Exercise Fuel Utilization and Metabolism: Fuel Sources, RER, and Lactate Dynamics
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What does the respiratory exchange ratio (RER) indicate?
It estimates fuel utilization during exercise.
What is the primary fuel source during low-intensity exercise (<30% VO2 max)?
Fats
What is the primary fuel source during high-intensity exercise (>70% VO2 max)?
Carbohydrates
At approximately what intensity does fat contribute ~66% to energy expenditure?
Low exercise intensities (~20% VO2 max)
What is the total energy expenditure at low exercise intensities?
3 kcal•min-1
What happens to fat oxidation at higher exercise intensities (~60% VO2 max)?
Fat oxidation increases to ~33% of total energy expenditure.
What is the effect of prolonged, low-intensity exercise on fuel selection?
Fats are preferred over carbohydrates due to increased lipolysis.
What is lipolysis?
The breakdown of triglycerides into glycerol and free fatty acids (FFA).
What is the significance of glycogen during prolonged high-intensity exercise?
Glycogen depletion leads to reduced glycolysis and fat oxidation.
What is the recommended carbohydrate intake for endurance performance?
30-60 g of carbohydrate per hour during submaximal, long-duration exercise.
What is the primary source of carbohydrate during high-intensity exercise?
Muscle glycogen
What is the primary source of carbohydrate during low-intensity exercise?
Blood glucose from liver glycogenolysis.
What are the primary sources of fat during higher intensity exercise?
Intramuscular triglycerides.
What role do proteins play during exercise?
Proteins can be broken down into amino acids, contributing ~2% to total energy production.
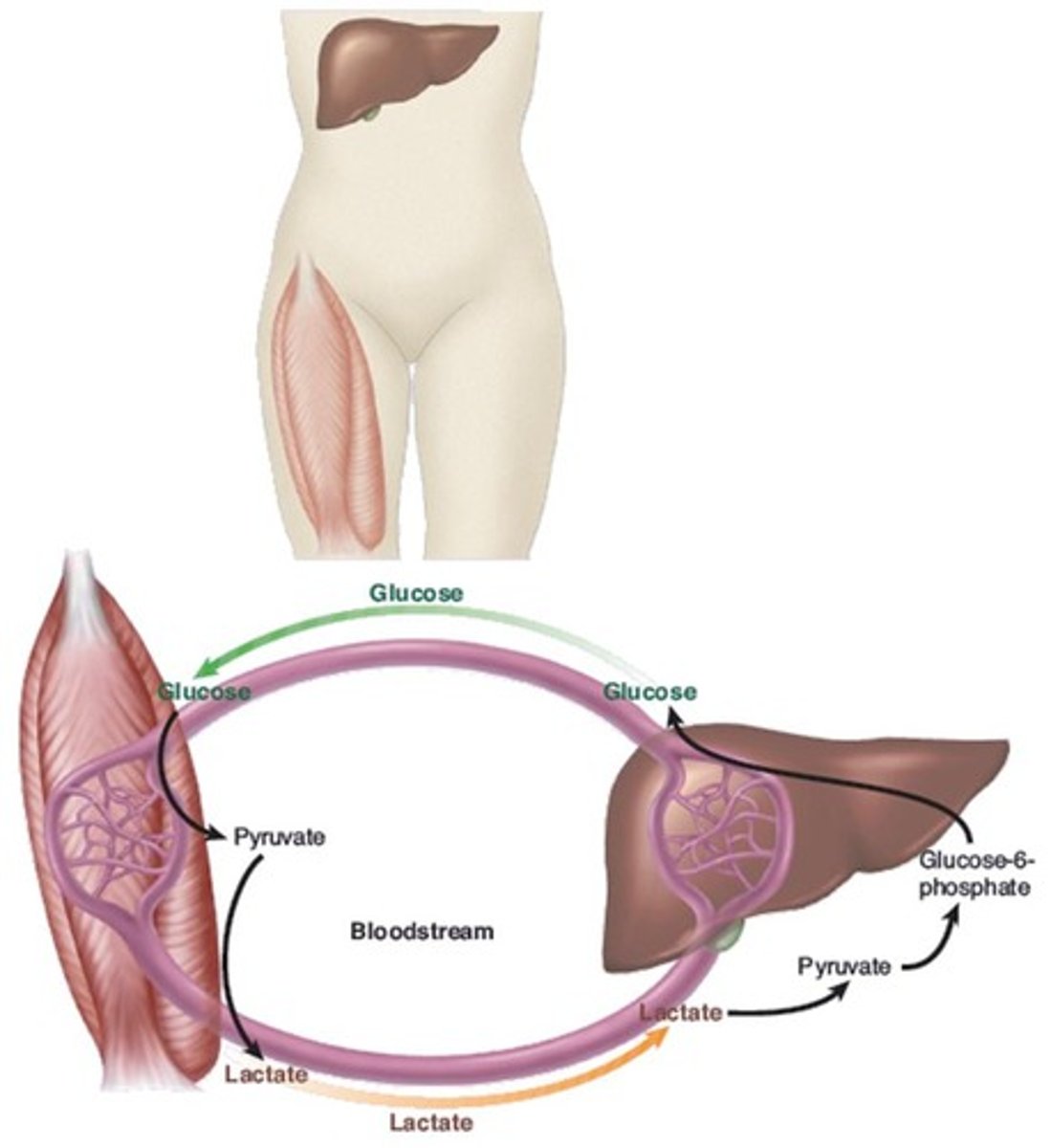
What is the Cori cycle?
The process where lactate produced by muscles is converted to glucose in the liver.
What is oxygen deficit?
The lag in oxygen uptake at the beginning of exercise, leading to anaerobic ATP production.
What is EPOC?
Excess post-exercise oxygen consumption, used to repay the oxygen deficit.
What happens to lactic acid following exercise?
70% is oxidized by cells, 20% is converted to glucose, and 10% to amino acids.
What is the primary ATP production method during short-term, high-intensity exercise?
ATP-PC system for the first 1-5 seconds.
What is the lactate threshold?
The exercise intensity at which lactate starts to accumulate in the blood, typically ~50-60% VO2 max in untrained individuals.
Does lactate cause muscle soreness?
No, lactate removal is rapid, and muscle soreness is caused by microscopic injury to muscle fibers.
What physiological factors influence VO2 max?
Genetics and training affect the maximum ability of the cardiorespiratory system to deliver oxygen to muscles.
What is the effect of prolonged exercise on ATP production?
ATP production is primarily from aerobic metabolism after 10 minutes.
What adaptations do trained individuals have regarding oxygen deficit?
Trained individuals have a lower oxygen deficit due to better aerobic capacity and cardiovascular adaptations.
What is the relationship between exercise intensity and oxygen uptake?
Oxygen uptake increases linearly with work rate until reaching VO2 max.
What happens to oxygen uptake in hot and humid environments during exercise?
There is an upward drift in oxygen uptake due to increased body temperature and blood epinephrine levels.