Credit 1 Winter Semester Past Paper Questions
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/178
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:28 AM on 11/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
1
New cards
Schizogony Sarcocystis ovicanis begins
a. In ovine lymph node endothelial cells
b. In the muscle cells of the dog
c. In sheep muscle cells
d. In ovine endothelial cells
e. In dog enterocytes
a. In ovine lymph node endothelial cells
b. In the muscle cells of the dog
c. In sheep muscle cells
d. In ovine endothelial cells
e. In dog enterocytes
In ovine endothelial cells
2
New cards
Sporulation of genus Sarcocystis bovicanis occurs in
a. Enterocytes of dogs
b. Enterocytes of cattle
c. Leukocytes of dogs
d. Lymphatic nodes of cattle
e. Environment
a. Enterocytes of dogs
b. Enterocytes of cattle
c. Leukocytes of dogs
d. Lymphatic nodes of cattle
e. Environment
Enterocytes of dogs
3
New cards
Babesia divergens is transmited by
a. Rhipicephalus sanguineus to dogs and humans
b. Haemaphysalis punctata to sheep and humans
c. Ixodes Ricinus to horse and humans
d. Ixodes Ricinus to cattle and humans
e. Dermacentor reticulatus to humans
a. Rhipicephalus sanguineus to dogs and humans
b. Haemaphysalis punctata to sheep and humans
c. Ixodes Ricinus to horse and humans
d. Ixodes Ricinus to cattle and humans
e. Dermacentor reticulatus to humans
Ixodes Ricinus to cattle and humans
4
New cards
Gametogony Plasmodium vivax takes place in
a. Tick intestinal cells
b. In human red blood cells
c. In human white blood cells
d. In the liver cells of humans
e. In the intestinal cells of mosquitoes
a. Tick intestinal cells
b. In human red blood cells
c. In human white blood cells
d. In the liver cells of humans
e. In the intestinal cells of mosquitoes
In the intestinal cells of mosquitoes
5
New cards
Endogenous development of Cystoisospora felis in parathenic host takes place
a. In the bones of rodents
b. In rodent mesenteric lymph nodes
c. In the intestines of cats
d. In the lymph nodes of the cats
e. In the striated muscles of cats
a. In the bones of rodents
b. In rodent mesenteric lymph nodes
c. In the intestines of cats
d. In the lymph nodes of the cats
e. In the striated muscles of cats
In rodent mesenteric lymph nodes
6
New cards
Which of the following coccidian life cycle stages results from the fusion of a macrogamete
and a microgamete?
a. First generation schizont
b. Sporulated oocysts
c. Trophozoite
d. Merozoite
e. Zygote
and a microgamete?
a. First generation schizont
b. Sporulated oocysts
c. Trophozoite
d. Merozoite
e. Zygote
Zygote
7
New cards
The developmental stages of Toxoplasma gondii are localized in all kind cells of the
intermediate hosts except
a. Muscle cells
b. Hepatocytes
c. Nervous cells
d. Erythrocytes
e. Lymphocytes
intermediate hosts except
a. Muscle cells
b. Hepatocytes
c. Nervous cells
d. Erythrocytes
e. Lymphocytes
Erythrocytes
8
New cards
The protozoa can have diverse life cycles with multiple morphological stages, depending
on species. What stage of the life cycle is the active, reproductive and feeding stage?
a. Infection stage
b. Trophozoite stage
c. Flagella stage
d. Sporozoites stage
e. Cyst stage
on species. What stage of the life cycle is the active, reproductive and feeding stage?
a. Infection stage
b. Trophozoite stage
c. Flagella stage
d. Sporozoites stage
e. Cyst stage
Trophozoite stage
9
New cards
The solid axis of the trichomonad cell forms
a. Parabasal filament
b. Kinetoplast
c. Axostyl
d. Flagellym
e. Costa
a. Parabasal filament
b. Kinetoplast
c. Axostyl
d. Flagellym
e. Costa
Axostyl
10
New cards
Taxonomy category with suffix “idae” is
a. Species
b. Family
c. Genus
d. Classis
e. Order
a. Species
b. Family
c. Genus
d. Classis
e. Order
Family
11
New cards
The diagnosis of leishmaniasis is based on
a. The finding of promastigote stage sin the stained slides of vector organs
b. Finding of amastigotic stages in the stained slides of vertebrate organs
c. The finding of amastigotic stages in the stained slides of vector organs
d. Finding leishmania in the blood
e. Finding of promastogotic stages in the stained slides of vertebrate organs
a. The finding of promastigote stage sin the stained slides of vector organs
b. Finding of amastigotic stages in the stained slides of vertebrate organs
c. The finding of amastigotic stages in the stained slides of vector organs
d. Finding leishmania in the blood
e. Finding of promastogotic stages in the stained slides of vertebrate organs
Finding of amastigotic stages in the stained slides of vertebrate organs
12
New cards
A protozoan cyst that contains four nuclei, median bodies and axonemes should be
identified as
a. Eimeria tenella
b. Cystoisospora spp.
c. Giardia duodenalis
d. Tritichomonas foetus
e. Spironucleus spp.
identified as
a. Eimeria tenella
b. Cystoisospora spp.
c. Giardia duodenalis
d. Tritichomonas foetus
e. Spironucleus spp.
Giardia duodenalis
13
New cards
What are diagnostic techniques for sarcocystosis in intermediate host?
a. Flotation method
b. Digestion method of tissues
c. Biopsy of bones
d. Biopsy of liver
e. Staining blood smear
a. Flotation method
b. Digestion method of tissues
c. Biopsy of bones
d. Biopsy of liver
e. Staining blood smear
Digestion method of tissues
14
New cards
Intravital diagnosis of bird Trichomonosis is done by
a. A deep swab form the pharynx mucosa
b. Finding trichomonas in the blood
c. Concentration flotation methods
d. Finding Trichomonas in the urine
e. A native preparation obtained by cloak wash
a. A deep swab form the pharynx mucosa
b. Finding trichomonas in the blood
c. Concentration flotation methods
d. Finding Trichomonas in the urine
e. A native preparation obtained by cloak wash
A deep swab form the pharynx mucosa
15
New cards
Acute human sleeping disease is caused by
a. Trypanosoma brucei rhodensiense
b. Trypanosoma brucei brucei
c. Trypanosoma lewisi
d. Trypanosoma brucei gambiense
e. Trypanosoma cruzi
a. Trypanosoma brucei rhodensiense
b. Trypanosoma brucei brucei
c. Trypanosoma lewisi
d. Trypanosoma brucei gambiense
e. Trypanosoma cruzi
Trypanosoma brucei rhodensiense
16
New cards
The infection stage of Cystoisosporosis is
a. Caused by the consumption of raw meat containing tissue cysts with bradyzoites
b. Sporulated oocyst with 2 sporocysts in each with four sporozoites
c. Caused by the consumption of raw meat containing tissue cysts with tachyzoites
d. Sporulated oocyst with 4 sporocysts in each with two sporozoites
e. Quad-nuclei cysts
a. Caused by the consumption of raw meat containing tissue cysts with bradyzoites
b. Sporulated oocyst with 2 sporocysts in each with four sporozoites
c. Caused by the consumption of raw meat containing tissue cysts with tachyzoites
d. Sporulated oocyst with 4 sporocysts in each with two sporozoites
e. Quad-nuclei cysts
Sporulated oocyst with 2 sporocysts in each with four sporozoites
17
New cards
Schizogony Eimeria intricata begins in
a. Enterocytes of domestic swine
b. Hen enterocytes
c. Sheep ileum enterocytes
d. Bovine duodenal enterocytes
e. Rabbit ileum enterocytes
a. Enterocytes of domestic swine
b. Hen enterocytes
c. Sheep ileum enterocytes
d. Bovine duodenal enterocytes
e. Rabbit ileum enterocytes
Sheep ileum enterocytes
18
New cards
Gametogony of Babesia canis begins
a. In the intestine of the dog by the formation of microgametocytes and macrogametocytes
b. In the intestine of the dog by the formation of a movable ookinete
c. In the salivary gland of the tick by the formation sporozoites
d. In the gut of the tick by the formation of gametes, radial bodies
e. In the gut of the tick, the formation of a zygote
a. In the intestine of the dog by the formation of microgametocytes and macrogametocytes
b. In the intestine of the dog by the formation of a movable ookinete
c. In the salivary gland of the tick by the formation sporozoites
d. In the gut of the tick by the formation of gametes, radial bodies
e. In the gut of the tick, the formation of a zygote
In the gut of the tick by the formation of gametes, radial bodies
19
New cards
For diagnosis of Giardia/giardiasis we use flotation solution
a. Kozak-Magra
b. Vajda
c. Breza
d. Zinc sulphate
e. Darling
a. Kozak-Magra
b. Vajda
c. Breza
d. Zinc sulphate
e. Darling
Zinc sulphate
20
New cards
Eimeria stiedai is located in
a. Large intestine of cattle
b. Small intestine of hens
c. Cecum of sheep
d. Liver of rabbit
e. Kidney of goose
a. Large intestine of cattle
b. Small intestine of hens
c. Cecum of sheep
d. Liver of rabbit
e. Kidney of goose
Liver of rabbit
21
New cards
Giardia divides by
binary fission
22
New cards
Which organelles form the apical complex?
polar ring, conoid, subpellicular microtubules, micronemes, rhopty, micropore
23
New cards
Sporogony of Cryptosporidium spp. occurs in ...?
definitive host
24
New cards
The life cycle of Plasmodium spp. has 4 stages:
1 sexual and 3 asexual
25
New cards
What does sporulated oocyst Cryptosporidium spp. look like? Draw and describe
small (4-6 μm)
oval
2 shells
4 sporozoites, no sporocysts
oval
2 shells
4 sporozoites, no sporocysts
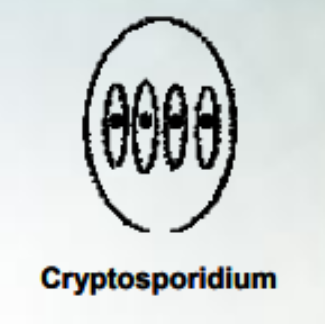
26
New cards
Macroschizonts of Theileria spp. are located in:
lymphocytes before moving to erythrocytes
27
New cards
Describe the morphology of Trypanosoma
spindle shaped, well developed undulating membrane, kinetoplast at posterior end, layer of subpellicular microtubules, free flagellum at anterior, cell surface has variable glycoproteins, nucleus in centre
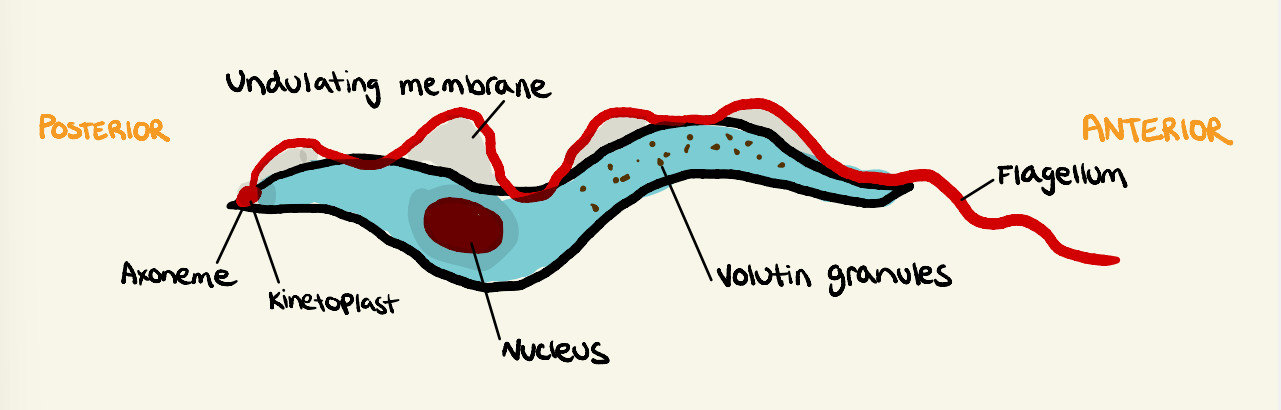
28
New cards
Fully sporulated oocysts were found in the faeces of a rabbit. What species is most likely represented? Write the name and describe
Eimeria magna, Eimeria intestinalis
small (12-14 μm)
oval
2 shells
4 sporocysts each containing 2 sporozoites
colourless/transparent
small (12-14 μm)
oval
2 shells
4 sporocysts each containing 2 sporozoites
colourless/transparent
29
New cards
Describe this life cycle (Sarcocystis)
Schizogony: Intermediate host
- Ingestion and excystation of oocyte in GIT (isospora type)
- Penetrate to blood – sporocyte -> meront -> merozoite
- 1st generations – artery epithelium, 2nd gen. capillary ep., 3rd gen in circulating lymphocytes
- Striated muscles – enclosed in cysts
- Merozoite -> metrozoite -> bradyzoites - infective
Gametogony: Final host
- Sarcocyst – bradyzoites liberated
- Differentiate into gametocyst in lamina propria
- Micro and macro gamete –Z oocyst (isospora type);
Sporogony: in lamina propria
- Ingestion and excystation of oocyte in GIT (isospora type)
- Penetrate to blood – sporocyte -> meront -> merozoite
- 1st generations – artery epithelium, 2nd gen. capillary ep., 3rd gen in circulating lymphocytes
- Striated muscles – enclosed in cysts
- Merozoite -> metrozoite -> bradyzoites - infective
Gametogony: Final host
- Sarcocyst – bradyzoites liberated
- Differentiate into gametocyst in lamina propria
- Micro and macro gamete –Z oocyst (isospora type);
Sporogony: in lamina propria
30
New cards
Eimeria stiedai: host and location?
rabbit, bile ducts
31
New cards
In Theileria, macroschizont in lymphocyte is known as?
Koch blue body
32
New cards
Which tissue/organ contains the highest number of Theileria?
spleen
33
New cards
In erythrocytes of Theileria we find:
piroplasms
34
New cards
T. cruzi belongs to:
Stercoraria
35
New cards
How is T. equiperdum transmitted?
mating
36
New cards
How is T. equiperdum diagnosed?
Clinical signs: pyrexia, local oedema of genitalia and mammary glands, oedematous cutaneous plaques
Demonstration of parasite: preputial or vaginal scrapings, aspiration of cutaneous oedematous plaque
Serological examination: CFT, ELISA, IFAT
Demonstration of parasite: preputial or vaginal scrapings, aspiration of cutaneous oedematous plaque
Serological examination: CFT, ELISA, IFAT
37
New cards
Tyrpanosoma belongs to which order?
Trypanosomatida
38
New cards
How many free flagella do Trypanosoma have?
1 or none depending on the developmental stage
39
New cards
What stage of T. cruzi multiplies in vertebrate host?
amastigote
40
New cards
Form of Leishmania in vertebrate host?
amastigote in macrophages
41
New cards
Form of Leishmania in vector?
promastigote
42
New cards
Clinical types of Leishmaniasis and species?
Visceral: L. donovani complex, L. infantum complex
Cutaneous: L. tropica, L. major, L. aethiopica
Mucocutaneous: L. mexicana complex, L. brasiliensis complex
Cutaneous: L. tropica, L. major, L. aethiopica
Mucocutaneous: L. mexicana complex, L. brasiliensis complex
43
New cards
What is the vector for Leishmania?
sandflies (Phlebotomus spp. and Lutzomyia spp.)
44
New cards
Location of Giardia intestinalis?
small intestine, extracellular
45
New cards
Giardia form of transmission
ingestion (faecal-oral, food, water)
46
New cards
number of flagella on Giardia?
8 (1 pair anterior, 2 pairs posterior, 1 pair caudal)
47
New cards
Which floatation solution is used for Giardia?
zinc sulfate, FAUST
48
New cards
How does Giardia reproduce?
binary fission (asexual)
49
New cards
Order of Giardia
Diplomonadida
50
New cards
Form of transmission of Trichomonas foetus
coitus, AI, gynaecological exam
51
New cards
Host of Trichomonas foetus?
bovine
52
New cards
What is the form of reproduction in family Trichomonadidae?
longitudinal binary fission
53
New cards
Principle host of Trichomonas gallinae
pigeon
54
New cards
Intravital diagnosis of Trichomonas in pigeons?
lesions in upper GIT contain parasites (mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, crop, proventriculus, liver)
55
New cards
How is Histomonas transmitted?
in the eggs of the caecal worm Heterakis gallinarum
56
New cards
Which group of protozoa possess an axostyle?
Trichomonadida Trichomonas spp. and Diplomonadida Giardia spp.
57
New cards
The diagnosis of Sarcocystosis of pigs we investigate
tissue samples
58
New cards
A facultative parasite is an organism:
an organism that exhibits both parasitic and non-parasitic modes of living and does not absolutely depend on the parasitic way of life, but is capable of adapting to it if placed on a host
59
New cards
Vertebrate host of Leucocytozoon is:
chicken
60
New cards
Oocysts of Cryptosporidium are?
smaller than 10 μm
61
New cards
Exoerythrocytic stage of Plasmodium falciparum is located in:
liver
62
New cards
Flagellated form of Histomonas meleagridis occurs in:
caeca
63
New cards
Endodyogony in Sarcocystis life cycle takes place in:
tissue cells of intermediate host
64
New cards
So called ring-worms are stages in the life cycle of:
Plasmodium spp.
65
New cards
Sporulation of genus Hepatozoon occurs:
inside the vector
66
New cards
Intermediate host is:
a host in which the parasite passes obligatory through part of its development
67
New cards
Leishmania spp. occurs in the vertebrate host in:
amastigote form
68
New cards
The vector of human Plasmodium is:
Anopheles
69
New cards
Visceral leishmaniosis is caused by:
L. donovani complex, L. infantum complex
70
New cards
Giardia intestinalis is located
extracellularly
71
New cards
Eimeria zuernii is located in:
ileum of cattle
72
New cards
The nematode Heterakis gallinae plays an important role in the life cycle of:
Histomonas meleagridis
73
New cards
The infectious stage of eimeriosis is:
sporulated oocyst with 4 sporocysts each containing 2 sporozoites
74
New cards
Sporogony of Babesia spp. occurs:
inside the salivary gland of the final host
75
New cards
What is the location of Histomonas meleagridis?
caecum, liver, digestive tract
76
New cards
Cryptosporidium: What type of sporogony occurs?
endogenous
77
New cards
What is the size of the oocyst of Cryptosporidium?
4-6 μm
78
New cards
Life cycle of Cryptosporidium
Schizogony:
- Host ingest oocyst, woth
4 sporozoites.
- Sporozoites released in
small intestine
- Attach (not penetrate) to
microvilli.
- Multiply and form
schizont -> division -> 8
merozoites
- One more round of
schizogony.
Gametogony:
- Formation of micro and
macrogamonts
- Gamestocyst form and fuse -> zygote
Sporogony:
- 2 types of oocyst are formed
- 80% develop into thick walled. Pass to the environment with feces.
- 20% develop into thin- walled oocyst and release their sporozoites in the
intestine representing the autoinfective life cycle form
- Host ingest oocyst, woth
4 sporozoites.
- Sporozoites released in
small intestine
- Attach (not penetrate) to
microvilli.
- Multiply and form
schizont -> division -> 8
merozoites
- One more round of
schizogony.
Gametogony:
- Formation of micro and
macrogamonts
- Gamestocyst form and fuse -> zygote
Sporogony:
- 2 types of oocyst are formed
- 80% develop into thick walled. Pass to the environment with feces.
- 20% develop into thin- walled oocyst and release their sporozoites in the
intestine representing the autoinfective life cycle form
79
New cards
Life cycle of Sarcocystis
Schizogony: Intermediat host
- Ingestion and excystation of oocyte in GIT (isospora
type)
- Penetrate to blood – sporocyte -> meront -> merozoite
- 1st generations – artery eoithelium, 2nd gen. capillary
ep., 3rd gen in circulating lymphocytes
- Striated mucles – enclosed in cysts
- Merozoite -> metrozoite -> bradyzoites - infective
Gametogony: Final host
- Sarcocyst – bradyzoites liberated
- Differentiate into gametocyst in lamina propria
- Micro and macro gamete –Z oocyst (isospora type)
Sporogony: in lamina propria
- Ingestion and excystation of oocyte in GIT (isospora
type)
- Penetrate to blood – sporocyte -> meront -> merozoite
- 1st generations – artery eoithelium, 2nd gen. capillary
ep., 3rd gen in circulating lymphocytes
- Striated mucles – enclosed in cysts
- Merozoite -> metrozoite -> bradyzoites - infective
Gametogony: Final host
- Sarcocyst – bradyzoites liberated
- Differentiate into gametocyst in lamina propria
- Micro and macro gamete –Z oocyst (isospora type)
Sporogony: in lamina propria
80
New cards
Texas cattle fever is caused by?
a. Babesia bovis
b. Babesia bigemina
c. Babesia gibsoni
a. Babesia bovis
b. Babesia bigemina
c. Babesia gibsoni
Babesia bigemina
81
New cards
Haemoproteus is a parasite of which animal?
birds
82
New cards
Phylum of Trichomonads?
Parabasala
83
New cards
Position of small and large Babesia in erythrocytes?
small: located on the periphery at obtuse angles
large: located in the centre at acute angles
large: located in the centre at acute angles
84
New cards
Pathology of Giardia
attachment of trophozoites causes:
shortening of villi
inflammation of crypts and lamina propria
lesions of mucosal cells
malabsorption syndrome (steatorrhea)
shortening of villi
inflammation of crypts and lamina propria
lesions of mucosal cells
malabsorption syndrome (steatorrhea)
85
New cards
What is the pathology of Cryptosporidium? How is it diagnosed?
watery acute diarrhoea
diagnosis: finding thick walled oocyst in faecal sample, Carbol fuchsin staining. ELISA, PCR
diagnosis: finding thick walled oocyst in faecal sample, Carbol fuchsin staining. ELISA, PCR
86
New cards
Pathology of Toxoplasma
trophozoites directly destroy host cells, especially parenchymal and reticuloendothelial cells
Lymph node infection
Local hypersensitivity
Blood vessel blockage
Abortions
Chorioretinitis
Hydrocephalus
Lymph node infection
Local hypersensitivity
Blood vessel blockage
Abortions
Chorioretinitis
Hydrocephalus
87
New cards
Pathology of Histomonas, what are its lesions?
lesions in caecum and liver, perforation in caecum and liver, large inflamed caecum, yellow diarrhoea, apathy, blackhead;
thickened mucosa that becomes necrotic, exudate can solidify into hard, cheesy plugs
thickened mucosa that becomes necrotic, exudate can solidify into hard, cheesy plugs
88
New cards
What are the important coccidian of poultry? Pathogenesis, clinical signs, treatment
Chicken: E. maxima, E. tenello
Turkey: E. galloparones, E. meleagrimitis, E. adenoeidea
Geese: E. truncata, E. anseris
Pathogenesis: destroys enterocytes, haemorrage, malabsorption, decreased production, weightloss, death;
Treatment: amprolium, sulphonamides, toltrazuril, tylosine, amoxicillin, vaccine, supportive care
Turkey: E. galloparones, E. meleagrimitis, E. adenoeidea
Geese: E. truncata, E. anseris
Pathogenesis: destroys enterocytes, haemorrage, malabsorption, decreased production, weightloss, death;
Treatment: amprolium, sulphonamides, toltrazuril, tylosine, amoxicillin, vaccine, supportive care
89
New cards
Life cycle of Entamoeba
-Ingestion of cyst -> excystation of ameba in small intestine
- Nucleare divition (4->8), cytoplasm -> 8 small amebalae
- Grow into trophozoites -> intestine, other organs.
- 2 forms can develop:
1. Forma minuta – Cronic, latent, 8-20um -> environment as cyst, encyctation in
lumen, 4 nuclei
2. Forma magna – (10 – 60um), invasive, dysenteric (no cysts), necrosis, flask
shape ulcers – perforate GIT -> peritonitis – ameboma, abscess, 2nd infection
- Nucleare divition (4->8), cytoplasm -> 8 small amebalae
- Grow into trophozoites -> intestine, other organs.
- 2 forms can develop:
1. Forma minuta – Cronic, latent, 8-20um -> environment as cyst, encyctation in
lumen, 4 nuclei
2. Forma magna – (10 – 60um), invasive, dysenteric (no cysts), necrosis, flask
shape ulcers – perforate GIT -> peritonitis – ameboma, abscess, 2nd infection
90
New cards
Trypanosoma brucei is transmitted by:
a. Tsetse fly - Glossina spp.
b. Mechanically
c. Mosquitoes
a. Tsetse fly - Glossina spp.
b. Mechanically
c. Mosquitoes
Tsetse fly - Glossina spp.
91
New cards
Acute sleeping sickness is caused by:
a. T. ethansi
b. T. gambeinsis
c. T. rhodensiensis
a. T. ethansi
b. T. gambeinsis
c. T. rhodensiensis
T. rhodensiensis
92
New cards
Leishmania tropica causes:
a. cutaneous
b. visceral
c. mucocutaneous form
a. cutaneous
b. visceral
c. mucocutaneous form
cutaneous
93
New cards
Life cycle of Lieshmania
Vector: (Phlebotomus spp. / Lutzomyia spp.)
-sucking of blood containing amastigote form in macrophages
-amastigote form is released and migrates to midgut
-adheres to gut: amastigote -> promastigote
-promastigote migrates to pharynx and injected into host
Host:
-promastigote is engulfed by macrophages
-promastigote -> amastigote
-amastigote multiplies by binary fission
-macrophages burst and release to blood
-migrate to other organs depending on species
--Cutaneous: localised to skin
--Visceral: internal organs (liver, spleen)
--Mucocutaneous: mucosae of mouth, nose, pharynx, larynx, ear
-sucking of blood containing amastigote form in macrophages
-amastigote form is released and migrates to midgut
-adheres to gut: amastigote -> promastigote
-promastigote migrates to pharynx and injected into host
Host:
-promastigote is engulfed by macrophages
-promastigote -> amastigote
-amastigote multiplies by binary fission
-macrophages burst and release to blood
-migrate to other organs depending on species
--Cutaneous: localised to skin
--Visceral: internal organs (liver, spleen)
--Mucocutaneous: mucosae of mouth, nose, pharynx, larynx, ear
94
New cards
Giardia intestinalis belongs to:
a. Apicomplexa
b. Diplomonadida
c. Microspora
a. Apicomplexa
b. Diplomonadida
c. Microspora
Diplomonadida
95
New cards
Cryprosporidium baileyi occurs in:
a. Calves
b. Piglets
c. Poultry
d. Human
e. Dog
a. Calves
b. Piglets
c. Poultry
d. Human
e. Dog
Poultry
96
New cards
What is the size of the oocyst of Toxoplasma gondii?
12 μm
97
New cards
Gametogony of T. gondii occurs in the small intestine of:
a. rodents
b. birds
c. carnivores (felidae)
a. rodents
b. birds
c. carnivores (felidae)
carnivores (felidae)
98
New cards
How is a human infected by Toxoplasma?
- ingestion of sporulated oocysts (cat faeces)
- ingestion of zoites (undercooked meat)
- congenital infection
- organ transplants
- blood transfusion
- ingestion of zoites (undercooked meat)
- congenital infection
- organ transplants
- blood transfusion
99
New cards
Life cycle of Babesia canis
Tick injects sporozoites into host → entering RBC
Schizogony: vertebrate
- Sporozoite in saliva (vermicles) -> rbc
- Trophozoites - binary fission – rbc rupture
- Merozoites -> blood -> new ec
Gamogony: tick
- Blood meal ingest Ec – gametocytes released
- Micro and macrogametes -> motile zygote
(ookinet)
- Reproduction system -> tick eggs
(treansovary/stadial)
- Salivary gland
Sporogony: tick
- Saliva and form sporont
- In salivary gland -> sporozoites
Schizogony: vertebrate
- Sporozoite in saliva (vermicles) -> rbc
- Trophozoites - binary fission – rbc rupture
- Merozoites -> blood -> new ec
Gamogony: tick
- Blood meal ingest Ec – gametocytes released
- Micro and macrogametes -> motile zygote
(ookinet)
- Reproduction system -> tick eggs
(treansovary/stadial)
- Salivary gland
Sporogony: tick
- Saliva and form sporont
- In salivary gland -> sporozoites
100
New cards
Sarcocystis is transmitted by:
a. cysts
b. trophozoites
c. air
a. cysts
b. trophozoites
c. air
cysts