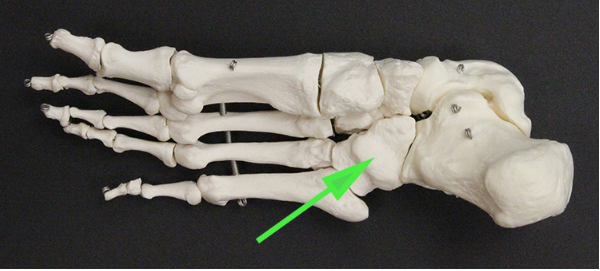
Name the tarsal bone marked by the green arrow.
Answer: Cuboid bone
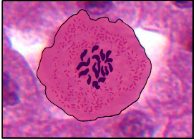
What phase of Mitosis is this cell in?
Prophase