Topic 10- aggregates
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Aggregates
Concrete is comprised of: Admixtures, Cement, Water, Air, Sand, Stone/gravel.
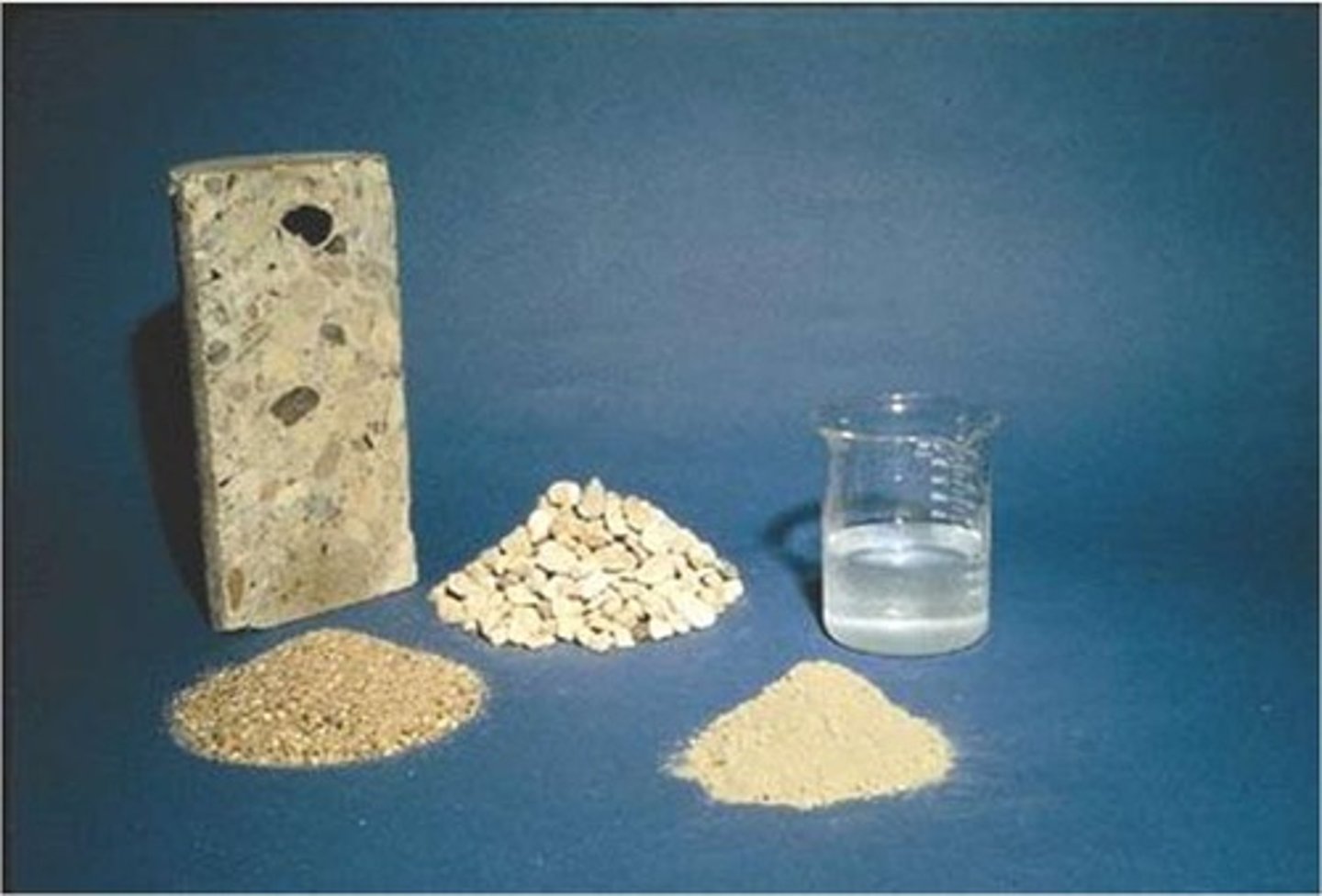

Fine Aggregate
Natural sand and/or crushed stone, < #4 sieve (4.75 mm, 0.1875 in.), Usually 35% to 45% by mass or volume of total aggregate.
Coarse Aggregate
Gravel and/or crushed stone, ≥#4 sieve (4.75 mm, 0.1875 in), Largest are typically between 3/8 and 1½ in.
Lightweight Aggregate
Includes materials such as Expanded Shale, Clay, Slate, Slag, Pumice, Scoria, Perlite, Vermiculite, Diatomite, and produces structural lightweight concrete and lightweight insulating concrete.
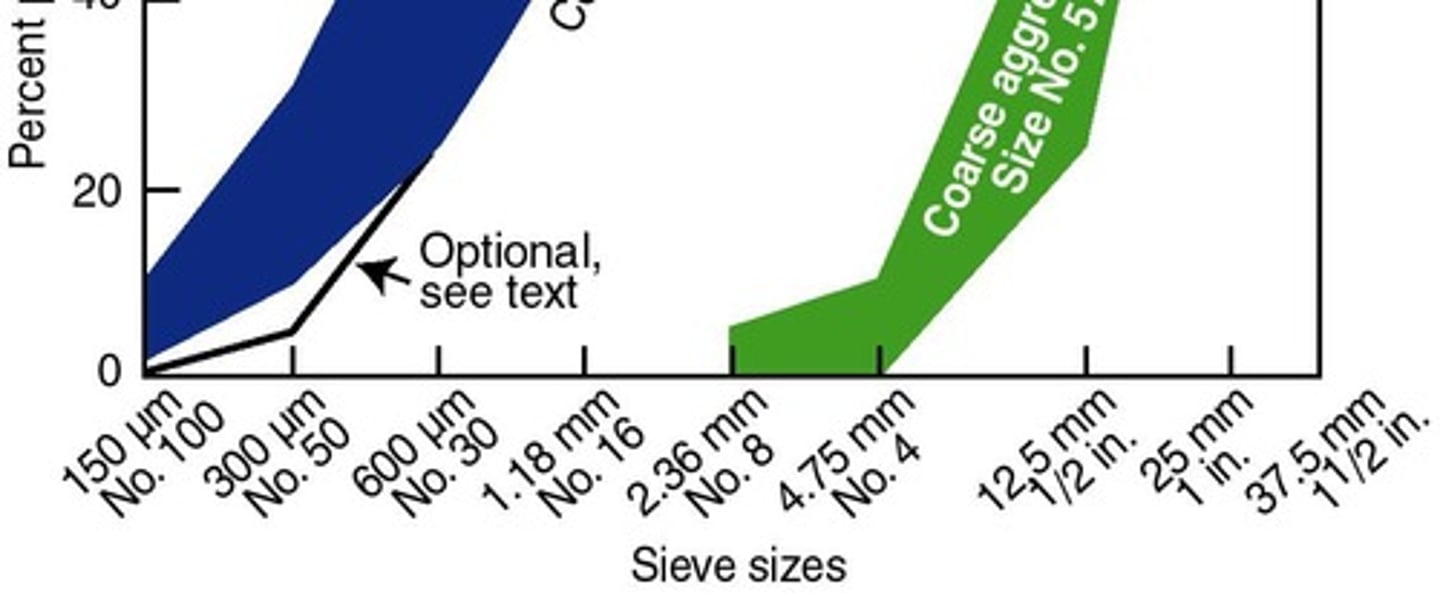
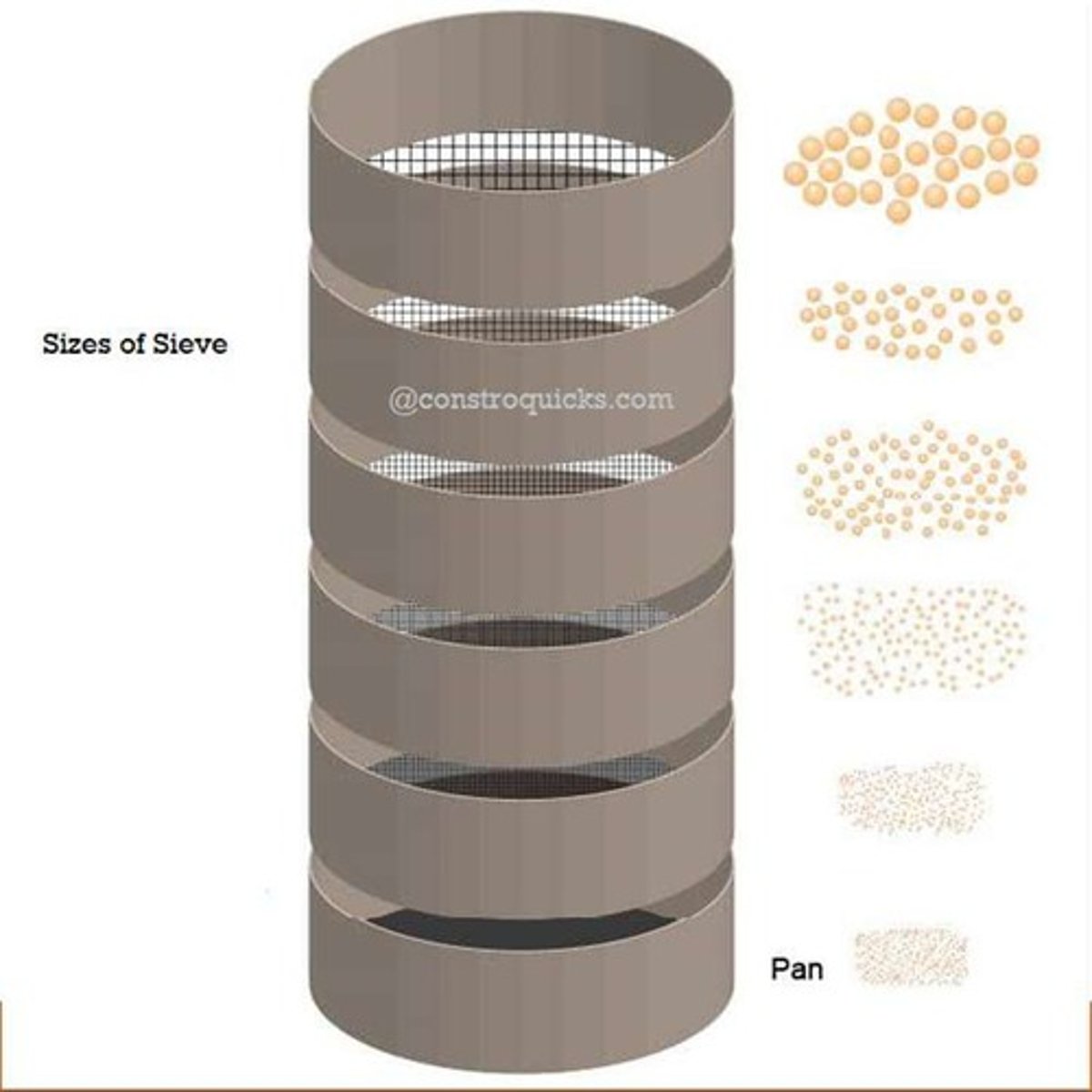
Grading
The particle-size distribution of an aggregate as determined by a sieve analysis using wire mesh sieves with square openings.
Fineness Modulus (FM)
The higher the FM, the coarser the aggregate, obtained by adding the sum of the cumulative percentages by mass of a sample aggregate retained on each of a specified series of sieves and dividing the sum by 100.
Void Content
The better the aggregates pack together, the fewer the voids between them.
Maximum size
The smallest sieve that all of a particular aggregate must pass through.
Nominal maximum size
The standard sieve opening immediately smaller than the smallest through which all of the aggregate must pass, which may retain 5% to 15%.
Specific Gravity
Relative density, the ratio of mass of material of a given volume to the mass of an equal volume of water, measured by comparing the weight of material in air compared to the weight in water.
Moisture Conditions
Important for Concrete Mixture Design.
Organic impurities
Affects setting and hardening, may cause deterioration.
Materials finer than the 75-µm (No. 200) sieve
Affects bond, increases water requirement.
Coal, lignite, or other lightweight materials
Affects durability, may cause stains and popouts.
Soft particles
Affects durability.
Clay lumps and friable particles
Affects workability and durability, may cause popouts.
Chert of less than 2.40 relative density
Affects durability, may cause popouts.
Alkali-reactive aggregates
Causes abnormal expansion, map cracking, and popouts.
ASTM C33
Standard Specification for Concrete Aggregates.
Grading Types
Uniformly Graded, Well Graded, Gap Graded.
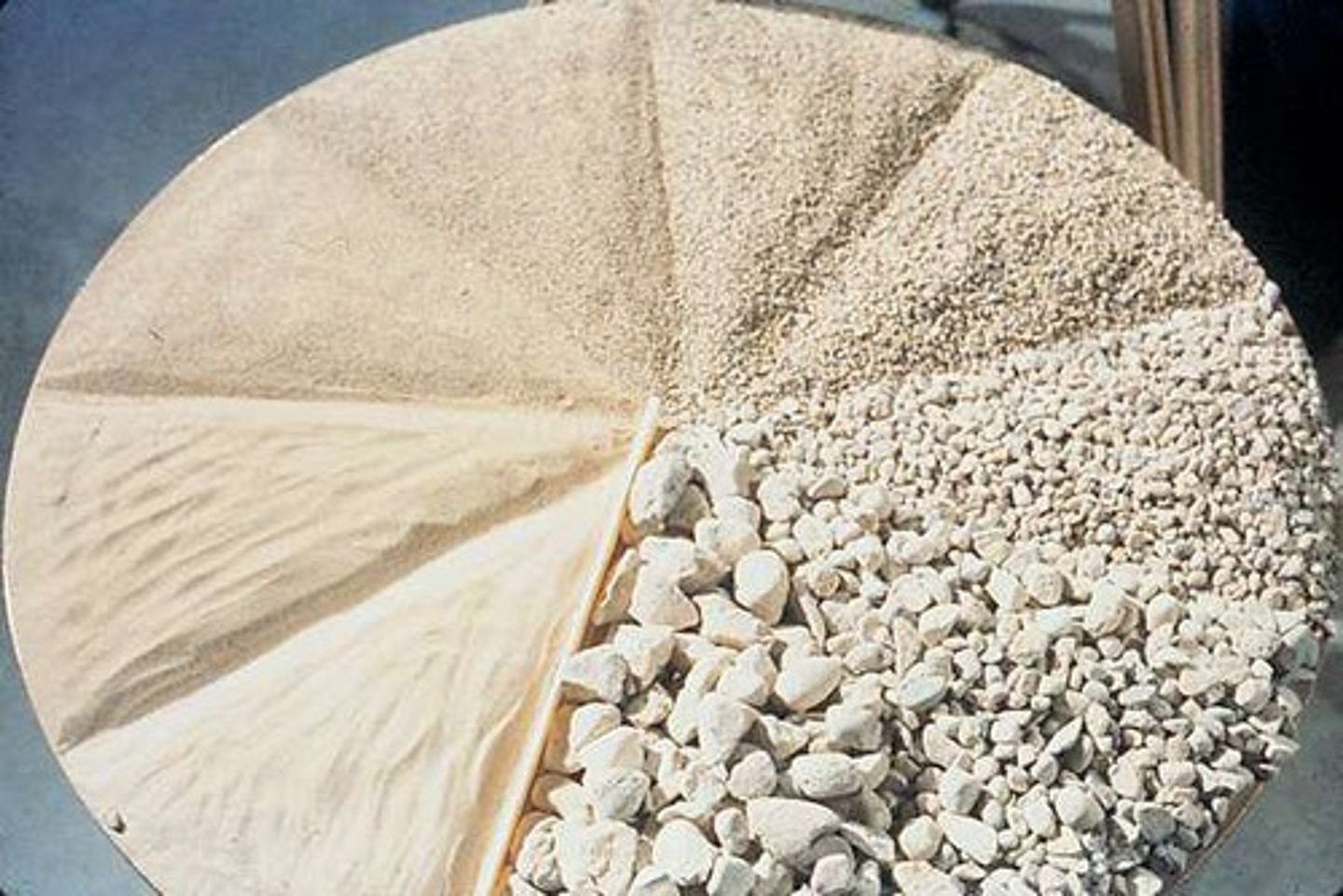

Uniformly Graded
Large percentage made up of a small range of particle sizes, high percentage of voids, poor interlocking.
Well Graded
Large range of grain sizes, each size contributing approximately the same amount, very few voids, excellent interlocking.
Gap Graded
Blend of small and large grain sizes, without many particles in the mid-size range, few voids, good interlocking.
Fineness Modulus Calculation
Fineness modulus = Total retained mass ÷ 100.