Photosynthesis, Photosynthesis
4.8(4)
4.8(4)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:20 PM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
autotroph or producer
An organism that can make its own food

2
New cards
heterotroph or consumer
An organism that cannot make its own food.

3
New cards
reactants
The 'inputs' of a chemical reaction. Located on the left side of a chemical equation.
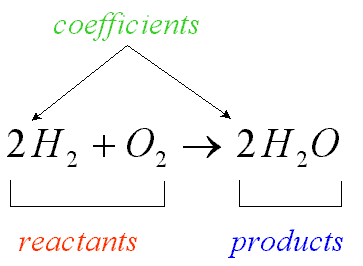
4
New cards
products
The 'outputs' of a chemical reaction. Located on the right side of a chemical equation.
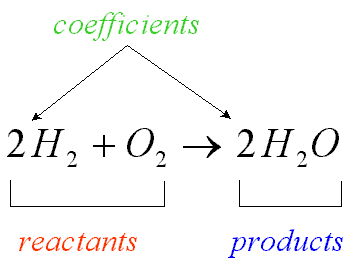
5
New cards
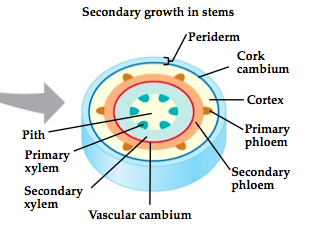
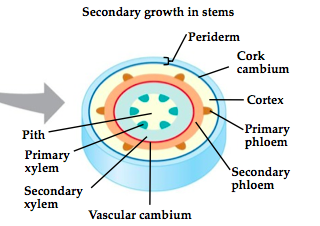
xylem
Carries water and minerals through a plant.
6
New cards
phloem
Carries food (glucose) through a plant.
7
New cards
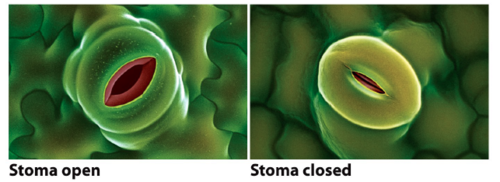
stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move. Where gas exchange occurs in a plant.
8
New cards
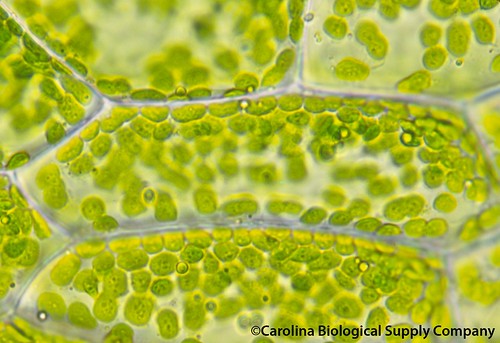
chloroplast
Location inside of a plant cell where the process of photosynthesis occurs.
9
New cards
chlorophyll
Pigment which 'fills' chloroplast. This pigment absorbs sunlight.
10
New cards
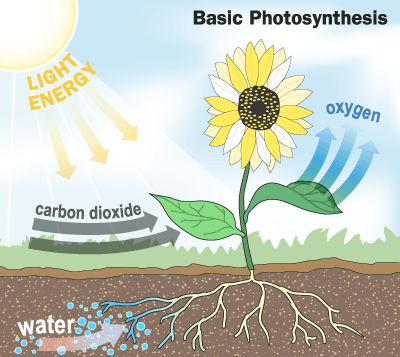
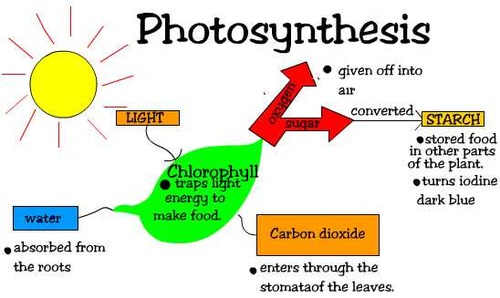
photosynthesis
A process plants use to turn sunlight into food.
11
New cards
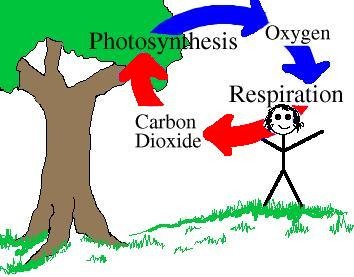
oxygen
A gas that plants release ( PRODUCT) during photosynthesis
12
New cards
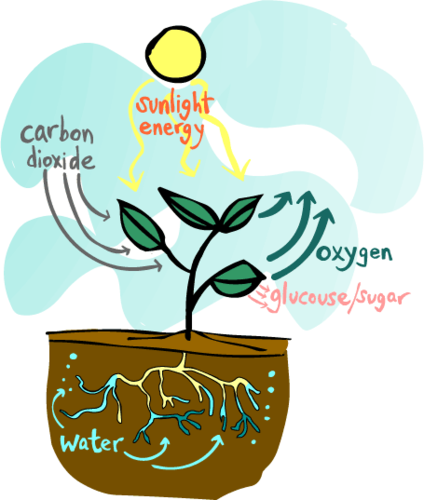
carbon dioxide
A gas that plants take in (REACTANT) through small holes in their leaves for the process of photosynthesis.
13
New cards
water, sunlight, carbon dioxide
3 main ingredients for photosynthesis (a.k.a. REACTANTS)
14
New cards
glucose
A simple sugar produced by plants and used as food.

15
New cards
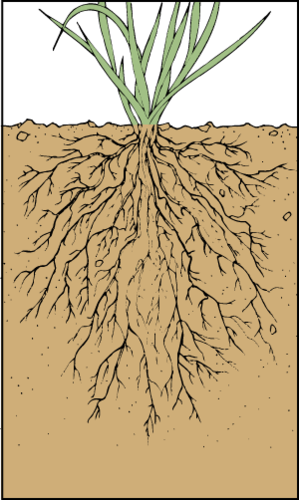
roots
Absorbs water and minerals from the ground. Anchors plant in ground.
16
New cards
sunlight
Taken in by the leaves of the plant to give the chloroplasts energy for food production.

17
New cards
Stem
supporting structure of a plant that connects roots and leaves and carries water and nutrients between them

18
New cards
O2
oxygen molecule
19
New cards
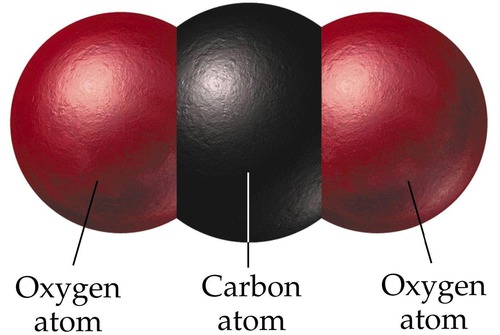
CO2
carbon dioxide
20
New cards
C6H12O6
glucose, also known as sugar

21
New cards
Consumers (heterotrophs)
Incapable of photosynthesis and must obtain their energy by consuming other organisms

22
New cards
-ose
sugar, carbohydrate

23
New cards
Carbohydrates
The starches and sugars present in foods; your digestive system usually breaks them down into GLUCOSE.

24
New cards
light-dependent reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
25
New cards
Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
set of reactions in photosynthesis that do not require light; energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugar; also called the Calvin cycle
26
New cards
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
27
New cards
ADP
a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP by the addition of a phosphate group
28
New cards
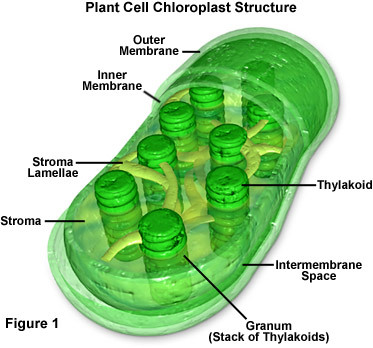
Thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy.
29
New cards
Stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
30
New cards
Grana
stacks of thylakoids