Lesson 4.1 Uniform circular motion
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
The motion of an object travelling at a constant speed in a circle. Examples include: toy plane on a string, carousel in a microwave, spin dryer, ceiling fan, and clock hands.
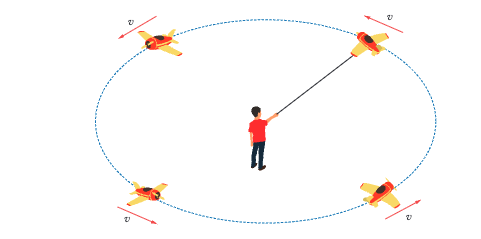
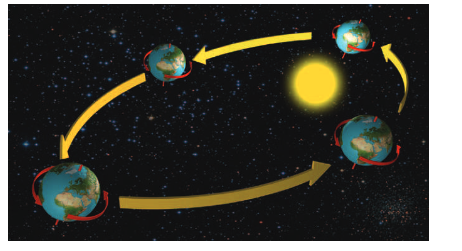
Revolving: moving in a circle around an external centre point (e.g. ball on string revolves around your hand or Earth revolves around Sun). Rotating: spinning around an internal axis (e.g. Earth rotates on its own axis once per day).
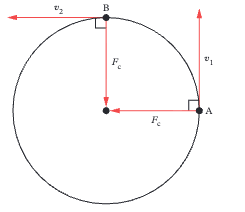
Velocity is a vector with both magnitude (speed) and direction. In circular motion the direction continuously changes so velocity changes. Since acceleration is the rate of change of velocity there must be acceleration even at constant speed.