Erosional Landscapes and Landforms
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Cracks, Caves, Arches, Stacks & Stumps
joint widens to form crack
crack erodes to form cave
caves eroded through into an arch
unsupported rock in the arch collapses into stack
weathering and erosion causes stack to become stump
Cliff Profiles
Steep Cliffs = rock is strong and resistant to erosion, no beach, long fetch, high energy environment promotes steep cliff development
Gentle Cliffs = weaker rocks, less resistant to erosion, prone to slumping, large beach reduces wave energy so prevents steep cliff from forming
structure involves the disposition of rock and its bedding planes which
determines its strength and the surface area exposed to wave erosion
and subaerial processes
structure involves the jointing of rocks which will also impact on
surface area and the physical resistance of rocks to erosion
lithology is the hardness or rock strength/make up
rock hardness affects its resistance to wave processes
lithology will also determine the porosity of rocks
Cliff Rate of Retreat
Rate of Retreat = cliffs more likely to retreat if they’re made of soft unconsolidated rock
Negative Feedback Mechanisms can help protect and restore a coast. If the cliff collapses the material can protect the base from erosion, reducing further cliff recession.
Wave-Cut Notch Platform
Occurs at steep cliffs:
erosion is concentrated around the high-tide line creating a wave-cut notch
as the notch becomes deeper the cliff face becomes unstable and collapses
leaves behind a platform of the unaffected cliff base
backwash carries away debris and wave cut platform is left
Negative Feedback occurs as the length of the platform is limited because eventually the waves an no longer reach the cliff, reducing erosion. Act of erosion creating the wave-cut platform has directly decreased rate of erosion in the future.
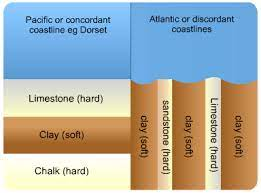
Bays + Headlands
weakness in rock on concordant coastline (e.g. joint)
erosion widens joint into crack, then a cave, then an arch, then the arch collapses and waves erode soft rock left at the coastline
wave refraction around jutting out hard rock forms semicircular bay
bay stops either because it hits another band of hard rock or because waves have lost energy as bay is to deep
Raised Beach
beach profile has shifted due to sea levels dropping or land rising
beach becomes land and offshore, which was underwater before, becomes the beach and erosion acts on it
vegetation succession occurs on raised beach that has become land
Concordant Coastline
layers of rock run parallel to the coastline
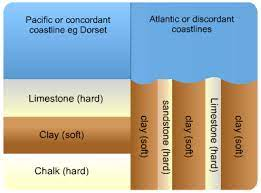
Discordant Coastline
layers of rock run perpendicular to the coastline