LEC.164 Lecture 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
Cleavage
Divisions of fertilized egg into cells, differentiation begins
2
New cards
Body axis
anterior-posterior/dorsal-ventral/left-right
3
New cards
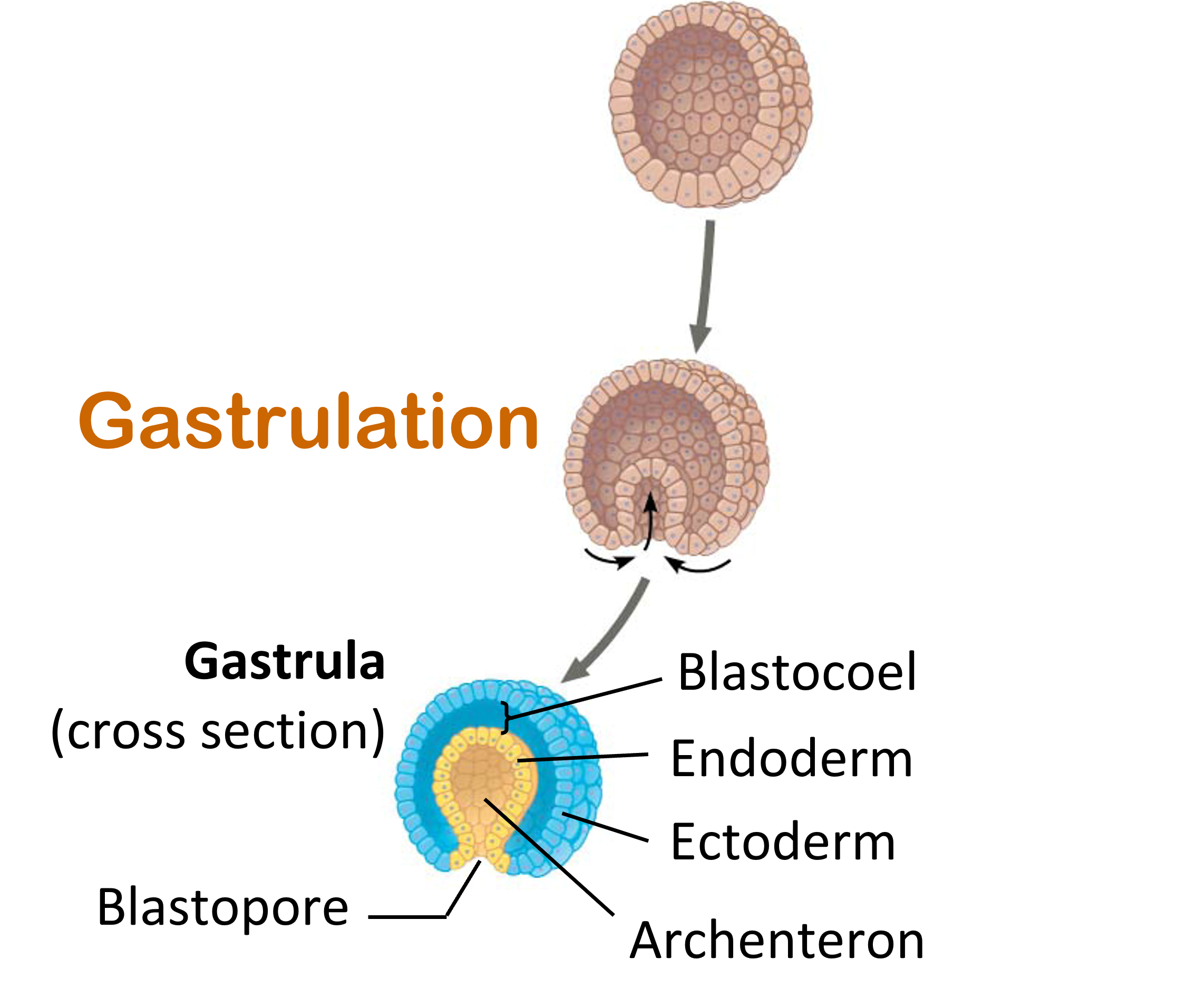
Gastrulation
Establishing gut and germ layers
\-cells move around embryo
\-cells move around embryo
4
New cards
Determination
What the cell is going to specialise into is decided
5
New cards
What does the blastula represent
The end of cleavage
6
New cards
What is the blastula
A hollow, fluid filled ball of cells
7
New cards
Gastrulation
Blastopore starts to form
8
New cards
What is seen in gastrulation
Blastocoel, endoderm, ectoderm, archenteron, blastopore
9
New cards
What are the smaller cells created during cleavage caused
Blastomeres
10
New cards
What are the different types of cleavage
holoblastic and meroblastic
11
New cards
what is holoblastic cleavage
complete division, eggs with small/moderate types of yolk
12
New cards
what is meroblastic cleavage
incomplete division, eggs with large yolks (preventing separation)
13
New cards
what type of cleavage do echinoderms do
holoblastic, planar division rotations
14
New cards
at what size can a space be seen in sea urchins
32 cells
15
New cards
Where does the majority of animal body derive from?
Divisions towards the animal pole
16
New cards
Where are more cells produced. Away from or close to yolk?
Away from the yolk
17
New cards
Xenopus 3rd cleavage
asymmetric, forms unequally sized blastomeres
18
New cards
What forms on top of the yolk
A disk of cells
19
New cards
What is superficial cleavage
Cleavage on the surface but not on the inside (where yolk is present)
20
New cards
What type of cleavage happens in mammals
Rotational on perpendicular planes
21
New cards
What is the end point of cleavage
The morula
22
New cards
Inner cell mass
the inner 8 cells
23
New cards
trophectoderm
the outer \~20 cells
24
New cards
what does the ICM form
the embryo
25
New cards
what does the trophectoderm become
the extra-embryonic tissues
26
New cards
when/where are the trophectoderm and icm established
in the blastocyte before implantation
27
New cards
Cleavage definition
rapid, synchronous cell division with no increase in embryo size
28
New cards
Order of cell division with growth
M, G1, S, G2
29
New cards
Why is cell division in cleavage faster
No growth/gap phases