Complex-Renal part 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What is the primary purpose of the urinary system and kidneys?
Remove waste products/drugs from the body
Balance the body's fluids
Release hormones to regulate blood pressure
Control production of red blood cells
What do the kidneys regulate?
Body osmolarity & volume
Electrolytes
Acid-base balance
Blood Pressure (BP)
What do the kidneys secrete? (hormones)
Erythropoietin for RBC production
1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol for vitamin D metabolism
Renin
Prostaglandin
What do the kidneys Excrete?
Metabolic waste products
Foreign substances (drug metabolites)
Excess fluid
Excess electrolytes
How do the kidneys regulate Osmolarity and volume?
Na+ & H2O balance
Thus, maintaining extracellular fluid volume (ECFV) homeostasis
What is the normal pH range?
7.35-7.45
What is the normal CO2 range?
35-45 mmHg
What is the normal HCO3 range?
18-24 mEq/L
What is the PaO2 normal range?
>90 mmHg
What is the normal SaO2 range?
94-100%
What Acid-Base imbalance is indicated if there is elevated CO2?
Acidosis (respiratory)
What Acid-Base imbalance is indicated if there is decreased CO2?
Alkalosis (respiratory)
What Acid-Base imbalance is indicated if there is an increased HCO3?
Alkalosis (metabolic)
What Acid-Base imbalance is indicated if there is a decreased HCO3?
Acidosis (metabolic)
How does the Cardiovascular center regulate BP?
within the brain, impacts BP (↑ or ↓) rapidly by adjusting CO or blood vessel dilation by way of:
The Sympathetic nervous system ↑ HR & vasoconstricts
The Parasympathetic nervous system ↓ HR (vagus nerve) and vasodilates
Baroreceptors- mechanosensitive nerve endings in carotid sinuses and aortic arch- function as arterial BP sensors; very sensitive & CX a reaction within milliseconds
How do the kidneys regulate BP?
by releasing hormones:
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) controls blood volume (BP) and construction of blood vessels (also BP) by releasing hormones
Why would the kidneys secrete EPO?
Produces RBCs and thus increases volume
Why do the kidneys secrete enzymes? (specifically 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3)
Converts inactive Vitamin D to active Vitamin D for Ca++ metabolism and maintains C++ balance in the body-bones!
Why do the kidneys secrete Renin?
Converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin I
Why do the kidneys secrete Prostaglandins?
These are lipids that help regulate renal hemodynamics by controlling Na+ & H2O and helps in regulating the renin-angiotensin system
What Renal Specific Health History is needed?
Chief complaint
Changes in voiding (hesitancy/frequency?)
Any DX procedures/surgeries or catheters?
OB/GYN history (female pts)
Kidney stones (current or PMH of)
S/S of anemia
Gastrointestinal s/s
Medications (including OTCs)
Tobacco (↑ risk for certain kinds of CA)
Illicit drugs or alcohol abuse
Advanced age?
Any other risk factors?
In a Genitourinary Focused Assessment, what cardiac measures would the nurse check?
Heart sounds (added heart sounds could mean fluid volume overload)
Vitals (ECG for dysthymias)
Central Venous Pressures (if possible) tells systemic volume status
In a Genitourinary Focused Assessment, what Pulmonary measures would the nurse check?
Breath sounds (fluid volume overload?)
Chest X-ray (fluid?)
O2 Sats (can indicated fluid issues if low)
In a Genitourinary Focused Assessment, what Neurological measures would the nurse check?
Confusion?
Could be a sign of toxicity if they have renal function issues.
In a Genitourinary Focused Assessment, what Integumentary measures would the nurse check?
Dry skin/lips/mouth-hydration status?
Color-Pallor? Patchy, itchy?
In a Genitourinary Focused Assessment, what Bladder measures would the nurse check?
Palpate and ask about sensation, voiding issues, how much
UOP (observed and a discussion with the patient)
In a Genitourinary Focused Assessment, what Circulatory system (vitals) would the nurse check?
↑BP could mean too much systemic volume (poor kidney function?)
↓ BP and ↓HR-dehydration/fluid volume depletion?
CVP if available
What is considered a Normal Urine Output (UOP)?
0.5 to 1.5 cc/kg/hour at least every 6 hours (at least 30cc/hour or 800-2L per day)
What is considered Excessive Urine Output?
Frequency - frequent voiding more than every 3 hours
Polyuria - ↑ volume of urine voided
What is considered Poor Urine Output?
Oliguria – decreased UOP < 0.5 mL/kg/hour (less than 400 in a day)
Anuria – means “without” urine
What things are found in our urine?
Bacteria
Protein
Blood
Sugar (glycosuria)
What can cause Oliguria? (UOP< 400mL/24 hr or <0.5mL/kg/h for 6hrs) (when it comes to the renal system)
AKI, CKD, dehydration
What can cause Anuria? (UOP<50mL/day)
AKI/CKD
What is a possible cause of Dysuria? (Difficulty voiding or Pain with urination)
Lower UTI, inflammations of the blader/ureter/ prostatitis
kidney stones, foreign bodies, bladder tumors
What is a possible cause of Urinary Frequency? (more than every 3 hours)
UTIs, obstruction of the ureters, anxiety, diuretics
benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), diabetic neuropathy
What is the possible cause of Urinary Hesitancy? (Delay or difficulty initiating voiding)
BPH, neurogenic bladder, obstruction, stones
What is the possible cause of Nocturia? (Awake at night to urinate)
Diabetes, heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, excessive water intake, cirrhosis
What is the possible cause of Polyuria? (Increased volume of urine voided)
Diabetes, DI, diuretics, excessive fluid intake, lithium toxicity, KDs
What is the possible cause of Bacteriuria? (Bacterial count >100,000 colonies/mL in urine)
Infection
What is the possible cause of Hematuria? (RBCs in the urine)
CAs, Acute glomerulonephritis, kidney stones, blood dyscrasias, sickle cell, rheumatic fever, extreme exercise, trauma
What is the possible cause of 3+ RBC (hematuria) in a urine analysis?
Infection, stones, neoplasm, trauma
What is the possible cause of Proteinuria in a urine analysis?
Benign finding (fever, exercise), DMII, HF, medications
What is the possible cause of altered specific gravity in urine analysis?
hydration status
What is the possible cause of Glucose in Urine Analysis?
Diabetes, pregnancy, kidney pathology
What is the possible cause of Casts in a urine analysis?
Dehydration, fever, HF, many kidney diseases
What is the possible cause of Leukocyte esterase and nitrate in a urine analysis?
Assoc. w/ increase WBC and infection
What are older adults at risk for with their kidneys?
Acute and chronic renal injury
Incomplete bladder emptying (structural changes)
Adverse drug effects and drug-drug interactions
Hypernatremia and fluid volume d/t ↓ thirst
Urinary incontinence much more common
UTI especially in older women
Polypharmacy is an issue
Often there is a loss of body mass (might need different RX dosage)
What diagnostics is used to evaluate kidney function?
Renal function tests (Serum)
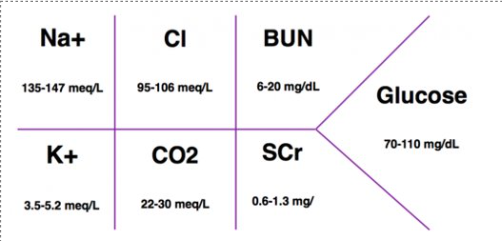
What do common serum lab tests check for?
Na+ (135-147 meq/L)
Cl (95-106 meg/L)
BUN (6-20 mg/dL)
K+ (3.5-5.2 meq/L)
CO2 (22-30 meq/L)
SCr (0.6-1.3 mg/dL)
Glucose (70-110 mg/dL)
What is Blood Urea Nitrate (BUN) and what does it tell us?
Serum BUN is one expression of renal function and fluid volume
The urea travels from your liver to your kidneys through your bloodstream
Healthy kidneys filter urea and remove other waste products from your blood
The filtered waste products leave your body through urine
What are some causes of Elevated Serum BUN levels? (Source-Blood)
Dehydration
Urinary tract obstruction
Congestive heart failure
Recent heart attack
Certain medications
Shock
High protein diet
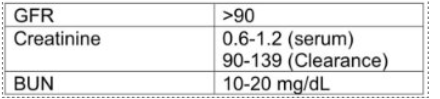
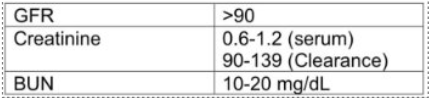
What is Serum Creatinine (SCr) and what does it tell us?
A chemical compound left over from energy-producing processes in your muscles (creatinine)
Healthy kidneys filter creatinine out of the blood
Creatinine exits your body as a waste product in urine
Tells us about the function of the kidneys
What are some of the causes of Elevated Serum Creatinine Levels?
Kidney infection
Glomerulonephritis (inflammation of kidney structures that filter blood)
Kidney stones (can block the urinary tract)
Kidney failure
Temporary elevations (causes can be multiple)
What does Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) do?
Tells how well the kidneys are working: Estimates how much blood passes through the glomeruli each minute
What is a Kidney, Ureter, and Bladder (KUB) study?
Delineates size/shape/position of kidneys
Reveals urinary system abnormalities
Can be done at bedside: often 1st diagnostic performed
Less costly than other diagnostics
What is a Renal Ultrasound?
Noninvasive view of GU system
Identifies:
Fluid accumulations
Masses
Congenital abnormalities
Obstructions
What does a CT scan identify in relation to renal issues?
masses, stones, infection, trauma
metastasis, soft tissue abnormalities
Can be used w/ contrast to enhance visualization
What needs to be done Pre-procedure prior to IVP dye (contrast dye)?
Allergy history (shellfish/contrast dye?)
DC nephrotoxic meds (NSAIDS, metformin, vancomycin, etc.)
IV access
Assess & Monitor kidney function
What Pre-procedure labs need to be drawn prior to IVP (contrast) dye injection?
(CMP-Creatinine, BUN, GFR)
Alert healthcare team of any abnormal renal labs
Administer an antihistamine (if patient allergic)
What pre-procedure medications are needed prior to IVP (contrast) dye injection?
Patients with AKI/CKI: IV Mucomyst (N-acetylcysteine)
Mucomyst-Contraindicated with sulfur allergies
NS IVF before, during, after the procedure (for non EKD pts)
What is needed post-procedure in relation to IVP (contrast) dye?
Complete Metabolic Panel
Alert medical team of abnormal renal labs
IVF (NS-preferred)
After contrast dye, flush the kidneys
Strict observation of UOP
one of the most valuable assessments for AKI
What is Cytoscopy?
Uses a scope to view the inside of the bladder and urethra
What does a Cytoscopy check for?
bladder cancer
bladder control issues
enlarged prostate
urinary tract infections
What does a Kidney biopsy help to diagnose/evaluate?
kidney disease (and severity)
Unexplained AKI
Persistent Proteinuria/hematuria
Transplant rejection
Glomerulopathies
What is needed pre-op before a Cystoscopy and Renal Biopsy?
Describe the procedure
NPO
What is needed post-op for a Cystoscopy and Renal Biopsy?
Relieving any discomfort or pain
Possible burn when voiding, blood-tinged urine, & urinary frequency
Moist heat to lower abdomen
Sitz baths
What is the formula for the 24-hr creatinine clearance?
Volume of urine (mL/min) x Urine creatinine (mL/dL) / Serum Creatinine (mg/dL)
What are the normal serum BUN levels?
7-20 mg/dL
What are the normal serum creatinine levels?
0.5-1.2 mg/dL
What is the typical GFR for an adult?
90-120 ml/min/1.73 m
What is the typical GFR for an elderly person?
60-89 ml/min/1.73 m
How much urine output is normal per hour?
30 mL (0.5-1.5 cc/kg/hr at least every 6 hrs)
How much urine output is normal per day?
800-2000 mL
What is considered Poor urine output?
< 0.5 mL/kg/hr (less than 400 per day)