NURS 2514 Week 1 - Glucose Regulation
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Which of the following processes is stimulated by insulin?
A) Glycogenolysis
B) Gluconeogenesis
C) Glycogenesis
D) Ketogenesis
C) Glycogenesis - Insulin promotes glycogenesis—conversion of glucose to glycogen for storage in liver and muscle.
Insulin promotes the movement of which substances into cells?
A) Glucose, sodium, calcium
B) Glucose, potassium, amino acids
C) Fatty acids, glucose, calcium
D) Glucose, magnesium, phosphate
B) Glucose, potassium, amino acids - Insulin increases cellular uptake of glucose, potassium, and amino acids.
Which hormone directly opposes insulin by stimulating hepatic glucose production?
A) GLP-1
B) Glucagon
C) Insulin
D) Amylin
B) Glucagon - Glucagon increases hepatic glucose production (via glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis).
The pancreas regulates blood glucose primarily through the action of:
A) Alpha and beta cells
B) Delta and gamma cells
C) Hepatocytes
D) Renal tubules
A) Alpha and beta cells - Alpha cells secrete glucagon, beta cells secrete insulin in the pancreas.
Glucagon acts mainly on which organ to increase blood glucose levels?
A) Muscle
B) Adipose
C) Liver
D) Pancreas
C) Liver - Glucagon acts on the liver to raise blood glucose.
Which hormone inhibits glucagon and enhances insulin secretion post-meal?
A) Cortisol
B) Epinephrine
C) GLP-1
D) Growth hormone
C) GLP-1 - GLP-1 enhances insulin secretion and suppresses glucagon post-meal.
Which of the following is a counter-regulatory hormone?
A) GLP-1
B) Insulin
C) Epinephrine
D) Amylin
C) Epinephrine - Epinephrine is a counter-regulatory hormone, increasing glucose via glycogenolysis.
Which of the following occurs when insulin levels are low or absent?
A) Increased glucose uptake by cells
B) Decreased hepatic glucose output
C) Increased lipolysis and ketone production
D) Glycogen synthesis
C) Increased lipolysis and ketone production - Insulin deficiency leads to fat breakdown and ketone formation.
Cortisol affects blood glucose by:
A) Inhibiting hepatic glucose production
B) Increasing peripheral glucose uptake
C) Stimulating gluconeogenesis
D) Blocking insulin secretion
C) Stimulating gluconeogenesis - Cortisol raises blood glucose by promoting gluconeogenesis in the liver.
Which hormone is released in response to stress and contributes to hyperglycemia?
A) GLP-1
B) Cortisol
C) Insulin
D) Amylin
B) Cortisol - Cortisol is released during stress, contributing to hyperglycemia.
Which tissue is insulin-dependent for glucose uptake?
A) Brain
B) Liver
C) Skeletal muscle
D) Kidney
C) Skeletal muscle - Muscle cells require insulin to uptake glucose; the brain does not.
After a carbohydrate-rich meal, which hormone increases the most?
A) Glucagon
B) Epinephrine
C) Insulin
D) Cortisol
C) Insulin - Insulin increases after a carbohydrate-rich meal to lower blood glucose.
Which hormone increases during fasting to maintain blood glucose?
A) GLP-1
B) Insulin
C) Glucagon
D) Amylin
C) Glucagon - Glucagon is released during fasting to maintain glucose levels.
The liver maintains glucose homeostasis by:
A) Storing glucose as fatty acids
B) Inhibiting glucagon
C) Producing glucose via gluconeogenesis
D) Promoting renal excretion of glucose
C) Producing glucose via gluconeogenesis - The liver synthesizes glucose during fasting via gluconeogenesis.
Growth hormone increases blood glucose by:
A) Enhancing insulin sensitivity
B) Inhibiting gluconeogenesis
C) Increasing lipolysis and decreasing glucose uptake
D) Blocking glucagon
C) Increasing lipolysis and decreasing glucose uptake - Growth hormone contributes to insulin resistance by decreasing glucose uptake.
Which of the following is not a role of insulin?
A) Moves glucose into cells
B) Stimulates protein breakdown
C) Inhibits ketogenesis
D) Encourages glycogenesis
B) Stimulates protein breakdown - Insulin promotes protein synthesis, not breakdown
Which condition would most likely require more insulin?
A) Sleep
B) Exercise
C) Stress
D) Fasting
C) Stress - Stress triggers counter-regulatory hormones, increasing insulin needs.
When insulin is deficient, what happens to potassium levels?
A) Serum K+ decreases
B) Serum K+ increases
C) K+ shifts into cells
D) Renal K+ excretion increases
B) Serum K+ increases - Insulin deficiency causes K+ to shift out of cells, raising serum potassium.
GLP-1 agonists lower blood glucose by:
A) Blocking insulin
B) Increasing glucagon secretion
C) Delaying gastric emptying and enhancing insulin release
D) Inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis
C) Delaying gastric emptying and enhancing insulin release - GLP-1 lowers glucose by slowing digestion and boosting insulin.
Which of the following inhibits gluconeogenesis and lipolysis?
A) Glucagon
B) Cortisol
C) Insulin
D) Epinephrine
C) Insulin - Insulin inhibits gluconeogenesis and lipolysis.
Type 1 diabetes is primarily caused by:
A) Insulin resistance
B) Autoimmune destruction of beta cells
C) Excess cortisol
D) Increased hepatic glucose production
B) Autoimmune destruction of beta cells - Type 1 DM results from immune-mediated beta-cell destruction.
Which of the following is typical of Type 2 Diabetes?
A) Onset in childhood
B) Absolute insulin deficiency
C) Insulin resistance with relative deficiency
D) Autoimmune etiology
C) Insulin resistance with relative deficiency - Type 2 DM involves insulin resistance plus impaired insulin secretion.
A distinguishing feature of Type 1 Diabetes is:
A) Obesity-related onset
B) Strong family history
C) Presence of ketoacidosis
D) Slow onset
C) Presence of ketoacidosis - DKA is a hallmark of uncontrolled Type 1 diabetes.
A key feature of Type 2 diabetes pathophysiology is:
A) Pancreatic islet destruction
B) Insulin resistance in muscle and fat cells
C) Decreased counter-regulatory hormones
D) Excess insulin secretion
B) Insulin resistance in muscle and fat cells - Insulin resistance is central to Type 2 DM pathophysiology.
Which of the following symptoms is more common in T1DM at presentation?
A) Polyphagia
B) Weight gain
C) Acanthosis nigricans
D) Mild fatigue
A) Polyphagia - Polyphagia (excessive hunger) with weight loss is typical in T1DM.
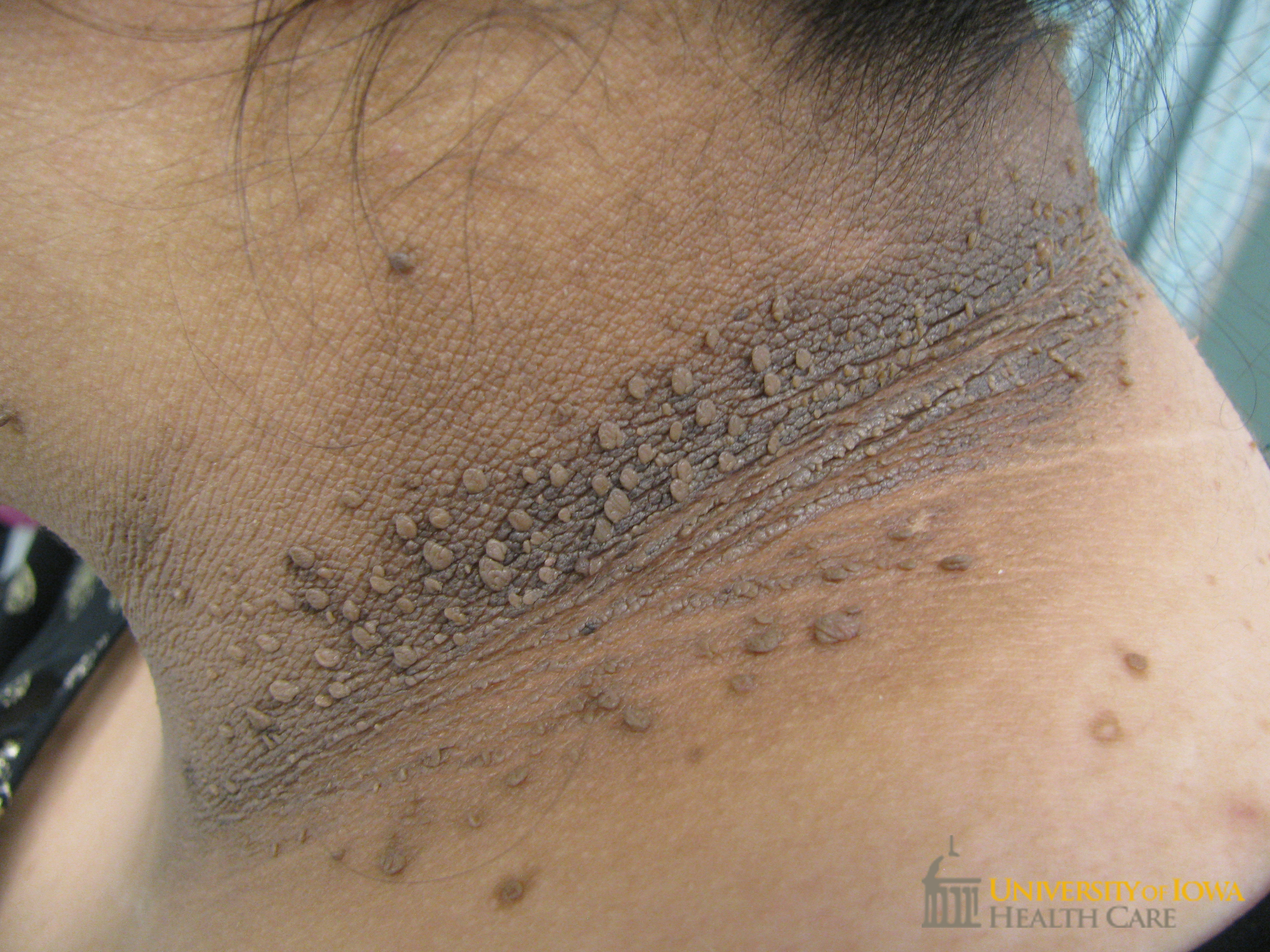
Acanthosis nigricans is most commonly associated with:
A) Type 1 DM
B) Type 2 DM
C) Diabetic ketoacidosis
D) Insulin overdose
B) Type 2 DM - Acanthosis nigricans is associated with insulin resistance seen in T2DM.
Type 2 DM is most commonly diagnosed in:
A) Children
B) Adolescents with weight loss
C) Overweight adults with gradual symptoms
D) Newborns
C) Overweight adults with gradual symptoms - T2DM often develops slowly in overweight adults.
Polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia result from:
A) Insulin resistance in the kidneys
B) Hyperinsulinemia
C) Hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis
D) Ketone toxicity
C) Hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis - Excess glucose causes water loss in urine, leading to polyuria/polydipsia.
Weight loss despite normal or increased appetite is classic in:
A) Type 2 DM
B) Type 1 DM
C) MODY
D) Gestational DM
B) Type 1 DM - T1DM patients lose weight despite eating due to insulin deficiency.
Which of the following is a microvascular complication of diabetes?
A) Coronary artery disease
B) Diabetic retinopathy
C) Peripheral vascular disease
D) Stroke
B) Diabetic retinopathy - Retinopathy is a microvascular complication affecting small retinal vessels.
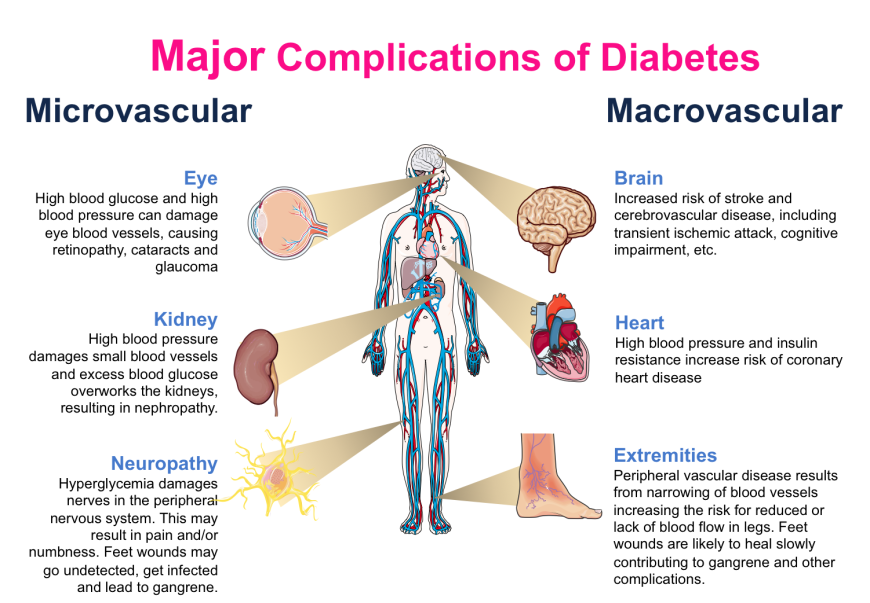
Macrovascular complications include all EXCEPT:
A) Peripheral vascular disease
B) Hypertension
C) Retinopathy
D) Coronary artery disease
C) Retinopathy - Retinopathy is microvascular; macrovascular complications include CAD, stroke, PVD.
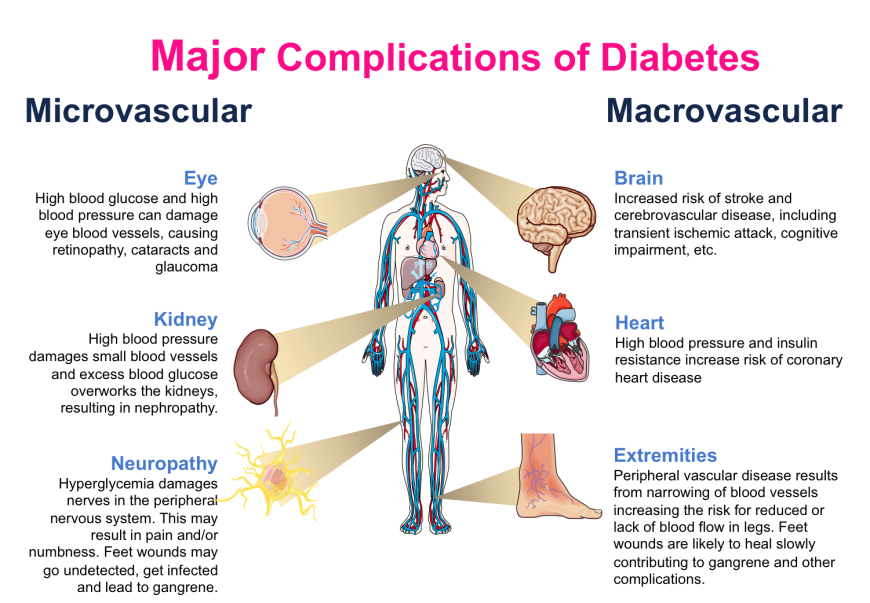
HHS differs from DKA in that:
A) It occurs only in T1DM
B) It involves ketosis
C) It features extreme hyperglycemia without ketones
D) It causes hypoglycemia
C) It features extreme hyperglycemia without ketones - HHS has minimal/no ketosis but very high glucose and dehydration.
Which symptom is most common in hypoglycemia?
A) Dry skin
B) Rapid heartbeat and sweating
C) Polyuria
D) Weight loss
B) Rapid heartbeat and sweating - Sympathetic activation (adrenergic symptoms) occurs first in hypoglycemia.
Which of the following would NOT be expected in HHS?
A) Blood glucose >34 mmol/L
B) Positive ketones
C) Dehydration
D) Altered LOC
B) Positive ketones - Unlike DKA, HHS has little to no ketone formation.
A client with DKA would most likely present with:
A) Fruity breath, rapid breathing
B) Bradycardia and constricted pupils
C) Normal potassium
D) Pale, cold extremities
A) Fruity breath, rapid breathing - Kussmaul respirations and acetone breath are hallmark signs of DKA.
The initial treatment for DKA includes:
A) Oral glucose
B) Subcutaneous insulin only
C) IV fluids and IV insulin
D) Beta blockers
C) IV fluids and IV insulin - Rehydration and insulin administration are critical to reverse DKA.
A nurse is reviewing labs for a client on metformin. Which lab value requires immediate follow-up?
A. ALT: 45 U/L
B. eGFR: 25 mL/min/1.73m²
C. Hemoglobin A1C: 8.5%
D. Creatinine: 0.9 mg/dL
B – Metformin is contraindicated when eGFR <30 due to the risk of lactic acidosis.
What is the primary pharmacodynamic action of metformin?
A. Stimulates insulin secretion
B. Inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis
C. Blocks carbohydrate absorption
D. Enhances renal glucose reabsorption
B – Metformin primarily decreases hepatic glucose production (gluconeogenesis)
Why is metformin often first-line in type 2 diabetes?
A. Causes significant hypoglycemia
B. Improves insulin sensitivity
C. Raises liver glucose output
D. Boosts pancreatic insulin production
B – Metformin improves insulin sensitivity, helping cells respond better to insulin.
A patient asks how metformin works. Which is the best response?
A. "It stimulates insulin release."
B. "It helps your liver make more glucose."
C. "It helps your body use insulin better."
D. "It increases sugar absorption in your gut."
C – It improves insulin sensitivity rather than increasing insulin production.
Metformin should be withheld before and after which procedure?
A. Blood transfusion
B. CT scan with contrast
C. Colonoscopy
D. EKG
B – Hold metformin 24–48 hours before and after contrast to avoid lactic acidosis.
Which client would you question the use of metformin in?
A. A 72-year-old with COPD
B. GFR of 35
C. Client scheduled for contrast CT
D. Type 2 diabetic with high cholesterol
C – Contrast + metformin increases lactic acidosis risk; must hold metformin.
Lactic acidosis from metformin is most likely in:
A. Liver failure
B. Well-controlled diabetes
C. Mild dehydration
D. GERD
A – Lactic acidosis risk increases in liver failure due to impaired lactate clearance.
What is the expected effect of metformin?
A. Increased insulin secretion
B. Lower fasting glucose
C. Increased appetite
D. Hypoglycemia when fasting
B – Metformin lowers fasting glucose through reduced hepatic output.
A risk of sulfonylurea therapy in older adults is:
A. Hyperkalemia
B. Hypoglycemia
C. Weight loss
D. Lactic acidosis
B – Hypoglycemia is a major risk, especially in older adults.
Which meal instruction is appropriate for gliclazide?
A. "Skip meals if not hungry."
B. "Take it only if your sugar is high."
C. "Take it with breakfast."
D. "Take it at bedtime."
C – Take with food to reduce risk of hypoglycemia.
Which medication interaction is most concerning with sulfonylureas?
A. Acetaminophen
B. Beta-blockers
C. Antacids
D. Multivitamins
B – Beta-blockers (such as metoprolol) can mask hypoglycemia symptoms.
Which statement shows understanding of repaglinide?
A. "It lowers sugar by helping me absorb more."
B. "It replaces my missing insulin."
C. "It helps my pancreas release insulin."
D. "It stops my liver from making sugar."
C – The primary action is helping the pancreas release insulin.
In which patient would you avoid sulfonylureas?
A. Low fasting insulin
B. Long-standing diabetes
C. Frequent hypoglycemia
D. Recent weight gain
C – Avoid in those prone to hypoglycemia due to increased risk.
Sulfonylureas are contraindicated in:
A. Older adults with renal impairment
B. Clients with obesity
C. Clients with hypertension
D. Clients on statins
A – Impaired renal function increases risk for hypoglycemia with sulfonylureas.
Sulfonylureas may cause weight gain due to:
A. Reduced liver glucose
B. Reduced satiety
C. Increased insulin levels
D. Glucose excretion
C – Increased insulin leads to more fat storage and weight gain.
Which insulin has the fastest onset?
A. Regular
B. NPH
C. Glargine
D. Lispro
D – Lispro is rapid-acting with an onset in 15 minutes.
A patient on insulin and metformin has a fasting glucose of 3.5 mmol/L. What is the priority?
A. Give orange juice
B. Administer insulin
C. Hold metformin
D. Give glucagon
A – Hypoglycemia is present; treat with fast-acting sugar.
Which insulin mimics basal secretion?
A. Lispro
B. NPH
C. Glargine
D. Regular
C – Glargine provides steady basal insulin over 24 hours.
A type 1 diabetic skips a meal after insulin. What is the concern?
A. Hyperglycemia
B. Hypoglycemia
C. Ketoacidosis
D. Infection
B – Skipping meals post-insulin increases risk of hypoglycemia.
When does NPH insulin typically peak?
A. 1 hour
B. 2–4 hours
C. 6–14 hours
D. 24 hours
C – NPH typically peaks 6–14 hours after administration.
How does glargine differ from regular insulin?
A. Shorter half-life
B. Immediate peak
C. Prolonged, steady action
D. More hypoglycemia
C – Glargine has a flat, prolonged action without peaks.
A patient with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes is prescribed metformin. What is the primary mechanism of action of metformin?
A. Stimulates pancreatic insulin secretion
B. Decreases hepatic glucose production
C. Enhances intestinal glucose absorption
D. Inhibits renal glucose reabsorption
B - Metformin decreases hepatic glucose production and improves insulin sensitivity.
A nurse is providing education to a patient on metformin. Which of the following should the nurse include as a common side effect?
A. Weight gain
B. Hypoglycemia
C. Metallic taste
D. Pancreatitis
C - Metallic taste is a common side effect of metformin; it rarely causes hypoglycemia.
A nurse should hold metformin prior to a CT scan with IV contrast due to risk of:
A. Pancreatic necrosis
B. Lactic acidosis
C. Diabetic ketoacidosis
D. Respiratory depression
B - IV contrast may impair renal function and increase risk of lactic acidosis with metformin.
Which of the following patients is most likely to benefit from GLP-1 receptor agonists?
A. A patient with type 1 diabetes
B. A patient who requires immediate insulin replacement
C. A patient with type 2 diabetes and obesity
D. A patient in hypoglycemic crisis
C - GLP-1 agonists aid in weight loss and are useful in T2DM patients with obesity (GLP-1 increases satiety and decrease appetite)
The nurse understands that the mechanism of action of sulfonylureas involves:
A. Increasing glucose excretion via urine
B. Inhibiting intestinal glucose absorption
C. Stimulating beta-cell insulin release
D. Slowing gastric emptying
C - Sulfonylureas stimulate pancreatic beta cells to secrete insulin.
Which adverse effect is most concerning when administering a sulfonylurea like gliclazide?
A. Constipation
B. Edema
C. Hypoglycemia
D. Blurred vision
C - Hypoglycemia is a major risk with sulfonylureas, especially in the elderly.
Acarbose is best administered:
A. On an empty stomach
B. After meals
C. With the first bite of a meal
D. Only at bedtime
C - Acarbose is taken with the first bite to inhibit carbohydrate absorption.
A patient taking pioglitazone should be monitored closely for which serious adverse effect?
A. Renal failure
B. Hepatotoxicity
C. Heart failure exacerbation
D. Anaphylaxis
C - Pioglitazone can cause fluid retention and worsen heart failure.
A nurse is reviewing labs for a diabetic patient on a thiazolidinedione (TZD). Which lab requires immediate attention?
A. AST 98 U/L
B. Fasting glucose 8.0 mmol/L
C. HbA1c 6.8%
D. Triglycerides 1.7 mmol/L
A - AST of 98 is high; TZDs can cause liver toxicity, requiring monitoring.
Which class of drugs slows the inactivation of incretin hormones?
A. Biguanides
B. Sulfonylureas
C. DPP-4 inhibitors
D. SGLT2 inhibitors
C - DPP-4 inhibitors prevent breakdown of incretins, enhancing insulin secretion.
A nurse should question the use of sitagliptin in a patient with:
A. Heart failure
B. Hypothyroidism
C. Chronic pancreatitis
D. Renal failure
C - Sitagliptin may increase risk of pancreatitis. Use caution or avoid if history present.
Which statement indicates understanding of SGLT2 inhibitors like canagliflozin?
A. “I may notice increased hunger.”
B. “I should drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration.”
C. “This medication may cause weight gain.”
D. “It increases insulin secretion from the pancreas.”
B - SGLT2 inhibitors cause diuresis; hydration is essential to prevent hypotension and AKI.
Which complication is associated with SGLT2 inhibitors?
A. Hypothyroidism
B. Lactic acidosis
C. Yeast infection in females
D. Hepatitis
C - SGLT2 inhibitors increase glucose in urine, promoting fungal infections.
Rapid-acting insulin (e.g., insulin lispro) should be administered:
A. 30 minutes after meals
B. 15 min before meals
C. Before bedtime
D. Without regard to meals
B - Rapid insulin should be given 15 mins before meals to match peak glucose rise.
A patient receives regular insulin subcutaneously at 0800. The nurse should monitor for hypoglycemia at what time?
A. 0815–0845
B. 1000–1200
C. 1300–1500
D. 1700–1900
B - Regular insulin peaks around 1–5 hours; monitor for hypoglycemia then.
A nurse is educating a patient on signs of hypoglycemia. Which symptom is most characteristic?
A. Bradycardia
B. Dry, flushed skin
C. Confusion and tremors
D. Slow deep breathing
C - Confusion, tremors, anxiety, and sweating are common hypoglycemia signs.
Which insulin has the longest duration of action?
A. Lispro
B. Regular
C. NPH
D. Glargine
D - Glargine is long-acting, lasting up to 24 hours.
The primary reason insulin glargine cannot be mixed with other insulins is:
A. It is acidic and incompatible
B. It causes rapid onset
C. It denatures other insulins
D. It causes injection site necrosis
A - Glargine's acidic pH makes it incompatible with other insulins.
The onset of action for NPH insulin is:
A. 5–15 minutes
B. 30–60 minutes
C. 1–2 hours
D. 4–6 hours
C - NPH insulin has an onset of 1–2 hours.
A nurse is teaching a patient starting insulin detemir. Which statement shows correct understanding?
A. “I can mix this with my rapid-acting insulin.”
B. “This insulin peaks in 30 minutes.”
C. “I should take this at the same time every day.”
D. “It needs to be taken right before meals.”
C - Detemir is long-acting and should be taken at the same time daily.
A patient on insulin therapy is found unconscious and diaphoretic. What is the nurse’s priority action?
A. Give IV potassium
B. Administer IV dextrose
C. Notify the physician
D. Start an insulin infusion
B - The priority is treating suspected hypoglycemia with IV glucose.
Which of the following reflects the dawn phenomenon in diabetes?
A. Hypoglycemia due to excessive nighttime insulin
B. Normal glucose at bedtime but high fasting morning glucose
C. Low fasting glucose due to missed dinner
D. Elevated glucose following steroid use
B - Dawn phenomenon = high morning glucose without preceding hypoglycemia.
Which lab value is most reliable in assessing long-term glucose control?
A. Random plasma glucose
B. Postprandial glucose
C. HbA1c
D. Serum insulin
C - HbA1c reflects 2–3 months of glucose control.
In type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance leads to:
A. Decreased glucagon levels
B. Decreased glucose reabsorption in kidneys
C. Increased hepatic glucose output
D. Increased pancreatic alpha cell destruction
C - Insulin resistance increases hepatic glucose production.
Which of the following is a contraindication to metformin use?
A. Mild hyperlipidemia
B. GFR <30 mL/min/1.73m²
C. BMI >30
D. Type 2 diabetes
B - Metformin is contraindicated if GFR is <30 due to lactic acidosis risk.
What is a common nursing consideration for GLP-1 receptor agonists like liraglutide?
A. Must be taken with meals
B. Risk of thyroid C-cell tumors
C. Causes immediate hypoglycemia
D. Given orally before meals
B - GLP-1 agonists carry black box warning for thyroid C-cell tumors.
Which symptom would require discontinuation of a GLP-1 agonist?
A. Nausea
B. Vomiting
C. Persistent abdominal pain
D. Decreased appetite
C - Persistent abdominal pain may indicate pancreatitis.
A patient on SGLT2 inhibitors should be taught to monitor for:
A. Hypokalemia
B. Vision changes
C. UTI symptoms
D. Constipation
C - SGLT2 inhibitors increase UTI and yeast infection risk.
Why are alpha-glucosidase inhibitors less likely to cause hypoglycemia?
A. They increase insulin production
B. They reduce hepatic glucose output
C. They slow carbohydrate absorption only
D. They increase glucose excretion
C - They only affect carbohydrate absorption—not insulin/glucose production.
Which insulin should be drawn up first when mixing NPH and regular insulin?
A. NPH
B. Regular
C. Doesn’t matter
D. Whichever is smaller in volume
B - “Clear before cloudy”: draw up regular (clear) before NPH (cloudy).
Which statement about insulin pens is correct?
A. Prime with 5 units before each use
B. Store all pens in the refrigerator
C. Share pens with close family only
D. Use the same needle multiple times
A - Always prime pens before use to ensure dosing accuracy.
Which antidiabetic drug class is most associated with weight loss?
A. Sulfonylureas
B. GLP-1 receptor agonists
C. Thiazolidinediones
D. Insulin
B - GLP-1 agonists promote satiety and weight loss.
The nurse should assess for which electrolyte imbalance in patients on SGLT2 inhibitors?
A. Hyponatremia
B. Hyperkalemia
C. Hypokalemia
D. Hypernatremia
A. SGLT2 inhibitors cause osmotic diuresis, which may lead to hyponatremia.
What is the best nursing action before administering NPH insulin?
A. Shake the vial vigorously
B. Roll the vial gently to mix
C. Dilute with sterile water
D. Warm in the microwave briefly
B - NPH insulin should be gently rolled to mix suspension.
A patient with diabetes has an HbA1c of 9.0%. What does this value indicate?
A. Excellent glucose control
B. Prediabetes
C. Poor long-term glucose control
D. Hypoglycemia risk
C - HbA1c >8% indicates poor control over time.
A nurse is monitoring a patient on sulfonylureas. Which adverse effect is most concerning?
A. Constipation
B. Dry mouth
C. Hypoglycemia
D. Weight loss
C - Sulfonylureas stimulate insulin release, causing hypoglycemia.
Which of the following best describes the MOA of sulfonylureas like gliclazide?
A. Enhances glucose excretion by kidneys
B. Inhibits carbohydrate digestion
C. Stimulates insulin release from beta cells
D. Delays gastric emptying
C - They promote insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells.
A patient reports they’ve been skipping meals while taking repaglinide. What is the nurse’s priority concern?
A. Hyperglycemia
B. Pancreatitis
C. Hypoglycemia
D. Dehydration
C - Skipping meals while on repaglinide increases hypoglycemia risk.
Which oral antidiabetic agent increases insulin sensitivity in muscle and fat but may cause weight gain?
A. Acarbose
B. Pioglitazone
C. Sitagliptin
D. Metformin
B - Pioglitazone improves insulin sensitivity but may cause weight gain due to fluid retention
A major adverse effect of thiazolidinediones like pioglitazone is:
A. Renal failure
B. Lactic acidosis
C. Fluid retention and heart failure
D. Severe hypoglycemia
C - Thiazolidinediones can cause fluid retention and worsen heart failure.
Which nursing assessment is most important before administering TZD?
A. Serum calcium
B. History of heart failure
C. Urine ketones
D. Liver ultrasound
B - Contraindicated in patients with heart failure.
Acarbose works by:
A. Stimulating insulin release
B. Delaying absorption of carbohydrates in the intestine
C. Suppressing hepatic glucose production
D. Enhancing insulin receptor sensitivity
B - Acarbose delays intestinal carbohydrate digestion.
Which symptom would warrant stopping acarbose therapy?
A. Mild bloating
B. Abdominal pain and severe flatulence
C. Soft stools
D. Decreased appetite
B - Severe GI symptoms may warrant discontinuation.