MICB Final Exam: Lecture 23 Viral Disease
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are the categories of Viral Diseases?
Airborne
Arthropod-Borne
Direct Contact
Food and Water
Zoonotic
(broken down by major mode of transmission)
What are the types of vaccines?
Inactivated (killed)
Attenuated (live but avirulent)
How do we make inactivated vaccines? What rxn does it have in the body? Drawbacks? Ex?
Treat viral pathogens with chemicals or heat
Rxn: Induce humoral immune response
Drawback: Requires booster
Ex: Rabies, Flu shot
How do we make attenuated vaccines? What rxn does it have in the body? Drawbacks? Ex?
Treat pathogens by inactivating specific genes (can reproduce but weakened)
-Rxn: Humoral (produce antibody B Cells) and T-cell mediated immune response
-Drawback: May Revert
-Ex: Chickenpox, MMR, Flu (intranasal)
How are vaccines made?
Eggs are incoulated with the virus
Herd Immunity
Protection of unvaccinated people in a population where most people are vaccinated due to lessened risk of disease transmission
What % population is needed to achieve herd immunity?
Depends on pathogen
-Highly contagious diseases like Pertussis (whooping cough) and Meases require 80-90%
Chicken Pox (Viral Category, Virus Name, Virus Family, Mode for Spread, Symptoms)
Catagory: Airborne
Cause: Varicella-Zoster Virus
Family: Herpesviridae (Envalope, Iscohedreal Capsule)
Spread: Inhalation or conjunctiva of eye (eye rubbing)
-Spread via blood, neuronal
Symptoms: ~10 days infection of skins leads to vesicular rash
Treatment and Prevention of Chicken Pox
Treatment: No specific med, use regular OTC for inflammatory
Prevention: Attenuated (live) Vaccine
Who are protected and vulnerable to shingles?
Protected: Individuals who recover from chicken pox
Vulnerable: Immunocompromised patients can reactive virus, leading to shingles
Shingles (Zoster) Latency
Viral DNA in dormant state in nuclei of nerves, sensory neurons
What happens in the primary and recurrence infection of chicken pox/shingles?
Primary: Chicken pox virus migrate up sensory nerve to spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion holds latent viral DNA
Recurrence: Activation of latent viral DNA due to environmental stress in dorsal root ganglion of spinal cord.
-Viruses migrate down sensory nerve
Shingles Vaccines
Zostavax: Live Attenuated
Shingrix: Viral Glycoprotein of Virus
Flu (Viral Category, Virus Name, Virus Family)
Category: Airborne
Cause: Influenze
Family: Orthomyxoviridae
Replication Cycle of the Flu
Attachment: Hemagglutinin
Entry: Endocytosis
Release Via Budding: Neuraminidase
What are the structural features of the Flu?
-Spike Proteins on envelope
-Envelope from host cell
-Segmented DNA genome
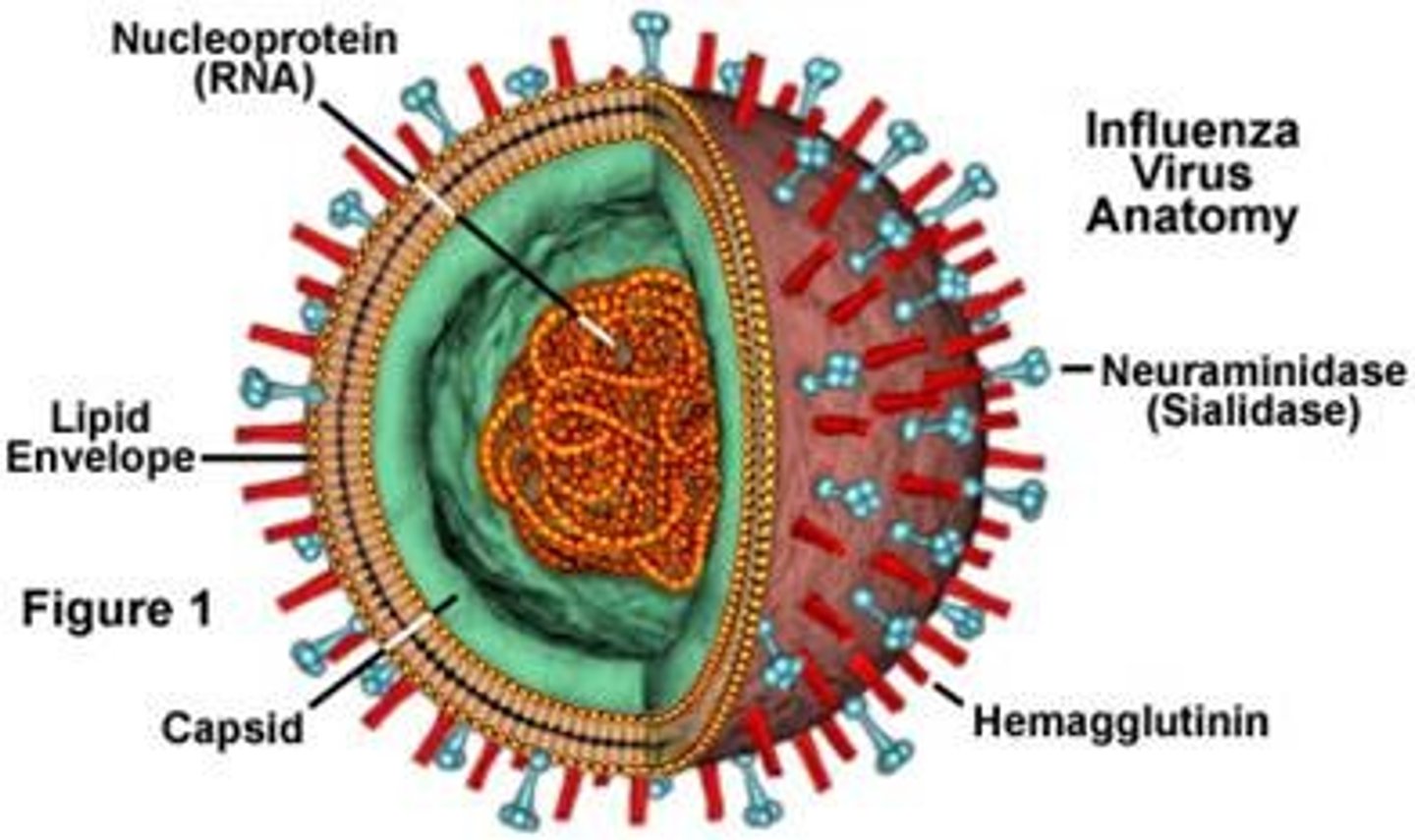
What must the flu virus bring in to read its mRNA? Why?
Segment genome needs DNA replicase
-Converts negative ssRNA to positive so it can be used as mRNA
Antigenic Drift (what, why, causes)
What: Minor mutations in viral genes in single strand
Why: Viral RNA replicase is error prone
Causes: An epidemic typically in a localized area
Ex: The Flu
Epidemic
Sudden increase in disease
Antigenic Shift
What: Major mutations in viral genome
Causes: New strains of disease, Pandemics
Pandemic:
Increase in disease in large, geographically widespread pop.
How does antigenic shifts lead to new strains of diseases?
Differential strains (animals or humans) infect cell
-Genome reassort leading to new strains
-New strain may spread to humans who have no immunity
-Ex: Spanish flu
Covid-19 (Viral Category, Virus Name, Virus Family, Mode for Spread)
Category: Airborne
Cause: Corona Virus strain SARS-CoV-2
Family: Coronaviridae
Spread: Respiratory Droplets
Corona virus structure
Enveloped
Linear +ssRNA
Uses host receptors to translate mRNA
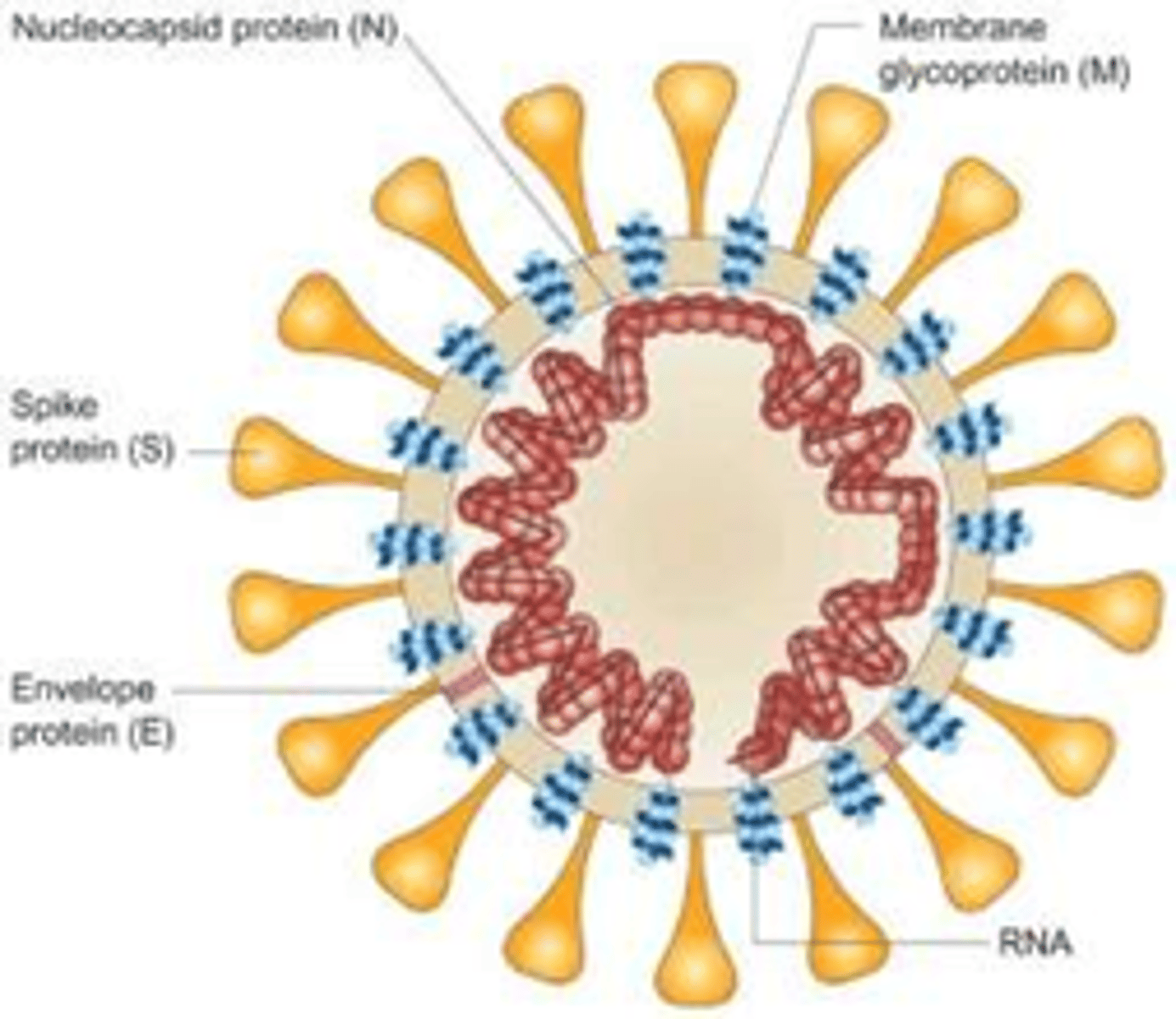
How does COVID replicate its genome?
Own viral RNA replicase to replicate
How do we test for COVID?
Antigen Tests: labeled antibody to detect nucleocapsid (N) protein
RT-PCR Serology: Antibody test using reverse transcriptase to convert RNA to DNA for PCR
Vaccines COVID-19
Moderna and Pfizer
mRNA vaccines
What are the components of the Covid vaccine?
mRNA encoding SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
-Too unstable alone need it to be enclosed in a lipid nanoparticle
-Our cells translate mRNA to antigen in form of spike protein
Measles, Mumps, Rubella (Viral Category, Virus Type)
Category: Airborne
Cause: RNA Viruses
Vaccine for Measles, Mumps, and Rubella
MMR attenuated vaccine
Measles, Mumps, and Rubella symptoms
Measles: Rubeola; physically feel bumps at virus site
Mumps: Salivary gland swelling
Rubella: German Measles, immune response of smooth rash patches
Arthropod-Borne Diseases (Cause, Viral Family, Examples)
Cause: Mosquito Vector
Family: Flavivirdae
Examples: Yellow Fever, West Nile Fever, Dengue Fever, Zika Virus Disease
What major symptom is caused by the zika virus during pregnancy?
Microcephaly
Arthropod-Borne Diseases Structure?
Enveloped, icosaheral
+ssRNA
Common Cold (Viral Category, Virus Name)
Viral Catagory: Direct Contact
Virus: Rhinovirus (major), coronaviruses, adenovirsus
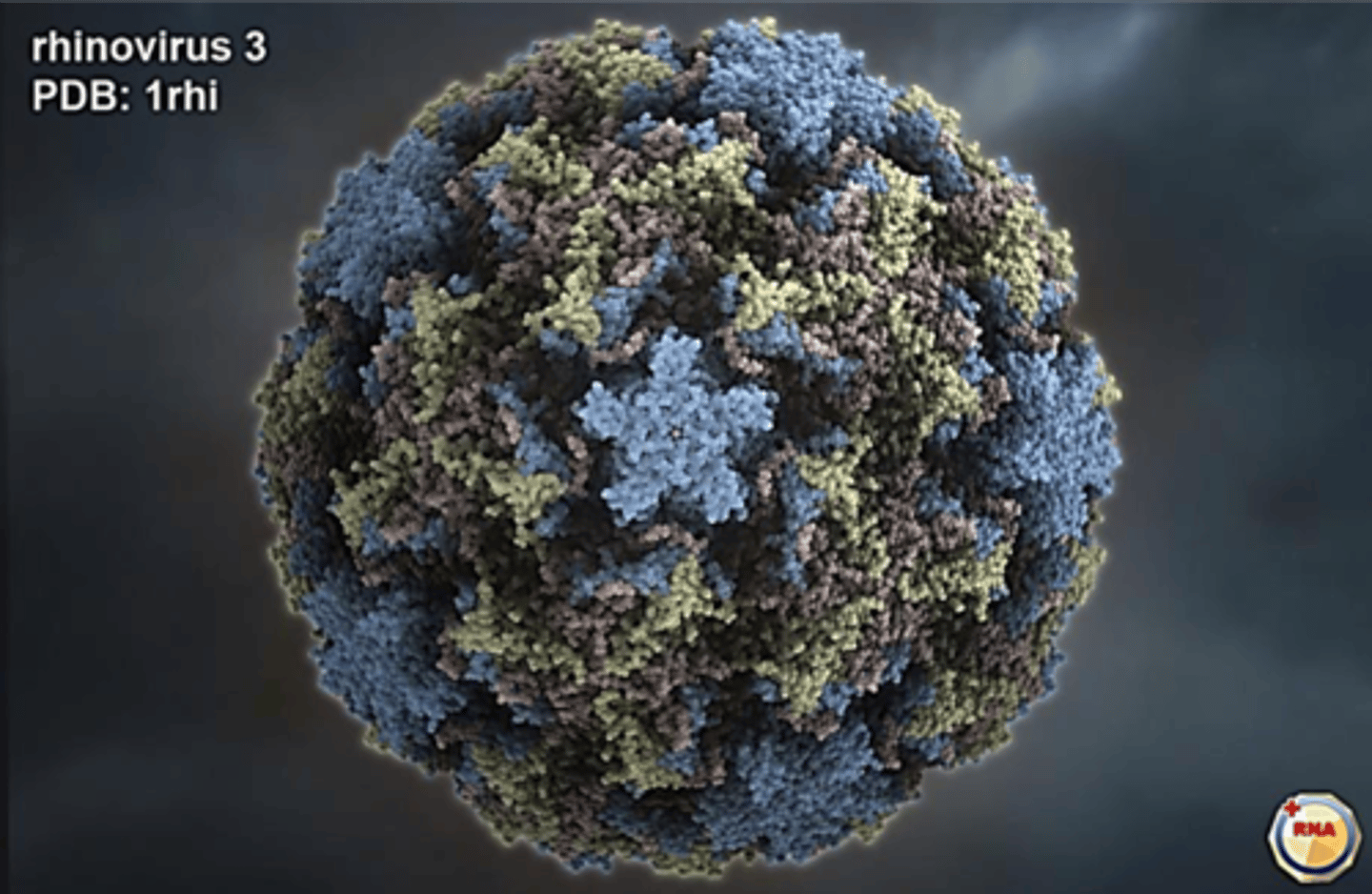
Rhinovirus Structure
naked icosahedral (no envelope)
+ssRNA
(over 100 serotypes)
Mononucleosis (Viral Category, Virus Name, Virus Family, Mode for Spread)
Category: Direct Contact
Virus: Epstein-Barr Virus
Family: Herpesviridae
Spread: Saliva
Mono structure
Envelope with spike proteins
Infection process of mono
1. Enters and replicates in throat epithelial cells
2. Infects B cells (can become latent)
3. Engage with MHC II Receptor to attach to host cell
Downey Cells
Enlarged T cells responding to infected B cells with mono
Other than mono, what other disease can the Epstein-Barr Virus cause?
Associated with Burkitts (B cell) lymphoma
What is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the US?
Genital warts
Warts (Viral Category, Virus Name)
Category: Direct Contact
Virus: Human Papillomaviruses (HPV)
Warts virus structure
Naked
DNA
Infection process of Warts
HPV protein E6 targets human p53 tumor suppressor protein which controls cell cycle and programmed cell death
Vaccine against HPV
Gardasil
-Virus like particle (VLP) vaccine
-Receive protein structure capsid but no genome (non-infectious)
Besides warts, what other disease is associated with HPV?
Oncogenic, cervical cancer
Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever (Viral Category, Virus Name, Virus Family, Mode for Spread)
Category: Direct Contact
Virus: Ebola Virus
Family: Filoviridae
Spread: Direct contact with blood or body fluids of infected symptomatic person
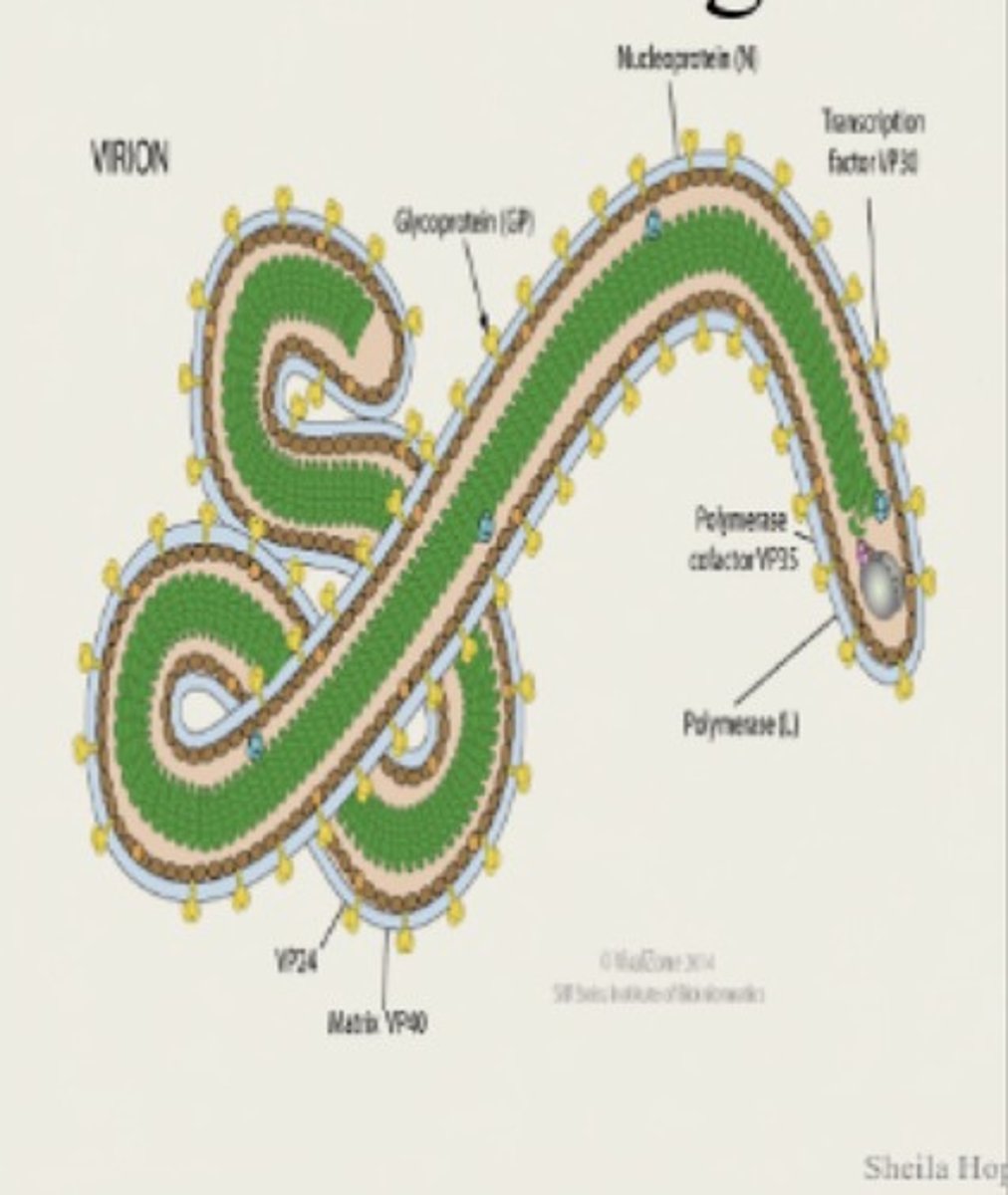
Ebola Virus Structure
Enveloped
RNA
Filamentous
Infection process of Ebola Virus
Viral proteins block interferon (antiviral cytokine)
Clot blood
What other viral category can ebola fit into?
Zoonotic: Fruit bats, primates
What is gastroenteritis?
inflammation of the stomach and intestines
What viruses cause gastroenteritis? Viral Category? Viral Structure? How is it spread?
Category: Food and Water Borne
Virus: Rotavirus, Norovirus
Structure: Naked, RNA viruses
Spread: Fecal-oral transmission, also person to person
Polio (Viral Category, Virus Name, Viral Structure, Spread)
Category: Food and Water Borne
Virus: Poliovirus
Structure: Enterovirus (intestinal tract), RNA genome
Spread: Stable in food, water (ingested)
Infection process of Polio
-Multiplies in throat and intestinal cells
-Targets motor nerve cells in spinal cord causing paralysis
(polio also known as infantile paralysis)
Polio Vaccines
Salk (killed) (recommended one b/c no chance of becoming viral)
Sabin (live, oral)
"iron lungs"
large metal tanks that change air pressure to help patients breath due to paralysis from polio
Estimate of infectious diseases that originate with animals
75%
What factors has caused the transmission of diseases from animals to humans?
Habitat changes altering ecosystems
-Deforestation
-Farming
-Climate changes
-Travel and Trade add to the quicker spread
Rabies (Viral Category, Virus Name, Viral Structure, Spread)
Catagory: Zoonotic
Virus: Rabis Virus
Structure: Bullet shaped, enveloped, RNA
Infection Process of Rabies
1. Multiples in salivary glands of animals
2. Viral replication in muscle and neuronal cells (Tropism)
3. Spread via CNS microtubule tracks using dynein and kinesin motor proteins
4. Spread to brain leading to paralysis
How long is the incubation period for rabies? What does this allow for?
2-16 week incubation period
-Slow disease allows for post-exposure vaccination
What kind of vaccine is the rabies vaccine?
Killed vaccine