chemistry - topic 5: monitoring/controlling chemical reactions
1/25
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is concentration?
Concentration is a measure of how much of a substance is present in a given volume.
How to convert mol/dm into g/dm?
Multiply by relative formula mass.
Why do you conduct a tittration?
To find out the concentration of solutions.
Describe a titration experiment (7 points).
Measure out a set volume of your alkali and put it in a conical flask on a white tile.
Add a few drops of a suitable indicator.
Fill a burette with a standard solution of acid.
Perform a rough titration by adding the acid drop-by-drop until it’s almost neutralised - swirl the flask regularly.
Record the volume of acid used (the titre).
Repeat this process a few times and then take the mean.
Only use concordant (within 0.1) titres in the mean.
What are the 2 formulas of concentration?
Conc = Mass / Volume
Conc = Moles / Volume
The volume occupied by one mole of gas is known as //
Molar Volume.
One mole of gas always occupies // at room temperature and pressure.
24dm3
What is percentage yield?
The comparison of actual yield to theoretical yield.
What is the calculation for percentage yield?
Actual yield/theoretical yield * 100
Define theoretical yield.
The amount of product produced in perfect chemical and practical conditions.
What is atom economy?
The percentage of reactants changed to useful products.
How do you calculate atom economy?
Total mass of desired products/Total mass of all products * 100
Why is high atom economy good? (2 points)
Raw materials are expensive, so it reduces waste.
Makes reactions profitable.
What is the equation for reaction rate?
Rate = Amount of products formed / Time
What are the three methods of measuring rate of reaction?
Precipitation - When two solutions mixed together form a precipitate. Observe a mark underneath the beaker. Faster it disappears, faster the reaction
Mass - Measure the loss of mass when a gas is released in a reaction with a gas as a product. Faster it goes down, faster the reaction
Volume given off - Use a gas syringe to measure the volume of gas given off. More gas in a time interval, faster reaction rate.
What investigation shows how surface area affects rate? (2 points)
Hydrochloric acid & Marble Chips
The marble chips produce gas
Finer particles (large surface area) with have a faster rate of reaction
A // concentration results in a higher rate.
Higher
Rate of reaction is // proportional to reaction time.
Inversely (as time increases, rate decreases).
What is the collision theory?
The rate of a chemical reaction depends on collision frequency and the energy transferred between each collision.
How does temperature increase rate?
Particles move quicker at high temperatures
More successful collisions
Higher rate of reaction
How does concentration/pressure increase rate?
More particles in a smaller space
More frequent successful collisions
Higher rate
How does surface area increase rate?
Increased surface area to volume ratio
More solid exposed
More frequent successful collisions
Higher rate
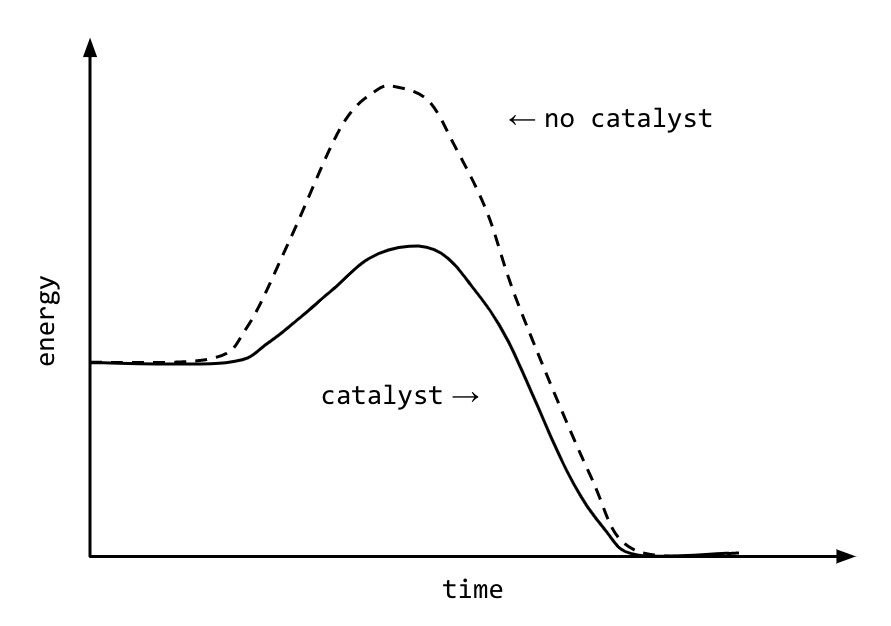
How do catalysts work?
They decrease the activation energy and provide an alternate reaction pathway that requires a lower activation energy.
What is (dynamic) equilibrium?
A reversible reaction in a closed system with a constant rate and concentration.
What is Le Chatelier’s principle?
If there’s a change in conditions of a system, the equilibrium position will shift to counteract the change.
What three things can change the equilibrium position, and how do they do so?
Temperature - If temperature is decreased, it’ll shift to the exothermic direction to produce more heat. If temperature is increased, it’ll do the opposite to absorb the extra heat.
Pressure - If pressure is increased, it’ll shift to the side with fewer moles of gas to reduce pressure. If pressure is decreased, it’ll shift to the side with more moles of gas to increase pressure.
Concentration - If concentration of reactants is increased, it’ll shift to the right to make more product, and vice versa. If concentration of reactants is decreased, it’ll shift to the left to make more reactants, and vice versa.