CGC 1D Unit 1 Topics for Review
1/65
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
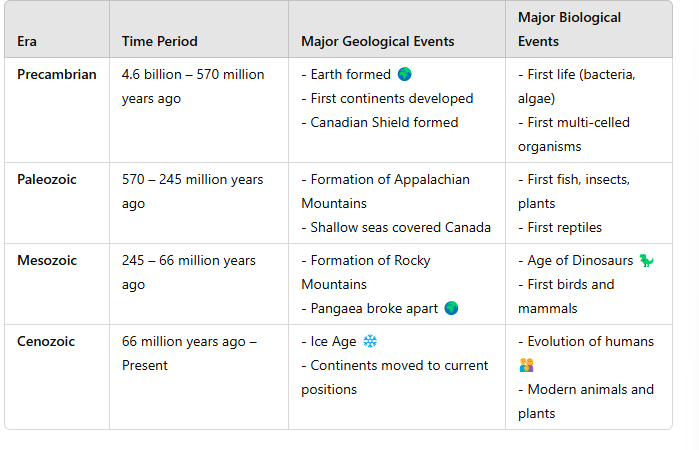
What is the Precambrian Era?
The Precambrian Era spans from the formation of the Earth around 4.6 billion years ago to about 541 million years ago and includes significant biological events like the emergence of simple life forms.
Major biological events of the Precambrian Era?
Multicellular organisms began to emerge and simple life forms like bacteria and algae dominated.
Major geological events of the Precambrian Era?
Formation of the Earth's crust, oceans, and atmosphere; the first supercontinents formed.
What is the Paleozoic Era?
The Paleozoic Era follows the Precambrian, lasting from 541 to 252 million years ago, and is characterized by the Cambrian explosion of life.
Major biological events of the Paleozoic Era?
Diversity of life increased rapidly, including the development of fish, amphibians, and the first plants.
Major geological events of the Paleozoic Era?
Formation of the Appalachian Mountains and the supercontinent Pangaea.
What is the Mesozoic Era?
The Mesozoic Era lasted from 252 to 66 million years ago and is known as the age of reptiles, including dinosaurs.
Major biological events of the Mesozoic Era?
Appearance of dinosaurs, mammals, and flowering plants.
Major geological events of the Mesozoic Era?
Breakup of Pangaea and significant volcanic activity.
What is the Cenozoic Era?
The Cenozoic Era spans from 66 million years ago to the present and is known as the age of mammals.
Major biological events of the Cenozoic Era?
The rise of mammals and birds, and the appearance of primates and humans.
Major geological events of the Cenozoic Era?
Formation of the Rocky Mountains, and significant climatic changes leading to ice ages.
Visual
representations of data or concepts, often used to enhance understanding in scientific contexts.
What is the capital city of Alberta?
Edmonton
What is the capital city of British Columbia?
Victoria
What is the capital city of Manitoba?
Winnipeg
What is the capital city of New Brunswick?
Fredericton
What is the capital city of Newfoundland and Labrador?
St. John's
What is the capital city of Nova Scotia?
Halifax
What is the capital city of Ontario?
Toronto
What is the capital city of Prince Edward Island?
Charlottetown
What is the capital city of Quebec?
Quebec City
What is the capital city of Saskatchewan?
Regina
What is the capital city of Northwest Territories?
Yellowknife
What is the capital city of Nunavut?
Iqaluit
What is the capital city of Yukon?
Whitehorse
What is the capital city of Canada?
Ottawa, located in Ontario.
How many provinces does Canada have?
Canada has 10 provinces.
How many territories does Canada have?
Canada has 3 territories.
What is the Rock Cycle Process?
The Rock Cycle includes: 1. Igneous rock forms from cooled lava. 2. Weathering & erosion break it into sediments. 3. Sediments compact into sedimentary rock. 4. Heat & pressure transform sedimentary rock into metamorphic rock. 5. Melting turns metamorphic rock back into magma.
What are Lowlands in Canada?
Flatlands that are good for farming.
What are Highlands in Canada?
Mountainous regions.
What is the Canadian Shield?
The oldest rock in Canada, rich in minerals.
What are the Interior Plains?
Also known as the 'Prairies,' known for agriculture.
What are the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands?
Densely populated, fertile land.
What are the Appalachian Mountains?
Old, eroded mountains in Canada.
What is the Western Cordillera?
Young, tall mountains in Canada.
Why do landform regions matter?
They affect settlement, economy, and climate.
What is a Climate Graph?
A visual representation of climate data over a period.
How do you calculate Temperature Range?
Temperature Range = Hottest temp – Coldest temp.
How do you calculate Average Annual Temperature?
Average Annual Temperature = Sum of all temps ÷ 12.
Where do most earthquakes occur in Canada?
Most earthquakes occur in Western Canada, especially British Columbia and Yukon.
What regions are known as 'Tornado Alley' in Canada?
Southern Ontario, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba.
What conditions lead to forest fires in Canada?
Fires occur in summer when vegetation is dry.
Where do most floods occur in Canada?
Ontario, Quebec, Manitoba, BC, and New Brunswick, often in spring.
What are common landslide hotspots in Canada?
British Columbia, Alberta, and Quebec.
What is the difference between Weather and Climate?
Weather refers to short-term conditions; Climate refers to long-term patterns (30+ years).
What is Maritime Climate characterized by?
Moist and mild conditions due to proximity to water.
What is Continental Climate characterized by?
Cold winters and hot summers due to lack of water regulation.