Urinary A&P
1/39
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
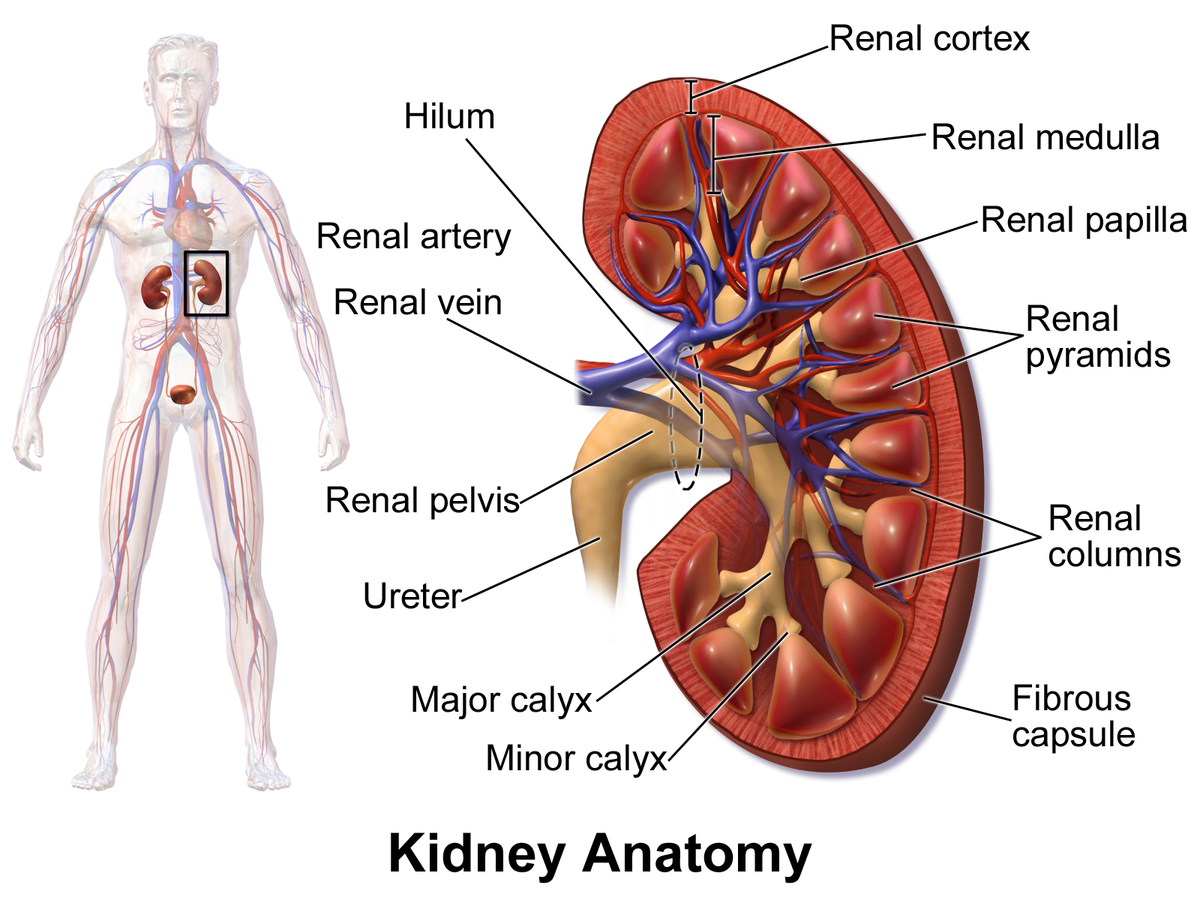
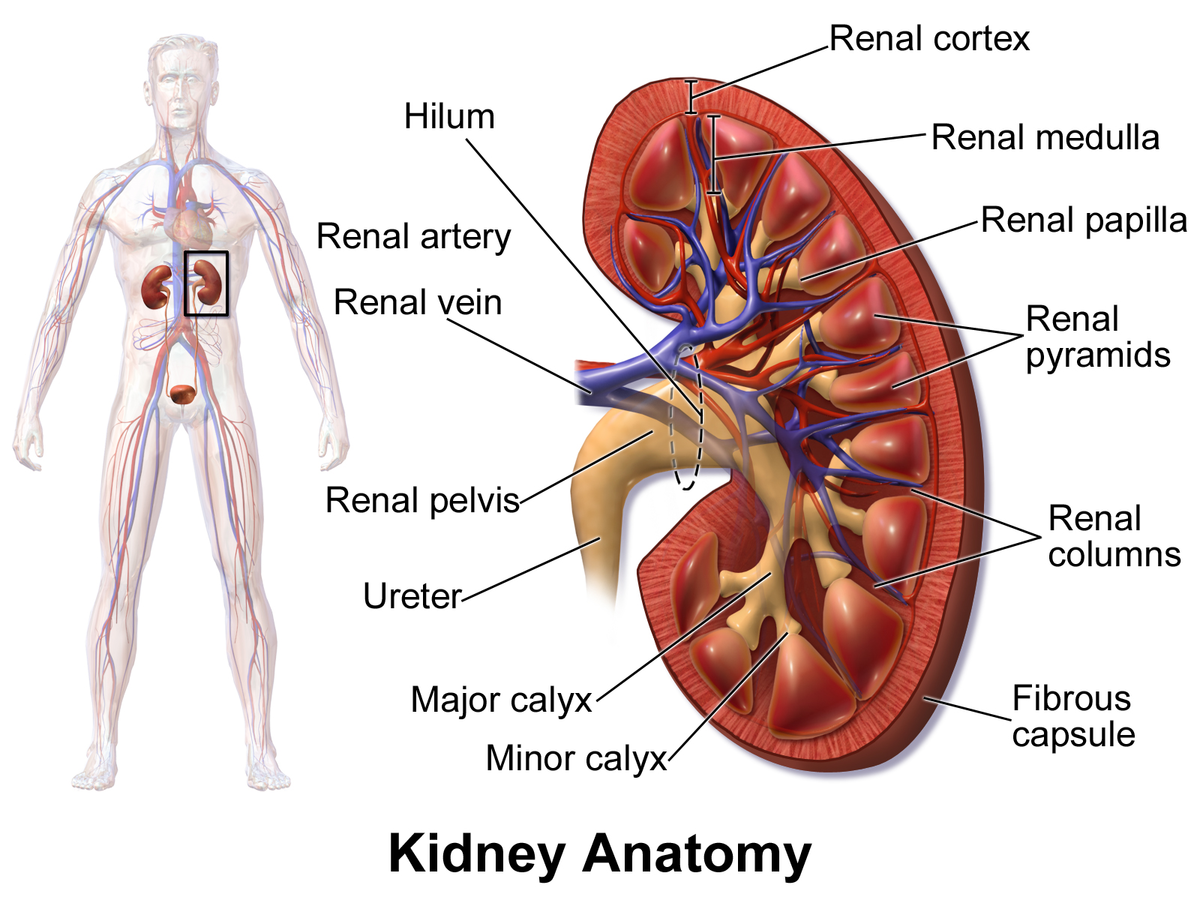
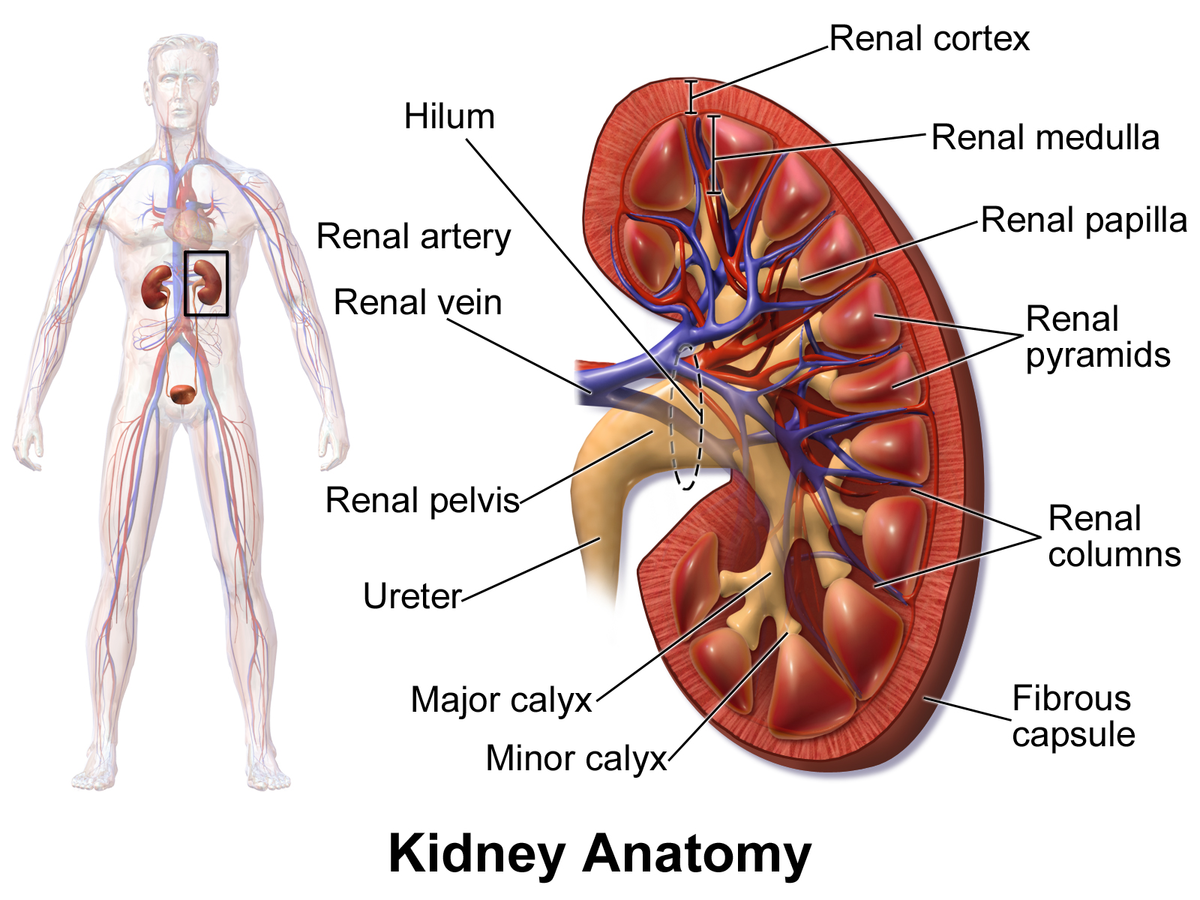
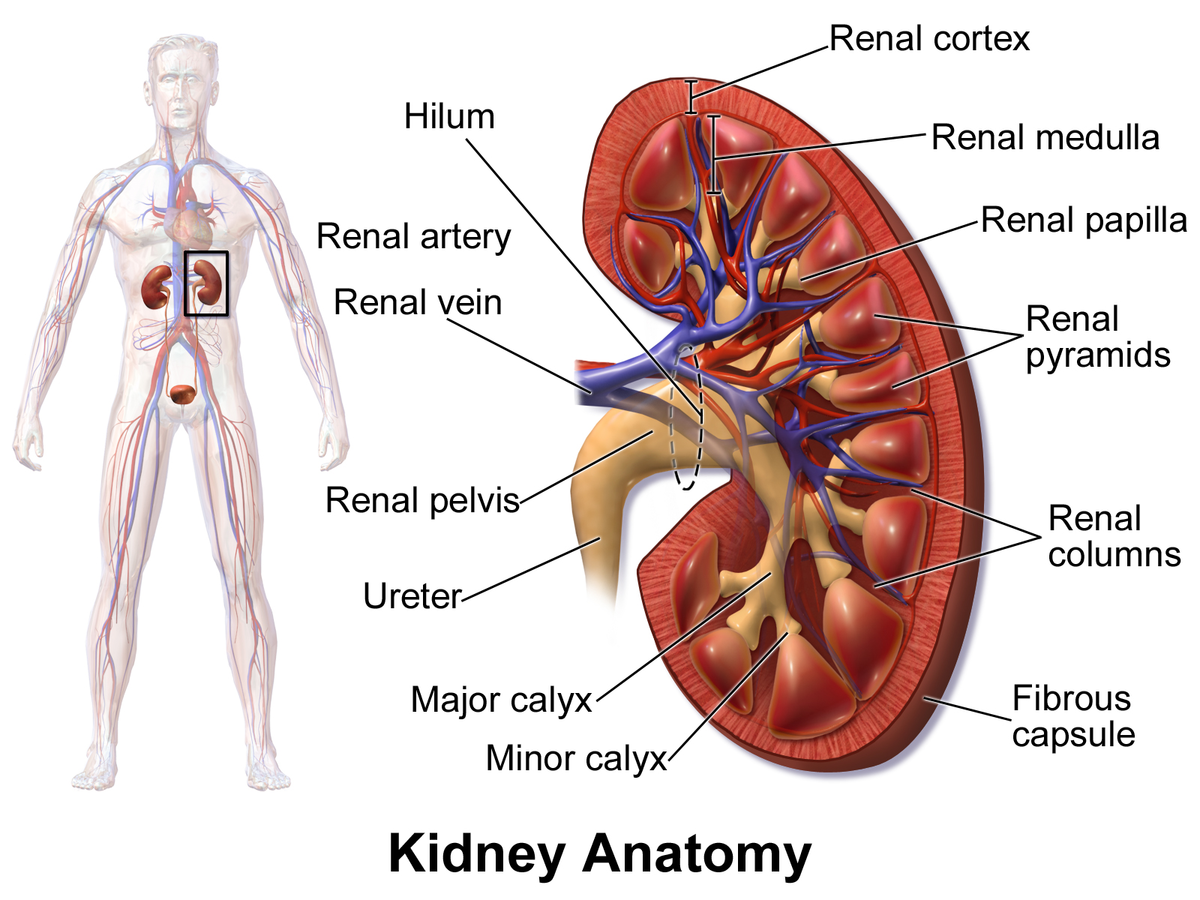
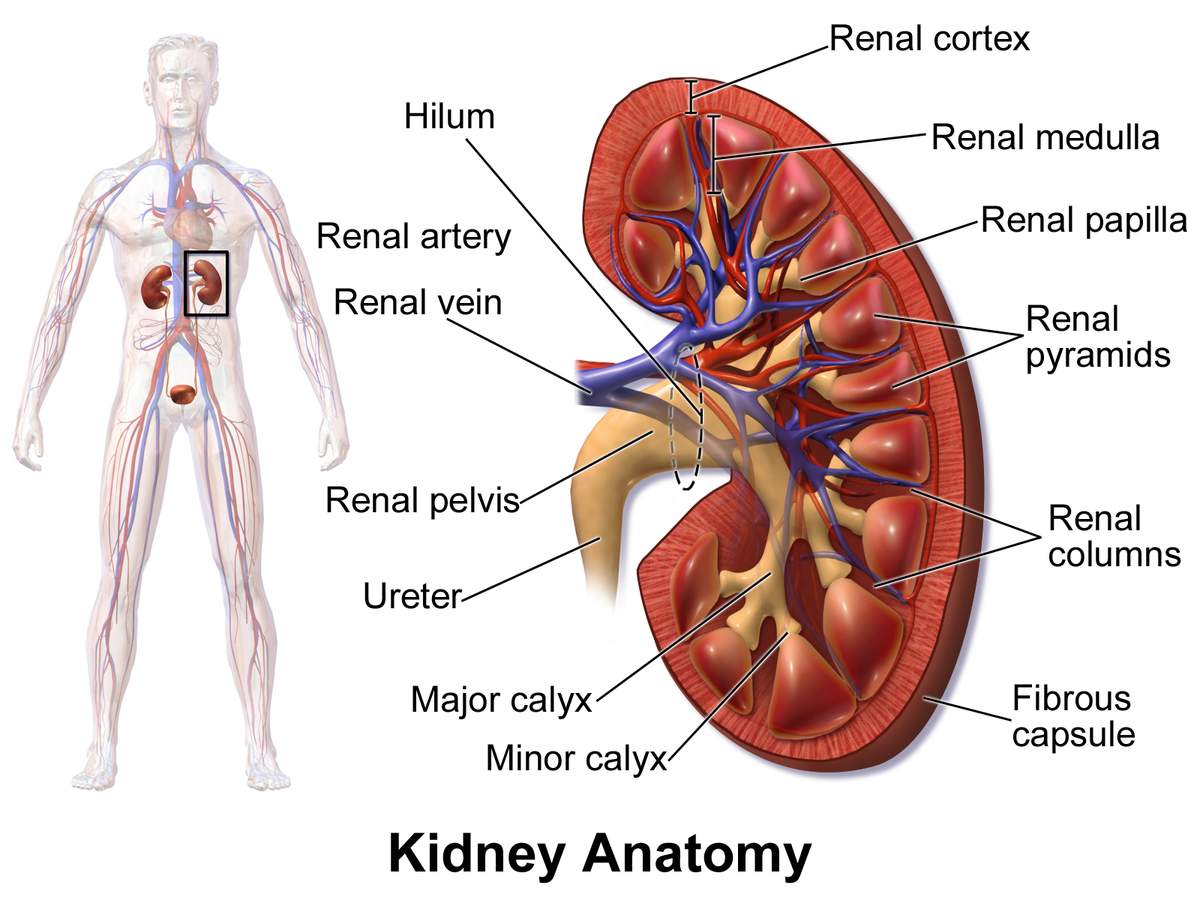
kidney
a pair of bean-shaped organs located below the rib cage that filter blood to remove waste and excess fluid; maintains blood pressure and balances minerals and vitamins
cortex
the outermost layer of the kidney, located just below the renal capsule; a granular, reddish-brown tissue that contains numerous nephrons
medulla
the inner region of the kidney responsible for filtering waste, reabsorbing water and electrolytes; helps balance salts and minerals; contains loops of henle and collecting ducts
renal columns
extensions of the renal cortex that project into the renal medulla, separating the cone-shaped renal pyramids; serve as structural support for the kidney, a pathway for blood vessels entering and exiting the cortex; contains urinary tubules and fibrous material
renal pyramids
cone-shaped structures in the kidneys inner part (renal medulla) responsible for concentrating urine; composed of parallel tubules that transport urine from outer cortex to the papillae where urine drains into the calyces.
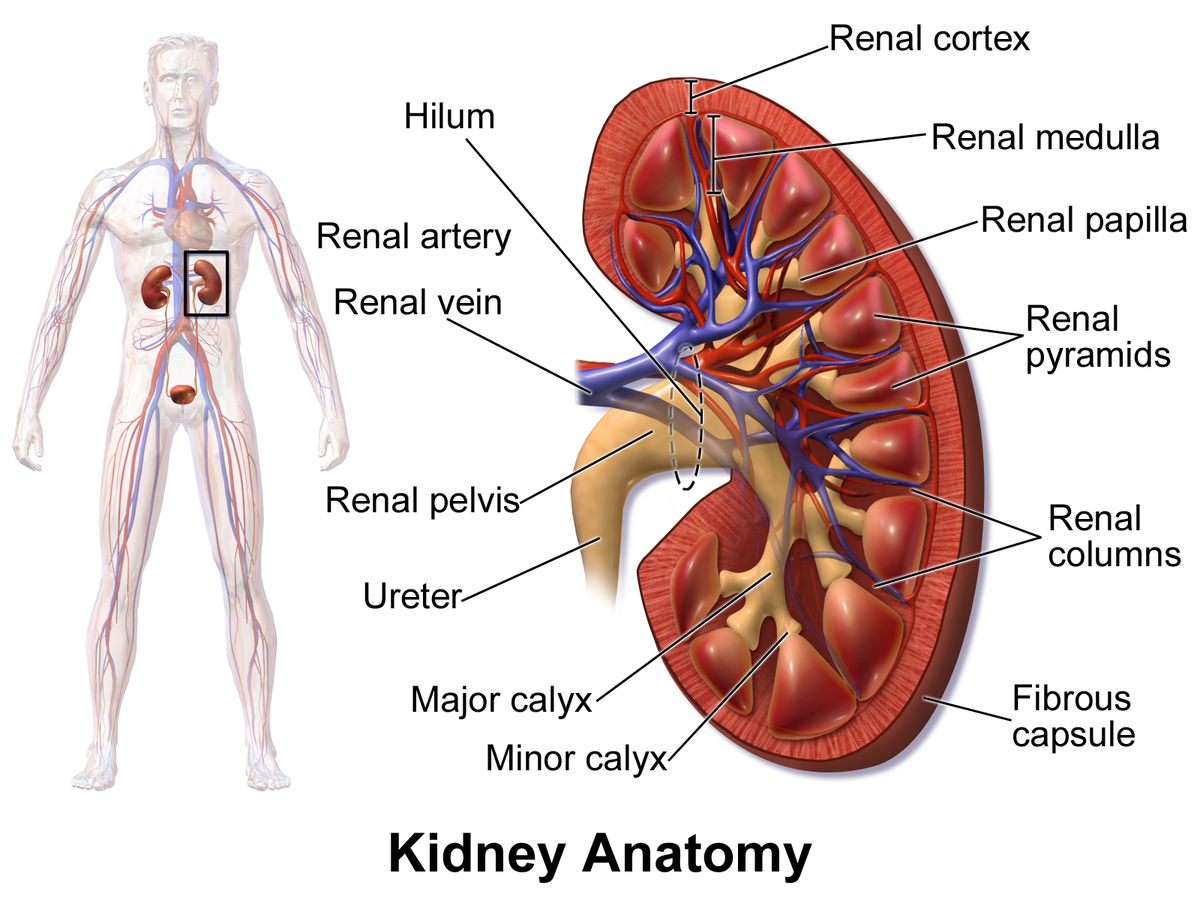
renal papilla
the tip of renal pyramids; a cone-shaped structure located at the apex of the renal pyramids in the kidney; collects urine from collecting ducts (calyces) and directs it into the renal pelvis
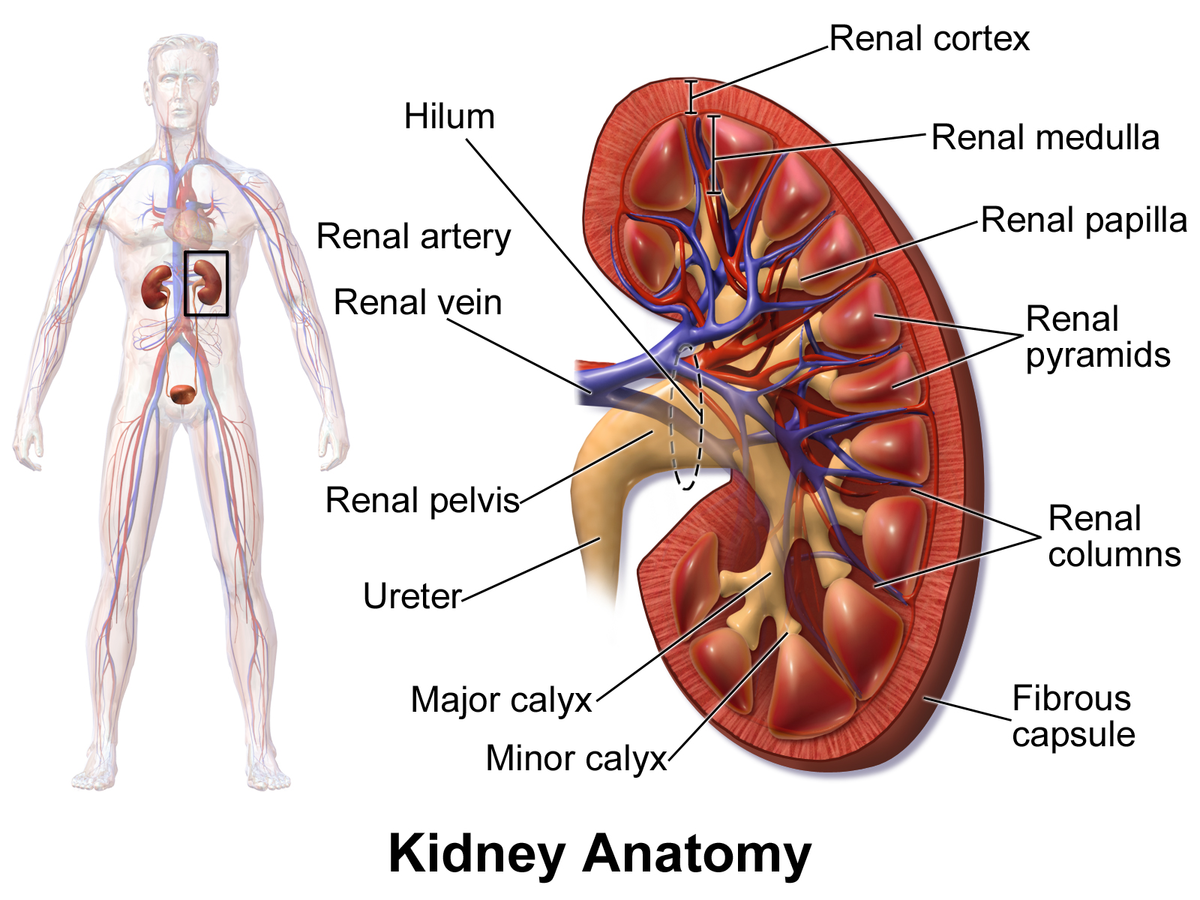
minor calyx
a small, funnel-shaped structure located in the kidney at the apex of each renal pyramid; collects and transports urine from renal pyramids to the major calyces
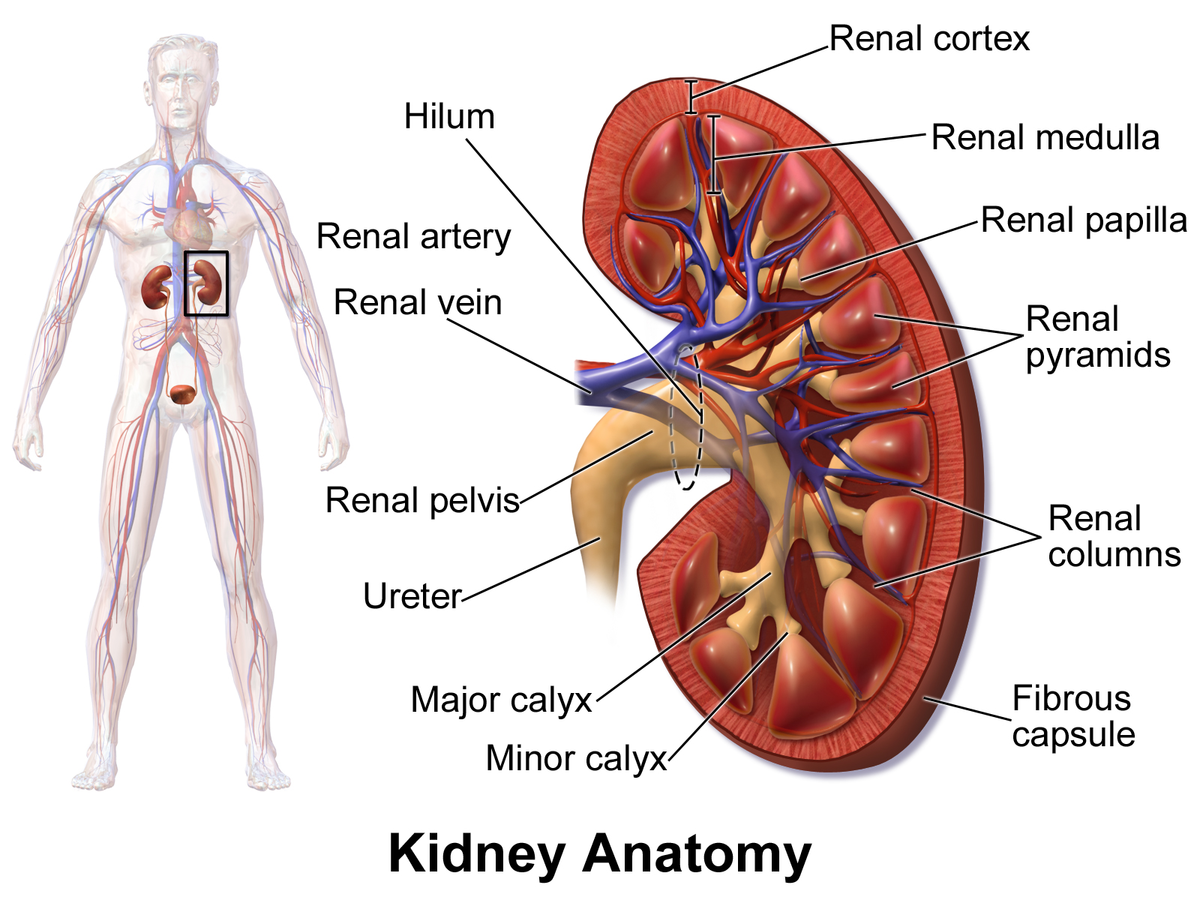
major calyx
a funnel-shaped structure in the kidney that collects urine from the minor calyces and directs it into the renal pelvis; located in renal sinus and occurs when two or more minor calyces join.
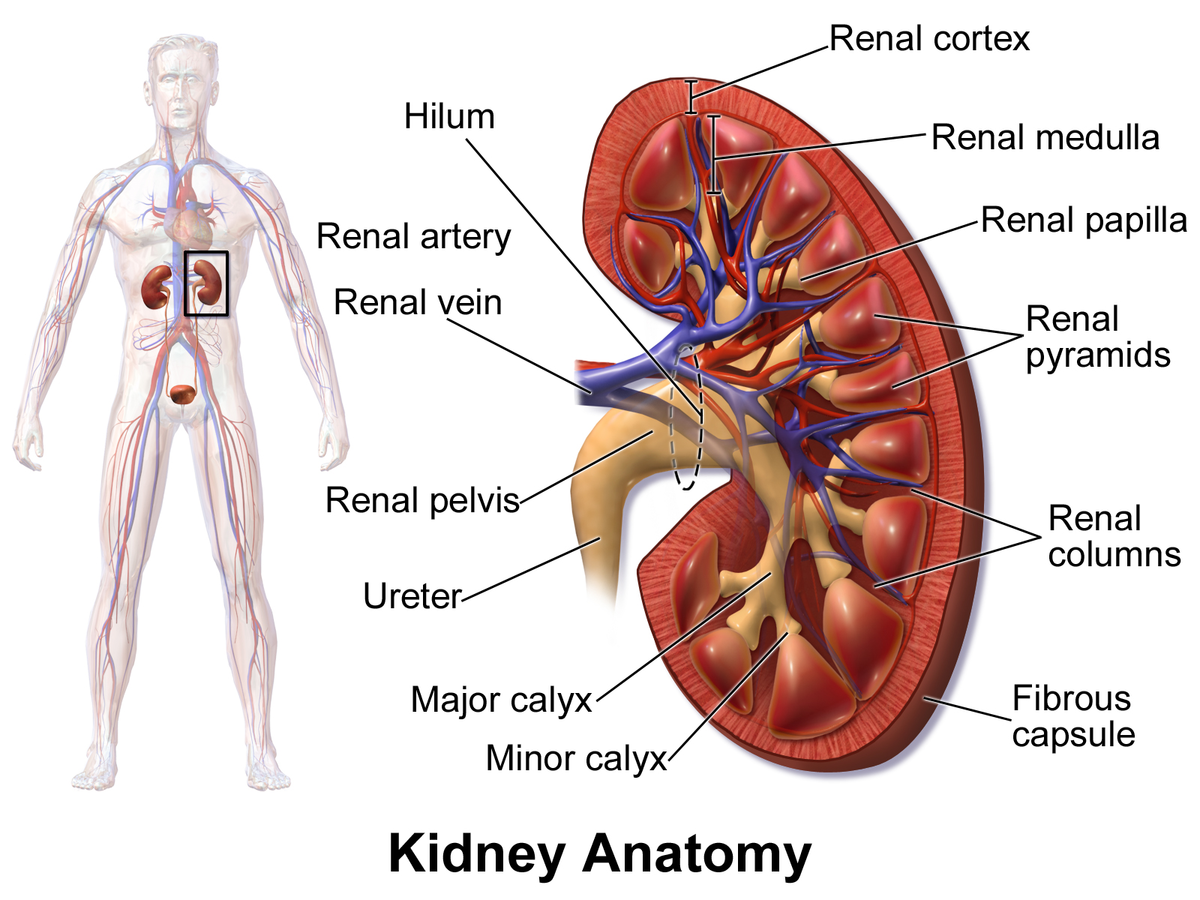
renal pelvis
a funnel-shaped structure located in the kidney that collects urine and directs it to the ureter; formed by the convergence of major calyces and exits the kidney through the renal hilum
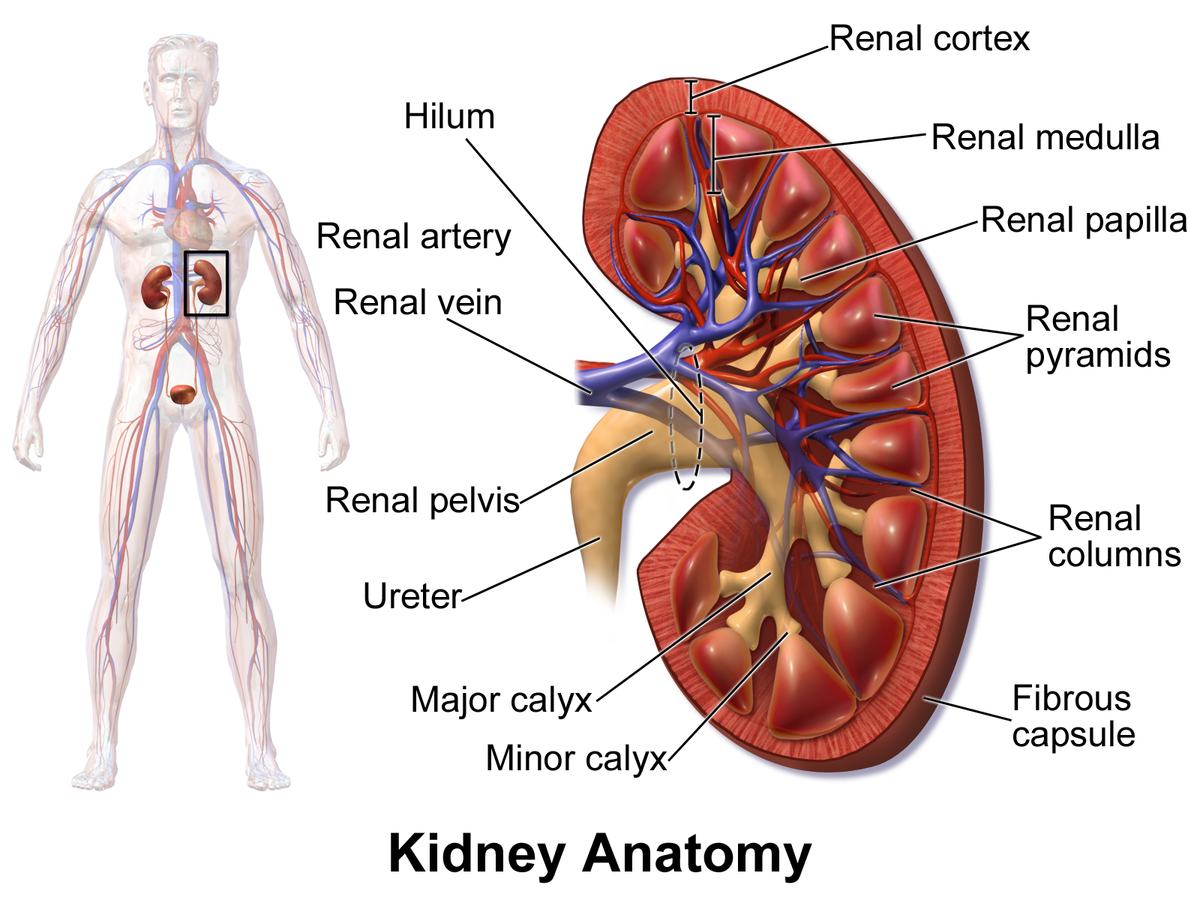
renal artery
two large blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to the kidneys; originates from abdominal aorta; supplies the kidneys with oxygen and nutrients necessary for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine
renal vein
two large blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava; transports waste products and excess fluid that has been filtered from the kidneys
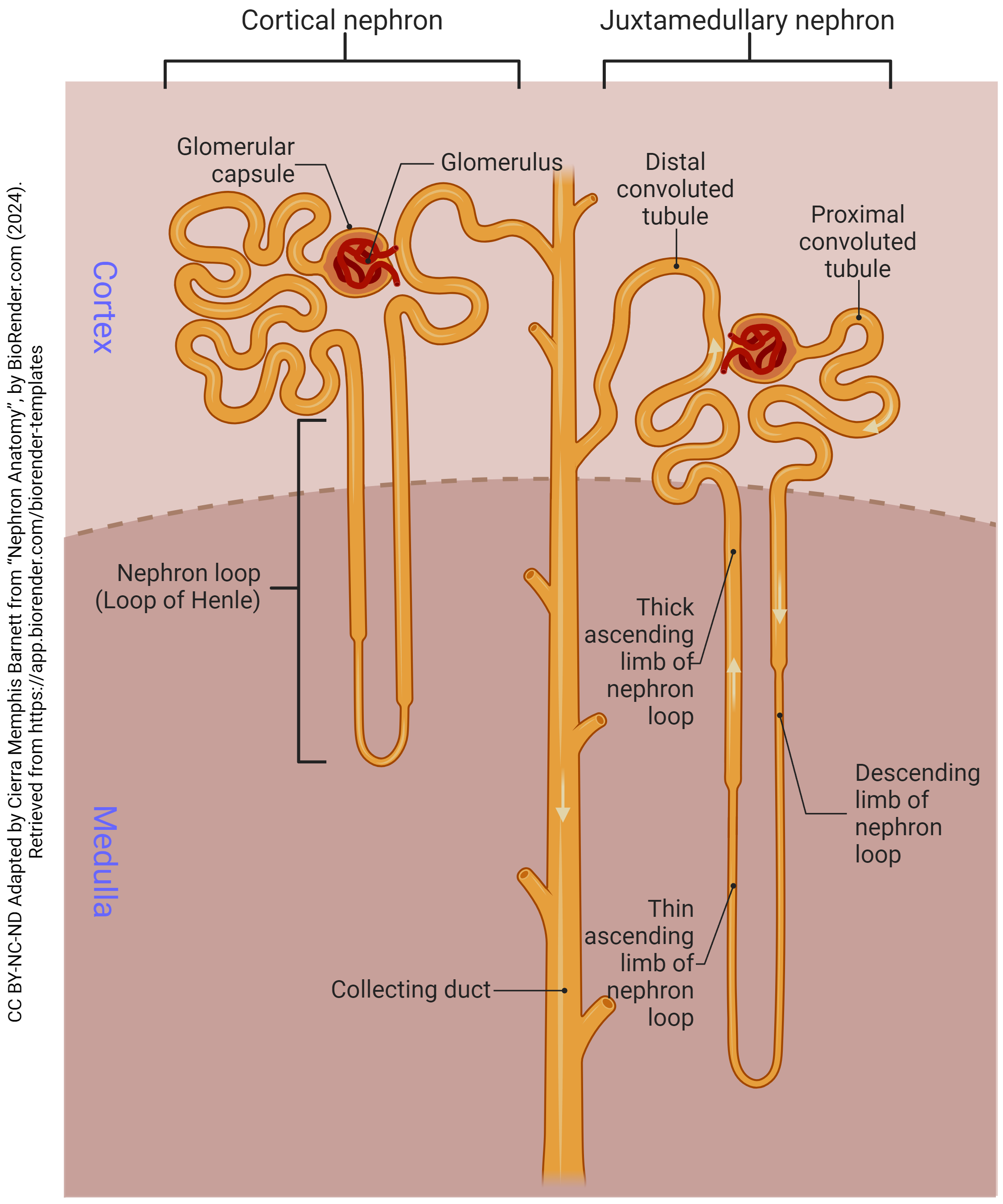
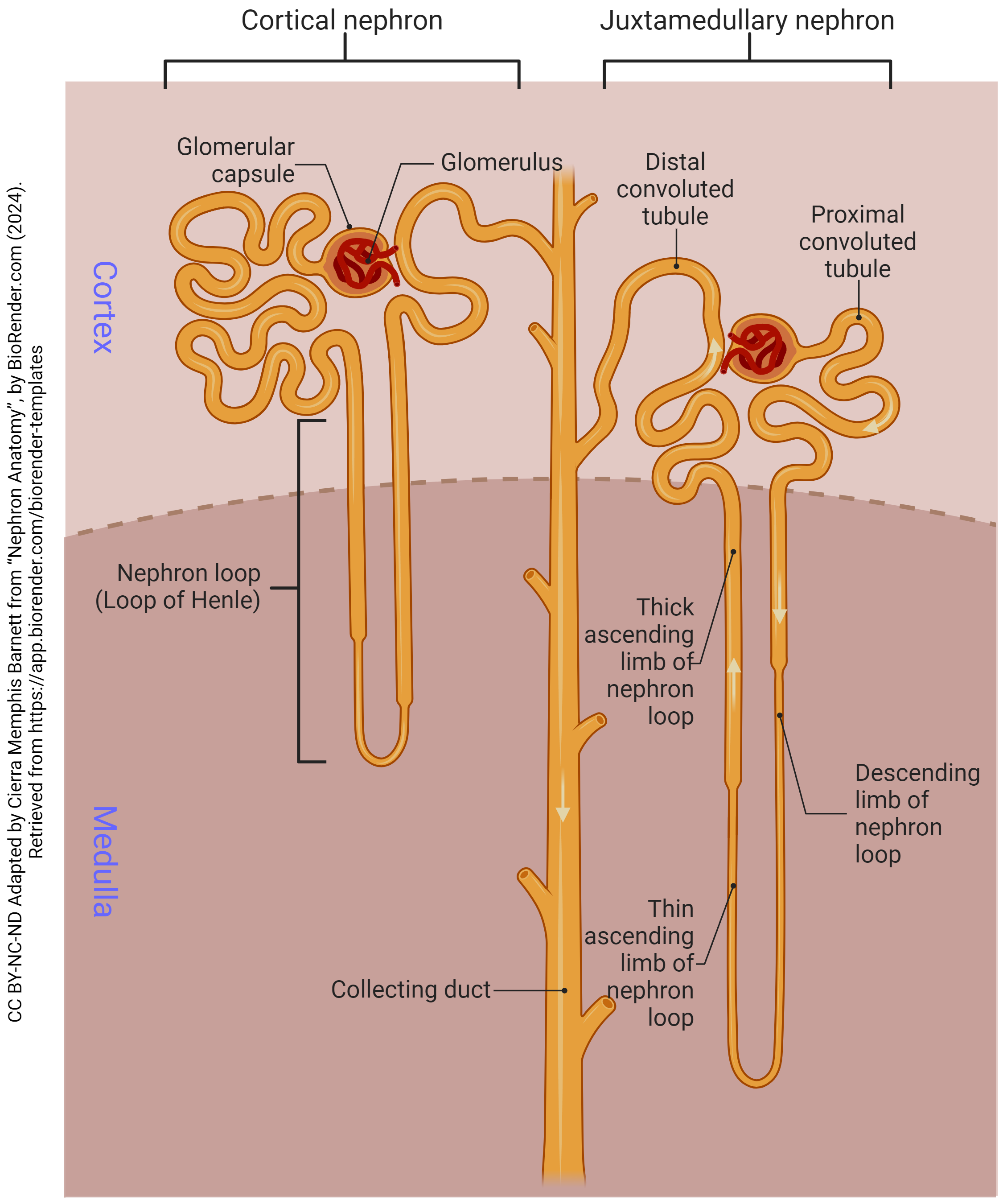
Nephron
has 5 parts, including renal corpuscle; the functional unit of the kidney, responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine; composed of the renal corpuscle, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of henle, distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct
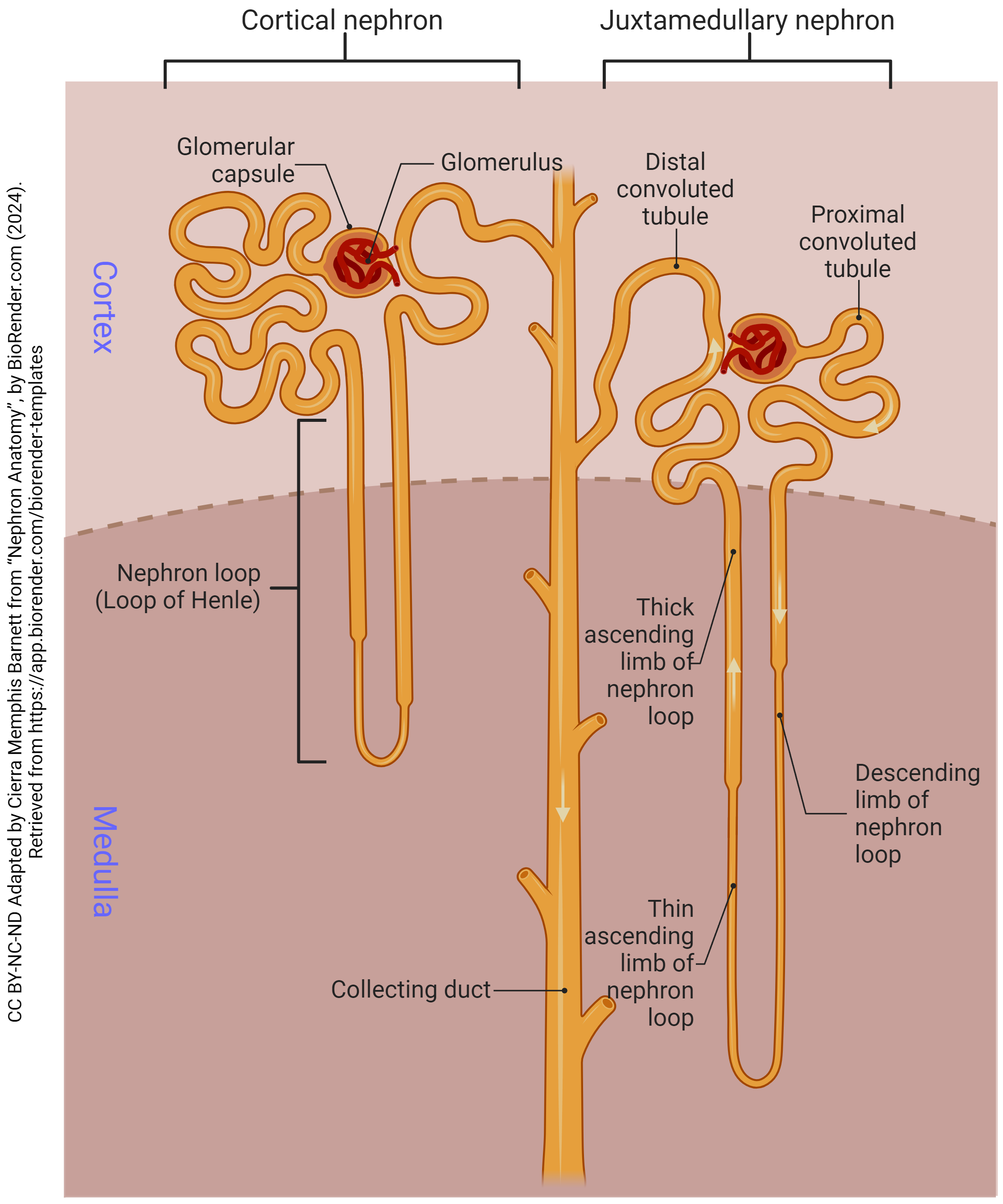
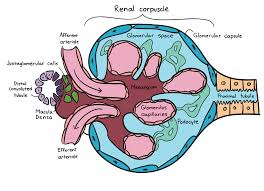
renal corpuscle
has 3 parts — glomerulus, bowman’s capsule and capsular space; part of the kidney’s nephron responsible for filtering blood; filters small molecules like water and ions from the blood, forming the initial filtrate that will later become urine.
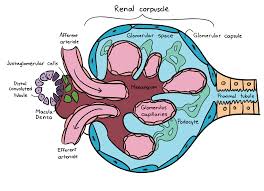
glomerus
view under histology?; a cluster of nerve endings, spores, or small blood vessels, in a particular cluster of capillaries around the end of a kidney tubule, where waste products are filtered from the blood
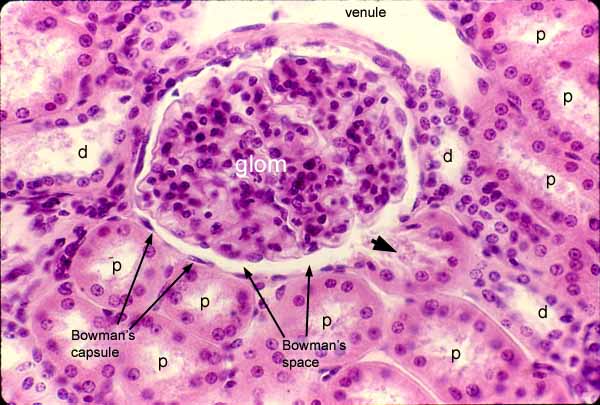
Bowmans capsule
a capsule-shaped membranous structure surrounding the glomerulus of each nephron in the kidneys of mammals that extracts wastes, excess salts, and water from the blood
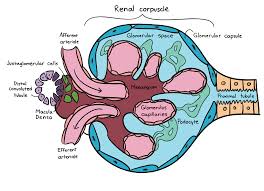
capsular space
a small, crescent shaped area located within the renal corpuscle of the kidney; the space between bowman’s capsule and the glomerulus
proximal convoluted tubule
the first coiled portion of the renal tubule in the nephron, located in the kidney’s cortex; primary functions are to reabsorb essential substances (glucose, amino acids, water, ions, vitamins) from the glomerular filtrate back into the blood while also secreting by-products
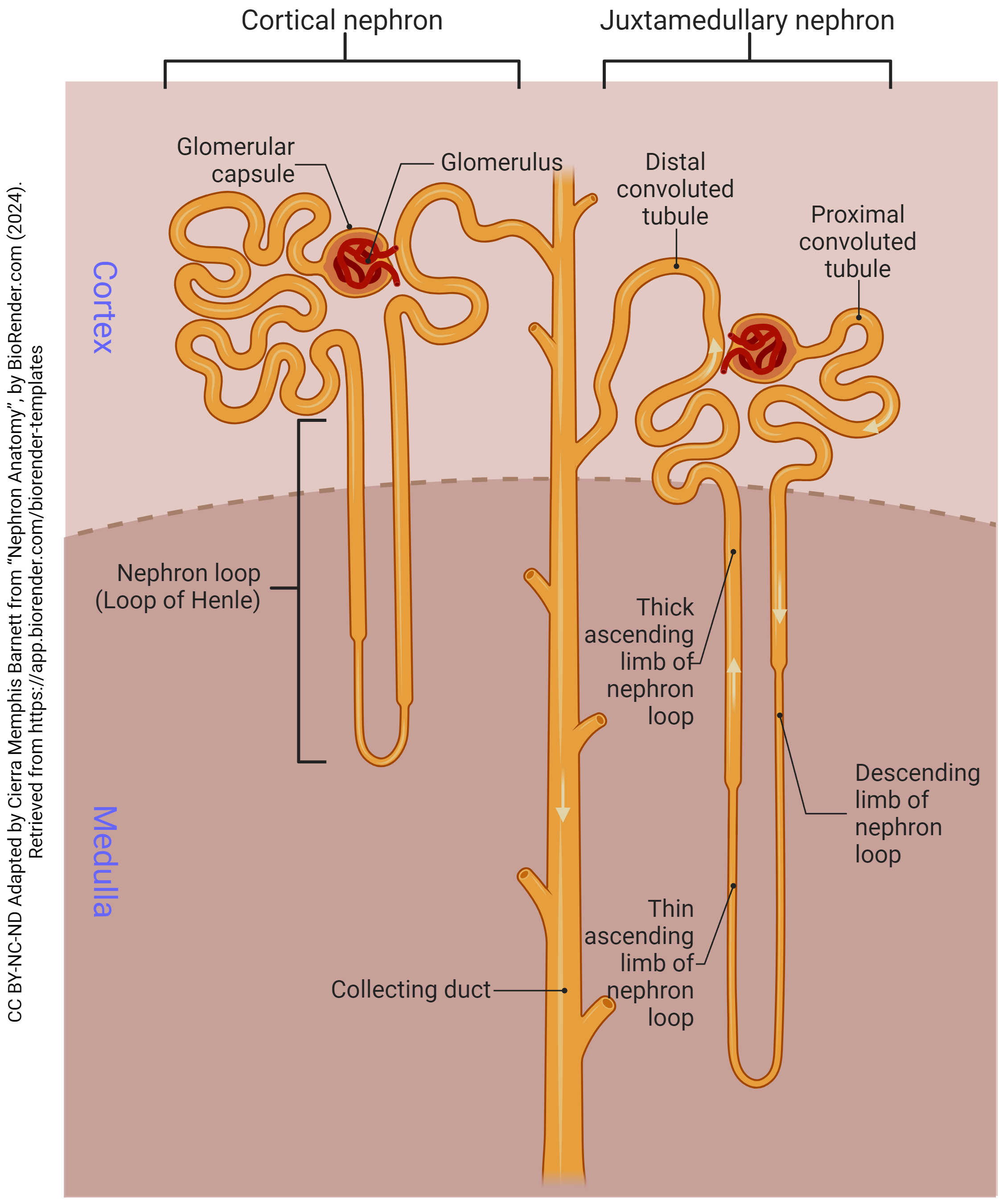
loop of henle
a u-shaped structure in the kidney’s nephron that filters blood, reabsorbs water and solutes and produces concentrated urine; creates a countercurrent multiplier mechanism that concentrates salt in the renal medulla which drives water reabsorption and concentrates urine
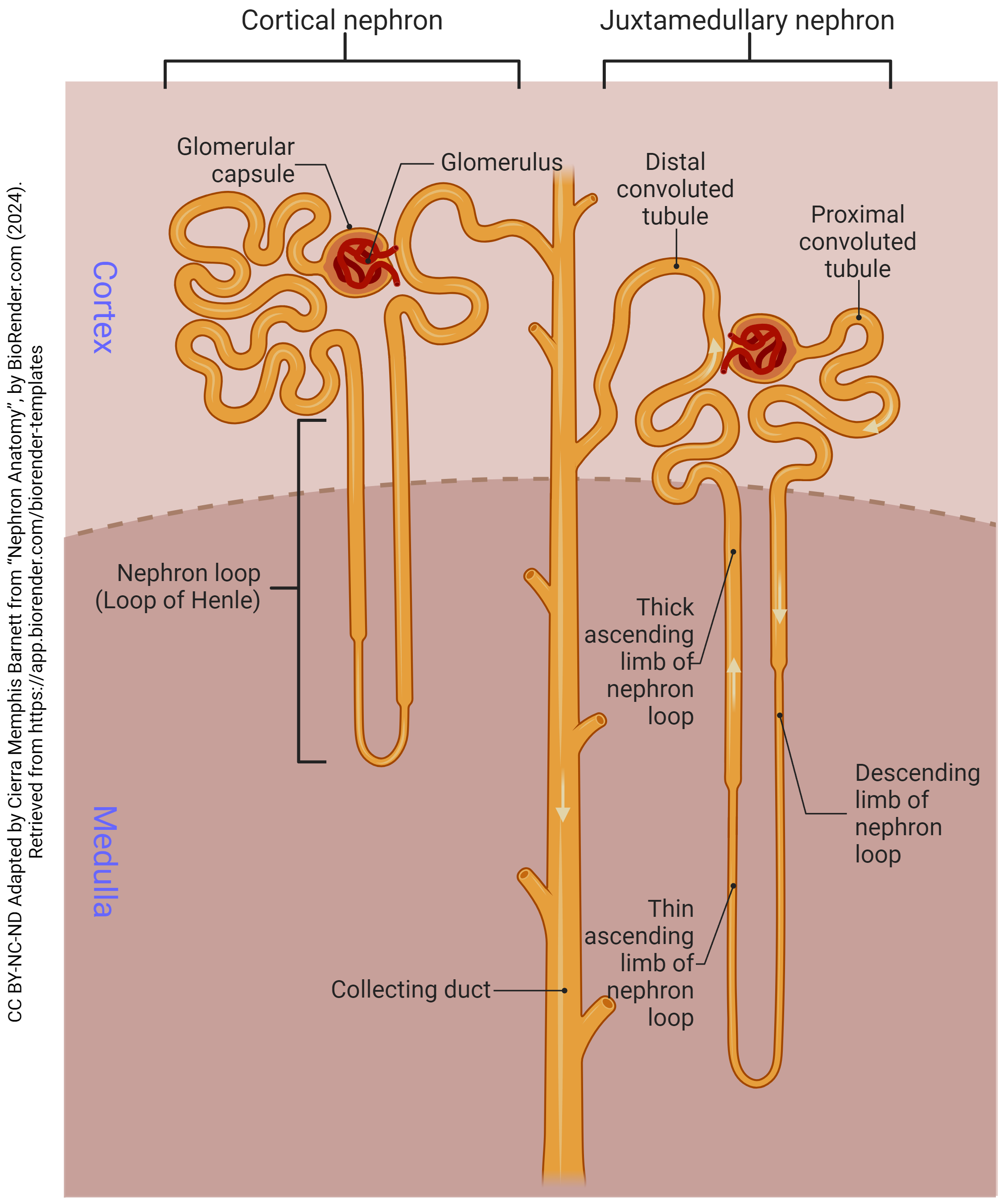
distal convoluted tubule
a section of the kidney’s nephron between the loop of henle and the collecting duct; where important reabsorption and secretion of ions occur; primary functions include reabsorbing sodium, chloride and calcium, and secreting potassium and protons to help maintain blood pressure and electrolyte balance
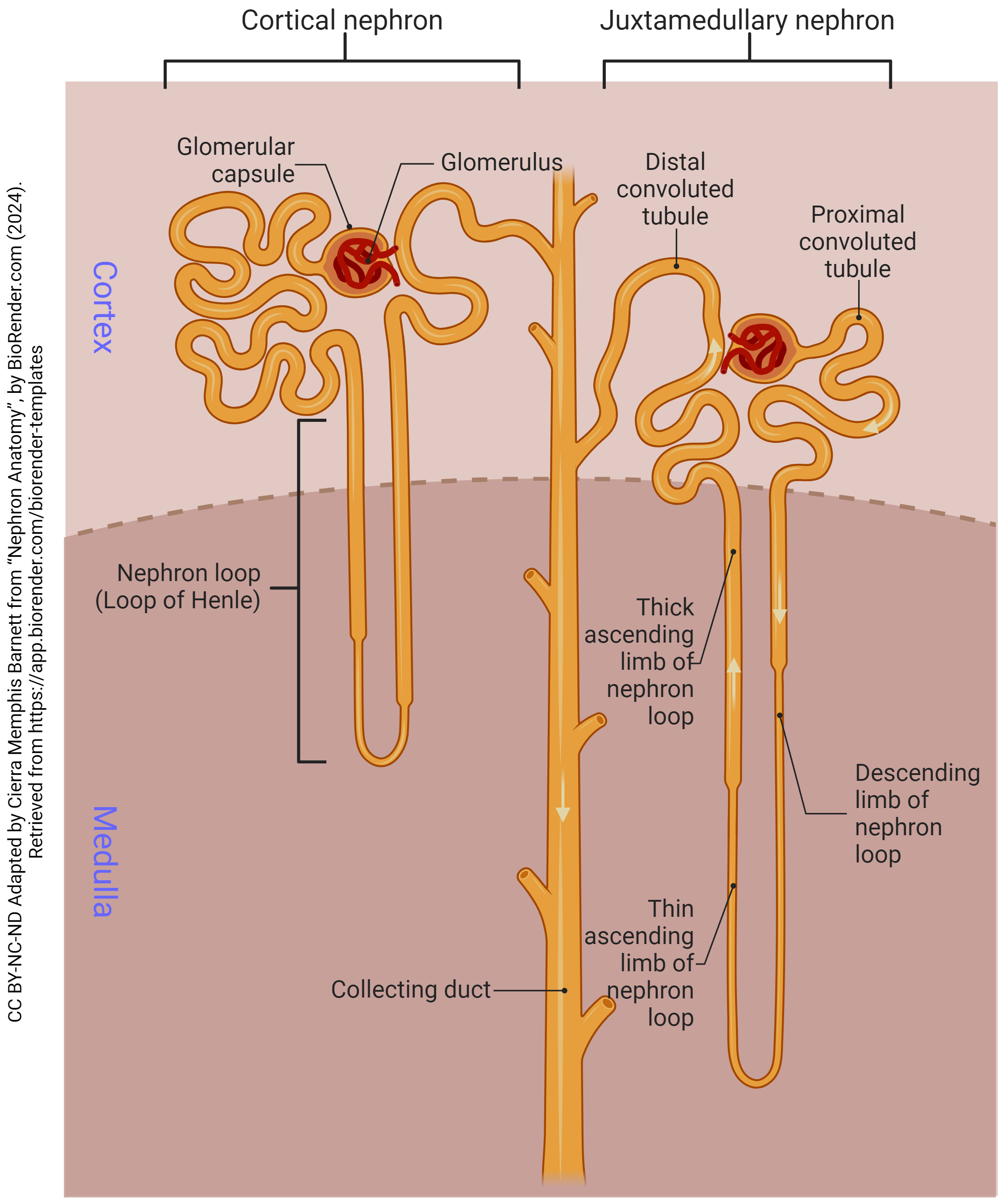
collecting duct
the final segment of the nephron; primarily serves to regulate water and electrolyte balance, contributing to the formation of concentrated urine
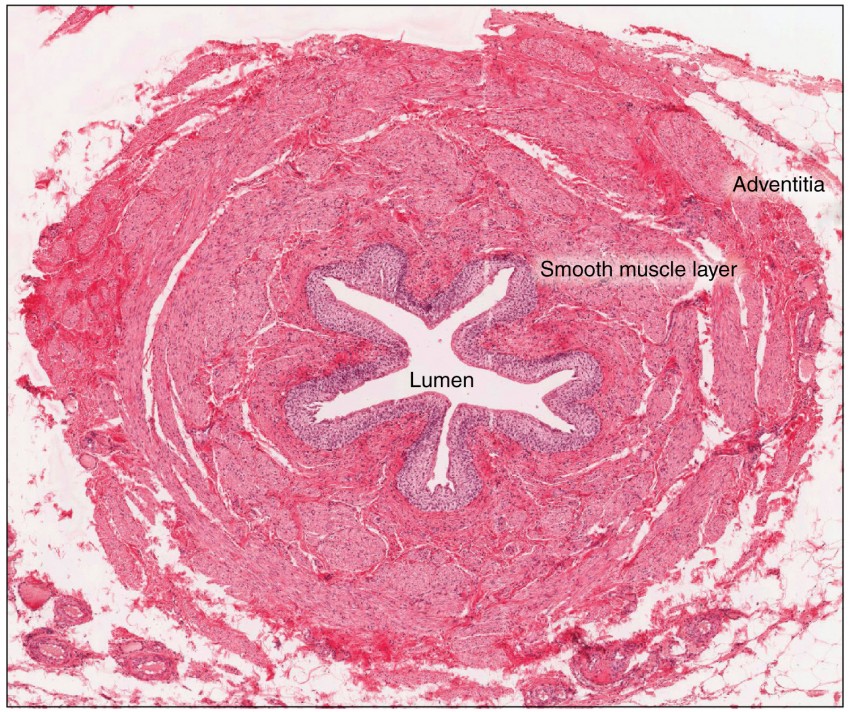
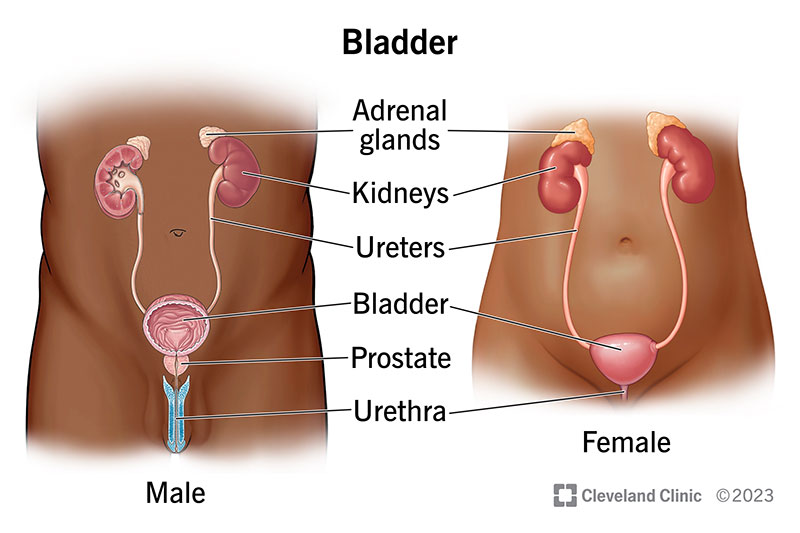
ureter
the duct by which urine basses from the kidney to the bladder
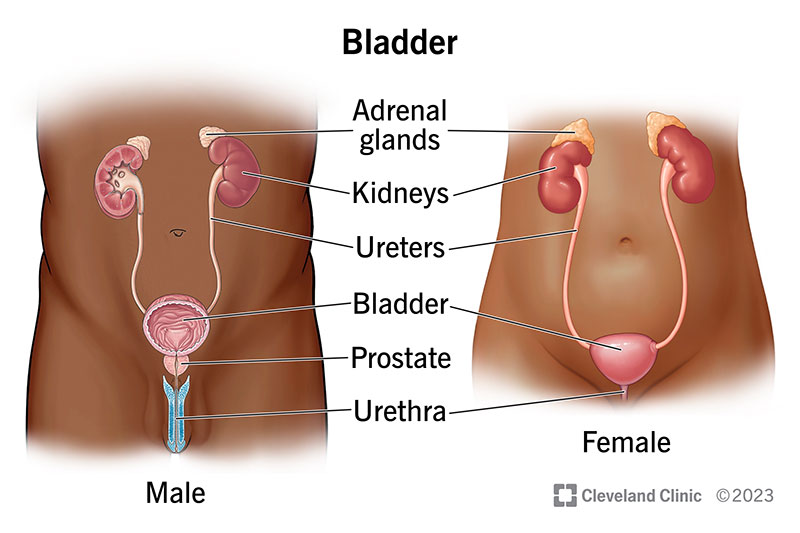
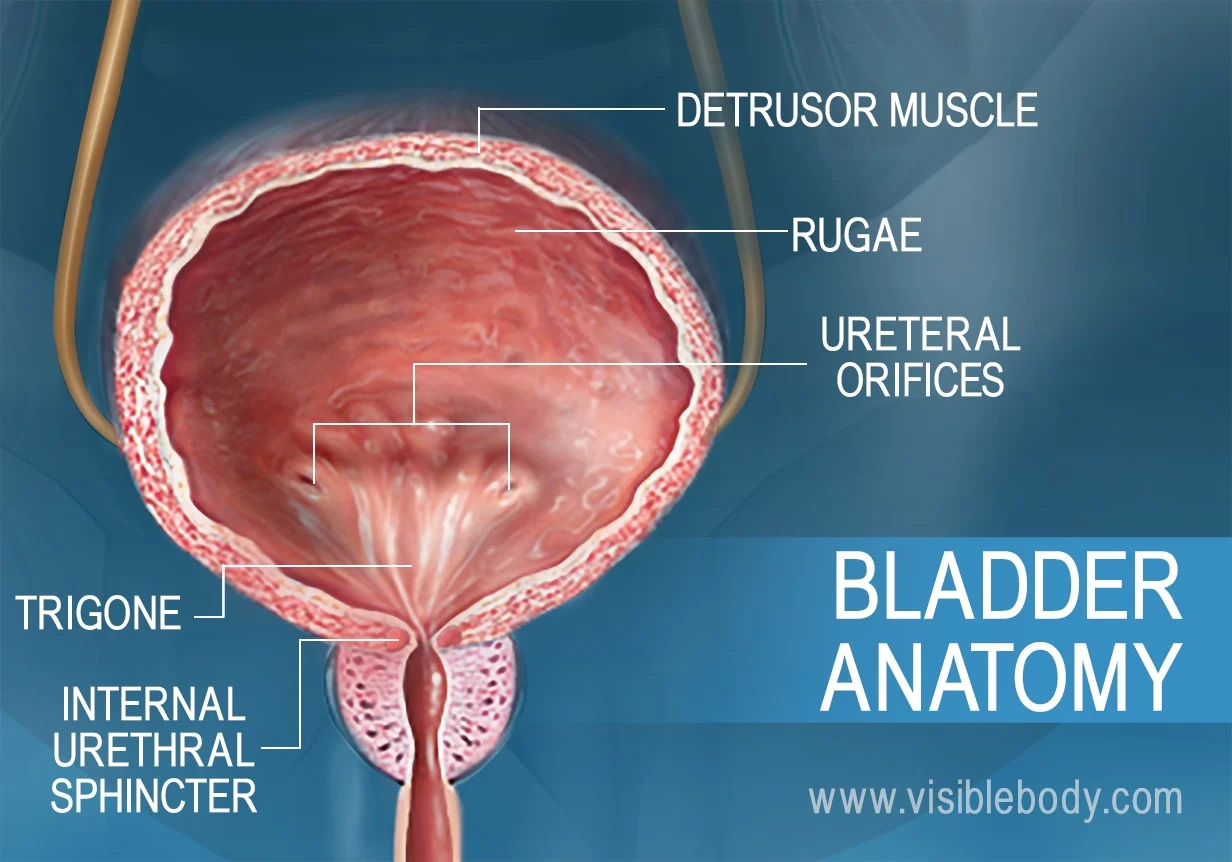
urinary bladder
located in the lower abdomen, behind the pubic bone; serves as a reservoir for urine; connected to TWO ureters that receive urine and ONE urethra to discharge urine
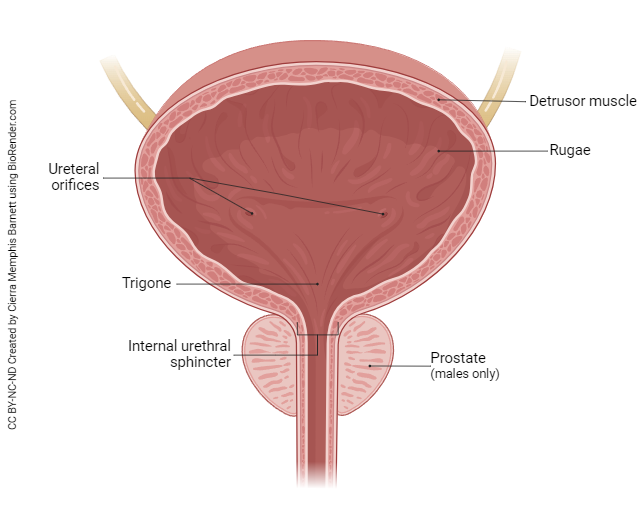
rugae
folds in the inner lining of the urinary bladder that allow it to expand and stretch as it fills with urine; prominent when the bladder is empty but unfold and flatten as the bladder fills
arterial openings
primarily in the renal artery which carries unfitted blood into the kidneys for filtration; branches into smaller vessels once in the kidney and arises from the abdominal aorta
internal urethral sphincter
a smooth muscle valve located at the junction of the bladder and the urethra; situated at the neck of the bladder and supports the upper part of the urethra
external urethral sphincter
a voluntary muscle located at the lower end of the urethra, which controls the flow of urine; situated in the pelvic floor, between the pubic bone and the perineum
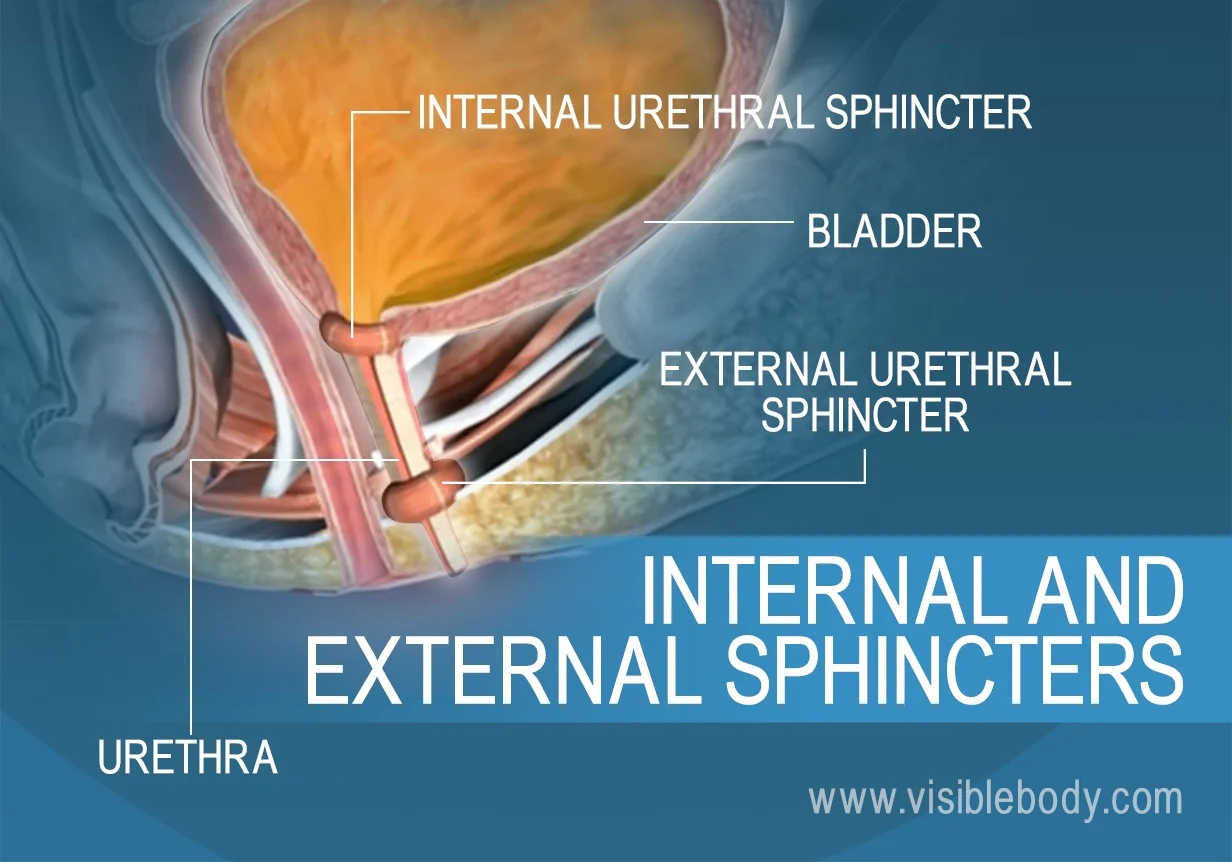
urethra
ova-uterine system urethra has no separate devisions; testicular system urethra has three divisions; the duct by which urine is conveyed out of the body from the bladder; conveys semen in men
testicular urethral divisions
prostatic, membranous and spongy
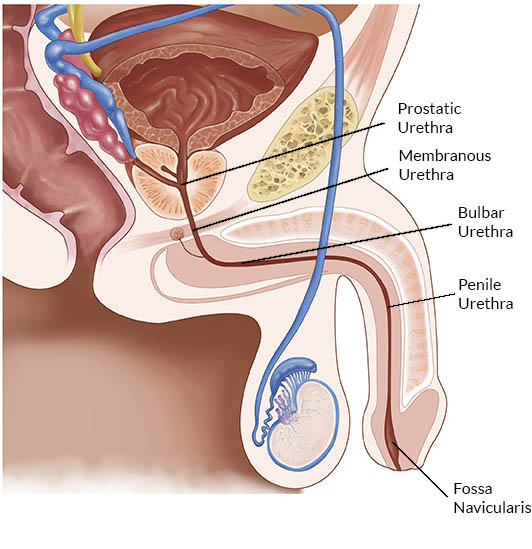
prostatic urethra
the section of the male urethra that passes through the prostate
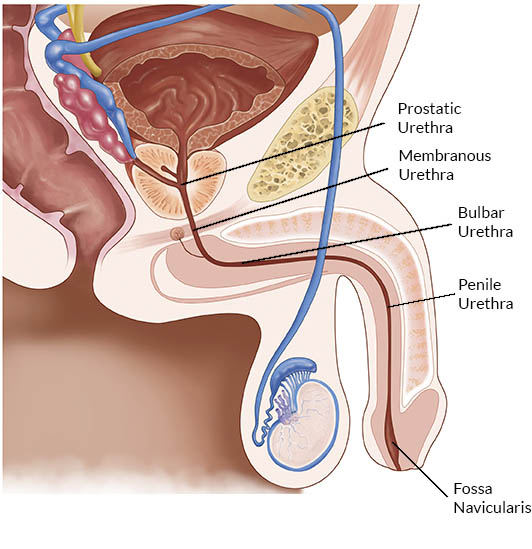
membranous urethra
the shortest and narrowest part of the male urethra, located between the prostate gland and the bulb of the penis; surrounded by the external urethral sphincter
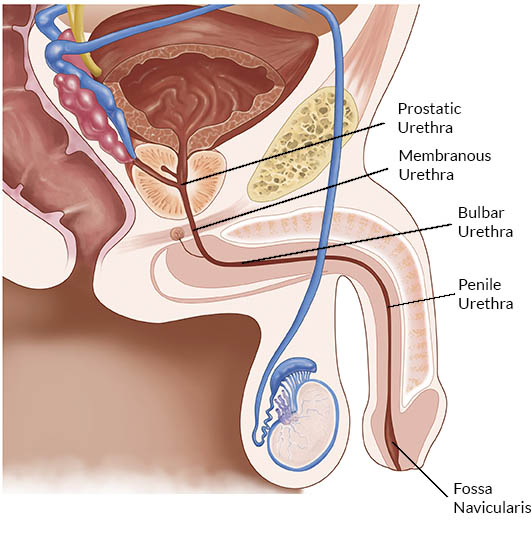
spongy urethra
the longest segment of the male urethra; AKA penile urethra; extends from the membranous urethra to the external urethral orifice and is entirely contained within the corpus spongiosum of the penis
normal pH range of urine
between 4.5 and 8.0
Abnormal urine constituents
glucose, bilirubin, ketones, blood, proteins, nitrites, & leukocytes
glucose
what's present in urine when glycosuria occurs; can be due to high blood sugar levels (due to diabetes), kidney damage and some medications
bilirubin
a yellow pigment that is produced by the breakdown of red blood cells; what’s present in urine when bilirubinuria occurs; can be due to liver damage, biliary obstruction; hemolysis and certain medications
ketones
a chemical produced when the body breaks down fat for energy instead of glucose; known as ketonuria when present in urine; can be due to diabetes, fasting; ketogenic diets; prolonged vomiting or diarrhea; alcohol intoxication and some medications
blood
known as hematuria when found in urine; caused by a UTI, kidney stones, bladder cancer, prostate problems, trauma, some medications and strenuous exercise
protein
known as proteinuria when present in urine; can be caused by kidney disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, strenuous exercise, infections, some medications and multiple myeloma
nitrites
Usually a sign of a UTI or a kidney infection; can be caused by some medications
leukocytes
present in urine when there is an inflammation or infection in the urinary tract; can be due to kidney infection, bladder inflammation, STIs, kidney stones, certain medications and autoimmune disorders