Unit 4: Price Controls
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
indirect taxes
taxes imposed on spending goods & services
paid partly by consumers & to the gov’t by producers
Types of Ind. Taxes
excise taxes: taxes imposed on particular goods n’ services
ie. gas, cigarettes, + alcohol
taxes on spending on (almost) all goods n’ services
ie. general sales taxes, value-added taxes
Types of Excise Taxes
specific taxes: fixed amount of tax/unit of a good or service sold
ad valorem taxes: fixed percentage of price of a good or service
amount of tax incr. as price of good incr.
direct taxes
taxes w/ a payment of them by taxpayers to gov’t
Why Gov’ts Impose Ind. Taxes
source of gov’t revenue
as PED decr., gov’t revenue incr; therefore, more taxes = more gov’t revenue
method to discourage consumption of goods harmful for the individual
consumption of goods (ie. cigarettes/alcohol) can be reduced via ind. taxes
use of redistributing income
taxes w/ focus on luxury goods can be taxed against high-income earners
payment of a tax on purchase = decr. post-tax income = lower class difference
method to improve allocation of resources via correcting negative externalities
market imperfections (form of neg. externalities) are remedied via ind. taxes
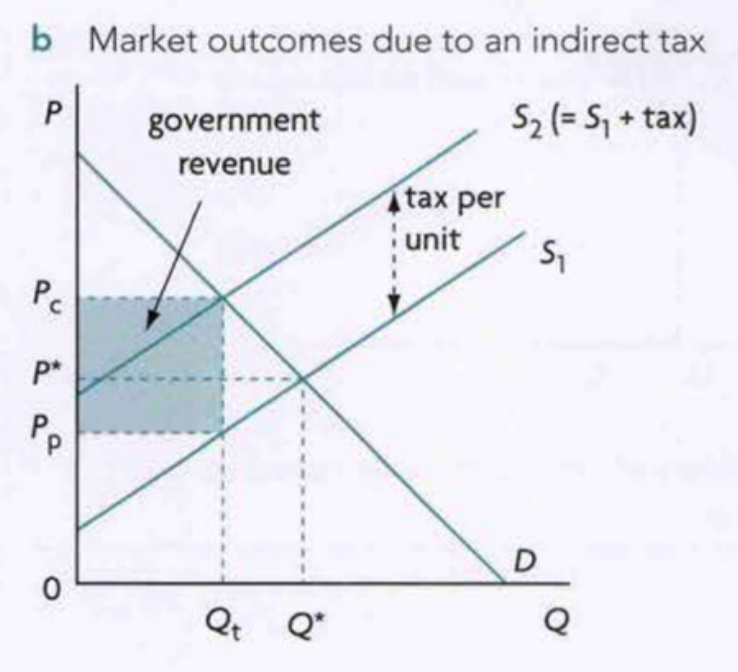
Market Outcomes w/ Ind. Taxes
Qeq. decreases (Q* → Qt)
Peq increased (P* → Pc)
consumer expenditure changes (P* x Q* → Pc X Qt)
price received by firms decreases (P* → Pp)
firm revenue decreases (P* x Q* → Pp X Qt)
gov’t receives tax revenue (Pc-Pp)Qt
under allocation of resources (Qt <Q*)
Consequences of Ind. Taxes
Consumers
increase Pgood
decrease Qbought
Producers (firms)
decrease in Preceives
decrease in Qoutput-sold
decrease in Revenue
Gov’t
revenue gained (Pc-Pp)Q
Workers
decrease in output (Q*→ Qt)
fewer workers needed = unemployment
Society as a Whole: Consumer + Producer Surplus
under allocation of resources
recudes consumers and produer surpluses
some to gov’t, some to welfate loss
Society as a Whole: Welfare Loss
received from consumer & producer surpluses
result of underproduction (MC>MC)