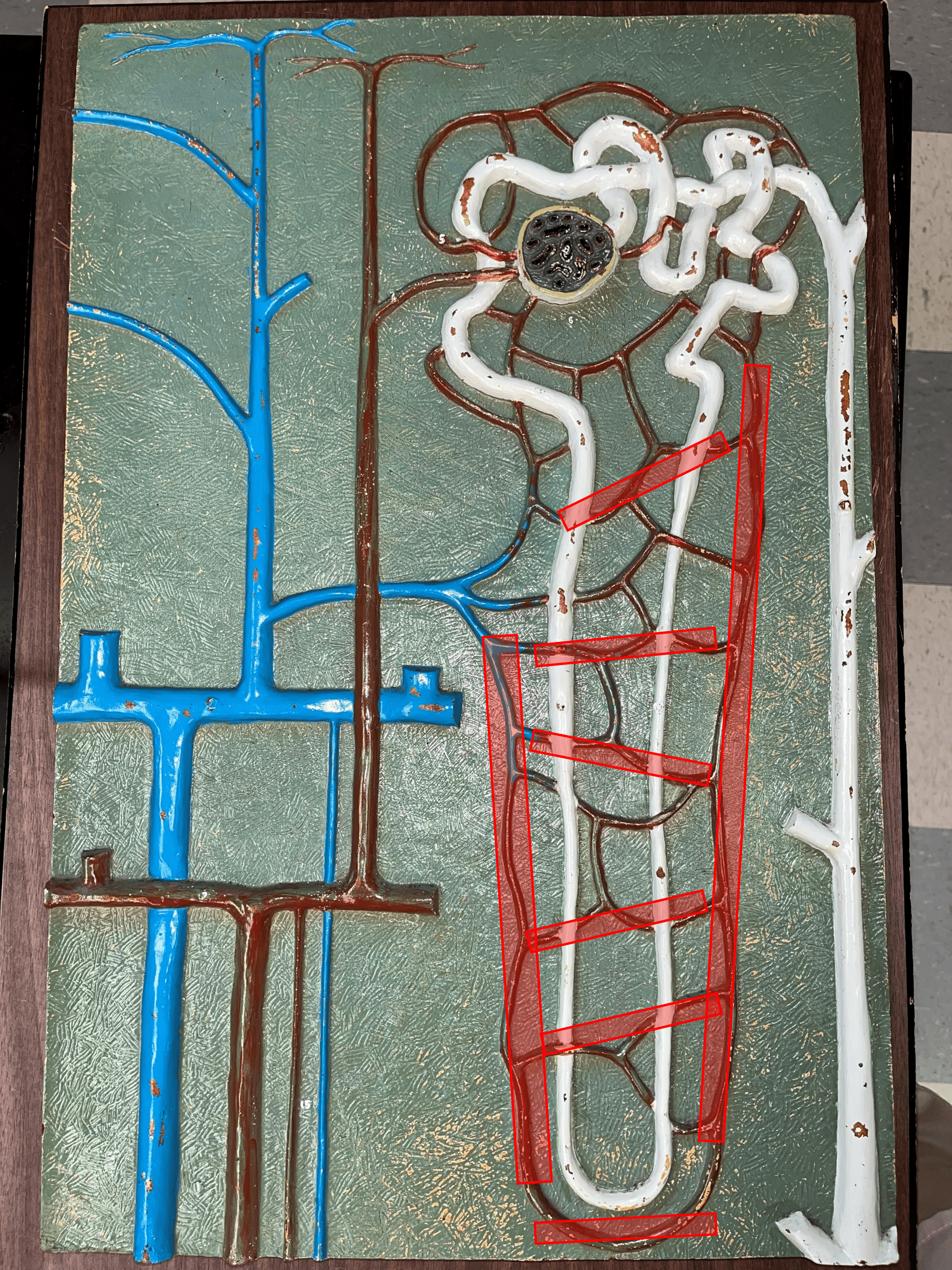BSC2086L E.9 Urinary System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
1
New cards
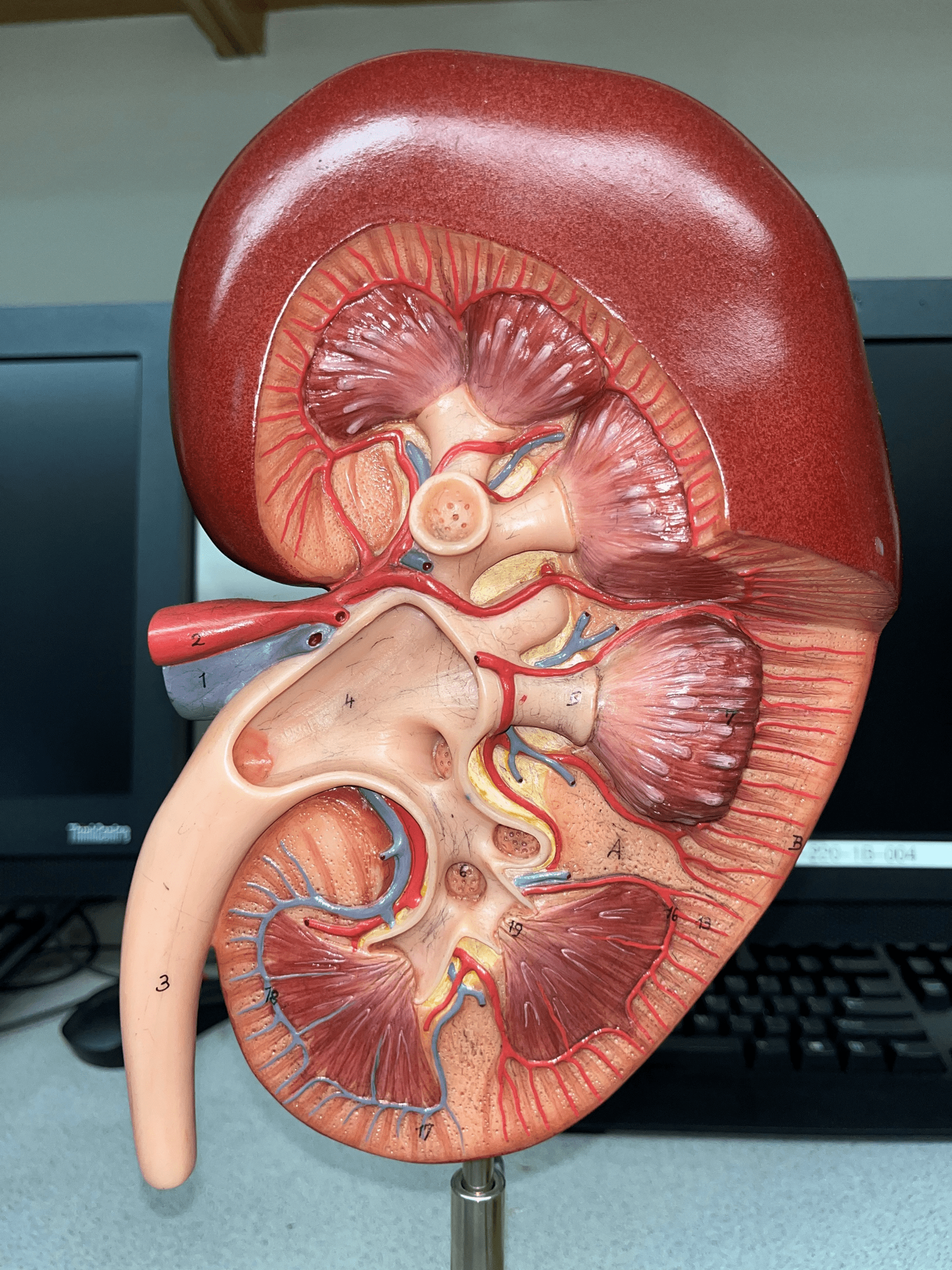
kidney
The organ that filters blood and excretes waste as urine.
2
New cards
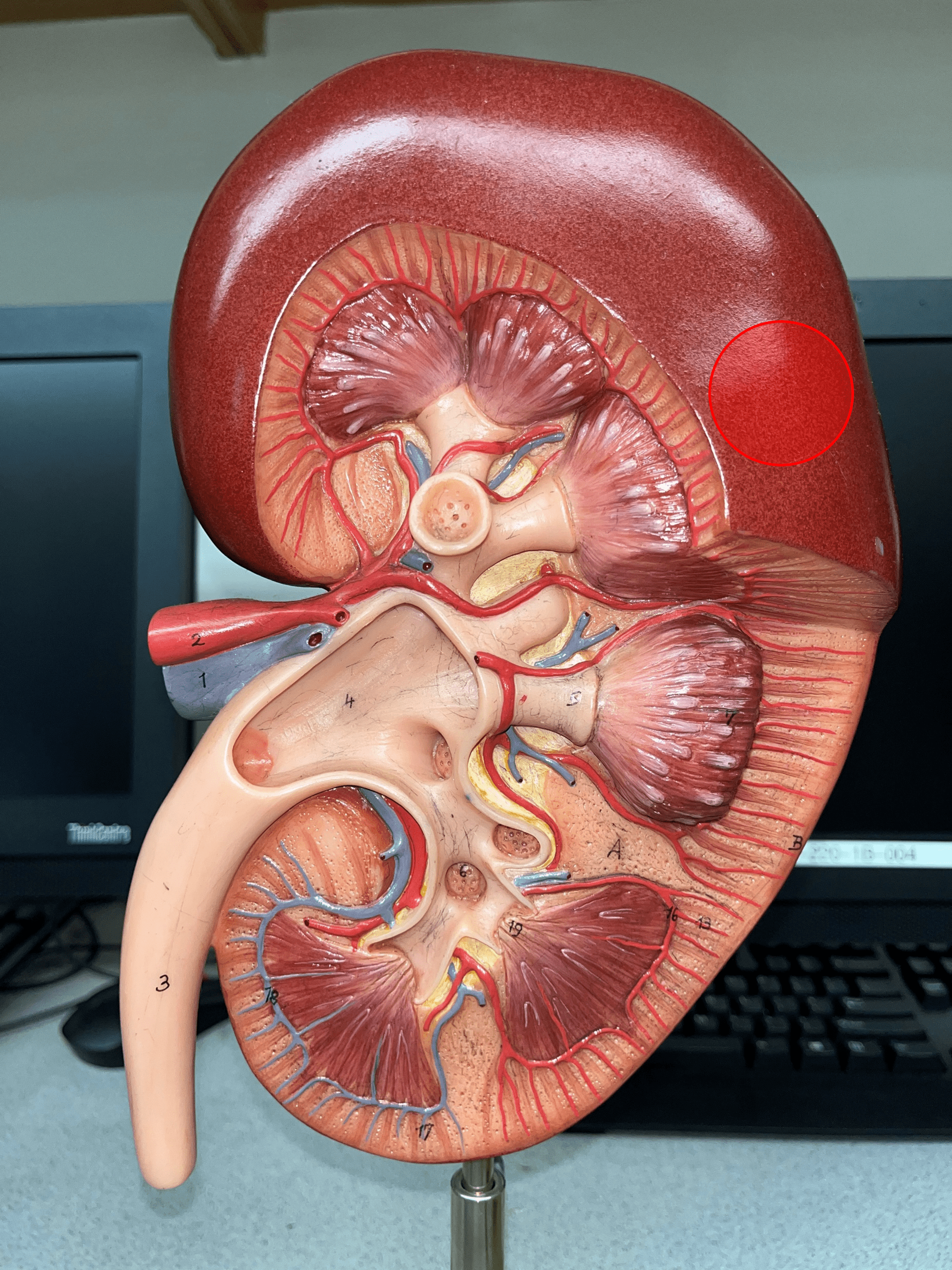
renal capsule
The thin outer shell of the kidney.
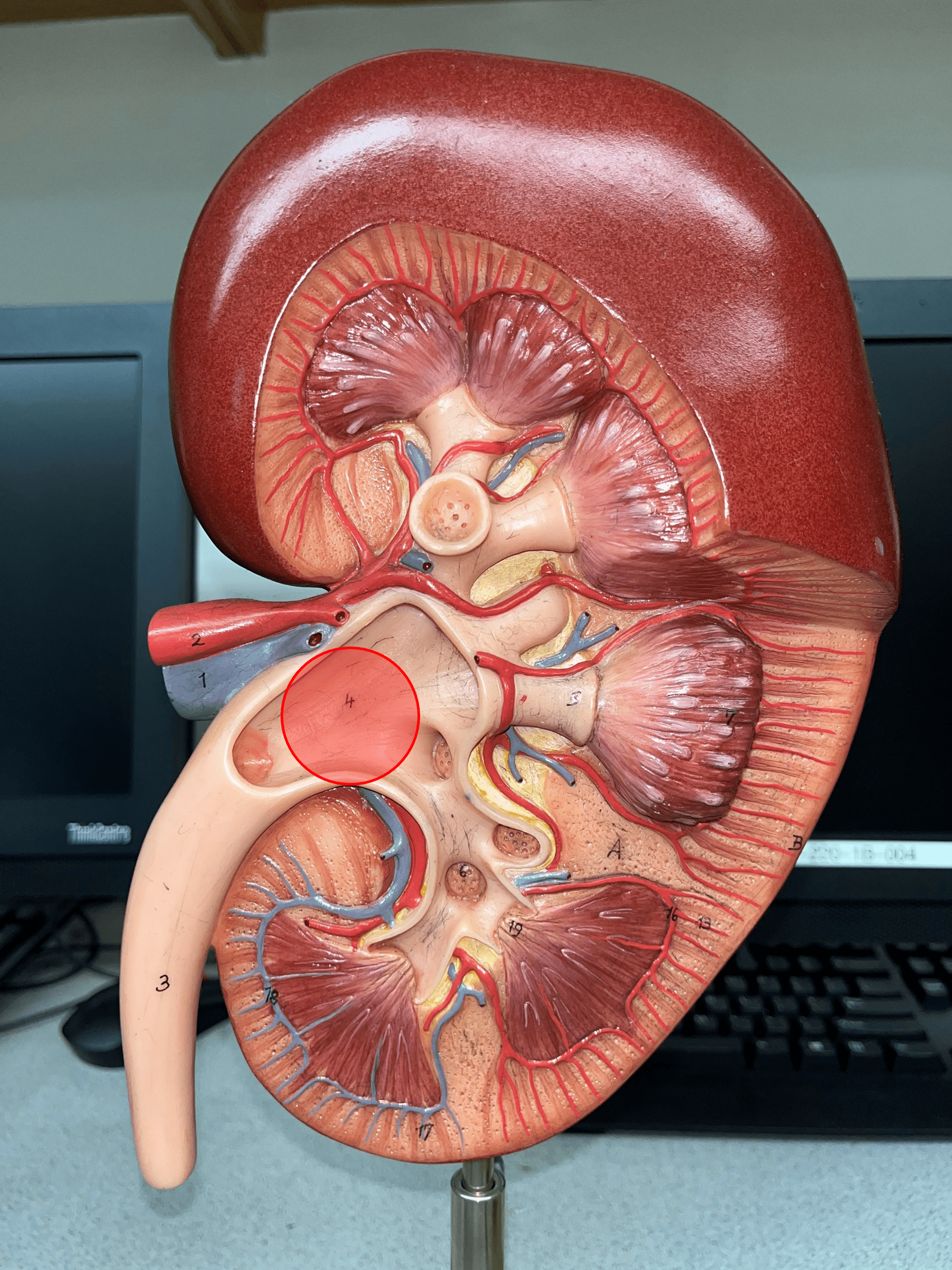
3
New cards
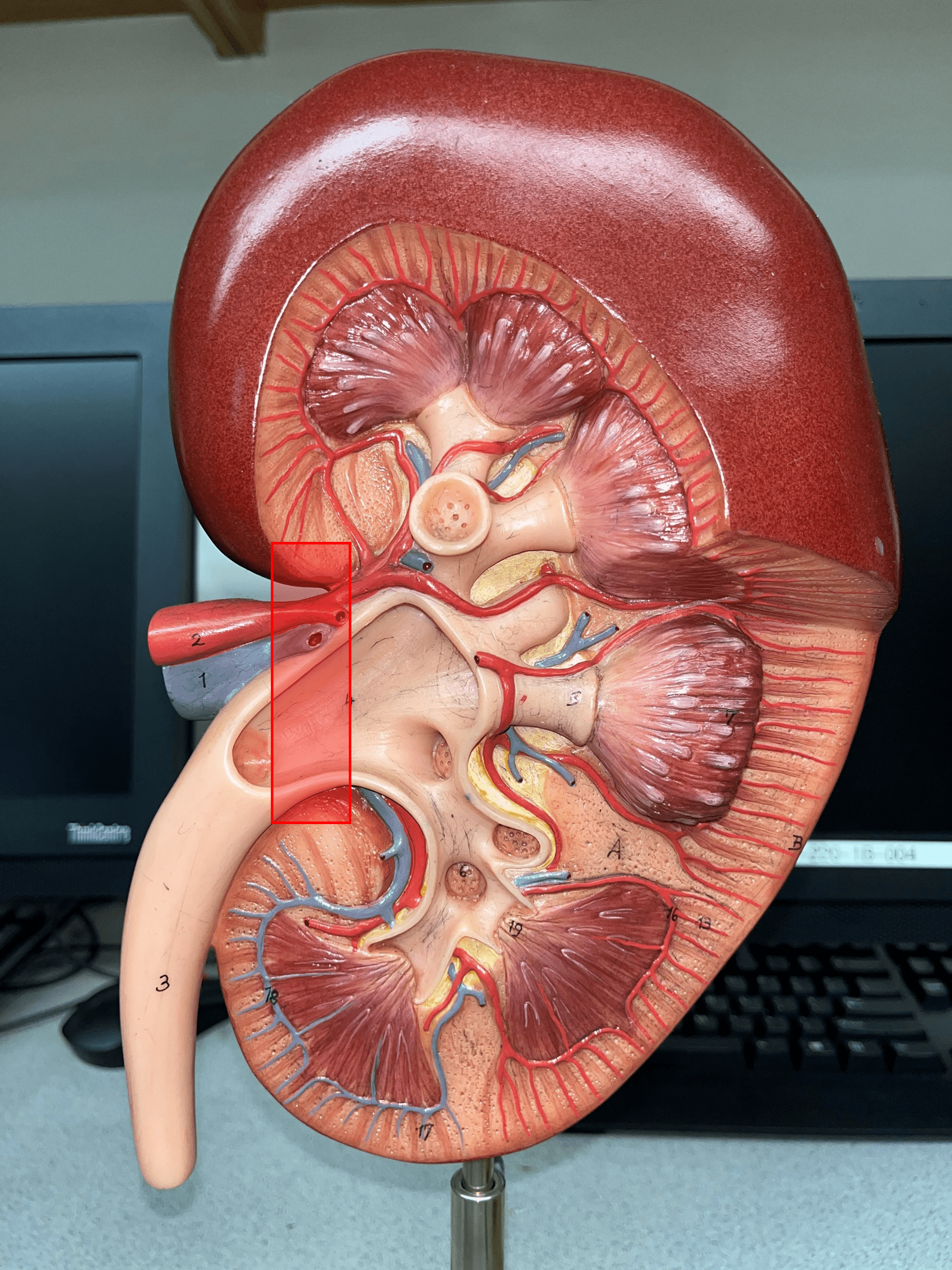
renal hilum
• The concavity of the kidney.
• Admits the ureters, renal a., renal v., lymphatics, and nerves.
• Also known as the hilus of the kidney.
• Admits the ureters, renal a., renal v., lymphatics, and nerves.
• Also known as the hilus of the kidney.
4
New cards
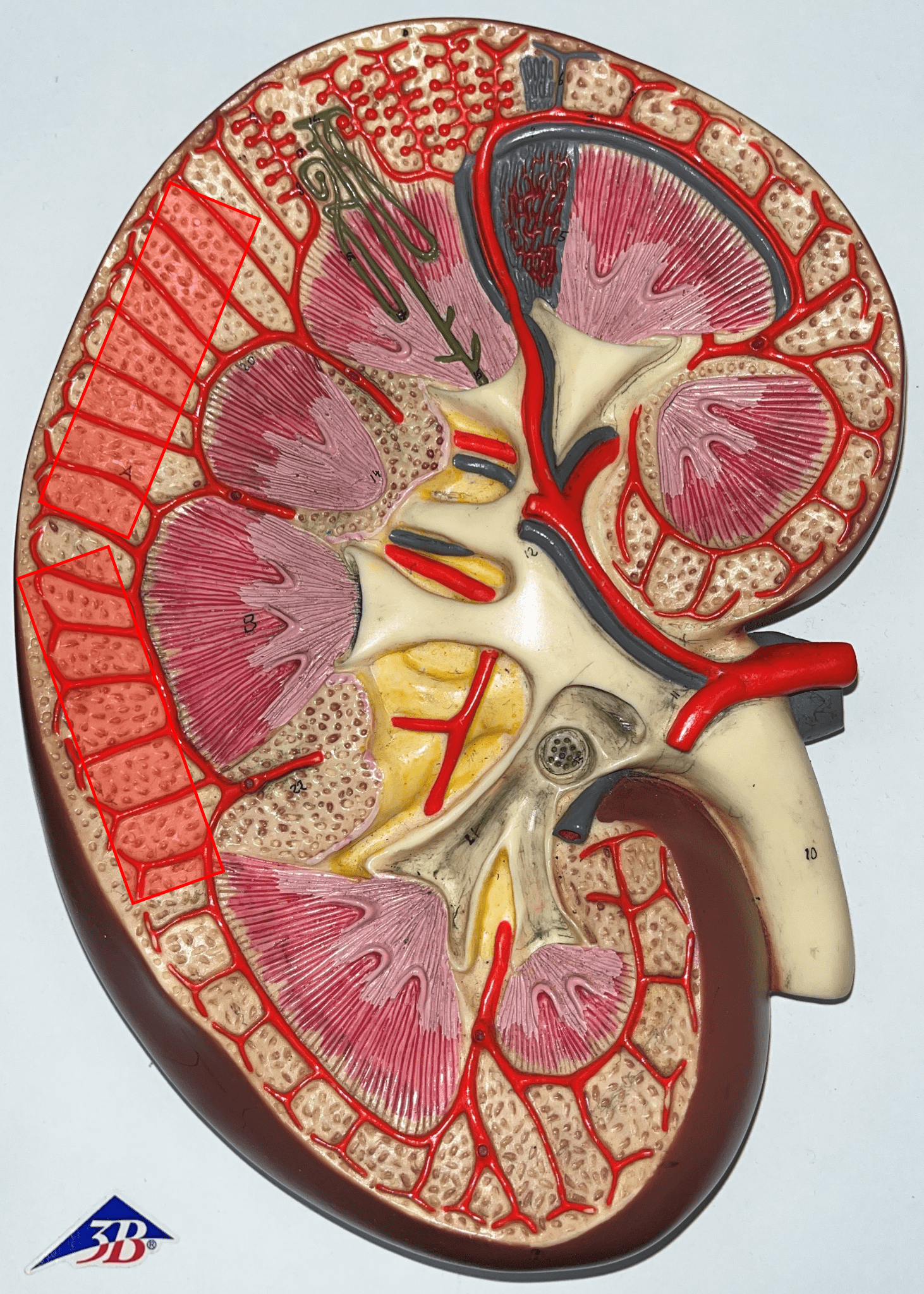
renal cortex
• The outermost region of the internal kidney.
• Superficial to the renal medulla.
• Appears slightly granular.
• Superficial to the renal medulla.
• Appears slightly granular.
5
New cards
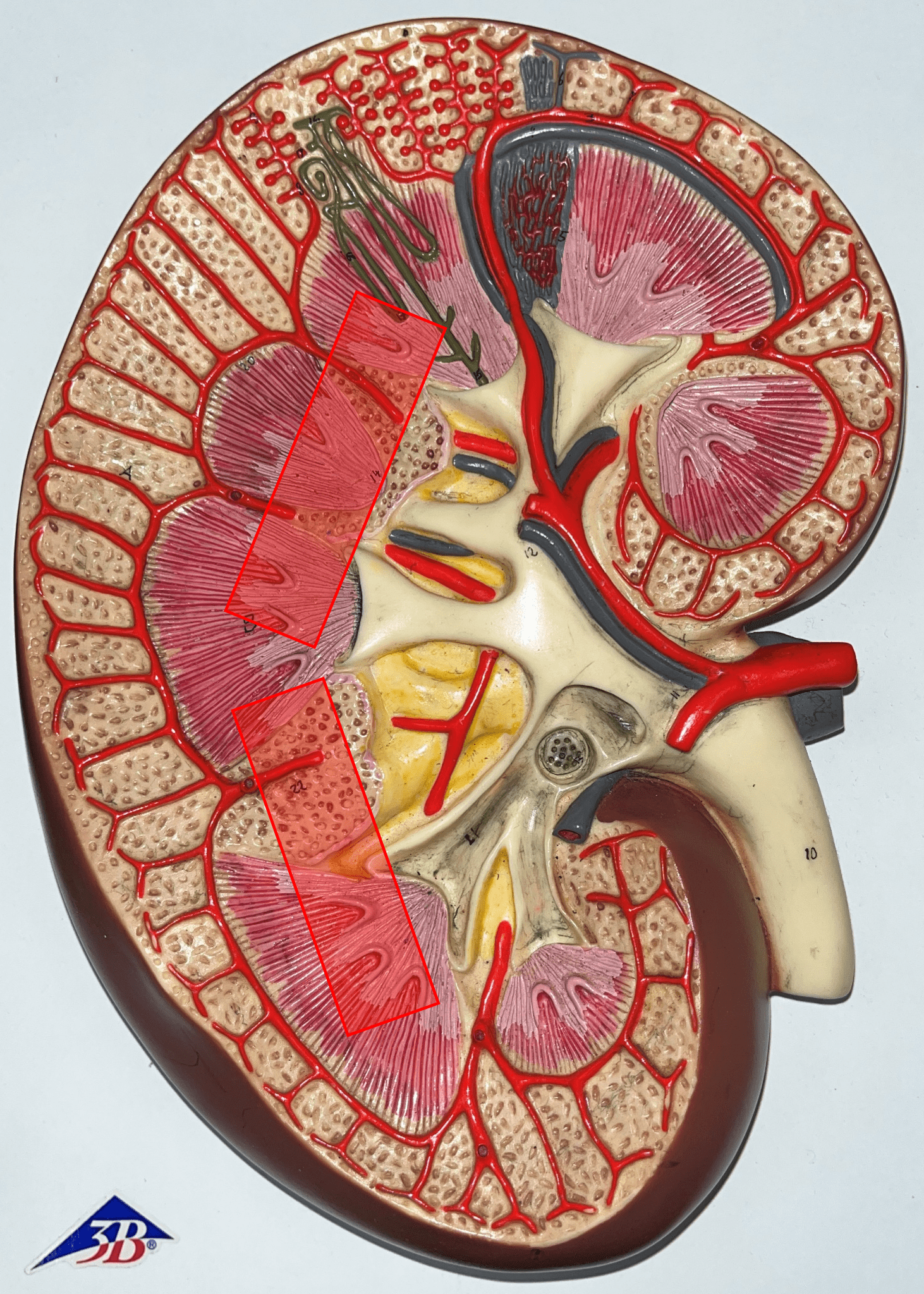
renal medulla
• The middlemost region of the internal kidney.
• Deep to the renal cortex and superficial to the renal pelvis.
• Contains triangular renal pyramids.
• Appears striated due to the presence of tubules and ducts.
• Deep to the renal cortex and superficial to the renal pelvis.
• Contains triangular renal pyramids.
• Appears striated due to the presence of tubules and ducts.
6
New cards
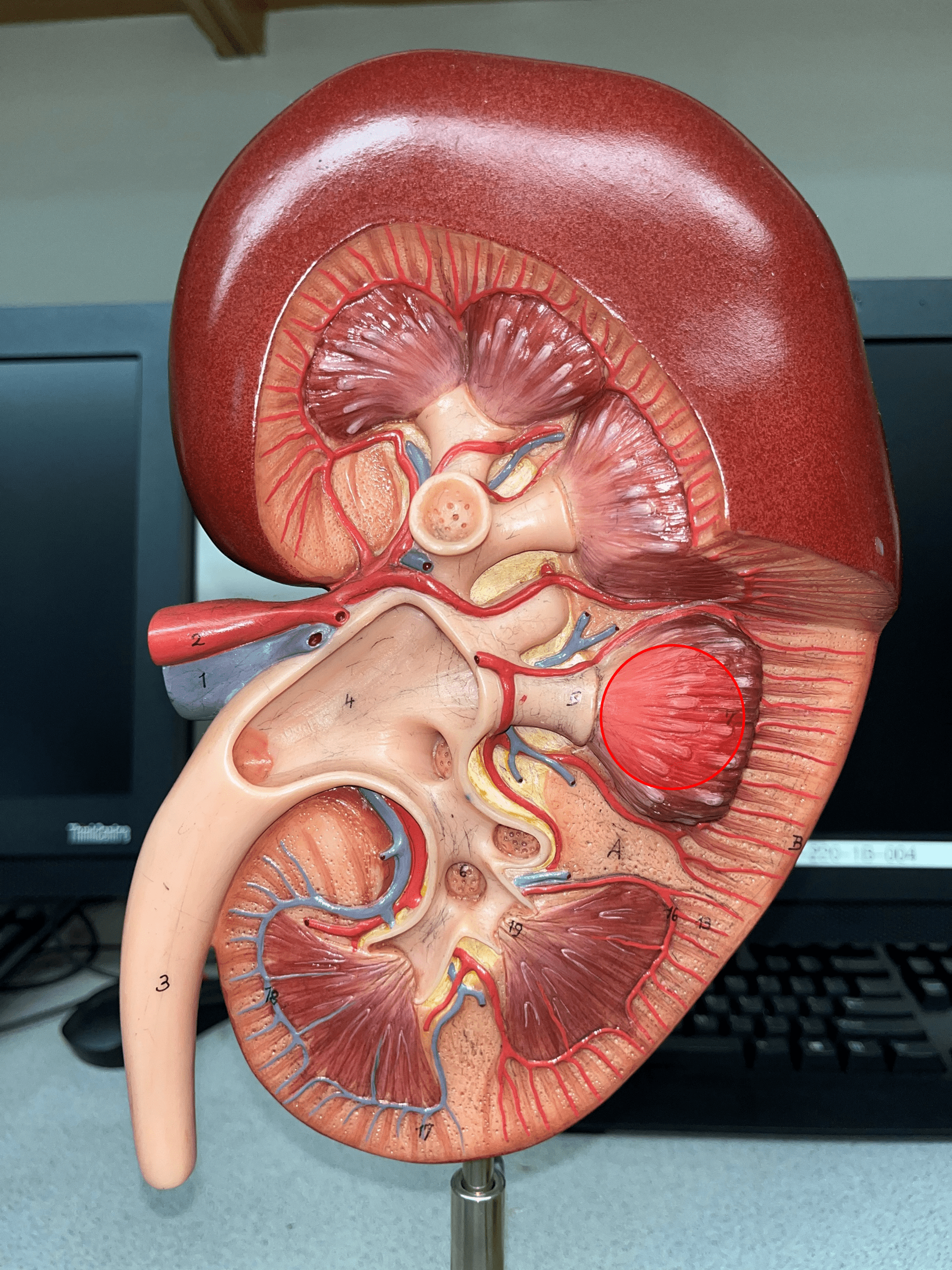
renal pyramid
• A triangular structure found in the renal medulla.
• The base faces the renal cortex.
• The renal papilla (apex) faces the renal pelvis.
• The base faces the renal cortex.
• The renal papilla (apex) faces the renal pelvis.
7
New cards
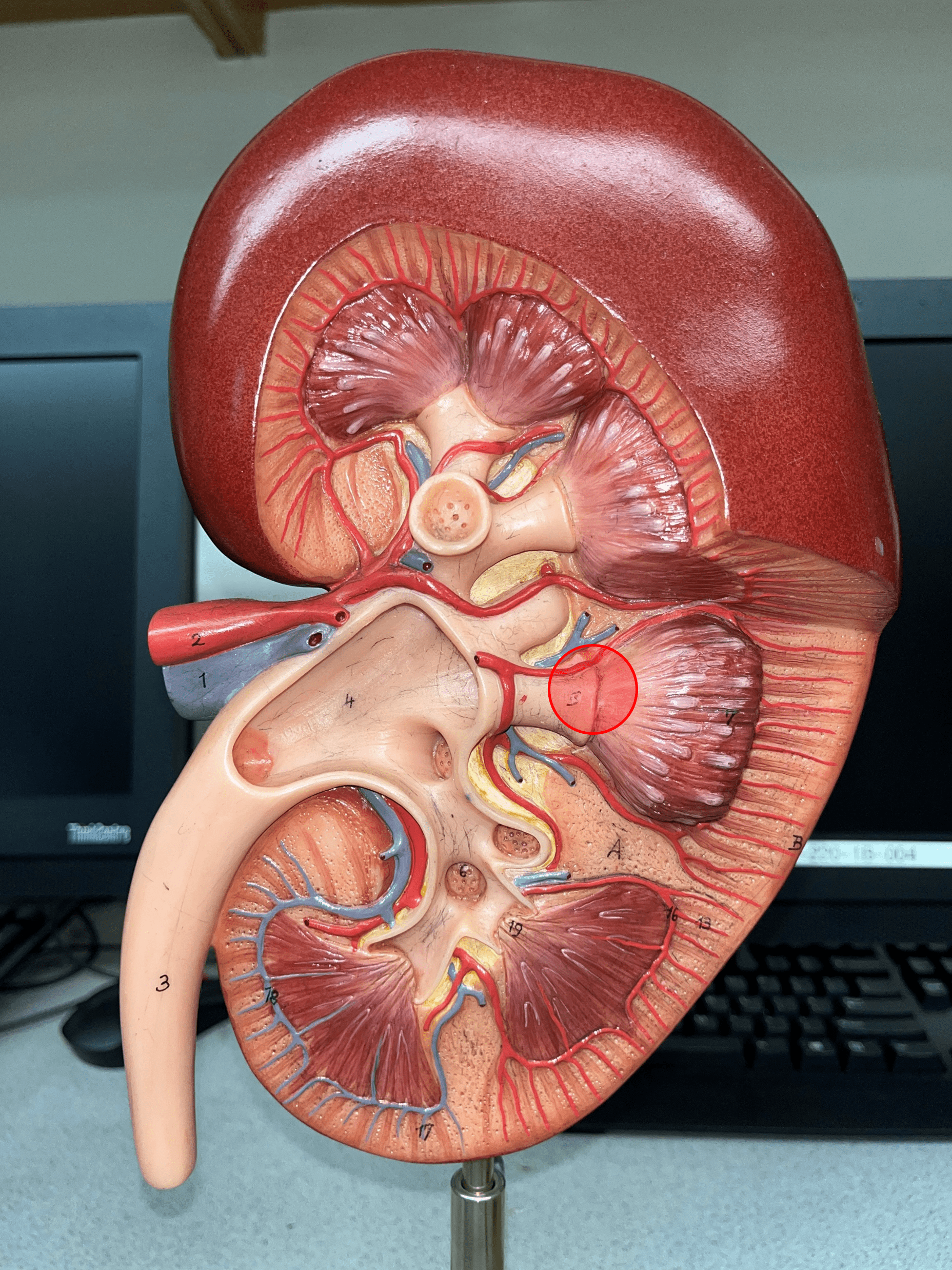
renal papilla
The apex of the renal pyramid facing the renal pelvis.
8
New cards
renal column
An area of granular tissue (similar to the cortex) between renal pyramids.
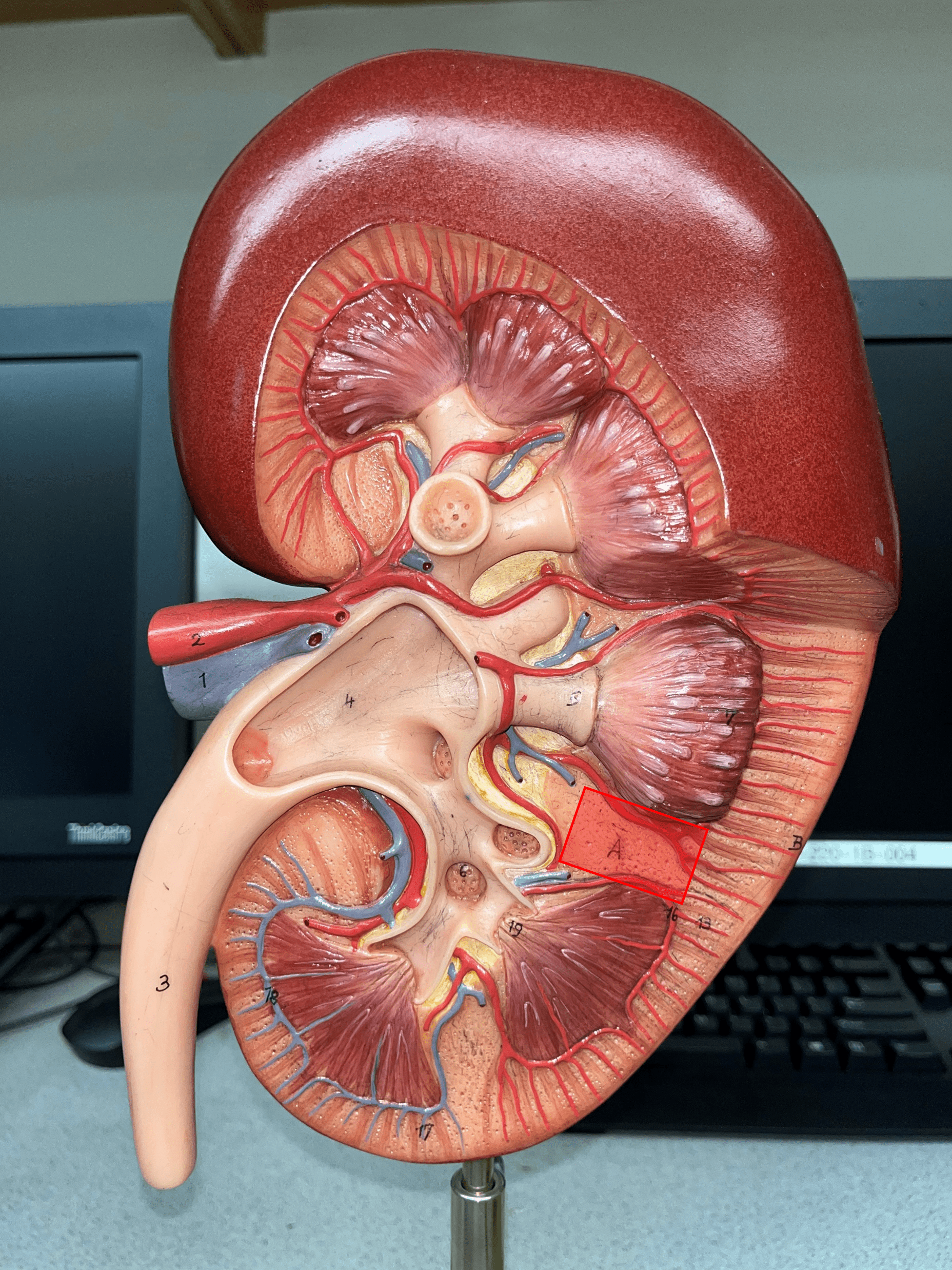
9
New cards
minor calyx
• A cup-like extension that collect urine from the renal papilla.
• Converges with others to form a larger major calyx.
• Converges with others to form a larger major calyx.
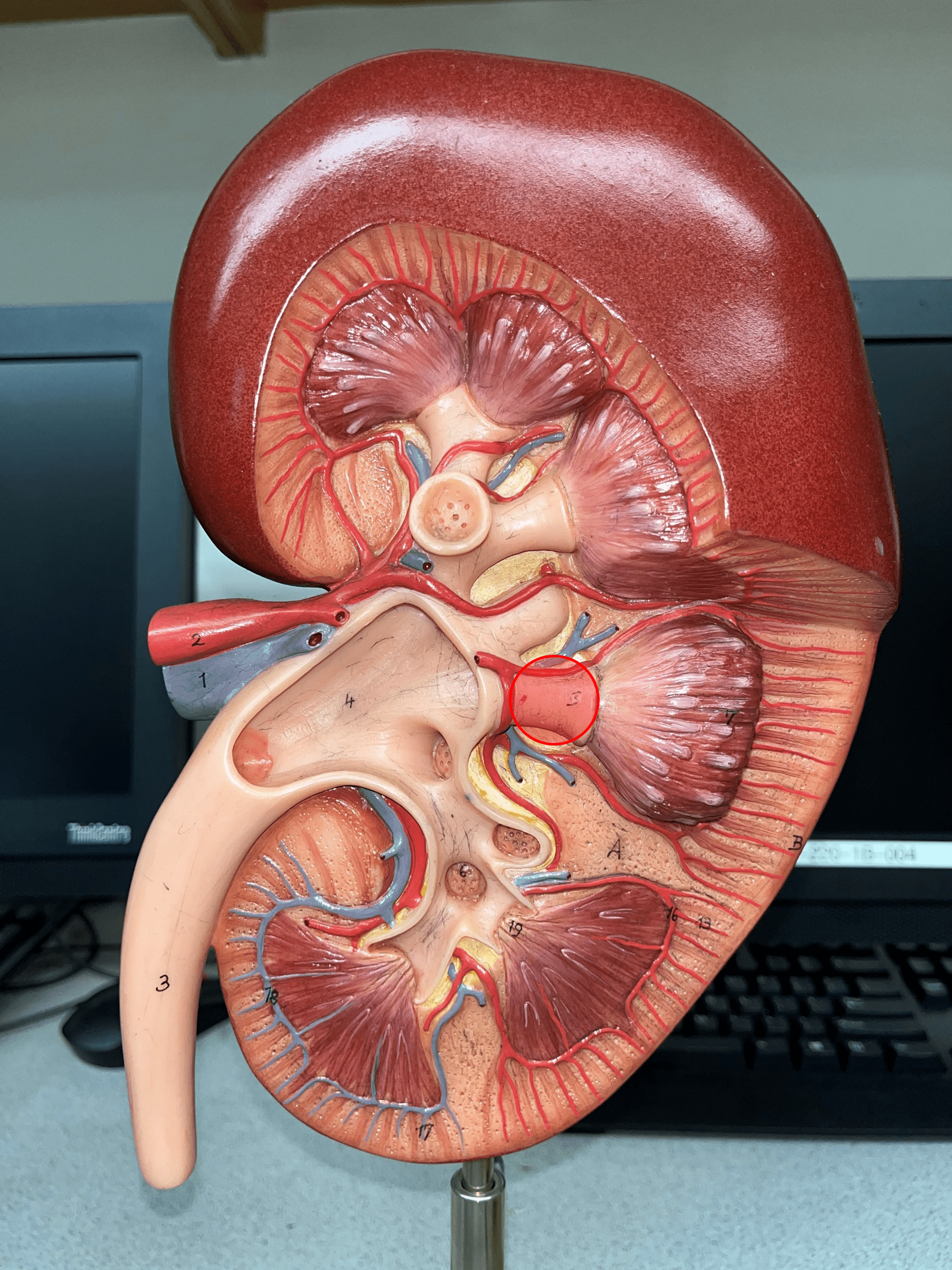
10
New cards
major calyx
• The convergence of several minor calyces.
• Drains into the renal pelvis.
• Drains into the renal pelvis.
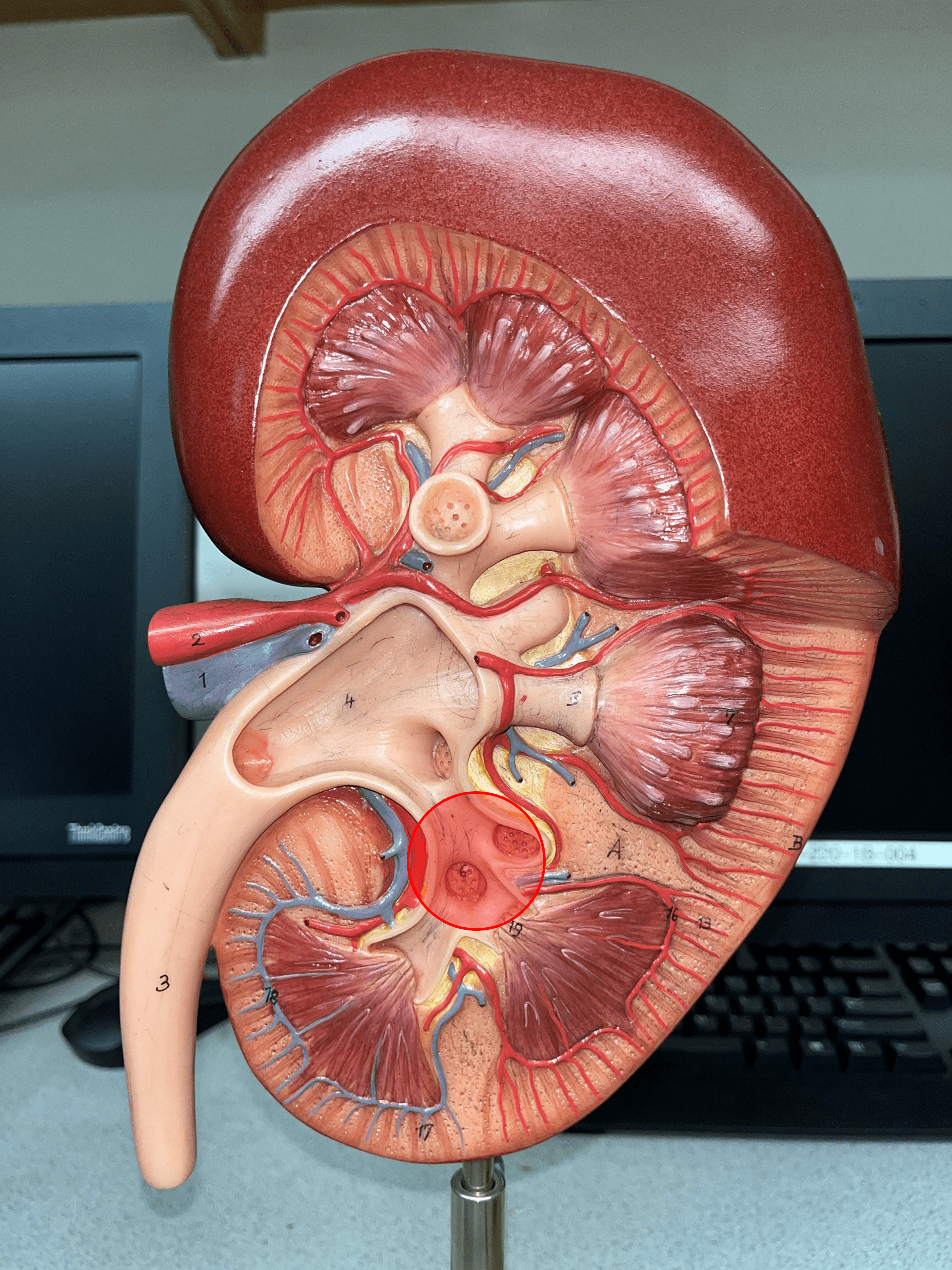
11
New cards
renal pelvis
• The innermost region of the internal kidney.
• Collects urine from the major calyces and drains it into the ureters.
• Includes the minor and major calyces.
• Collects urine from the major calyces and drains it into the ureters.
• Includes the minor and major calyces.
12
New cards
renal artery
• The largest a. of the kidney.
• Supplies the entire kidney.
• Branches into smaller segmental aa.
• Supplies the entire kidney.
• Branches into smaller segmental aa.
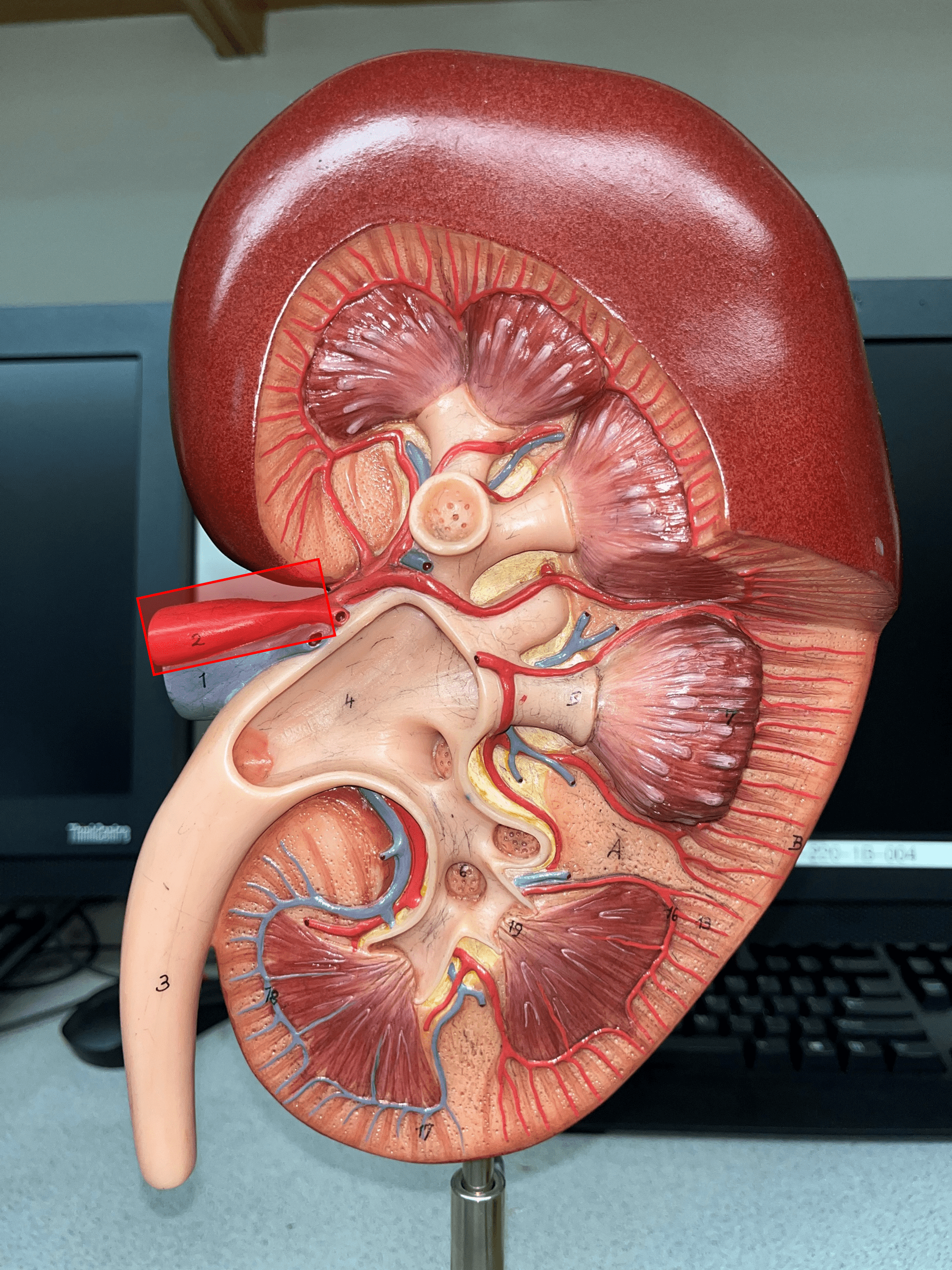
13
New cards
segmental artery
• Branches of the renal a.
• Branches into smaller interlobar aa.
• Branches into smaller interlobar aa.
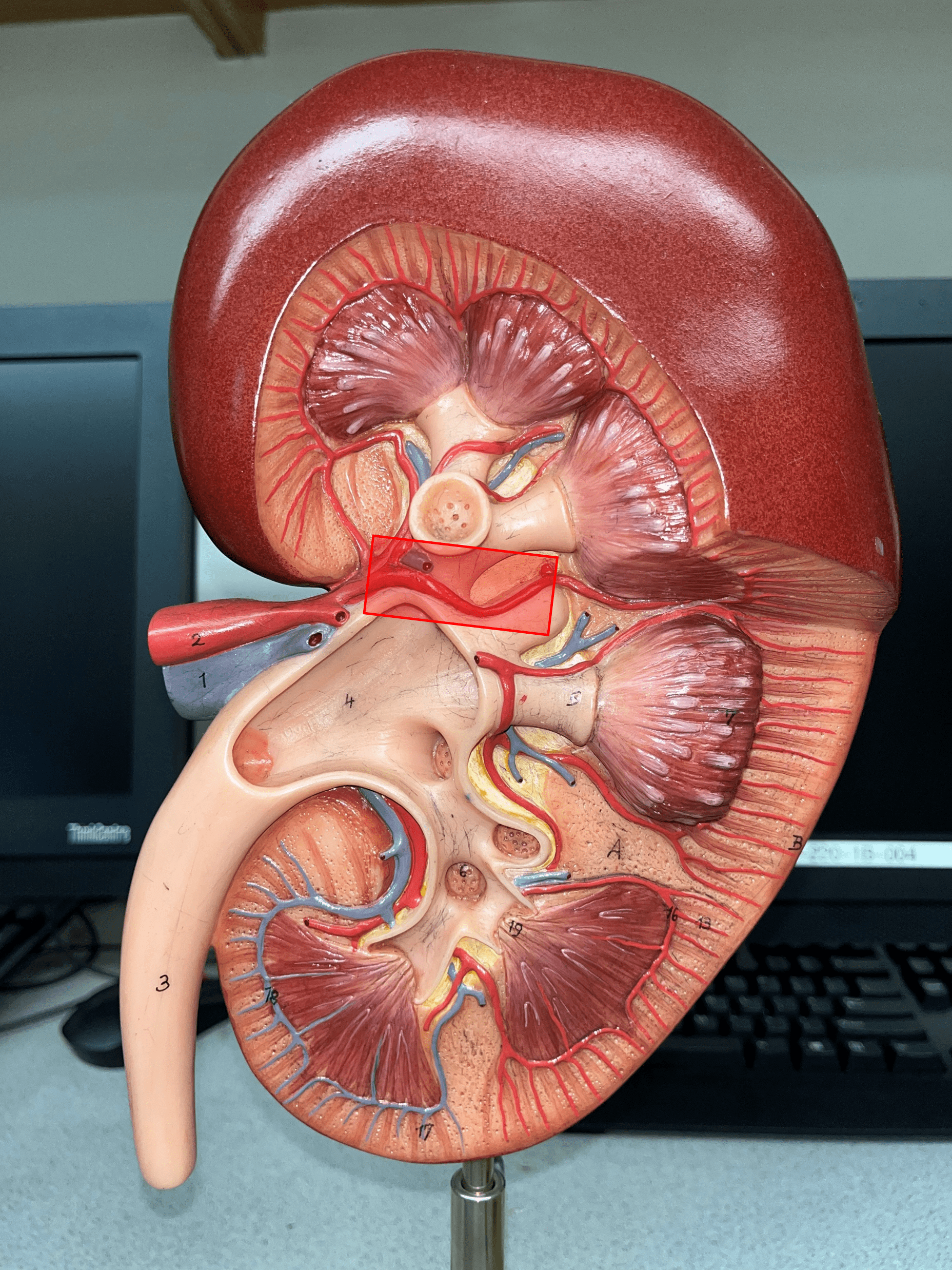
14
New cards
interlobar artery
• Extends between the renal pyramids.
• Branches of a segmental a.
• Branches into smaller arcuate aa.
• Branches of a segmental a.
• Branches into smaller arcuate aa.
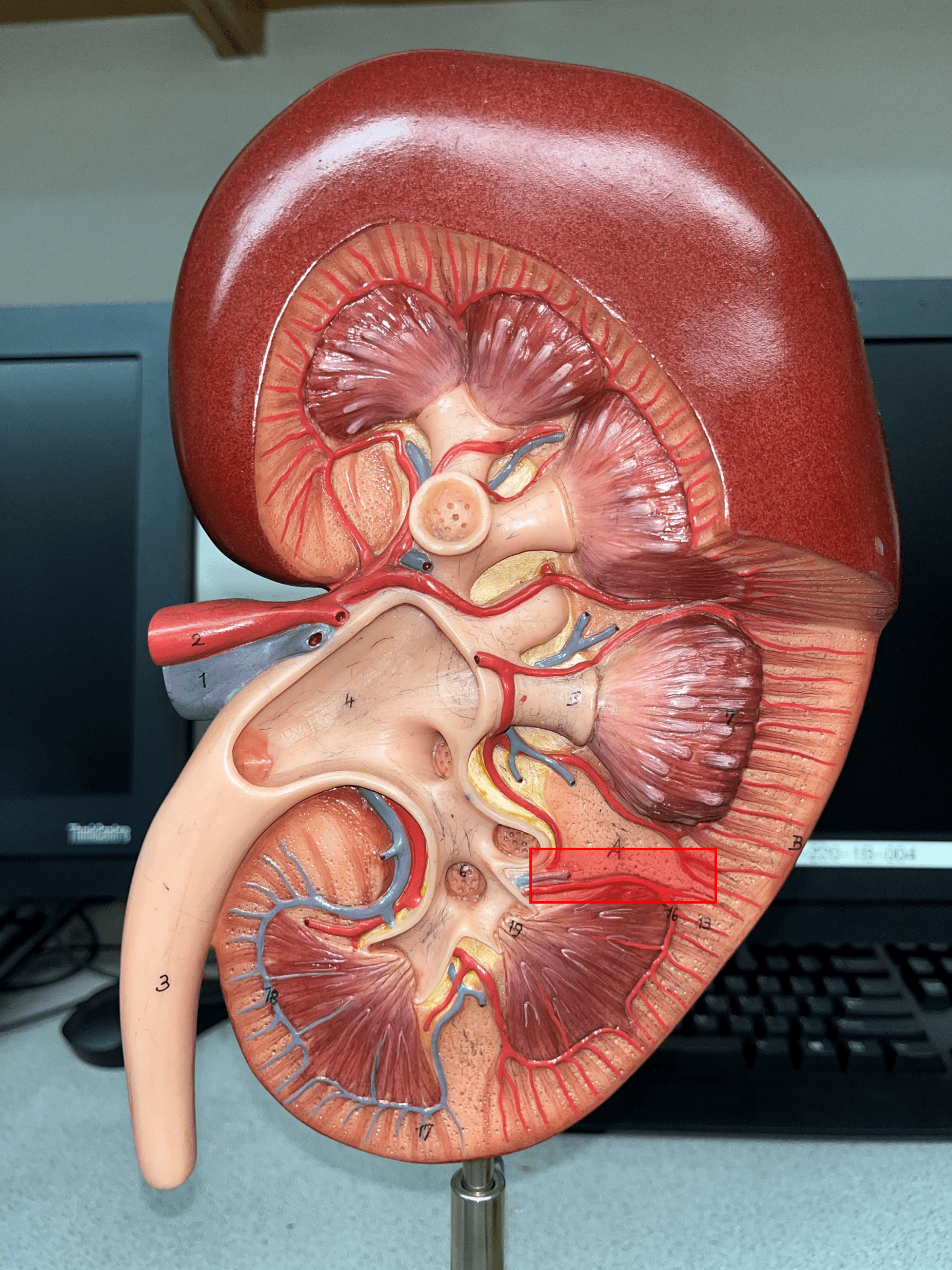
15
New cards
arcuate artery
• Extends along the base of the renal pyramids.
• Branches of an interlobar a.
• Branches into smaller interlobular aa.
• Branches of an interlobar a.
• Branches into smaller interlobular aa.
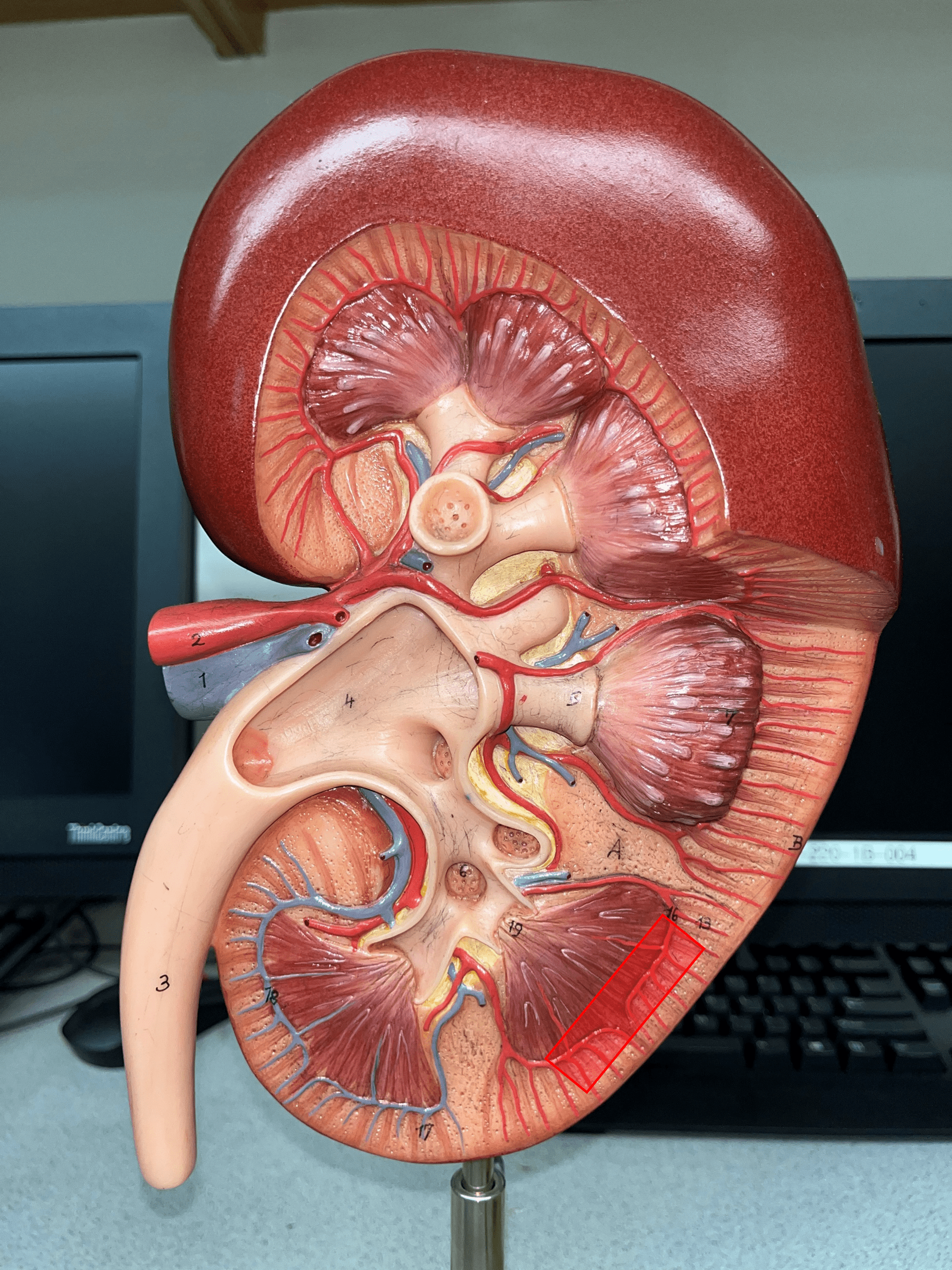
16
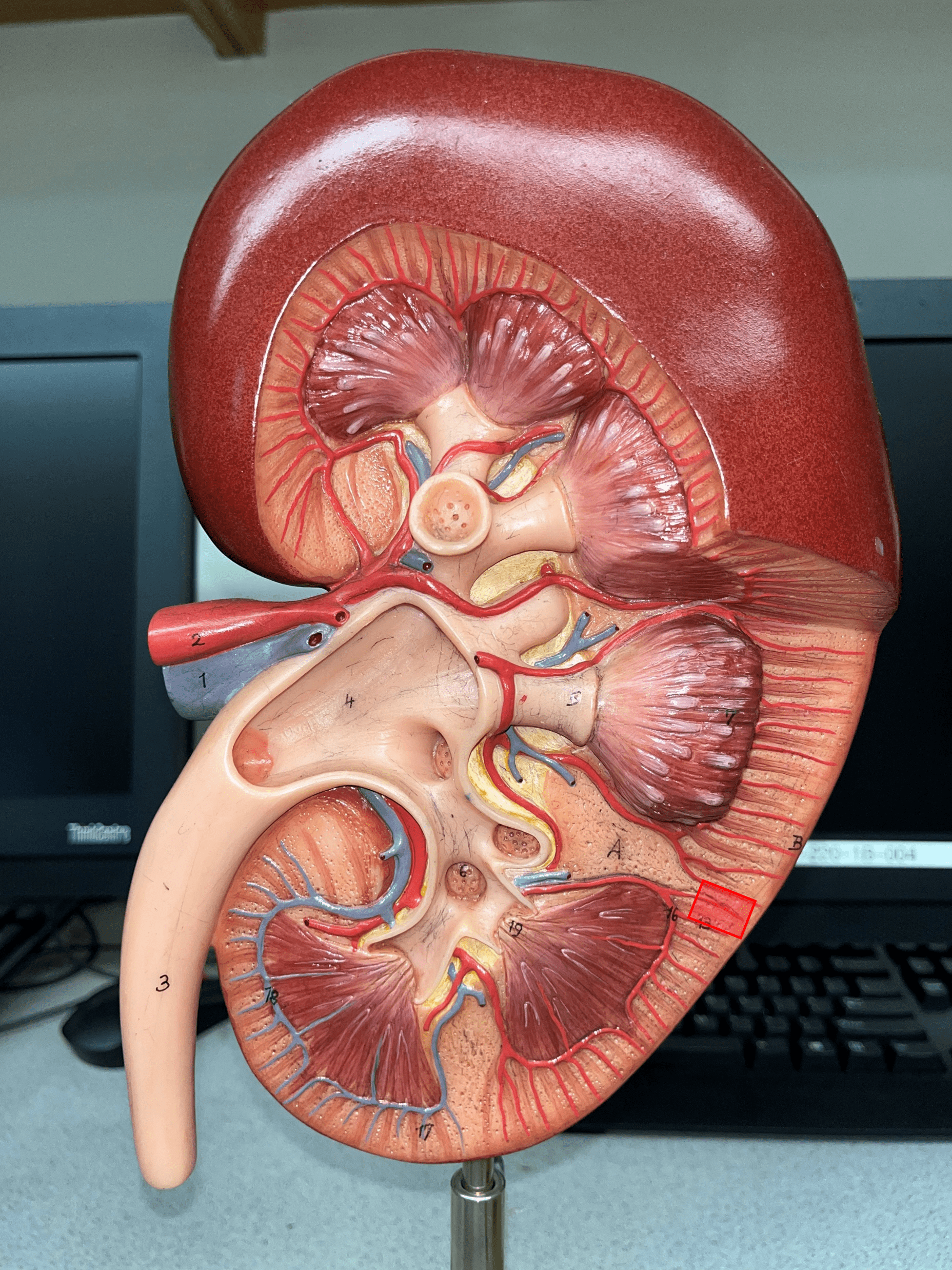
New cards
interlobular artery
• Extends through the renal cortex.
• Branches of an arcuate a.
• Branches into an afferent arteriole of a glomerulus.
• Branches of an arcuate a.
• Branches into an afferent arteriole of a glomerulus.
17
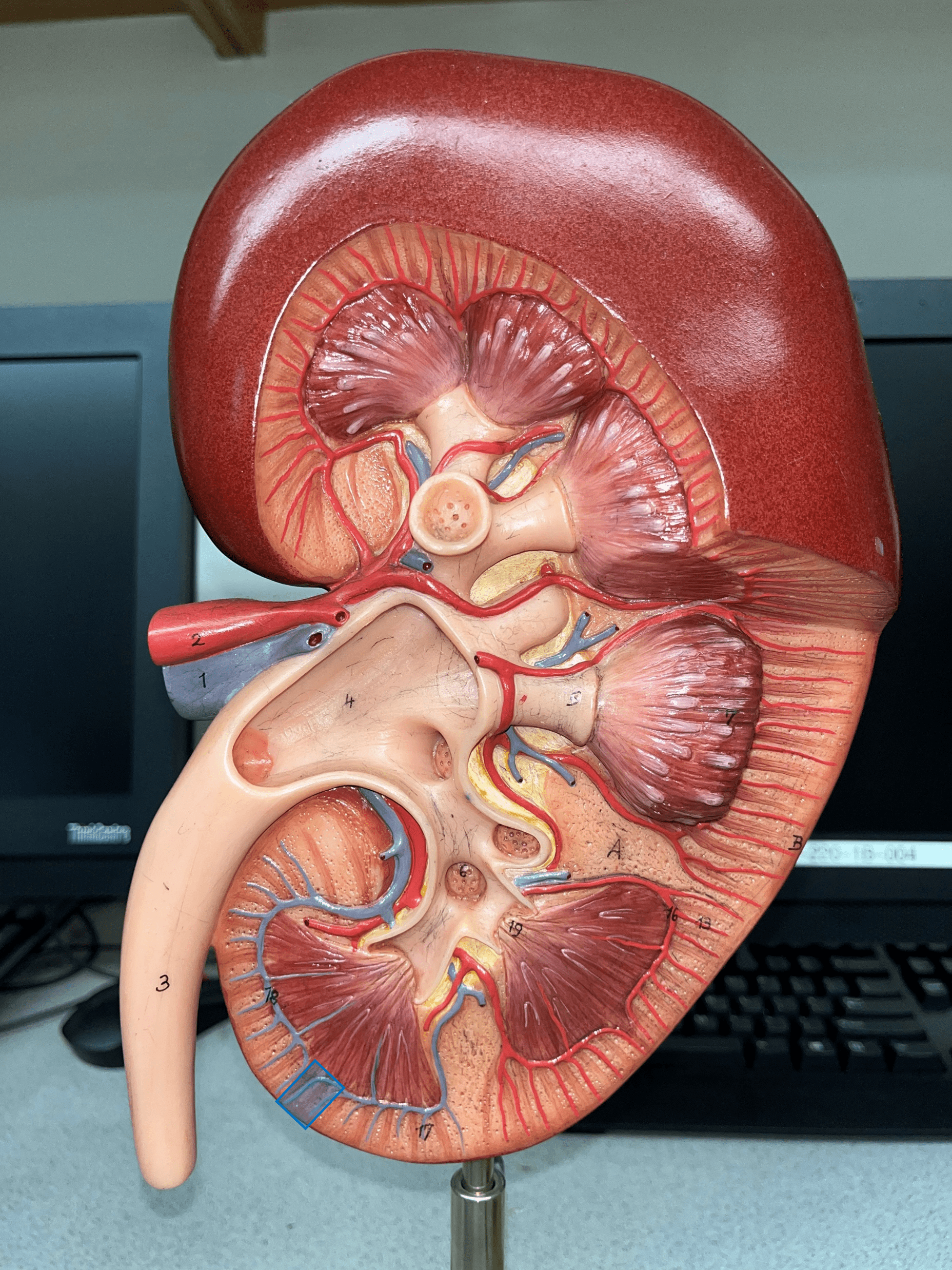
New cards
interlobular vein
• Extends through the renal cortex.
• Converges into an arcuate v.
• Converges into an arcuate v.
18
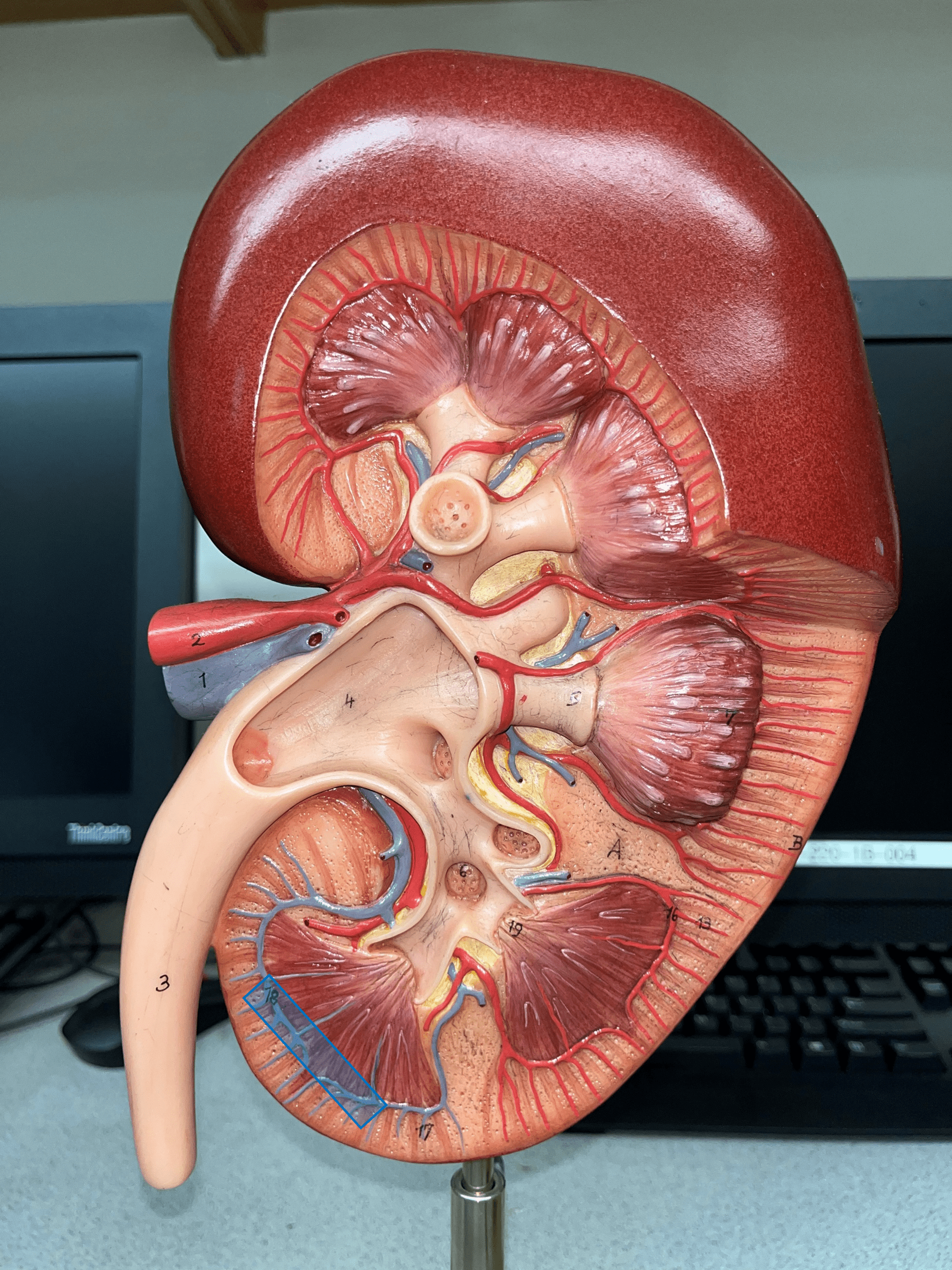
New cards
arcuate vein
• Extends along the base of the renal pyramids.
• The convergence of interlobular vv.
• Converges into an interlobar v.
• The convergence of interlobular vv.
• Converges into an interlobar v.
19
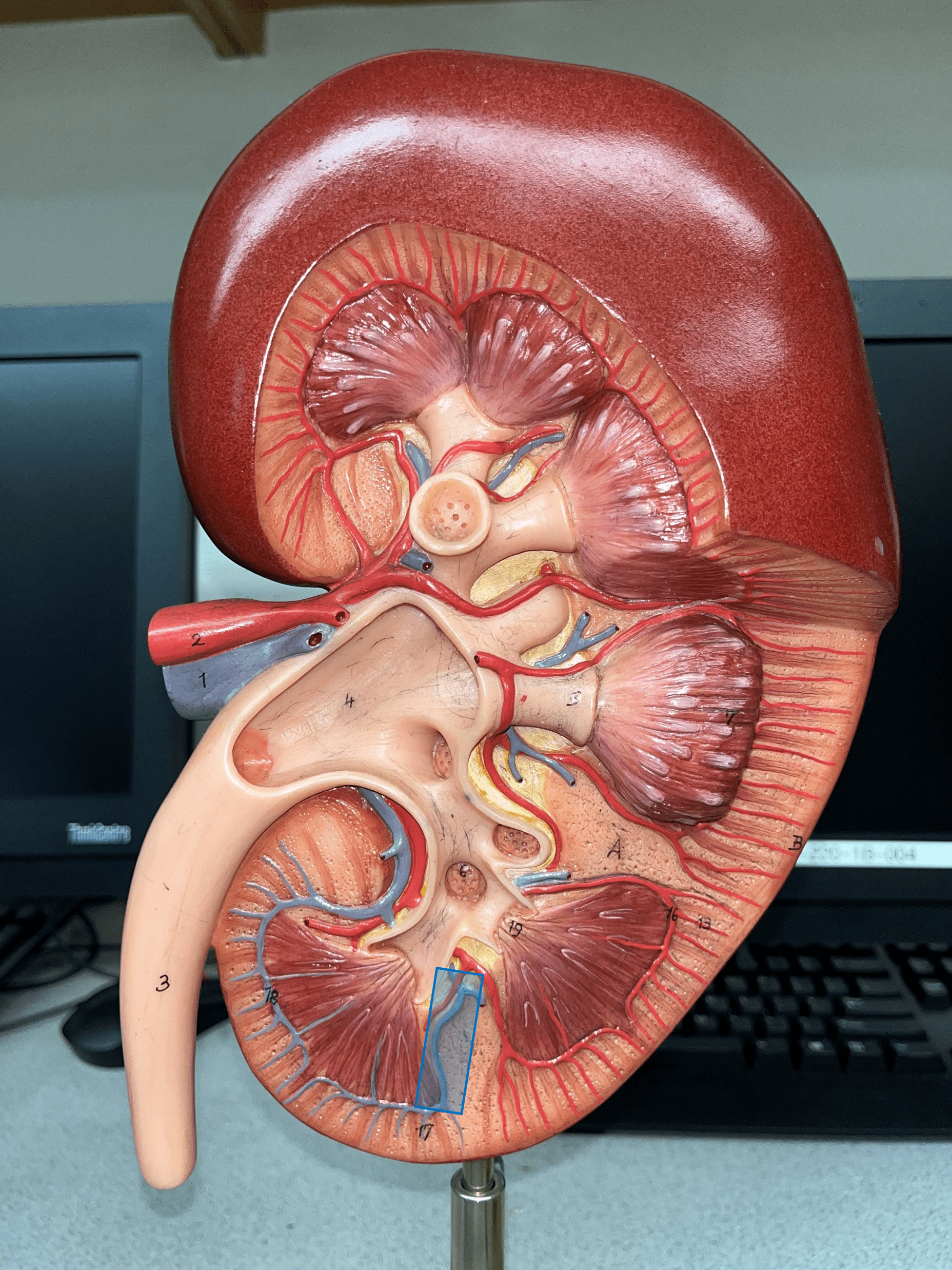
New cards
interlobar vein
• Extends between the renal pyramids.
• The convergence of arcuate vv.
• Converges into the renal vein.
• The convergence of arcuate vv.
• Converges into the renal vein.
20
New cards
renal vein
• The largest vein of the kidney.
• Drains blood from the entire kidney.
• The convergence of interlobar vv.
• Drains blood from the entire kidney.
• The convergence of interlobar vv.
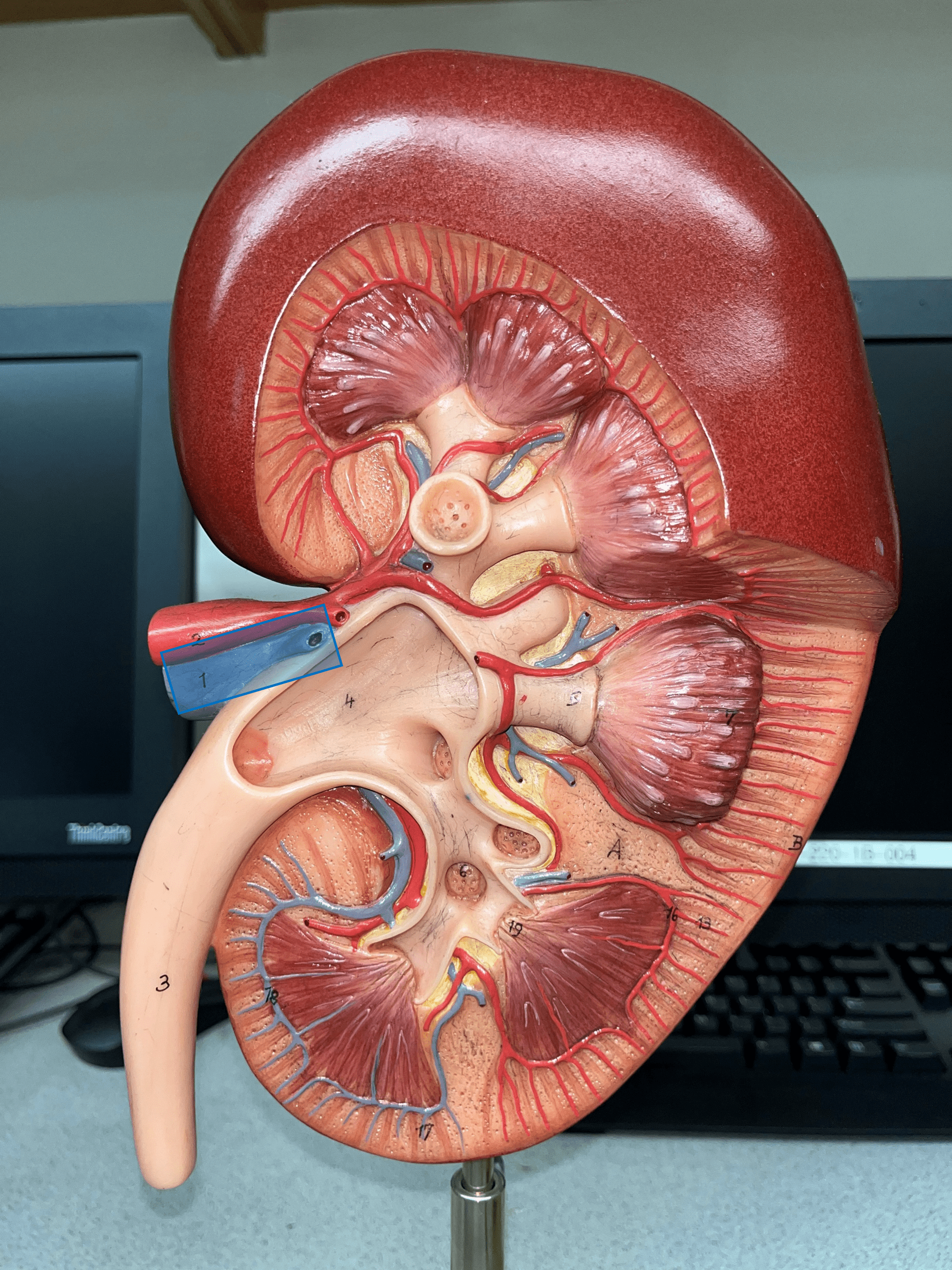
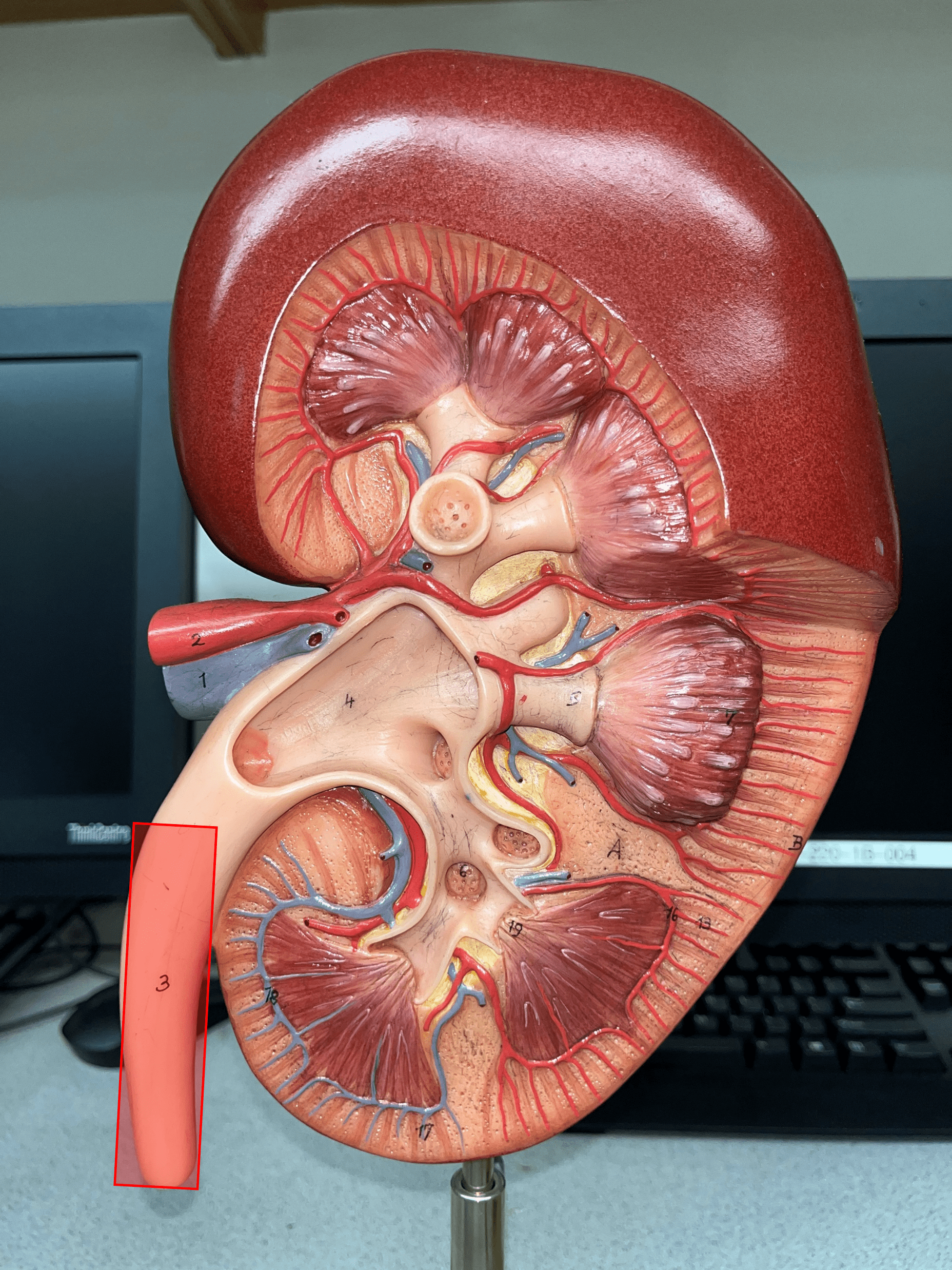
21
New cards
ureter
• A narrow tube channeling urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
• Composed of an outer adventitia, middle muscularis, and inner mucosa.
• Composed of an outer adventitia, middle muscularis, and inner mucosa.
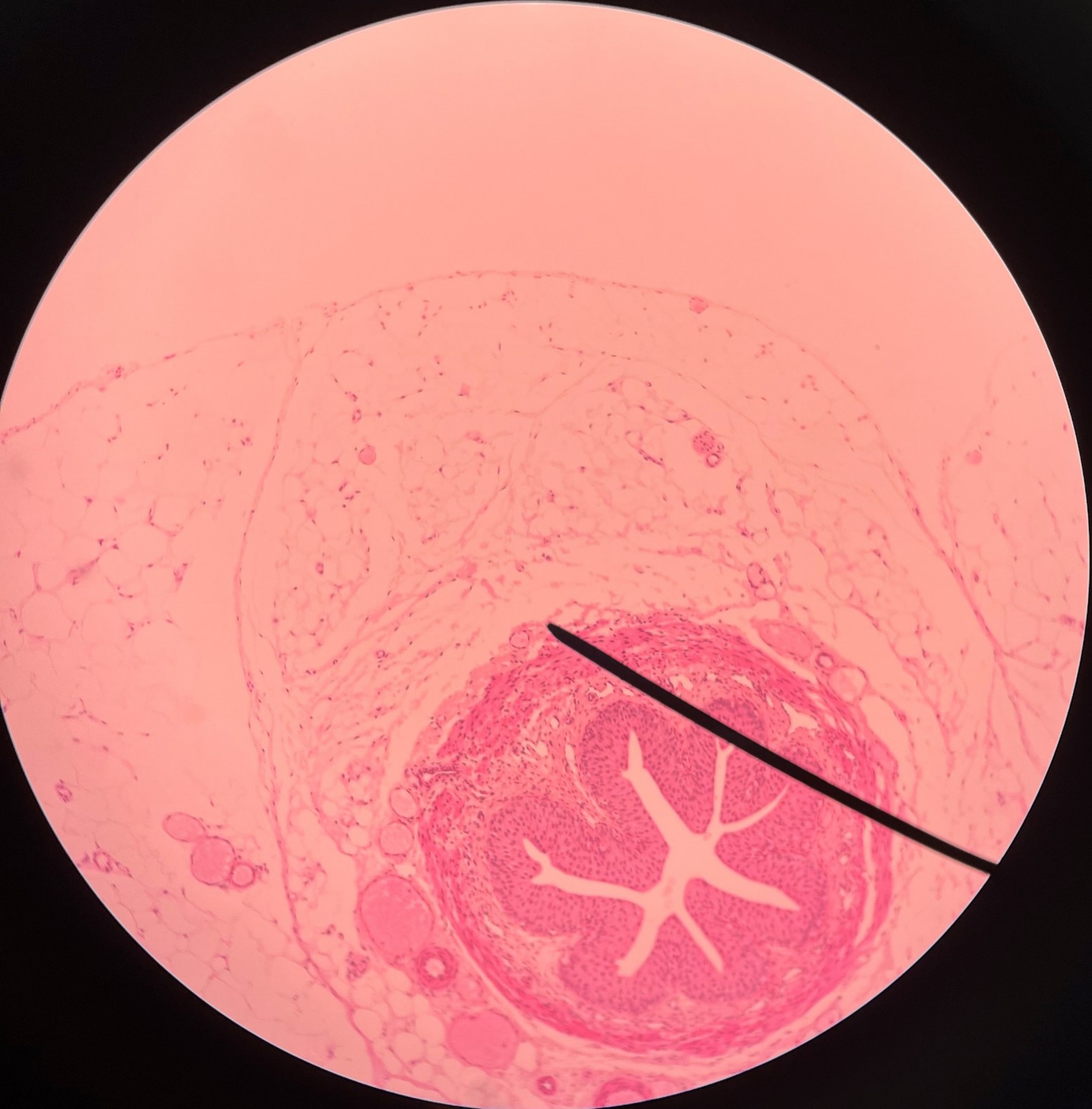
22
New cards
adventitia
• Slide histology of the ureter.
• The outermost layer of the ureter.
• Composed of connective tissue.
• Superficial to the circular layer of the muscularis.
• The outermost layer of the ureter.
• Composed of connective tissue.
• Superficial to the circular layer of the muscularis.
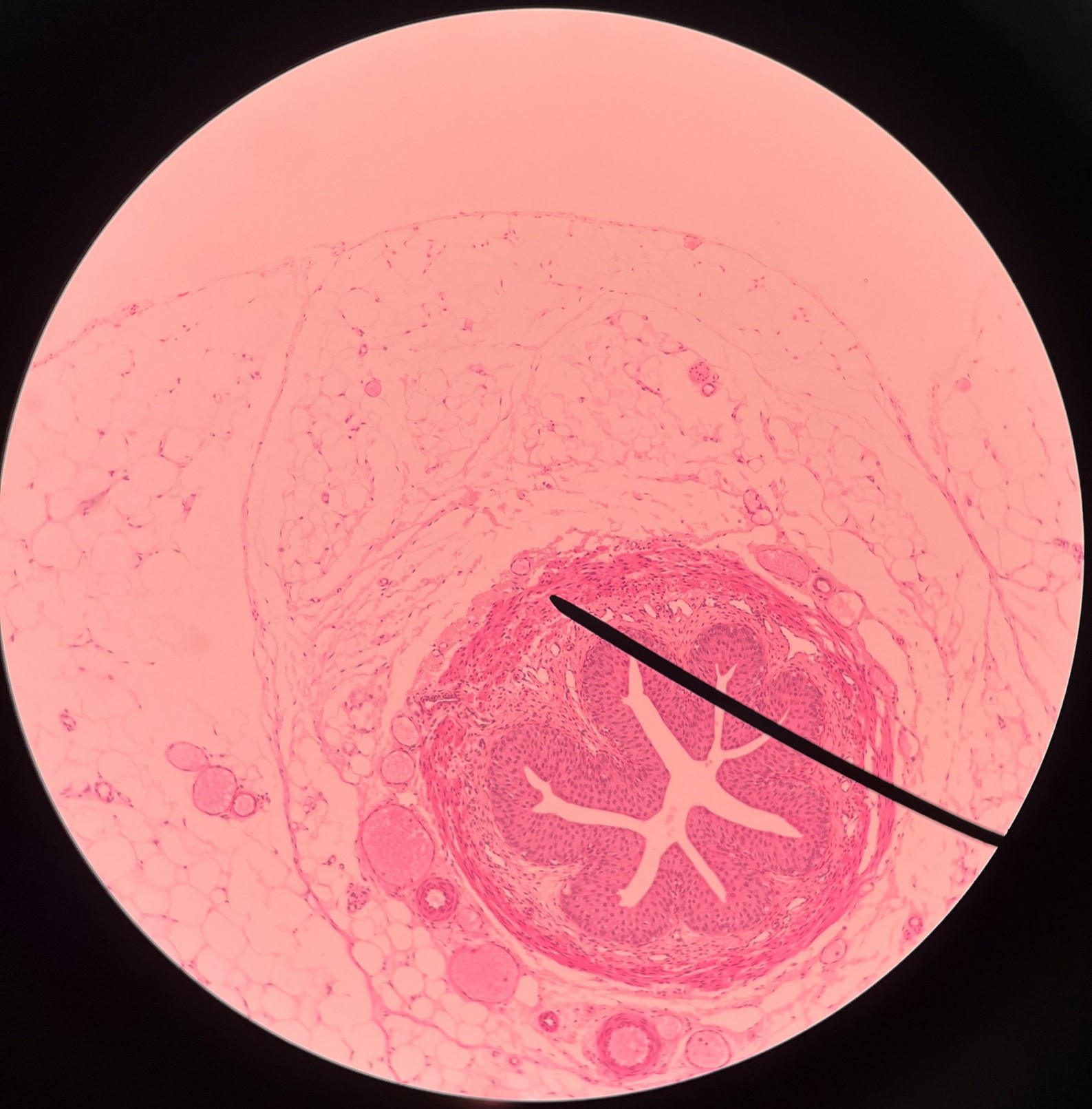
23
New cards
circular layer of muscularis
• Slide histology of the ureter.
• A smooth muscle layer of the ureter.
• Superficial to the longitudinal layer of the muscularis and deep to the adventitia.
• A smooth muscle layer of the ureter.
• Superficial to the longitudinal layer of the muscularis and deep to the adventitia.
24
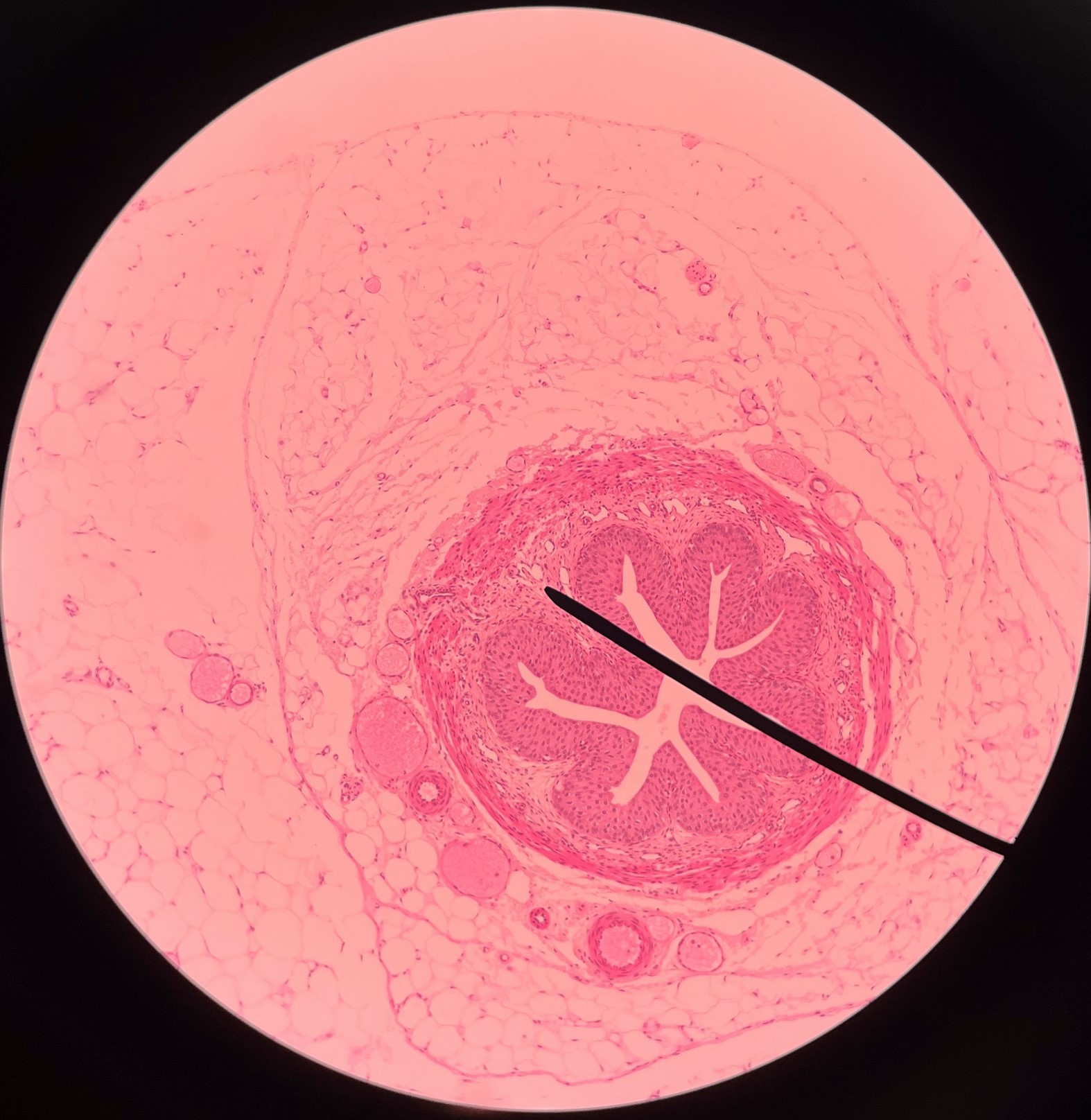
New cards
longitudinal layer of muscularis
• Slide histology of the ureter.
• A smooth muscle layer of the ureter.
• Superficial to the mucosa and deep to the circular layer of the muscularis.
• A smooth muscle layer of the ureter.
• Superficial to the mucosa and deep to the circular layer of the muscularis.
25
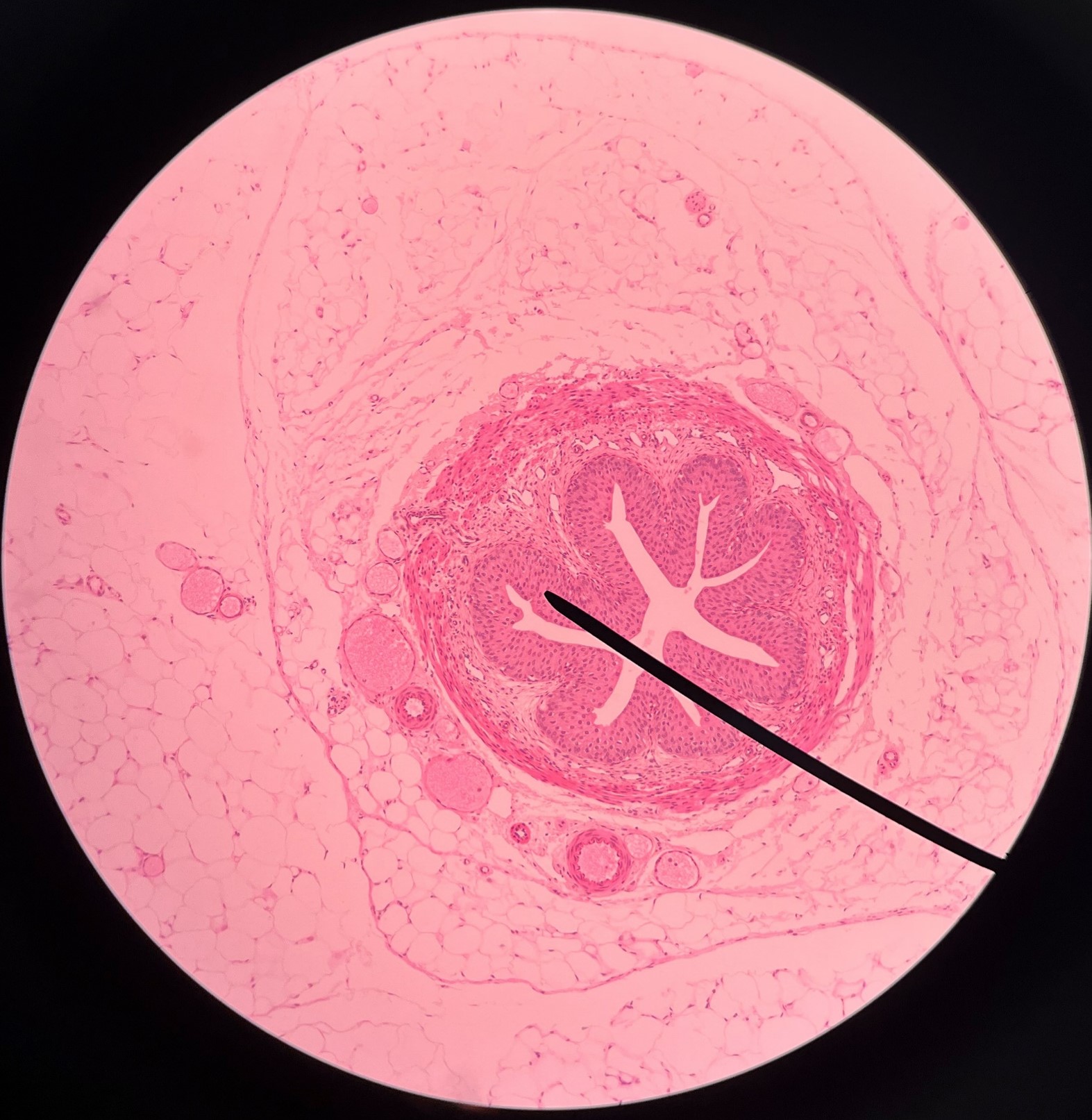
New cards
mucosa
• Slide histology of the ureter.
• The innermost layer of the ureter.
• Composed of urothelium.
• Faces the lumen of the ureter and is deep to the longitudinal layer of the muscularis.
• The innermost layer of the ureter.
• Composed of urothelium.
• Faces the lumen of the ureter and is deep to the longitudinal layer of the muscularis.
26
New cards
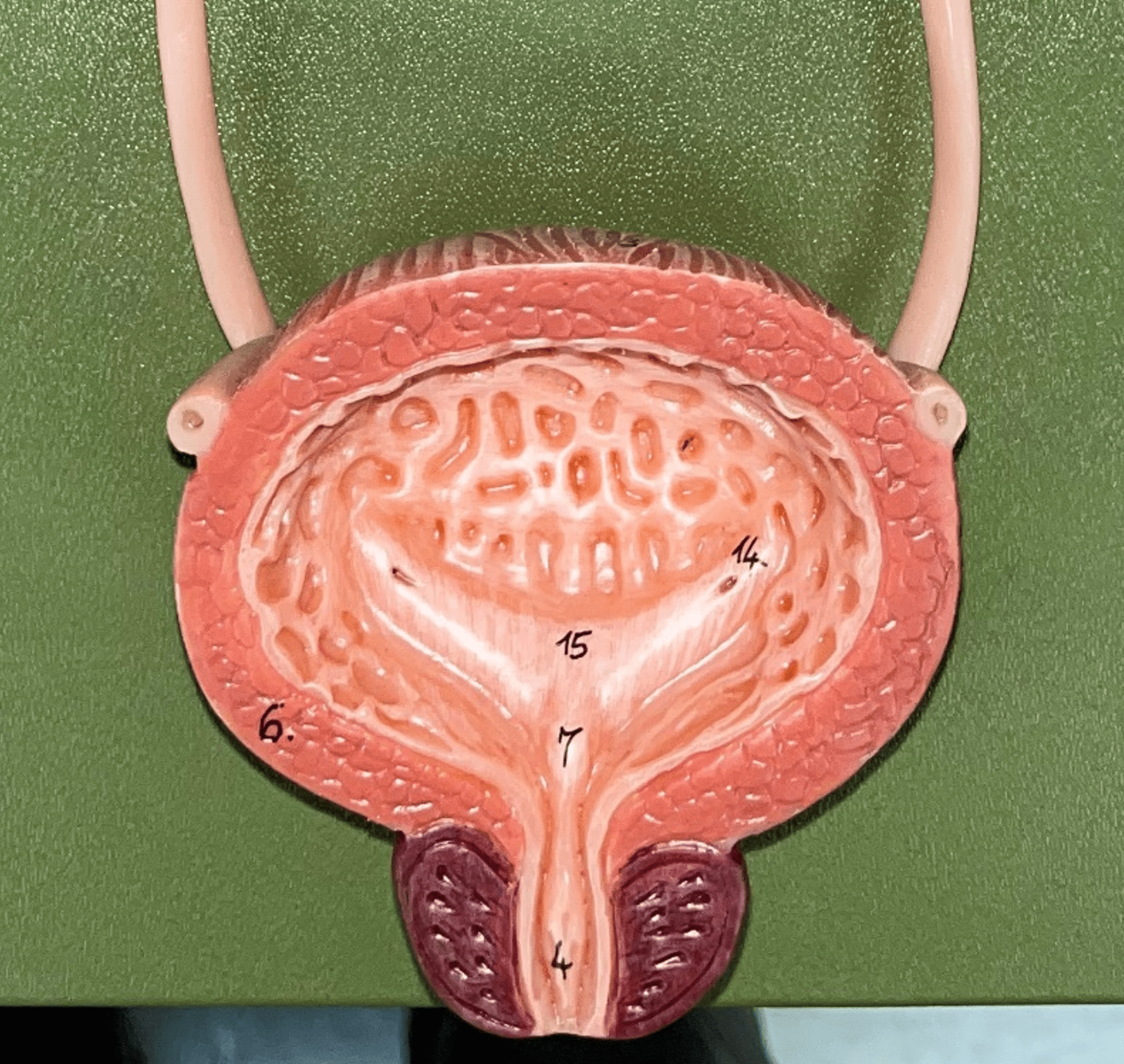
urinary bladder
The hollow sac organ that collects and temporarily stores urine.
27
New cards
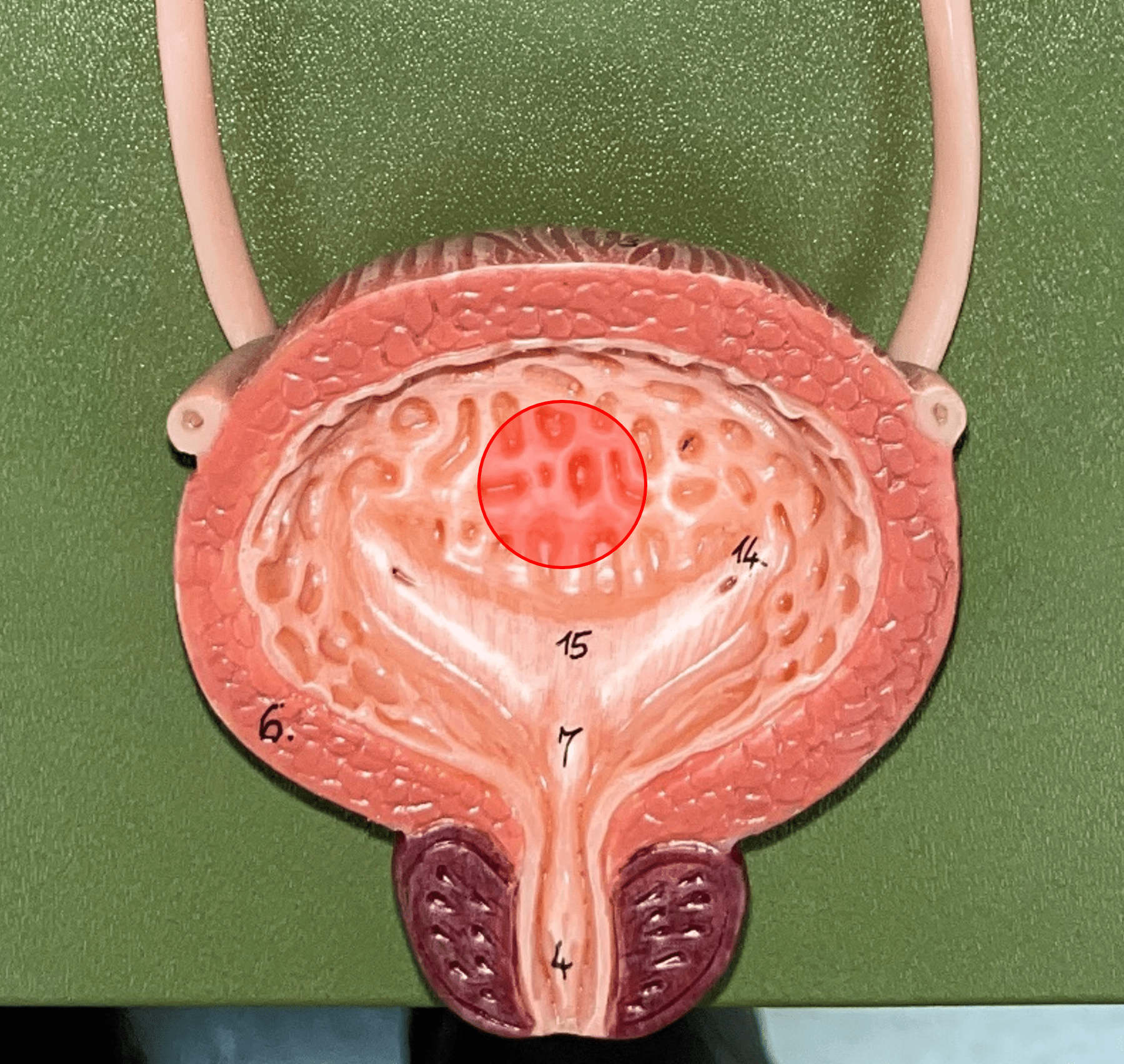
rugae
• Part of the urinary bladder.
• Folds of the mucous membrane of the bladder.
• Flattens as the bladder fills with urine to increase capacity.
• Folds of the mucous membrane of the bladder.
• Flattens as the bladder fills with urine to increase capacity.
28
New cards
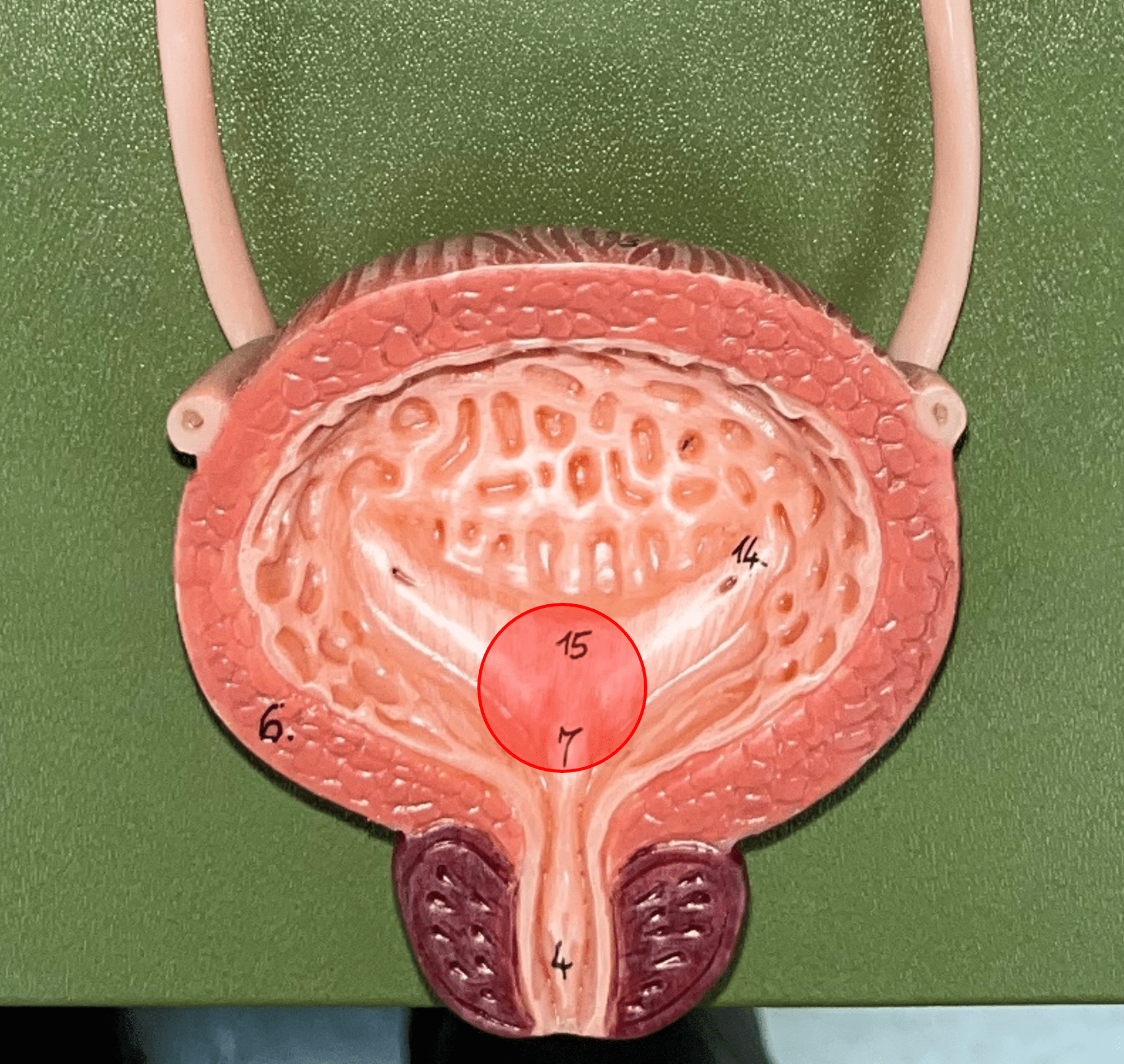
trigone
• Part of the urinary bladder.
• The triangle formed by the ureteral openings and internal urethra orifice.
• The triangle formed by the ureteral openings and internal urethra orifice.
29
New cards
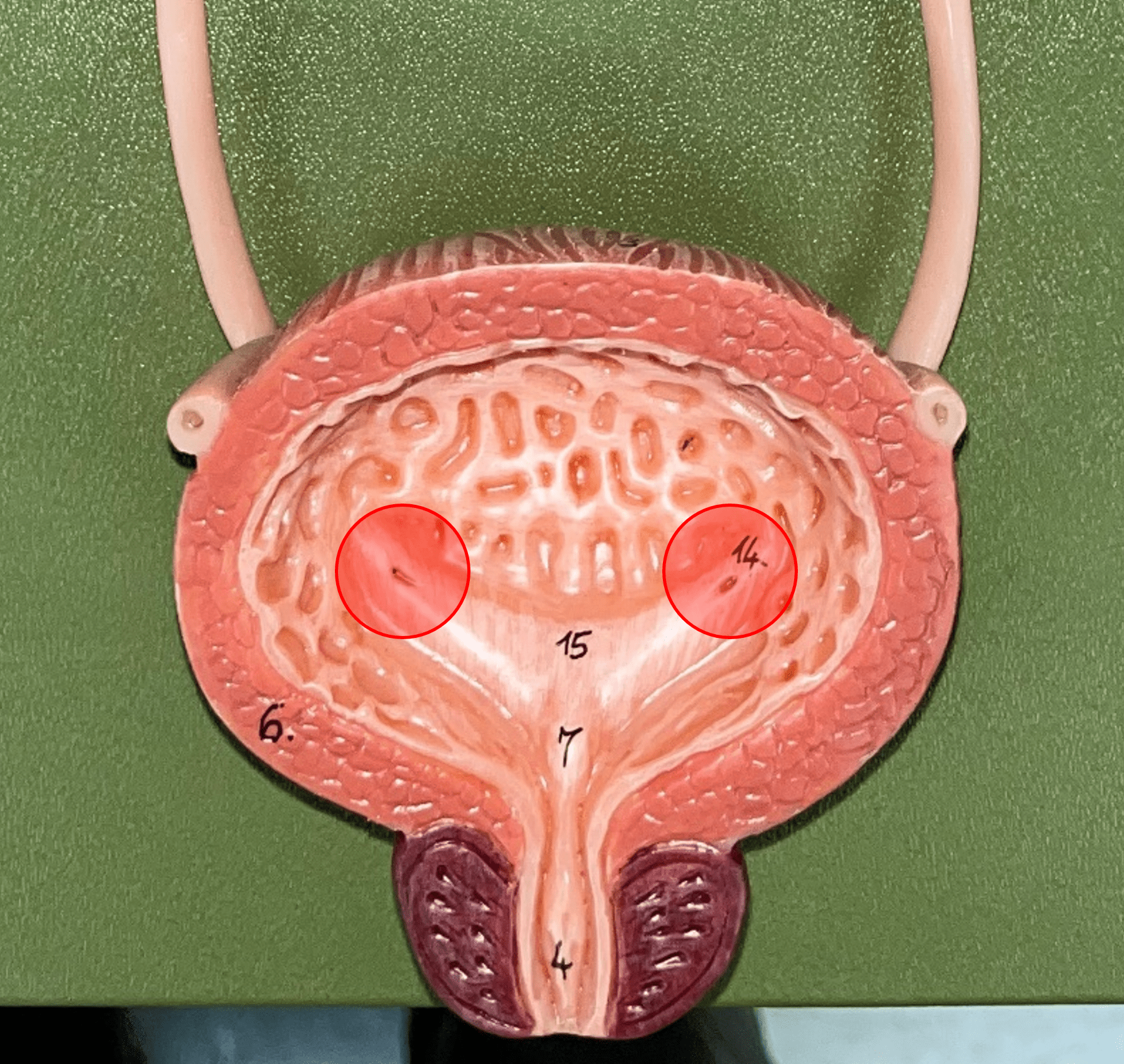
ureteral opening
• Part of the urinary bladder.
• A posterior opening on either side of the of the bladder led in by the ureters.
• A posterior opening on either side of the of the bladder led in by the ureters.
30
New cards
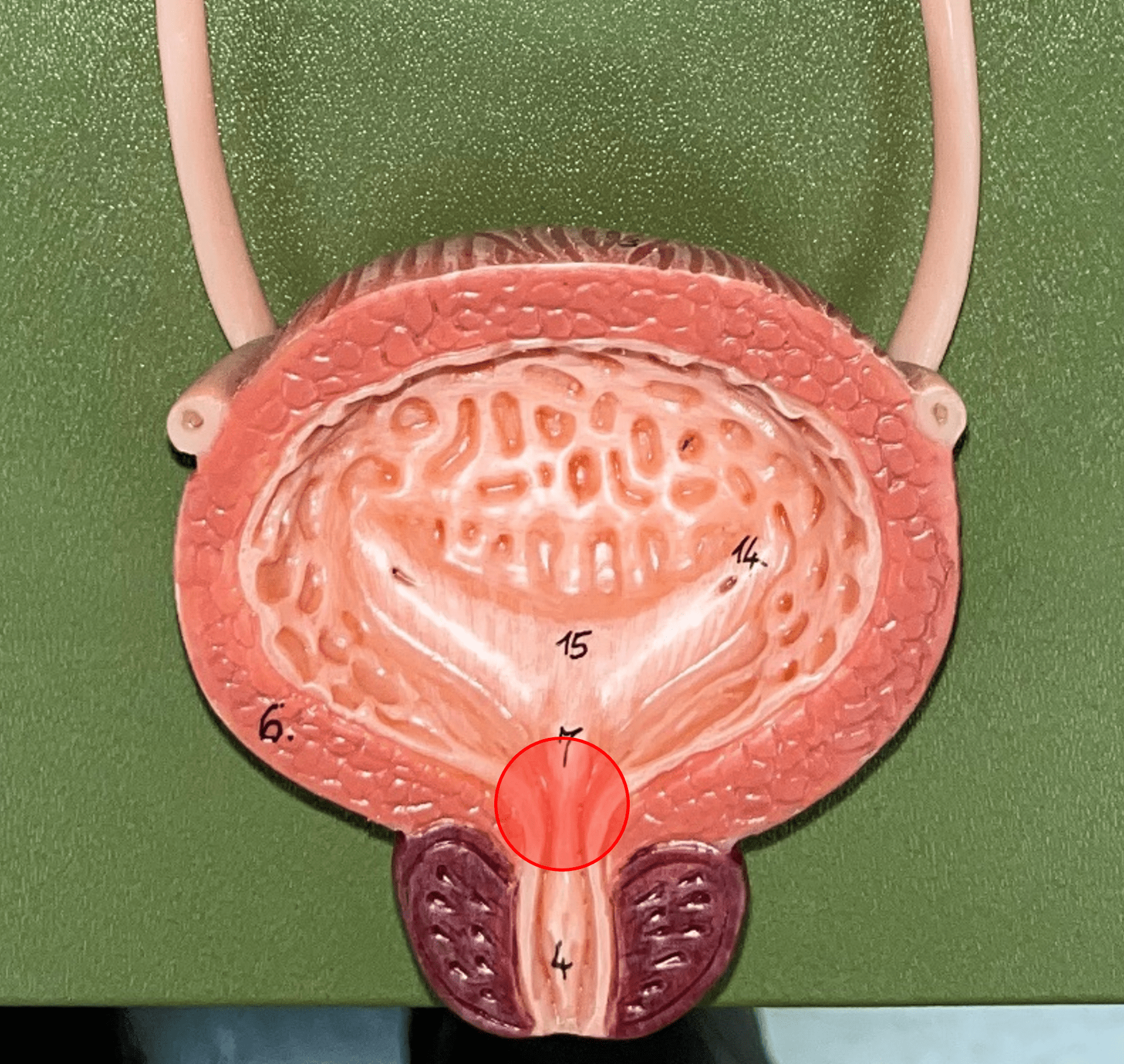
internal urethral orifice
• Part of the urinary bladder.
• The anterior opening of the bladder leading to the urethra.
• The anterior opening of the bladder leading to the urethra.
31
New cards
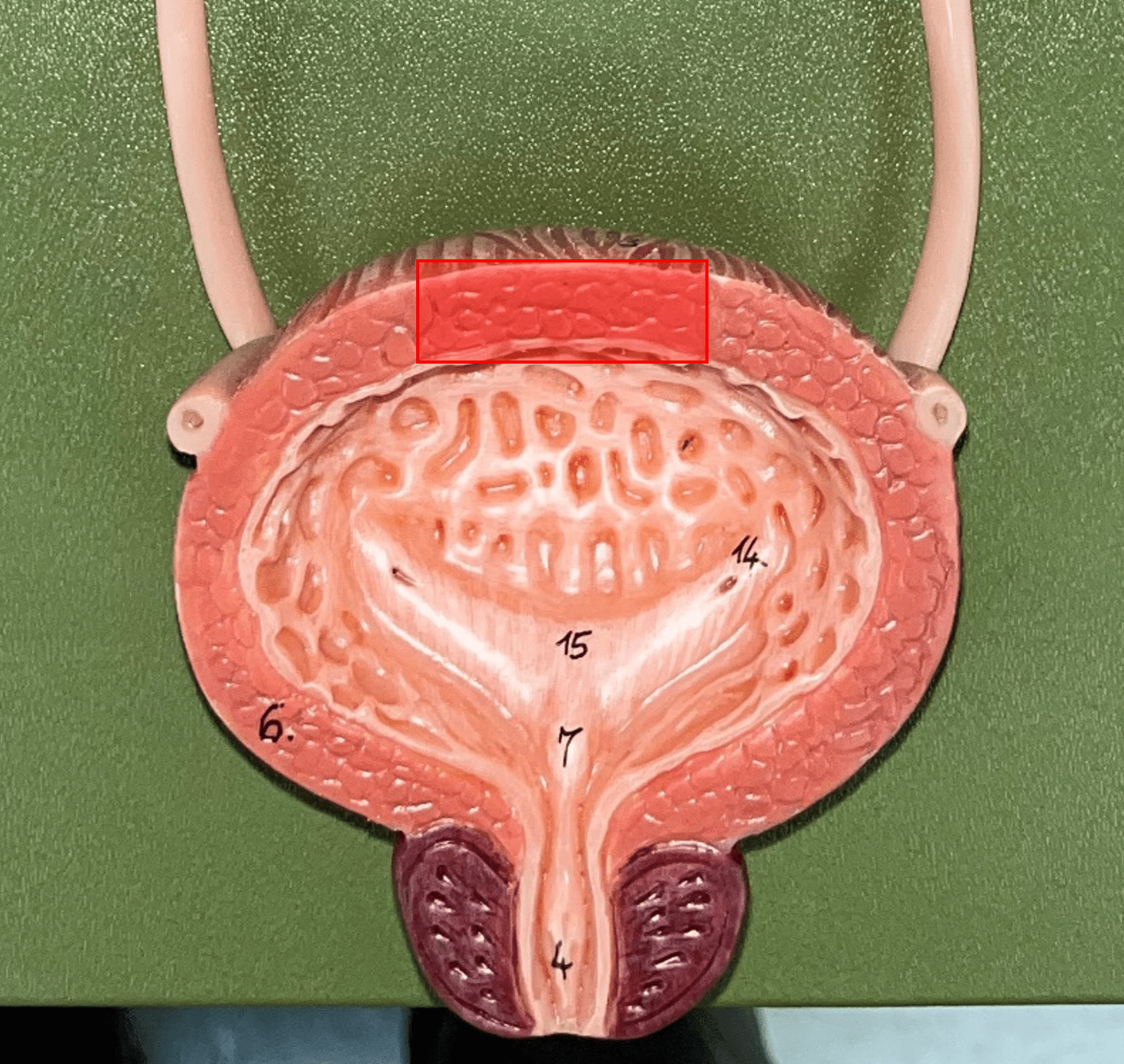
detrusor muscle
• Part of the urinary bladder.
• The muscularis of the bladder.
• Contracts to expel urine from the bladder.
• The muscularis of the bladder.
• Contracts to expel urine from the bladder.
32
New cards
mucosa
• Slide histology of the bladder.
• The innermost layer of the bladder.
• Composed of urothelium.
• Faces the lumen of the bladder and is deep to the submucosa.
• The innermost layer of the bladder.
• Composed of urothelium.
• Faces the lumen of the bladder and is deep to the submucosa.
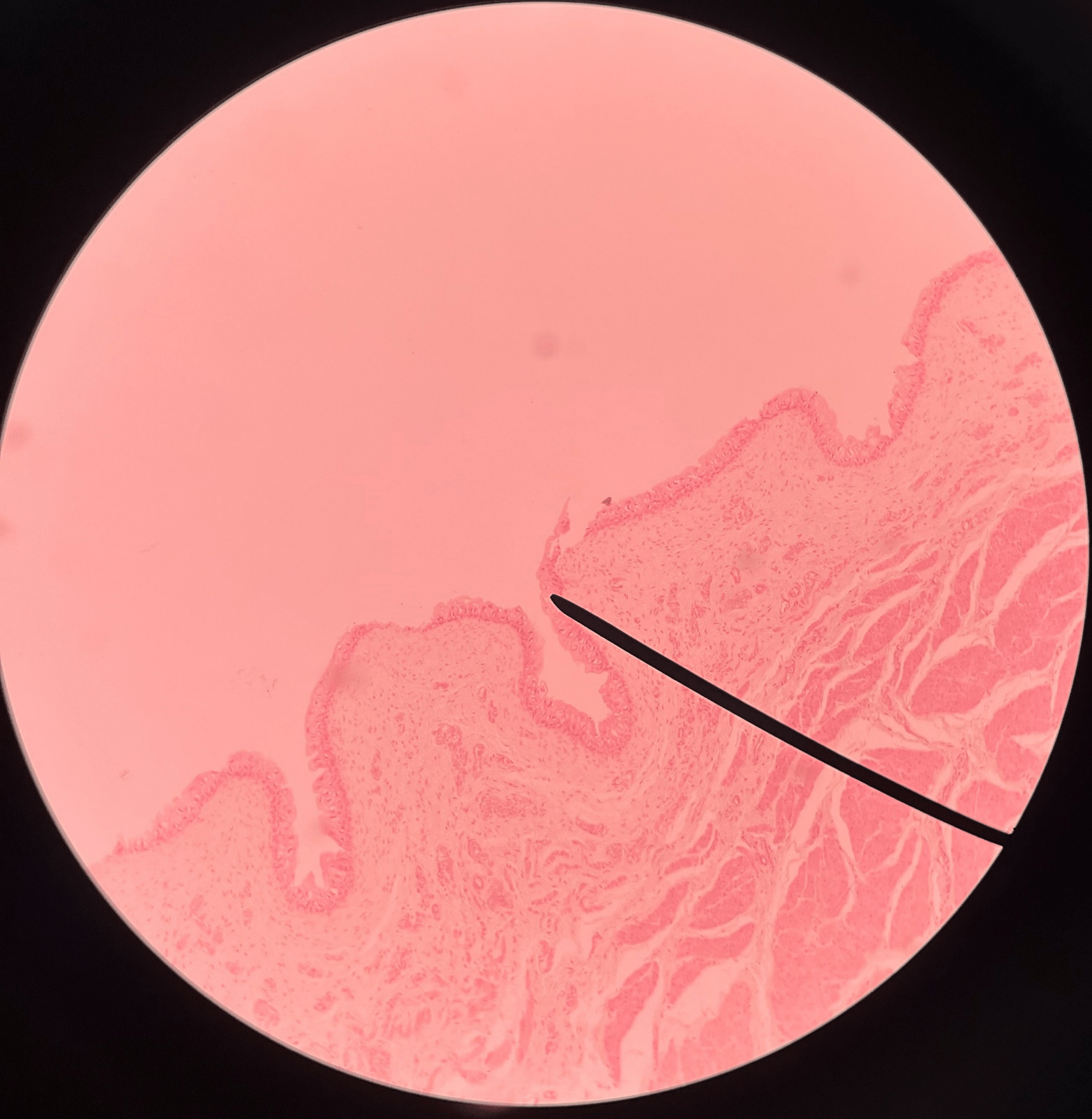
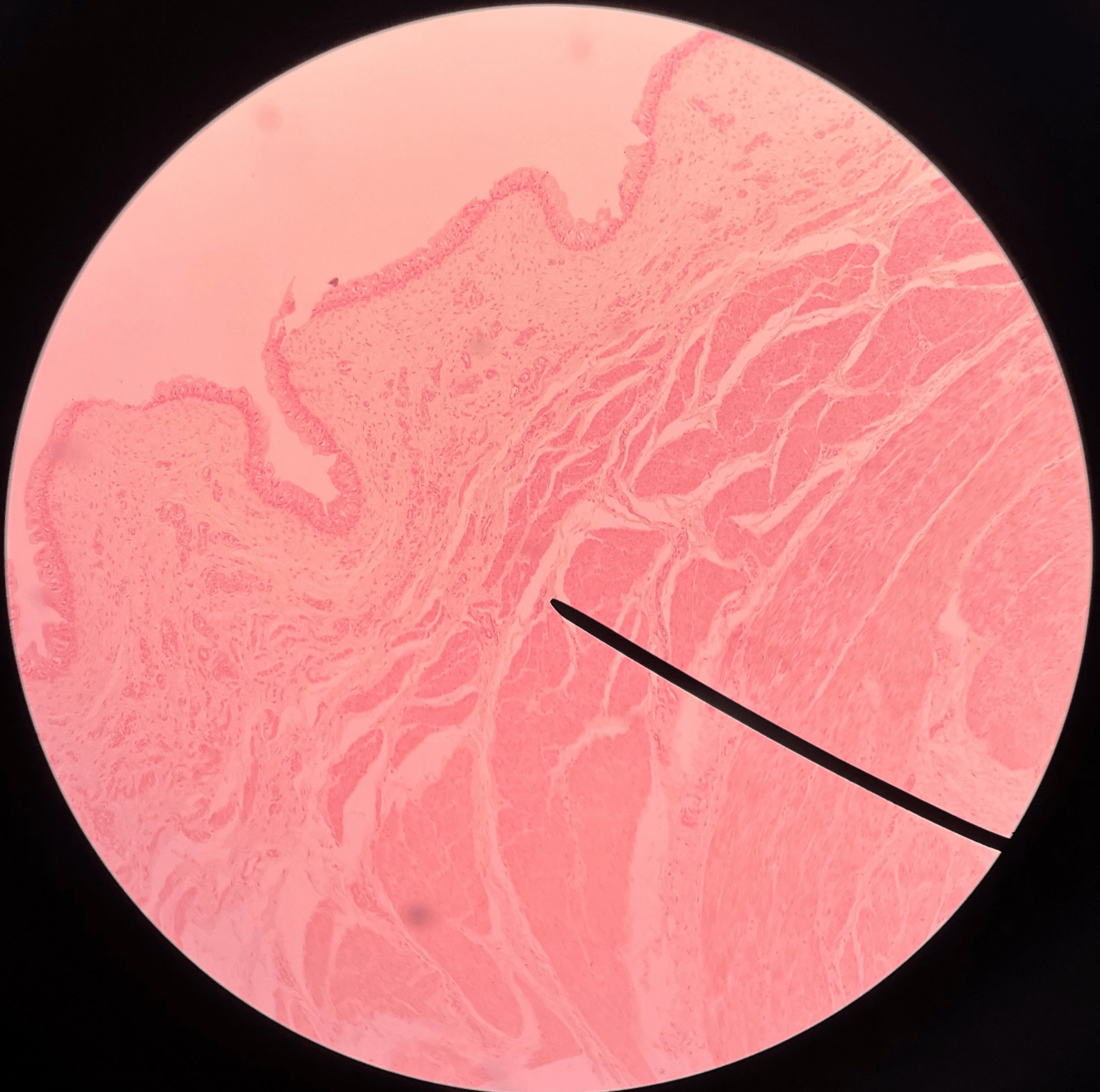
33
New cards
submucosa
• Slide histology of the bladder.
• A layer of the bladder.
• Superficial to the mucosa and deep to the muscularis.
• A layer of the bladder.
• Superficial to the mucosa and deep to the muscularis.
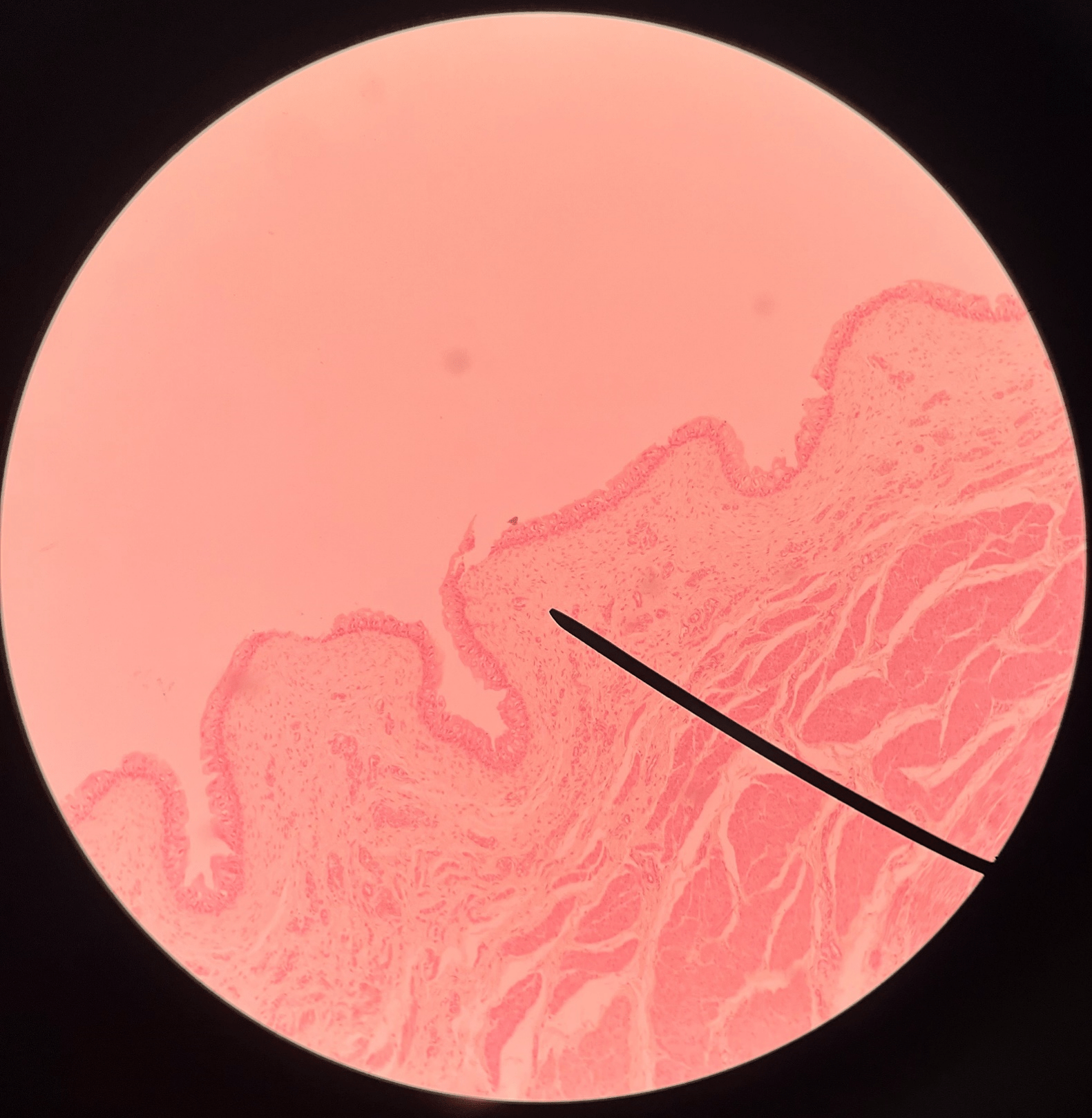
34
New cards
muscularis
• Slide histology of the bladder.
• A muscular layer of the bladder.
• Also known as the detrusor muscle.
• Superficial to the submucosa.
• A muscular layer of the bladder.
• Also known as the detrusor muscle.
• Superficial to the submucosa.
35
New cards
urethra
A tubular organ carrying urine from the bladder to the exterior during micturition (voiding of urine).
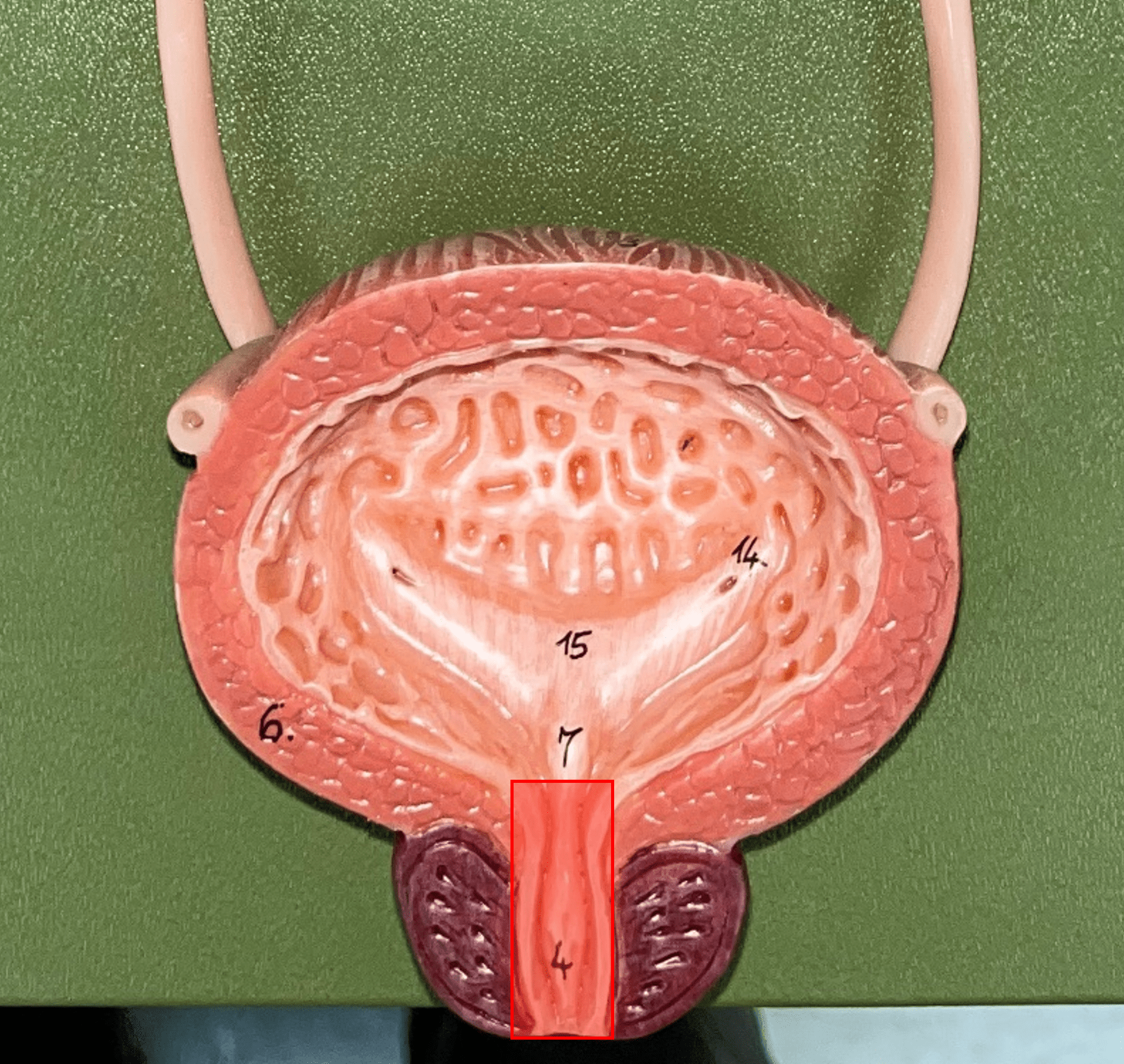
36
New cards
external urethral orifice
• Part of the urethra.
• The opening of the urethra to the exterior.
• The opening of the urethra to the exterior.
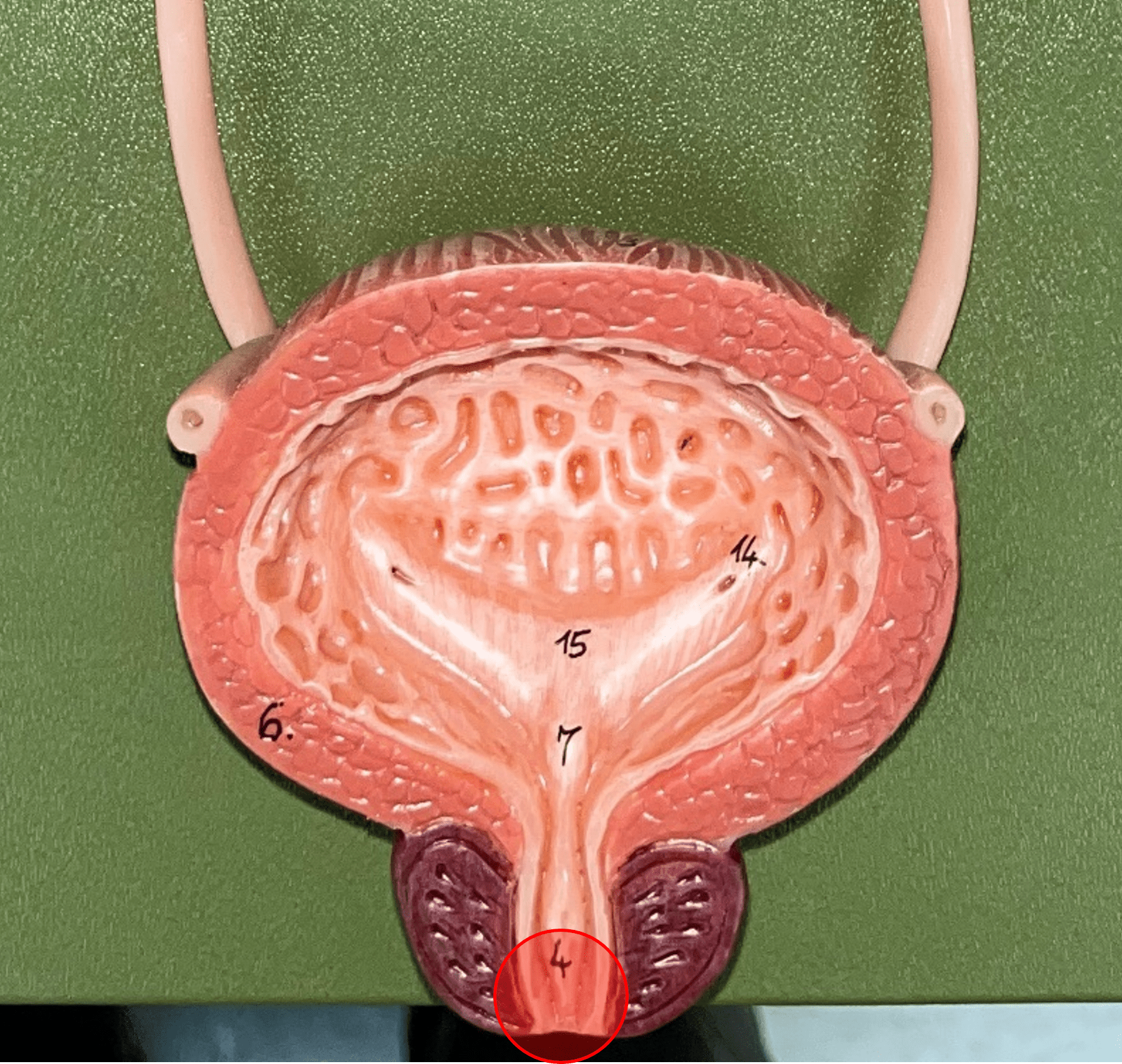
37
New cards
internal urethral sphincter
\
• Part of the urethra.
• A circular layer of circular smooth muscle located just after the internal urethral orifice.
• Involuntary muscle allowing urine to flow outward.
• Part of the urethra.
• A circular layer of circular smooth muscle located just after the internal urethral orifice.
• Involuntary muscle allowing urine to flow outward.
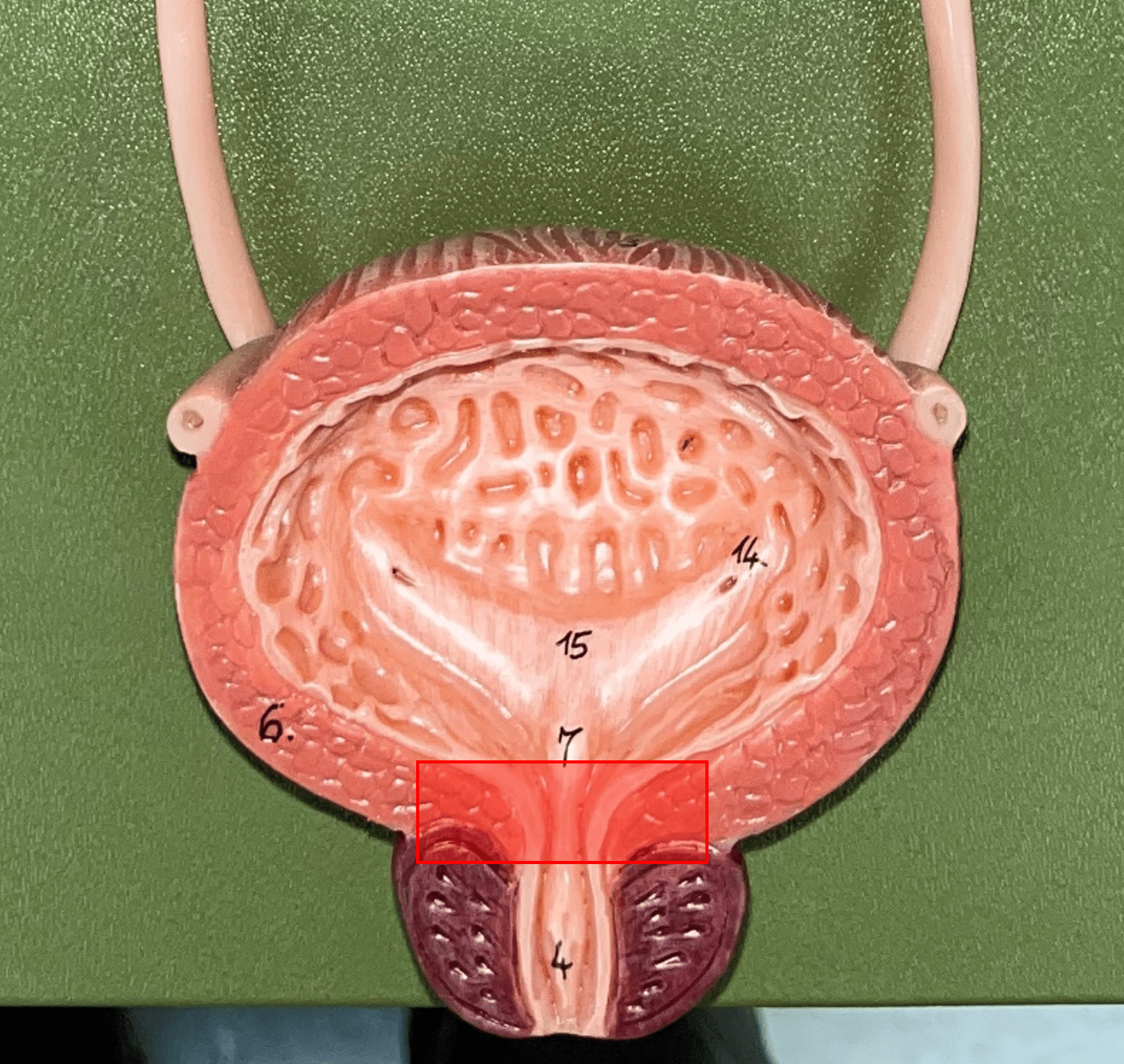
38
New cards
external urethral sphincter
• Part of the urethra.
• A layer of skeletal muscle located just before the external urethral orifice.
• Voluntary muscle allowing urine to flow out to the exterior.
• A layer of skeletal muscle located just before the external urethral orifice.
• Voluntary muscle allowing urine to flow out to the exterior.
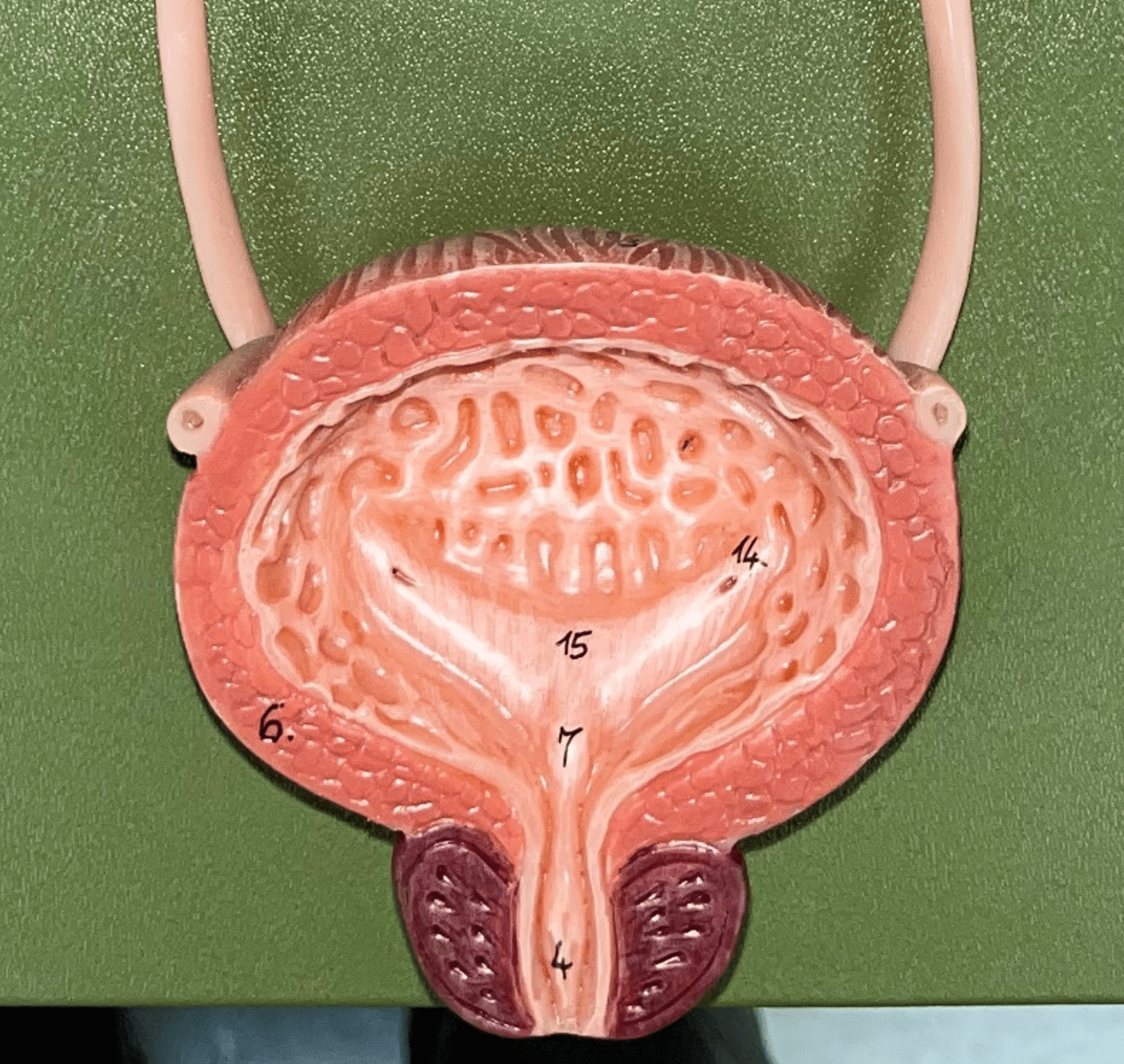
39
New cards
nephron
• The functional subunit of the kidney.
• Site of urine formation and renal function.
• Composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.
• Site of urine formation and renal function.
• Composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.
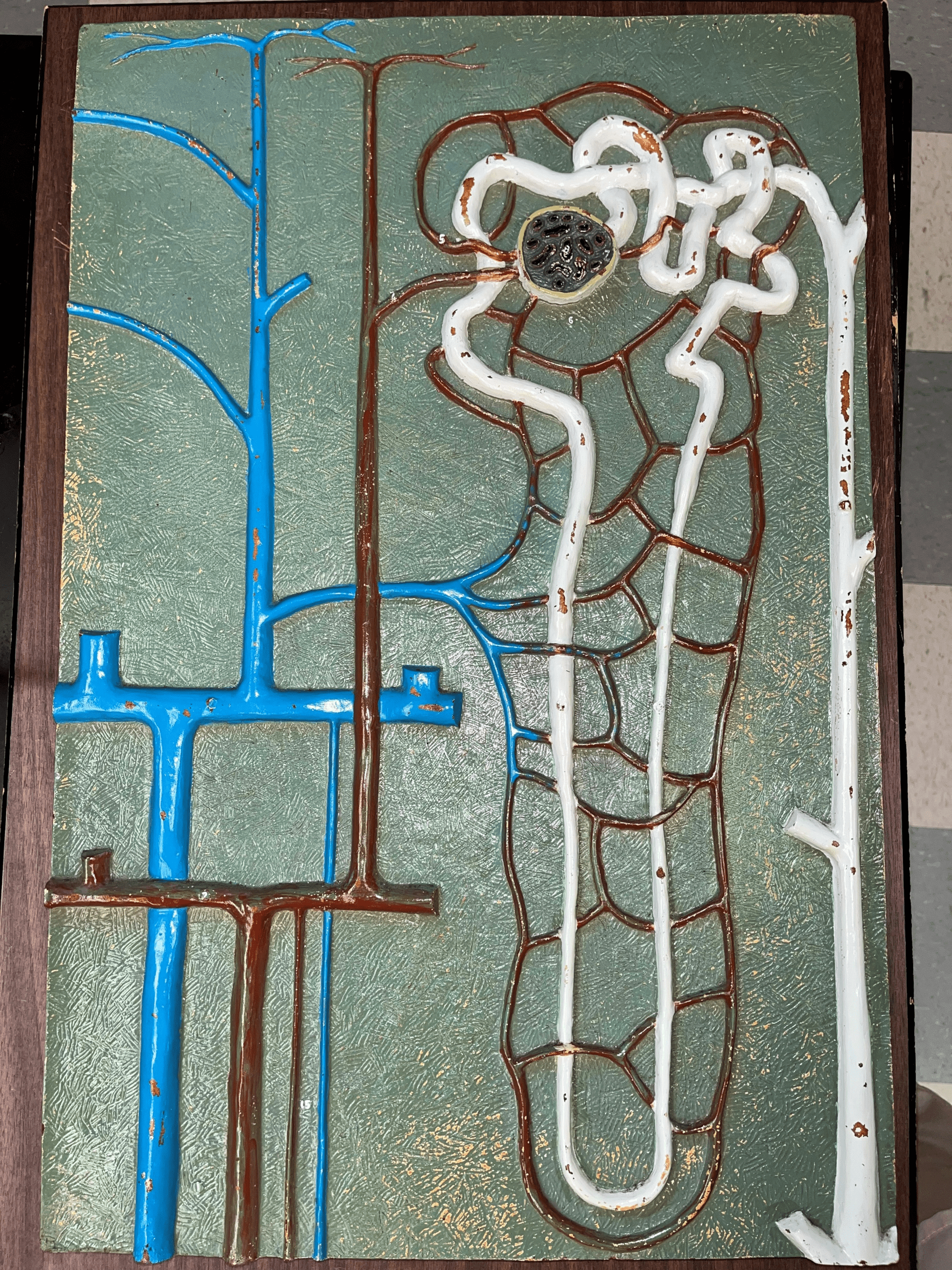
40
New cards
renal corpuscle
• Part of a nephron.
• Filters blood.
• Composed of a glomerulus enclosed within a glomerular capsule.
• Filters blood.
• Composed of a glomerulus enclosed within a glomerular capsule.
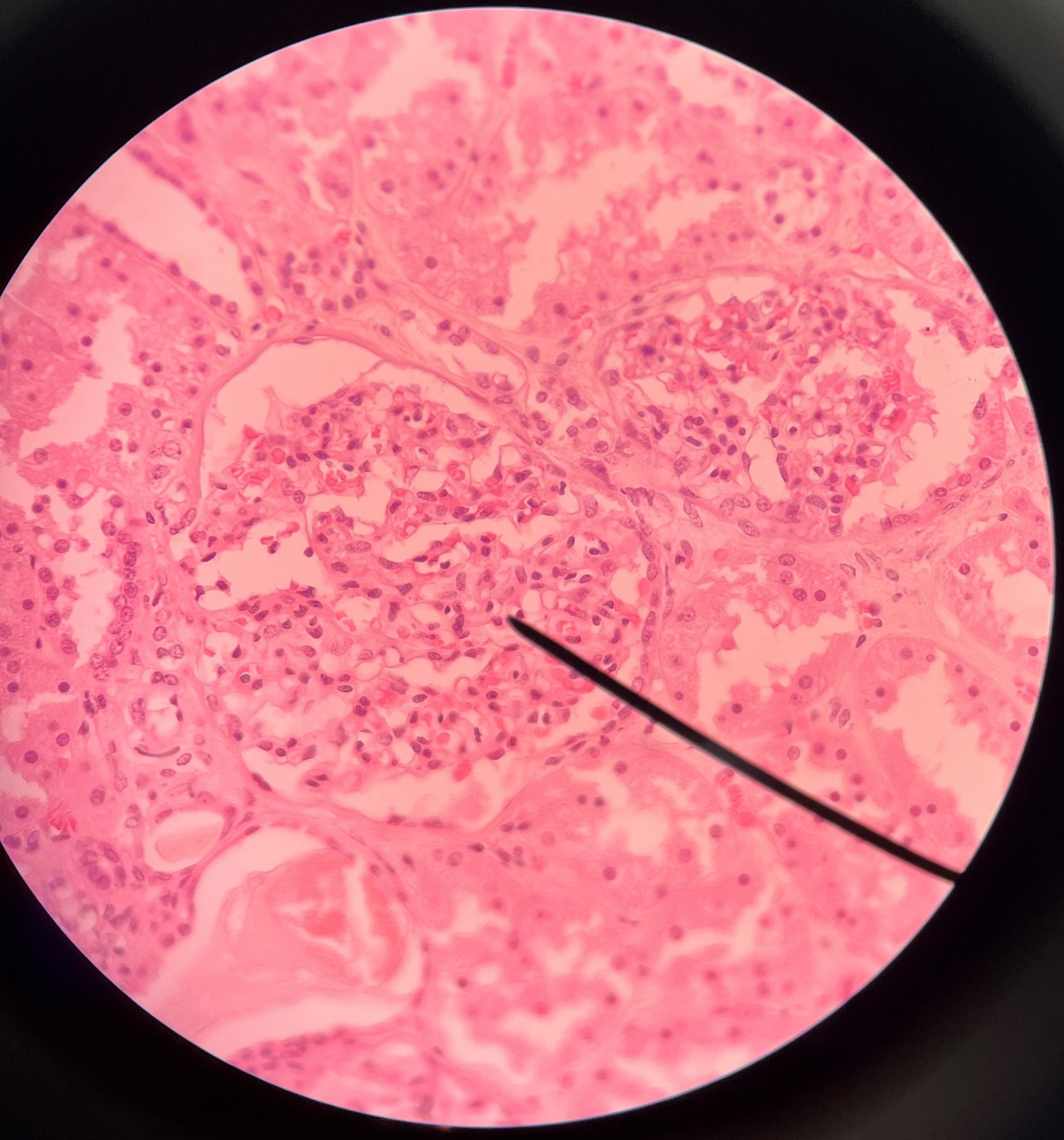
41
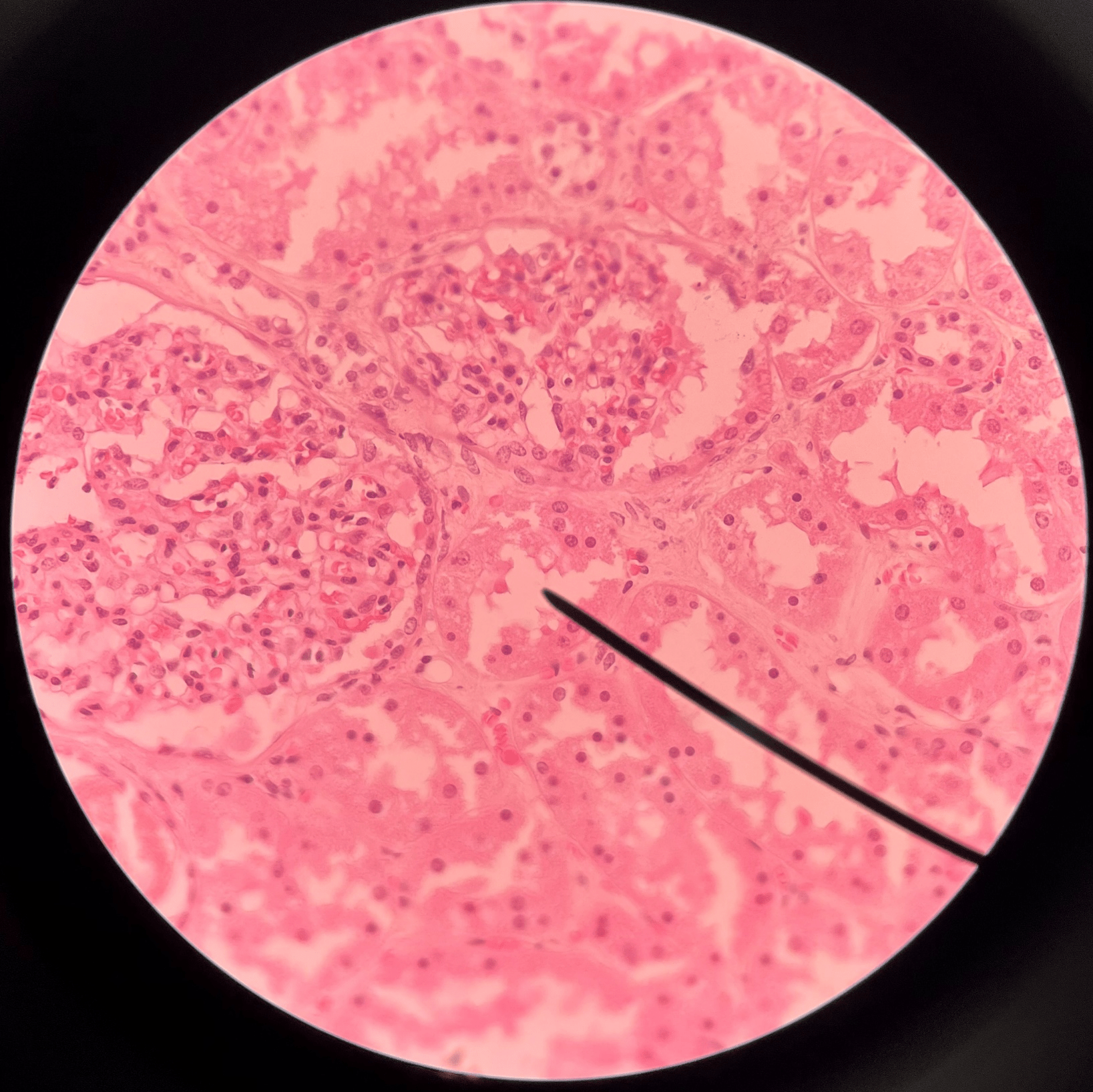
New cards
glomerulus
• Slide histology of the nephron.
• Part of a renal corpuscle.
• The capillary network of a renal corpuscle.
• Part of a renal corpuscle.
• The capillary network of a renal corpuscle.
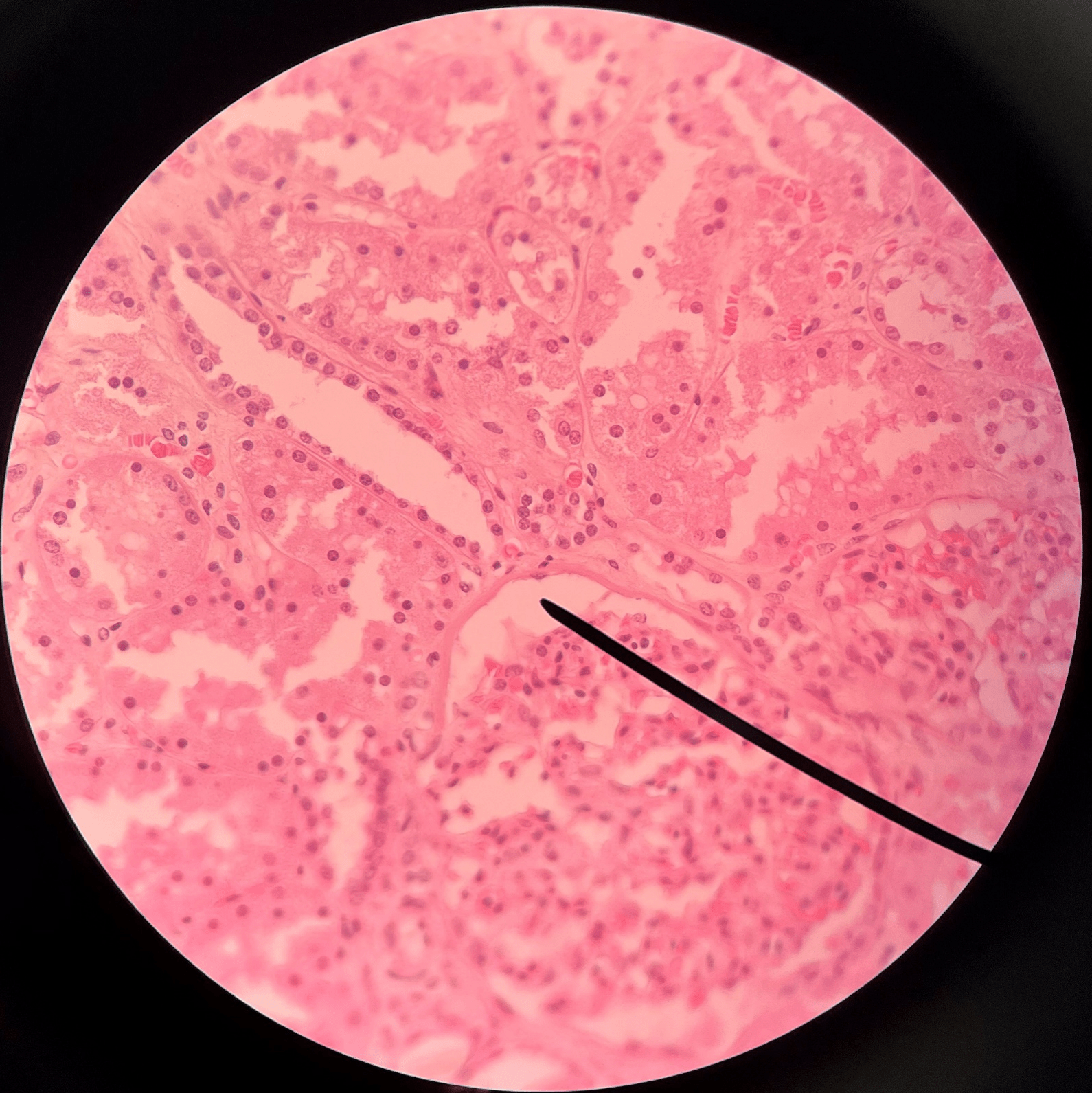
42
New cards
capsular space
• Slide histology of the nephron.
• Part of a renal corpuscle.
• The interior of the glomerular capsule.
• Part of a renal corpuscle.
• The interior of the glomerular capsule.
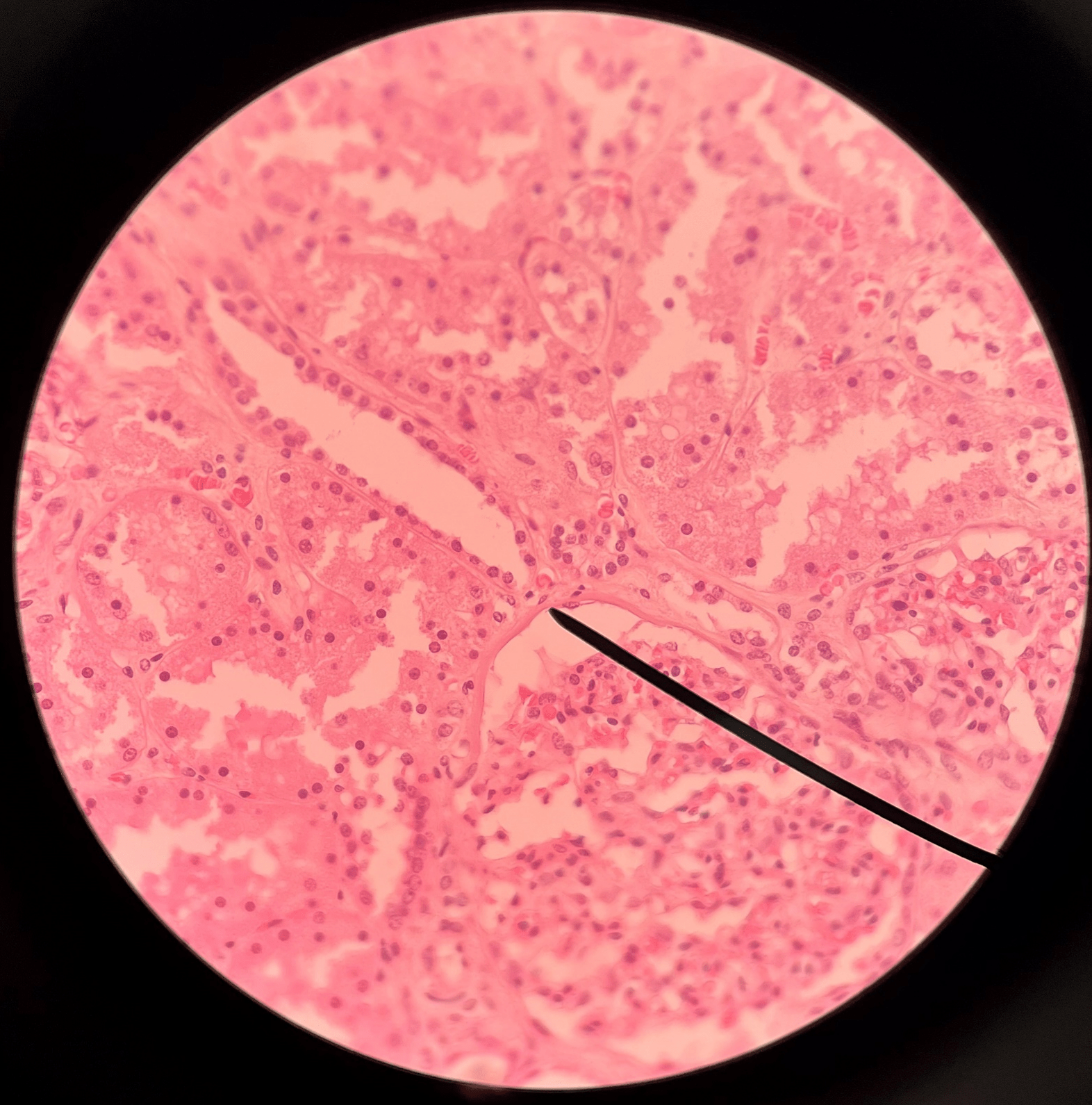
43
New cards
glomerular capsule
• Slide histology of the nephron.
• Part of a renal corpuscle.
• A wall enclosing the glomerulus.
• Shown in the image is the parietal layer.
• Part of a renal corpuscle.
• A wall enclosing the glomerulus.
• Shown in the image is the parietal layer.
44
New cards
podocyte
• Part of a renal corpuscle.
• A cell with pedicels.
• Wraps around the glomerulus and forms the visceral layer of the glomerular capsule.
• A cell with pedicels.
• Wraps around the glomerulus and forms the visceral layer of the glomerular capsule.
45
New cards
pedicel
• Part of a renal corpuscle.
• A foot-like process of a podocyte forming part of the filtration membrane.
• A foot-like process of a podocyte forming part of the filtration membrane.
46
New cards
macula densa
• Part of a renal corpuscle.
• A group of columnar cells in the DCT that monitors fluid composition and filtration rate.
• A group of columnar cells in the DCT that monitors fluid composition and filtration rate.
47
New cards
renal tubule
• Slide histology of the nephron.
• Part of a nephron.
• Modifies glomerular filtrate by reabsorption and secretion of water and ions.
• Divided into the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule.
• Part of a nephron.
• Modifies glomerular filtrate by reabsorption and secretion of water and ions.
• Divided into the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule.
48
New cards
proximal convoluted tubule
• The first part of a renal tubule.
• Primary site of water and solute reabsorption.
• Begins immediately after the renal corpuscle.
• Abbreviated PCT.
• Primary site of water and solute reabsorption.
• Begins immediately after the renal corpuscle.
• Abbreviated PCT.
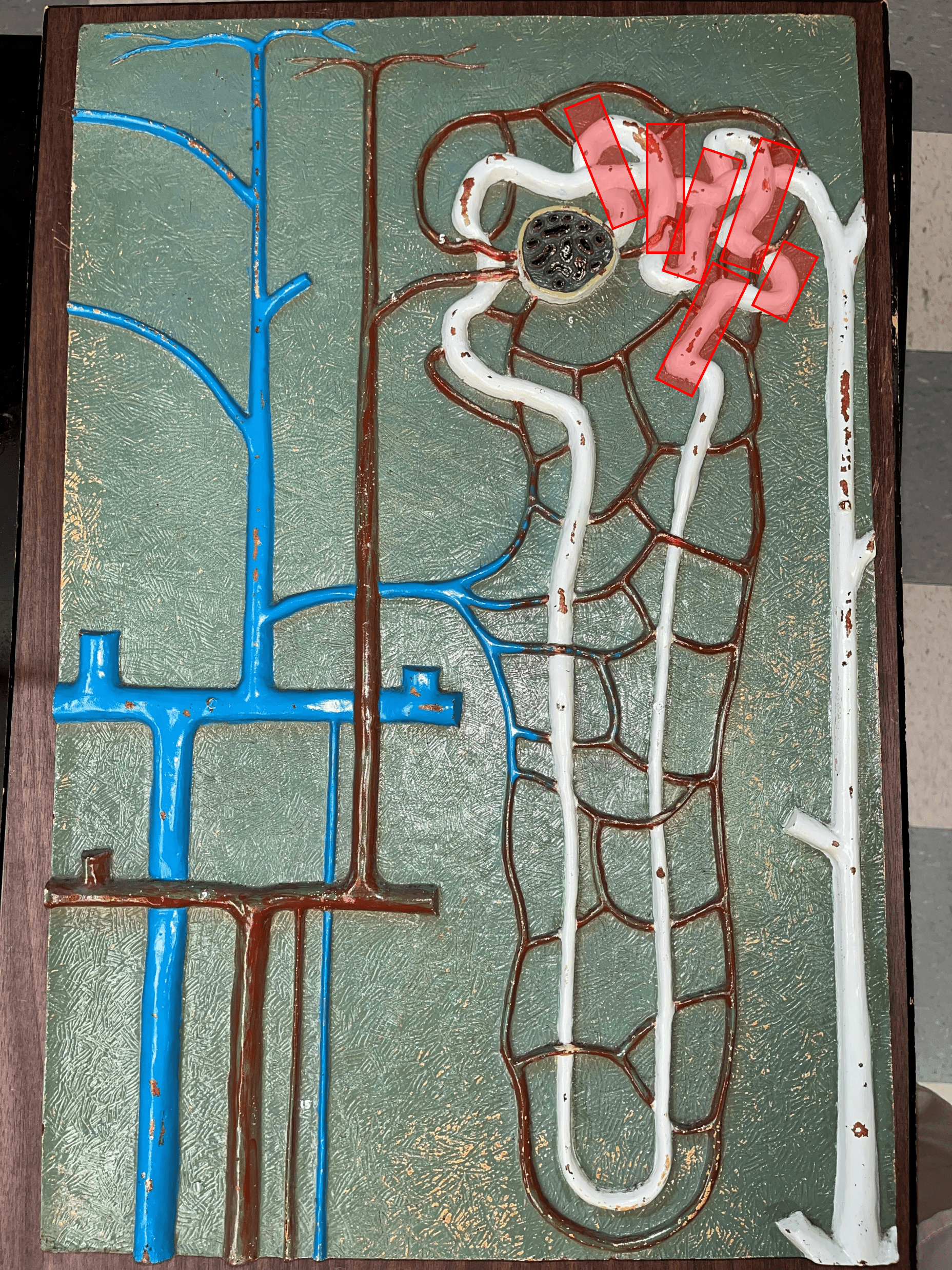
49
New cards
descending limb
• The proximal second part of a renal tubule.
• Part of the loop of Henle.
• Permeable to water but not solutes.
• Part of the loop of Henle.
• Permeable to water but not solutes.
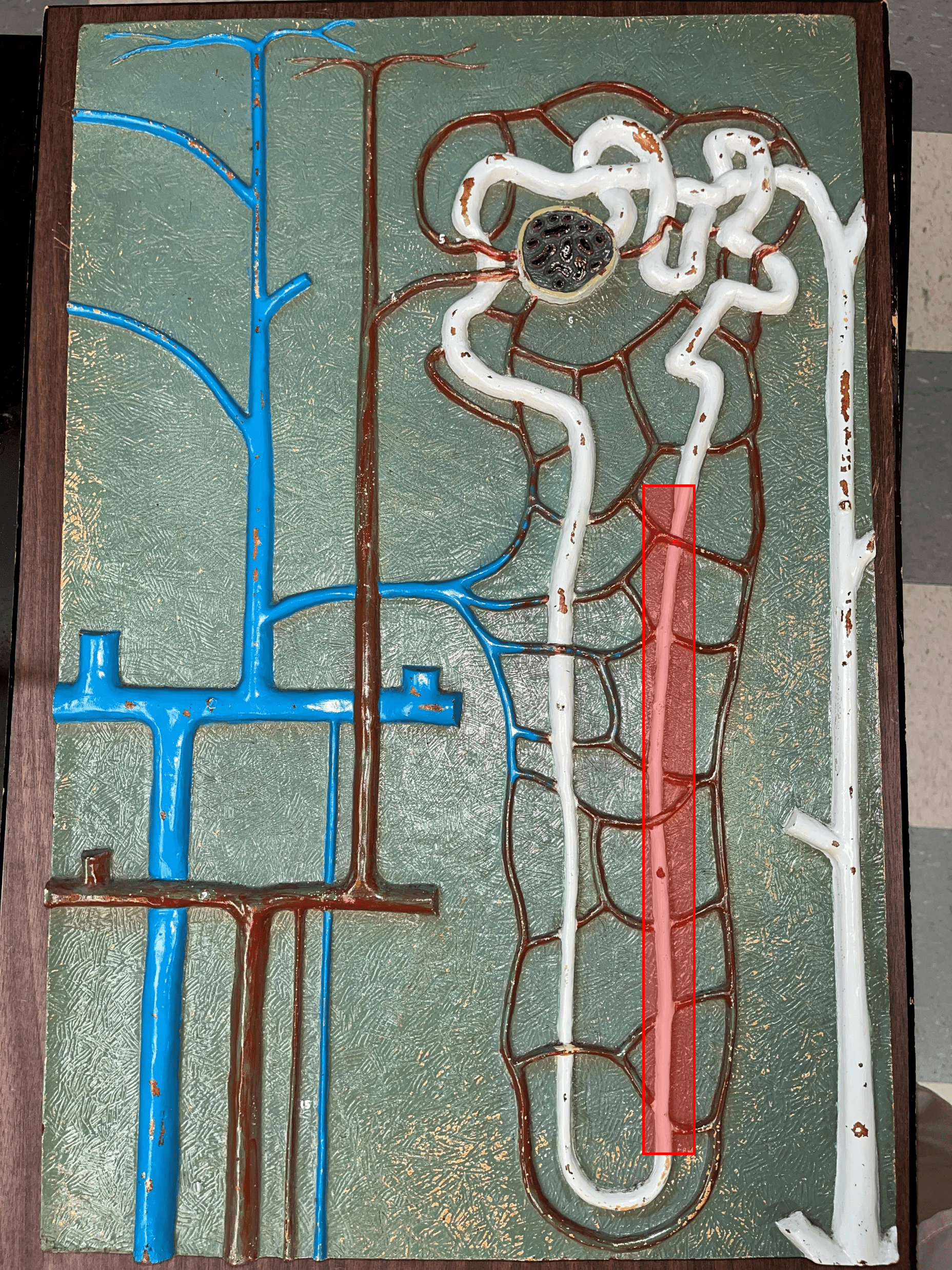
50
New cards
ascending limb
• The distal second part of a renal tubule.
• Part of the loop of Henle.
• Permeable to solutes but not water.
• Part of the loop of Henle.
• Permeable to solutes but not water.
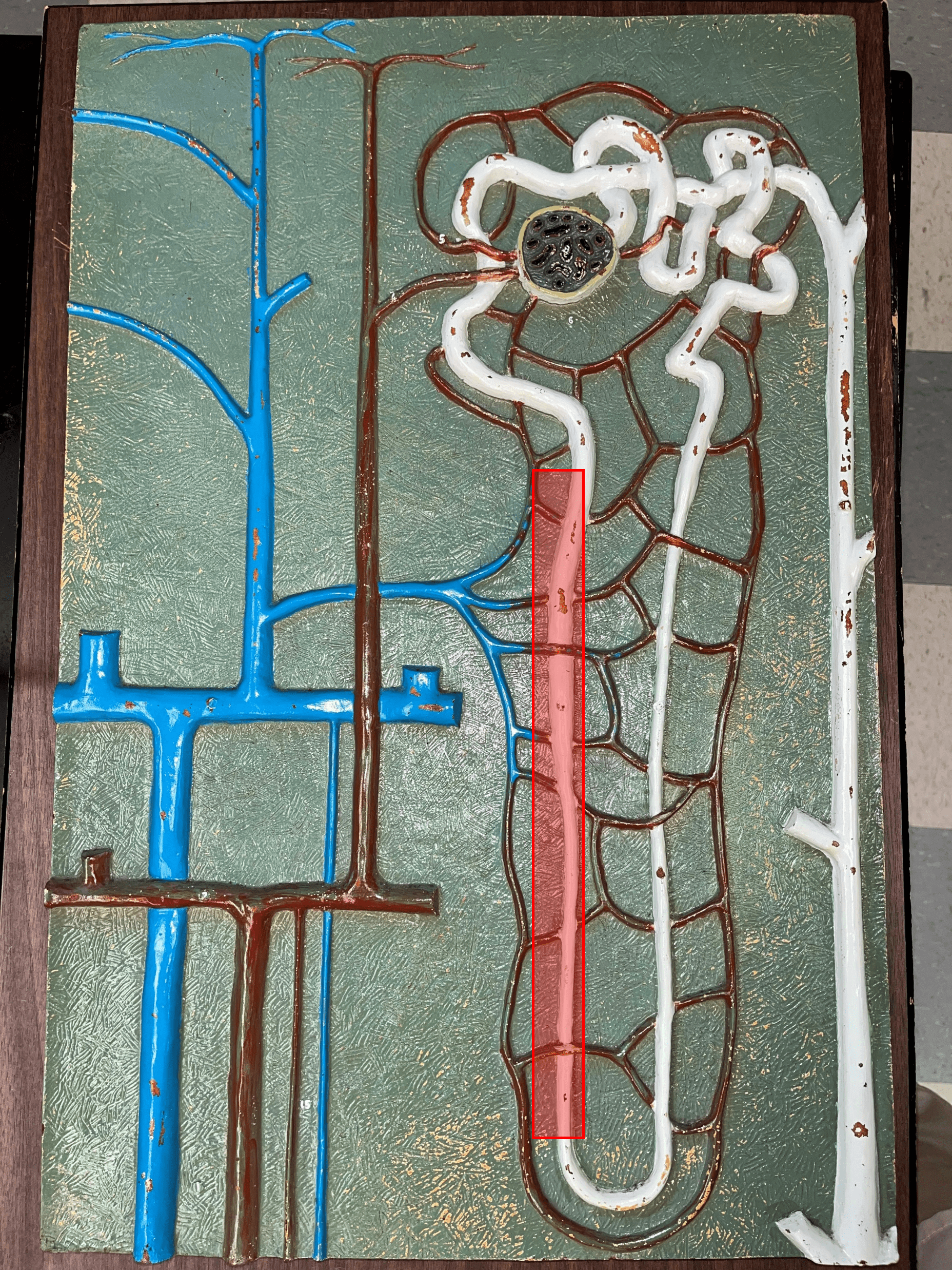
51
New cards
distal convoluted tubule
• The third part of a renal tubule.
• Primary site of secretion of excess solutes.
• Abbreviated DCT.
• Primary site of secretion of excess solutes.
• Abbreviated DCT.
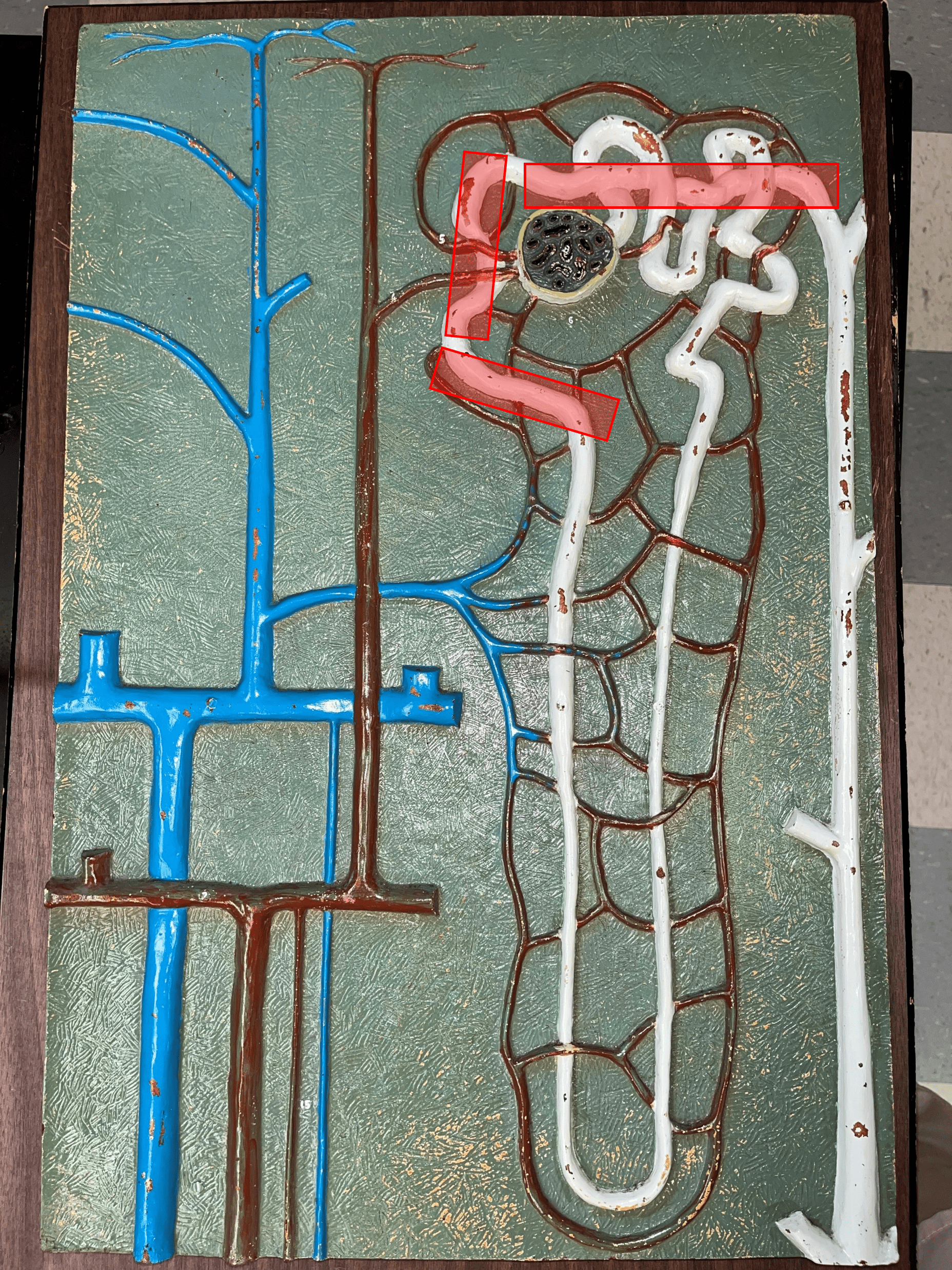
52
New cards
collecting duct
• The convergence of several distal convoluted tubules.
• Descends through the renal pyramid.
• Merges with others to form larger papillary ducts that drain into the minor calyces.
• Abbreviated CD.
• Descends through the renal pyramid.
• Merges with others to form larger papillary ducts that drain into the minor calyces.
• Abbreviated CD.
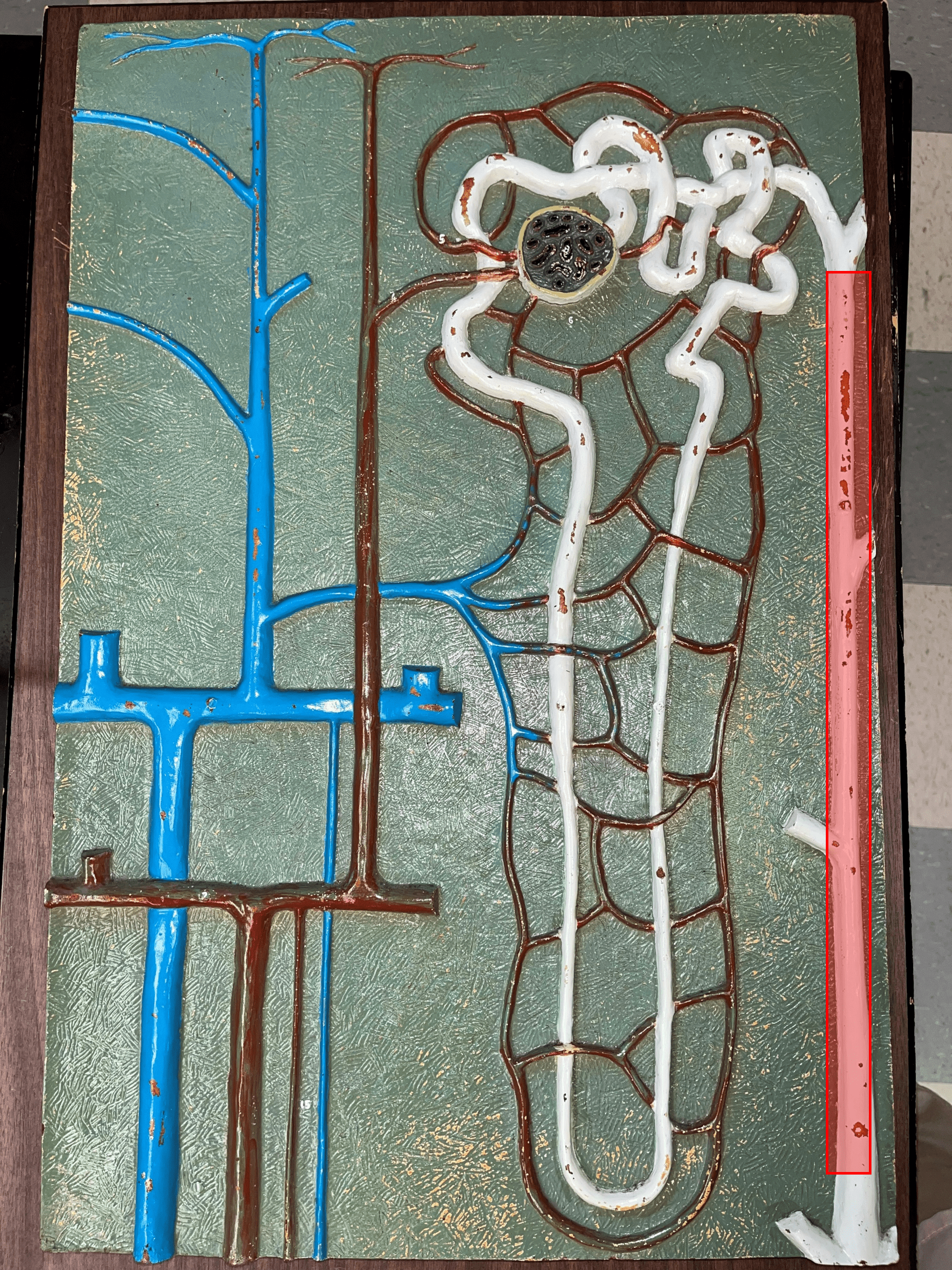

53
New cards
afferent arteriole
• Branches of an interlobular artery.
• Supplies the glomerulus of a nephron for blood filtration.
• Supplies the glomerulus of a nephron for blood filtration.
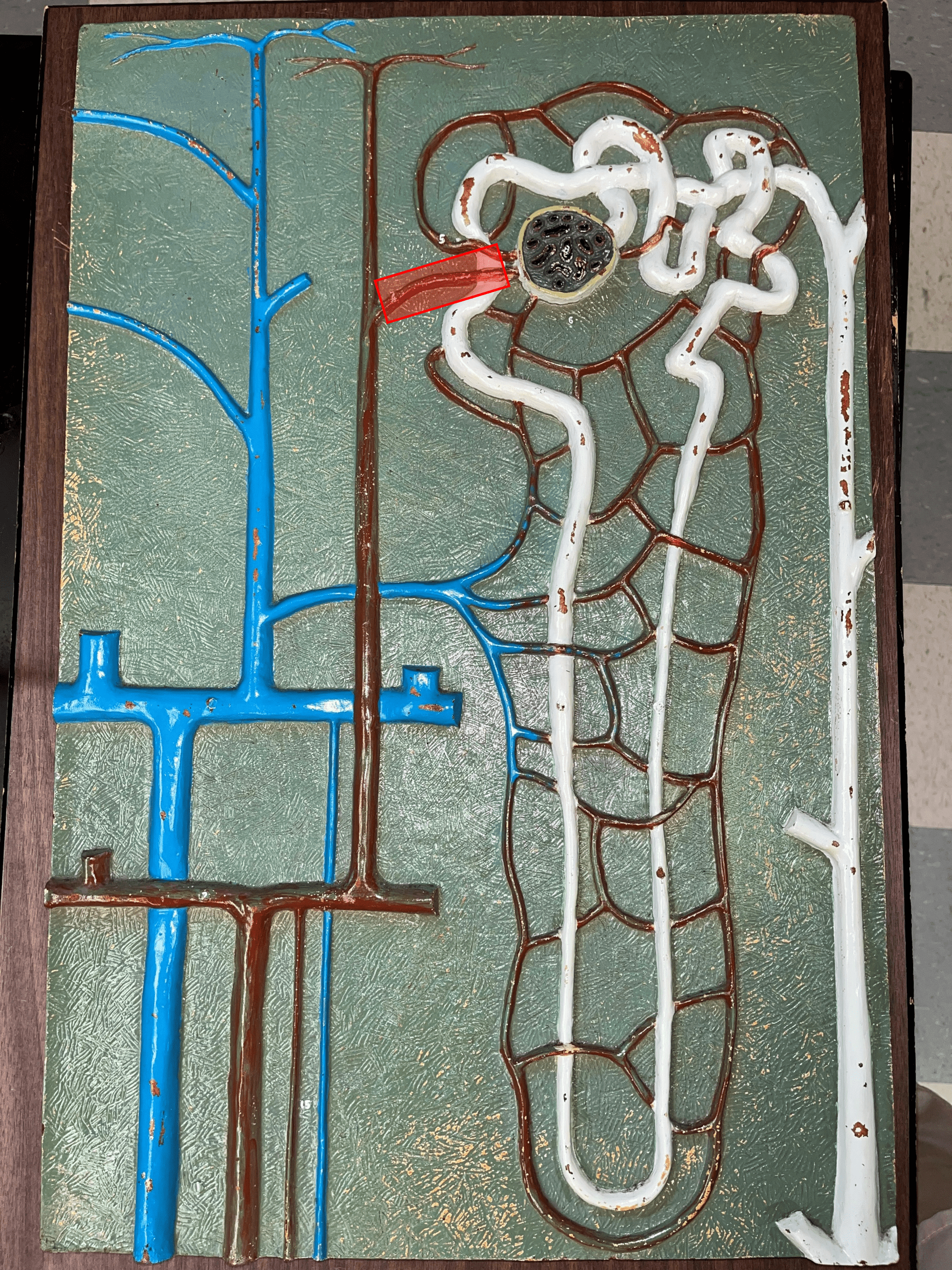

54
New cards
efferent arteriole
Vessel carrying blood away from the glomerulus to the peritubular capillaries.
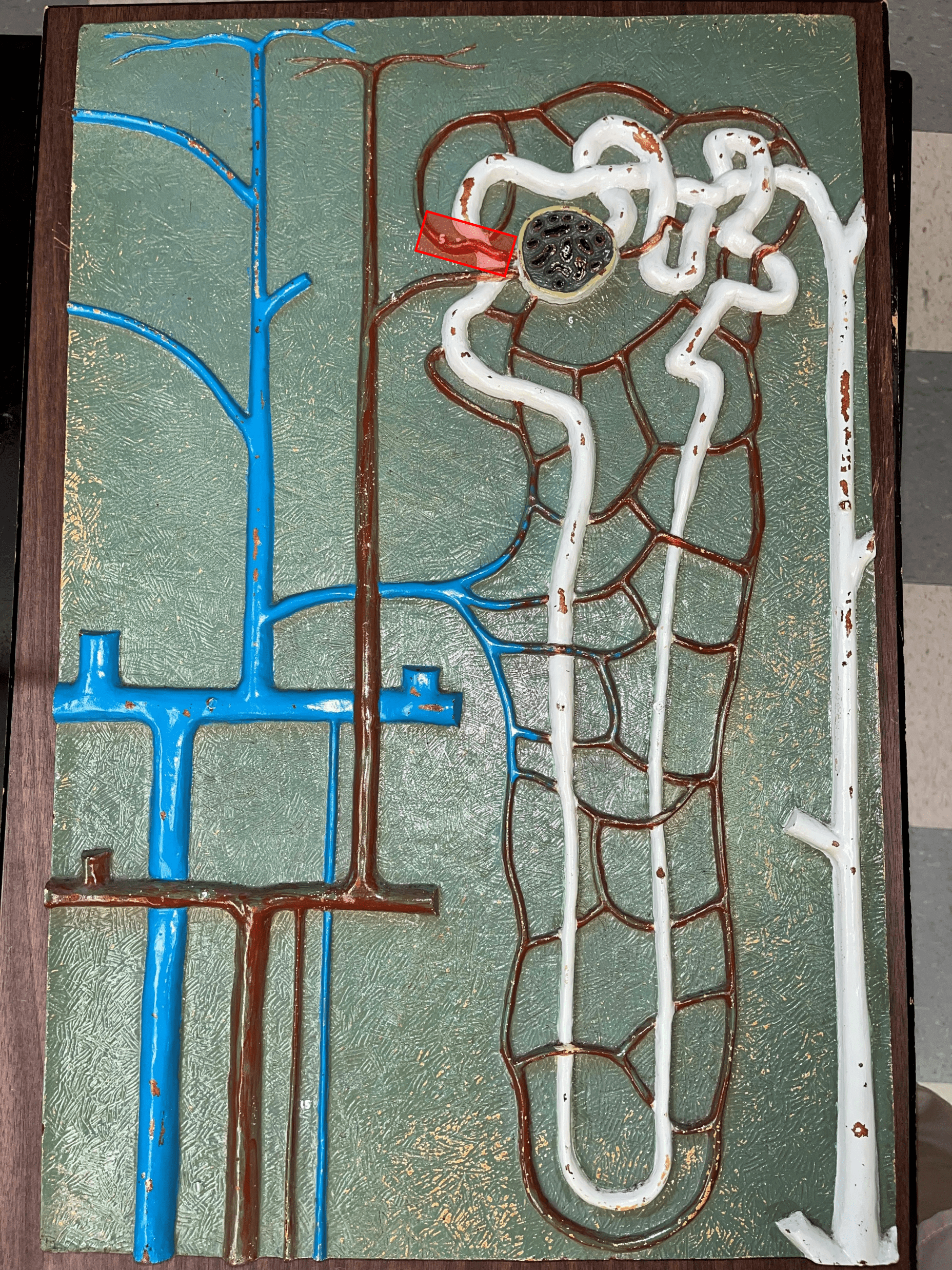

55
New cards
peritubular capillaries
• Branches of an efferent arteriole.
• Supplies the adjacent renal tubules in the renal cortex.
• Supplies the adjacent renal tubules in the renal cortex.
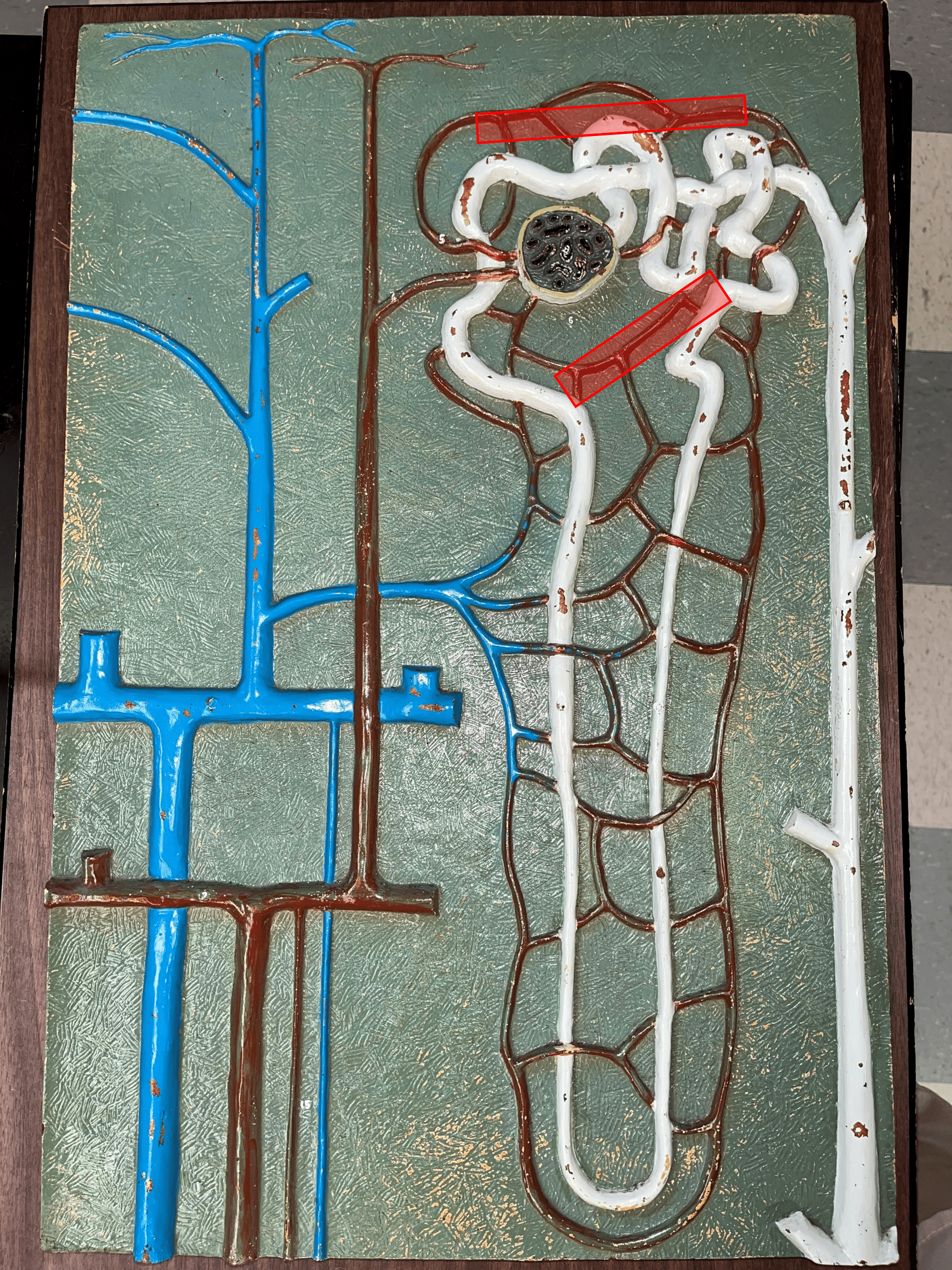

56
New cards
vasa recta
• Branches of an efferent arteriole.
• Supplies the loops of Henle in the renal medulla.
• Supplies the loops of Henle in the renal medulla.