Week 3 - Pregnancy at Risk: Social and Physiological Factors
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
risk considerations of adolescent pregnancy
ages 10 to 19 years are at risk of eclampsia, infection, etc.
maternal mortality
perinatal complications (lead to maternal deaths)
early pregnancy / marriage causes dropout of school
impact of adolescent pregnancy
may interfere with developmental milestones
social isolation
fear of child services
stigma (actual & perceived)
need to be perceived as a "good mother"
adolescent friendly perinatal care includes...
being nonjudgemental
forming a connection
individualizing nursing care (be flexible and adaptable)
**treat everyone the same, be self-reflective
advanced maternal age and risks
pregnancy > 35 years
maternal death
miscarriage
stillbirth
low birth weight
perinatal mortality
down syndrome
women with disabilities and pregnancy
higher risk for social, economic, physical problems
-stigma / assumptions of care provides and family
-higher risk for social service involvement
-need for pre-planning, social support
IPV: who is at risk during pregnancy?
pre-pregnancy abuse
women under 25
SU by women or partner
single or lone parents
recently or abt to be separated
Indigenous women
women with disability
lesbian, bisexual, transgender
low SES
IPV and pregnancy is associated with...
preterm labour, prematurity, LBW, neonatal & infant/maternal mortality
maternal depression, SU
IPV screening tools: RADAR
Remember to ask abt IPV routinely
Ask directly abt violence (**interview in private)
Document findings r/t to violence in chart
Assess pt's safety
Review options with pt (referrals to shelters, support groups, legal advocates)
IPV screening tools: HITS
physically Hurt you
Insult or talk you down
Threaten you with harm
Scream or curse at you
**Likert scale: total score more than 10 suggests IPV
role of CHN and IPV
duty to report if there is a child under 16
show you believe and that there is help
do not judge; leaving takes time
reinforce that abuse is not her fault and apologies won't end abuse
reinforce their safety as top priority
offer referral, provide info, leave many resources
SU during pregnancy and risks
drugs can easily pass from mom to baby through placenta (eg. alcohol, cocaine, heroin, met)
bleeding complications, miscarriage, stillbirth
prematurity
low birth weight
sudden infant death syndrome
congenital anomalies
SU during pregnancy
-barriers to tx
-legal considerations
-guilt, fear, shame, fear of losing custody of child
-SU tx programs don't usually address issues impacting pregnant women
-long waiting lists, lack of women-only spaces
-non-judgemental and person-centred approach
-harm reduction model
-encourage prenatal care, counselling, tx
SU nursing care
assess for hx of violence, abuse, MH concerns, SDH
ensure confidentiality, non-judgemental, trauma-informed approach
harm reduction: supporting a pt's desire to stop using as well as assisting them in reducing risks
opioid agonist therapy (OAT) - methadone or buprenorphine tx recommended
education on use and side effects during pregnancy
postpartum follow up visits
early pregnancy bleeding
ANYTHING BEFORE 20 WKS = miscarriage/abortion
**miscarriage (spontaneous abortion): loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks gestation
early pregnancy bleeding: early vs late loss
early loss: before 12 weeks
-majority r/t **chromosomal abnormalities, teratogenic drugs, placental abnormalities, infections, etc.
late loss: 12-20 weeks
-advance maternal age, **premature dilation of cervix, chronic infection, use of recreational drugs
threatened abortion
threat that miscarriage could occur
slight bleeding, mild cramping, closed cx, no expulsion of products
bed rest, assess hCG and progesterone levels to determine if alive
inevitable abortion
miscarriage that cannot be prevented
mod bleeding, mild to severe cramping, open cx, no expulsion of products
bed rest if no bleeding or pain, rupture of mem/bleeding = uterus emptied via D&C
incomplete abortion
expulsion of products not fully out yet
heavy bleeding, severe cramping, closed cx, expulsion of products
may need dilation, suction curettage may be performed
complete abortion
all products are expelled
slight bleeding, mild cramping, closed cx
no further intervention if no hemorrhage or infection, suction curettage may be performed
missed abortion
death of a fetus or embryo within the uterus that is not naturally expelled after death
no bleeding or spotting, no cramping, closed cx, no expulsion of products
usually occurs before 1 month, monitor clotting factors and coagulation conditions, no fetal heartbeat on ultrasound
septic abortion
presence of infection
malodorous bleeding, cramping, cx open, expulsion
immediate termination, C&S, anitbiotics, treat spetic shock as needed
recurrent abortion
two or more consecutive spontaneous abortions
bleeding, cramping, cx open, expulsion
cerclage may be performed for premature cervical dilation
assessment & care: initial/general assessment for preg bleeding
VS, allergies, N/V, LOC
# of pregnancies, # of live births
last menstrual period / estimated DOB
pregnancy hx (previous & current)
pain (onset, quality, precipitating event, location)
bleeding or coagulation issues
emotional status and need for support
assessment & care: early pregnancy
confirmation of pregnancy w laboratory testing
bleeding (bright or dark, spotting or continuous)
pain (type, intensity, location, persistence)
vaginal discharge
assessment & care: late pregnancy
estimated DOB
bleeding (amt, pinky, menstrual-like, heavy)
pain (location, severity, intermittent, continuous)
vaginal discharge
amniotic membrane status
uterine activity, fetal HR and movement felt
management of incomplete abortion
-expectant management
-medical management
-surgical management
1. allows miscarriage to expel on its own
2. use of 2-drug combination - Mifepristone (for uterus prep) & Misoprostol (soften and dilate cx to aid in miscarriage)
2. dilation and curettage (D&C) - cx gently opened (dilation) and pregnancy removed with suction device (curettage)
discharge teaching after preg loss
*report any heavy, profuse, bright red bleeding
scant, dark discharge may persist for 1 to 2 weeks
avoid putting anything into vagina for 2 weeks or until bleeding has stopped
*take antibiotics as prescribed
*report temp elevated or foul-smelling discharge
eat foods high in iron and protein
encourage to speak with family, seek support from friends, groups, counselling
*postponed pregnancy for at least 2 months
ectopic pregnancy: manifestations, medical management
fertilized ovum implanted outside uterine cavity (most occur in fallopia tube on ampullar)
abd pain (one sided or lower quad), missed period, abnormal bleeding, referred shoulder pain
methotrexate - antimetabolite and folic acid antagonist; destroys rapidly dividing cells
teaching for methotrexate therapy
avoid intake of foods and vitamins containing folic acid
avoid eating "gas-forming" foods
avoid sun exposure
avoid sexual intercourse until β-hCG level is undetectable
contact HCP immediately if experiencing severe abd pain (impending or actual tubal rupture)
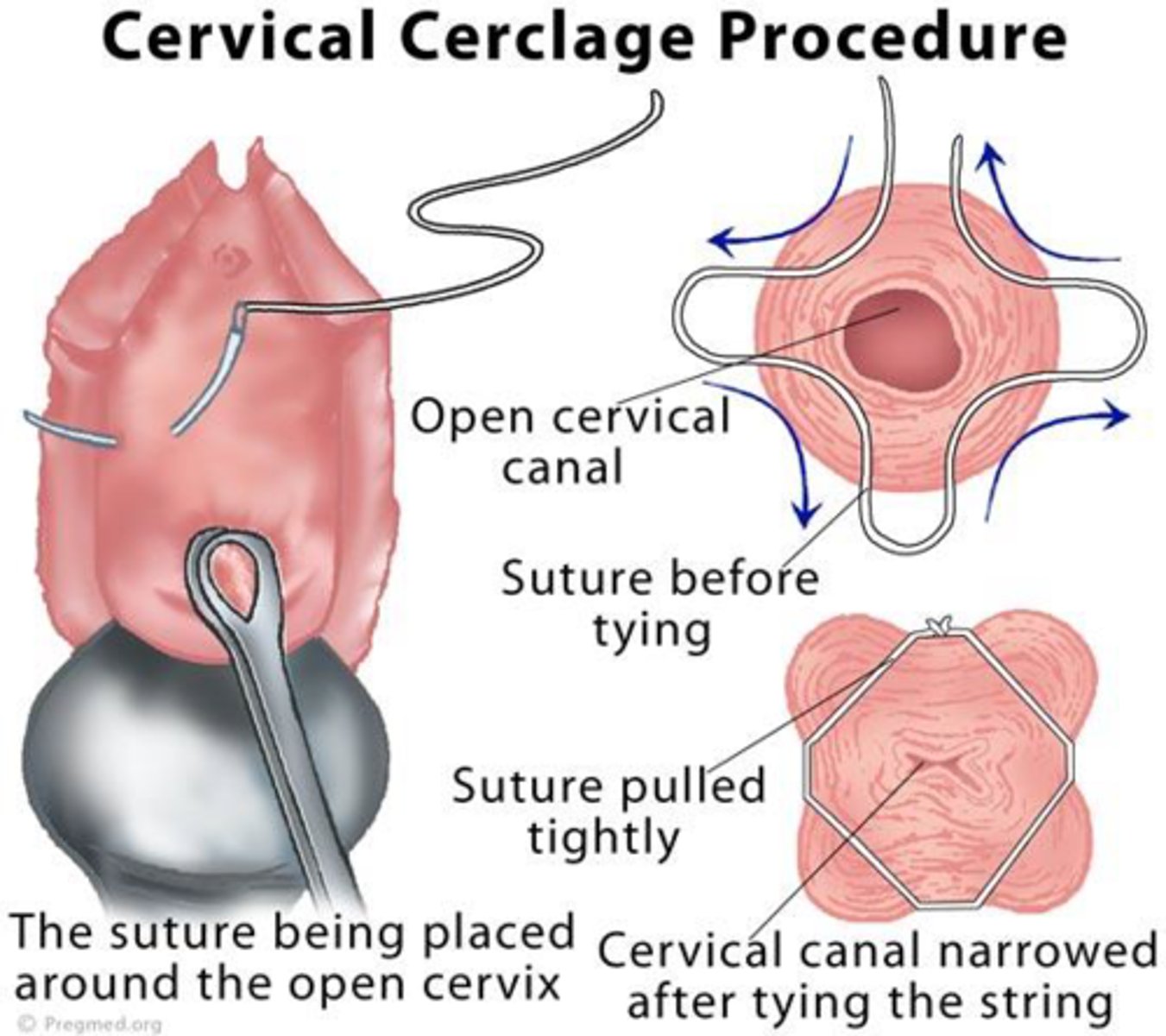
premature dilation of cervix
cervical insufficiency - dilation of cx w/o contractions or labour; painless
d/t structural weakness of cervix tissue (collagen disorder) or cervical trauam
nursing and interdisciplinary care for premature dilation of cervix
cervical cerclage
continuous close observation and supervision for rest of pregnancy
report signs of preterm labour, rupture of membranes, infection
ER if strong contractions, urge to push
late pregnancy bleeding: placenta previa
ANYTHING AFTER 20 WKS = preterm
placenta implanted in lower uterine segment near or over internal cervical os
3 types: low-lying, marginal, complete placenta previa
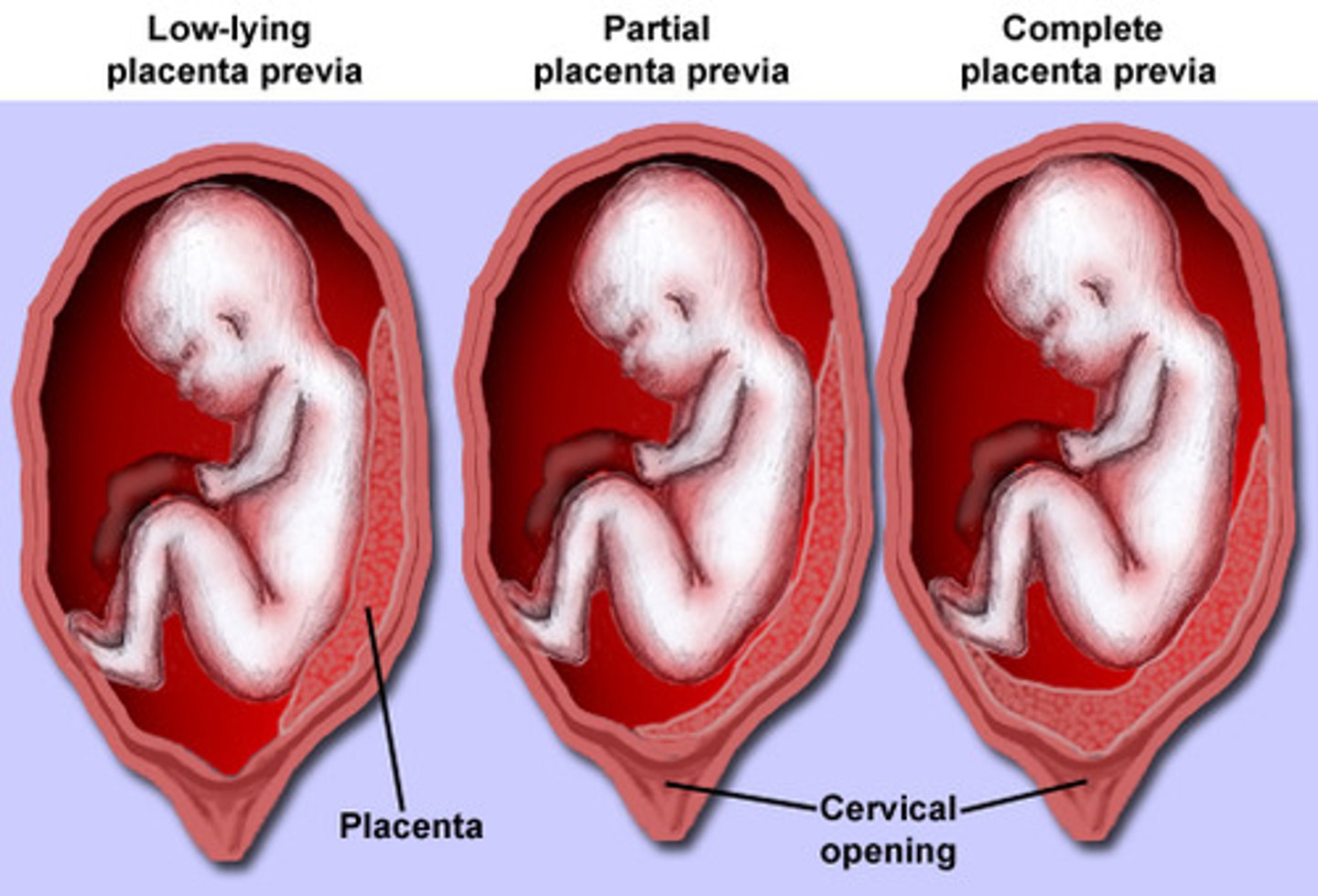
placenta previa: clinical presentation, diagnosis, complications
bright red bleeding, pain absent, uterine is normal, normal fetal HR
transabdominal or vaginal ultrasound
bleeding, preterm birth, IUGR
risk factors for placenta previa
smoking, cocaine use
multiparity
erythroblastosis
POC, low SES
infertility tx, prior uterine surgery
recurrent abortions
advancing age (> 35)
*multiple gestation (larger SA of placenta)
placenta previa nursing and interprofessional care
potential emergency d/t risk of massive blood loss
expectant management - reduce activity, close observation -when pt < 36 wks, not in labour, minimal bleeding
-no vaginal/rectal examinations, ultrasounds q2wks
-bleeding assessed thru amt of bleeding on pads (1g = 1ml)
-antepartum steroids (betamethasone) to promote fetal lung maturity
active management - C section
-when fetus is mature or pt w/ excessive bleeding; active labour
late pregnancy bleeding: placental abruption
ANYTHING AFTER 20 WKS = preterm
premature separation of placenta
3 grades of separation: 1 (mild), 2 (mod), 3 (severe)
*major cause of antepartum haemorrhage*
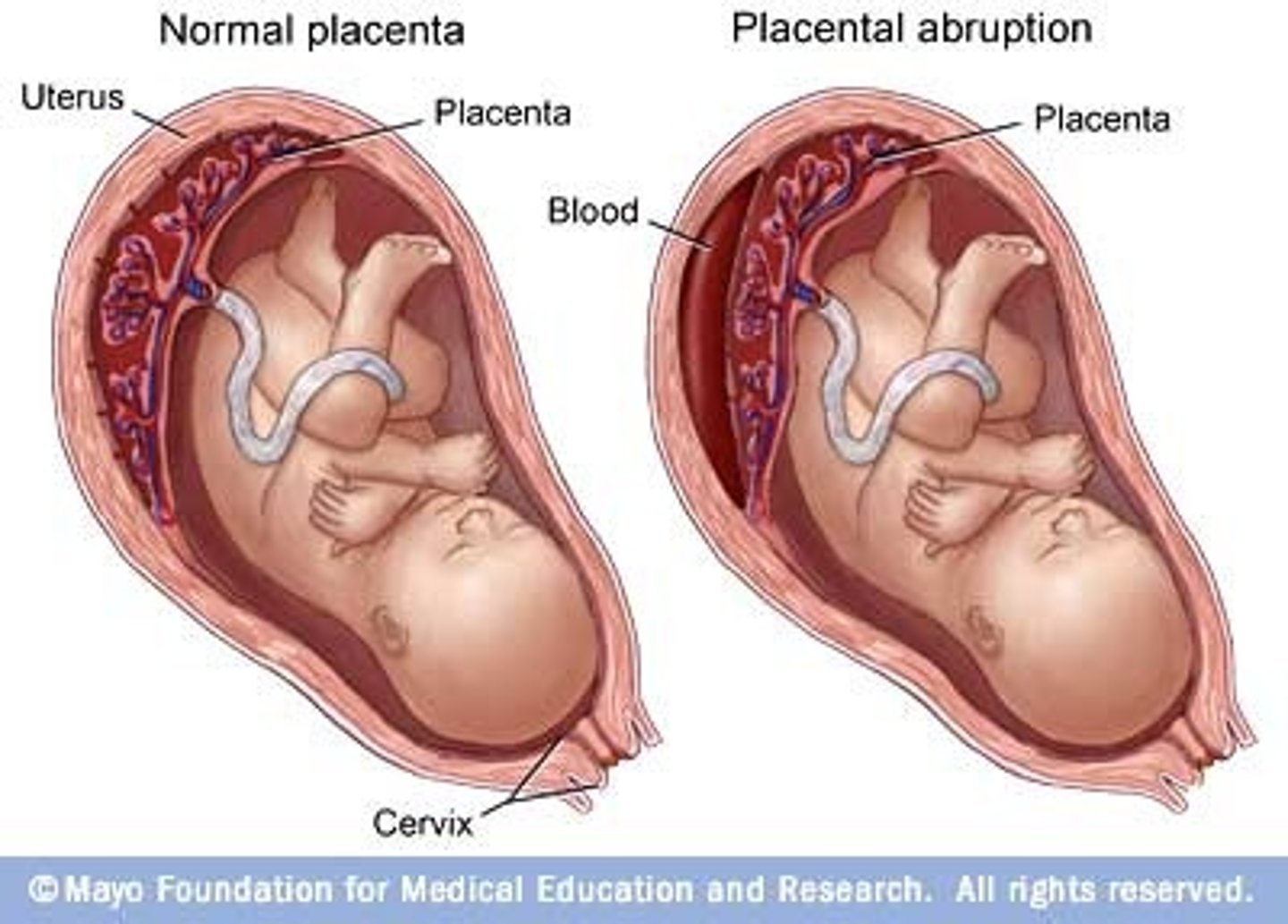
placental abruption: clinical presentation
vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, uterine tenderness, contractions
risk factors for placental abruption
maternal HTN / preeclampsia
age, increasing parity, multiple gestations
polyhydramnios (excess amniotic fluid), chorioamnionitis
preterm PROM
trauma (assault or motor vehicle)
SU (eg. cocaine)
**hx of abruption
maternal and fetal complications of placental abruption
maternal
-hemorrhage, hypovolemic shock
-DIC
-infection
fetal
-IUGR, preterm birth, hypoxemia, stillbirth
-risks for neurological defects, death
placental abruption nursing and interprofessional care
expectant management - < 36 wks
-pt hospitalized
-fetal monitoring
-maternal VS for deterioration
-use corticosteroids to accelerate fetal lung maturity
-Rh -ve mom given Rho(D) immunoglobulin if baby Rh +ve
-emotional supports
DIC
disseminated intravascular coagulation
proteins controlling blood clotting becomes overactive, thus uses up all clotting factors = external & internal bleeding
DIC is often triggered by release of large amts of tissue thromboplastin (clotting factor) caused by
placental abruption (most common)
retained dead fetus syndrome
amniotic fluid embolus
pre-eclampsia, HELLP syndrome
gram-negative or gram-positive sepsis
stages of DIC
stage 1 - overactive clotting -> blood clots throughout blood vessel -> clots can reduce/block blood flow -> damages organs
stage 2 - overactive clotting uses platelets & clotting factors up that help blood to clot -> absence of platelets and clotting factors -> internal bleeding
physical examination of DIC
spontaneous bleeding from gums, nose
oozing, excessive bleeding from IV sites, foley entrance
petechiae (where BP cuff was)
bruising
hematuria
GI bleed
tachycardia, diaphoresis
coagulation screening test of DIC
platelets and fibrinogen decreased
clotting factors decreased
PT and PPT prolonged
d-dimer test increased
red blood smear - fragmented RBCs
DIC nursing and interprofessional care
correction of underlying cause (tx of infection, eclampsia; removal of placenta abruption)
**volume expansion, rapid replacement of blood products & clotting factors
vit K administration, recombinant activated factor VIIa, fibrinogen concentration
urinary output needs w in-dwelling catheter
keep pt warm w forced air warming system, warmed blankets, fluid warmers
severe vs chronic vs gestational HTN & pre-eclampsia/eclampsia
severe HTN: SBP > 160 mmHg and DBP > 110 mmHg
chronic HTN: prepregnancy HTN is present prior to 20 weeks of gestation
gestational HTN: develops after 20 weeks of gestation (absence of proteinuria)
pre-eclampsia/eclampsia: gestational HTN with proteinuria and/or other target organ involvement
pre-eclampsia & eclampsia
gestational or chronic HTN and new onset proteinuria
additional organ dysfunction may be present - acute kidney or liver dysfunction, neuro & hematological complications
pre-eclampsia (no convulsions), eclampsia (convulsions)
risk factors of pre-eclampsia & eclampsia
nulliparity, age > 40 yrs
family hx of pre-eclampsia
SGA pt
obesity/gestational DM
multifetal gestation
pre-eclampsia or poor outcome in previous pregnancy
pre-existing medical/genetic conditions
chronic HTN, renal disease, type 1 (insulin resistance) DM
pre-eclampsia etiology
poor perfusion from vasospasm => increased BP
smaller blood vessels impedes blood flow to all organs and increases BP
maternal complications of pre-eclampsia
multi organ failure
CNS - seizure, cerebral oedema, cerebral hemorrhage, stroke
kidney - renal failure, oliguria, hypo-proteinuria
lungs - pulmonary edema
liver - hepatic failure, hepatic rupture
hematological - DIC, HELLP
fetal complications of pre-eclampsia
preterm birth
still birth (IUFD)
fetal distress
uteroplacental insufficiency
placenta abruption → IUGR, hypoxic neurological
HELLP syndrome
severe pre-clampsia accompanied by...
-hemolysis (H)
-elevated liver enzymes (EL)
-low platelets (LP)
HTN and proteinuria, epigastric/RUQ pain, N/V, headache, malaise
HELLP syndrome associated with increased risk for...
placental abruption
renal failure
pulmonary edema
ruptured liver hematoma
DIC
pre-eclampsia & HELLP nursing care
BP assessment
deep tendon reflexes - bicep reflex, patellar reflex
fetal health surveillance (nonstress test [NST], contraction stress test [CST], biophysical profile [BPP], FHR ultrasonography, fetal movement counting)
activity restriction
pre-eclampsia pt teaching
report increase in BP (monitor)
dipstick test clean-catch urine sample to assess protein
decreased fetal movement (5 or less in 2 hours)
meds for pre-eclampsia & HELLP
control BP - hydralazine, labetalol, methyldopa, adalat
magnesium sulphate (antiseizure) - observe signs of toxicity (loss of reflexes, resp depression, oliguria, low LOC)
eclampsia/seizure precautions
quiet, non stimulating
lighting subdued
seizure precautions (have Mg sulphate available)
suction equipment tested and ready
O2 administration equipment tested and ready
call button within easy each
eclampsia nursing care
usually occurs after headache, blurred vision, photophobia, abd pain, altered mental status
immediate care = ensure patent airway, meds (Mg sulphate), assess fetal status
postpartum care = VS, I&O, reflexes, LOC
future = prenatal care assessment & early interventions
immediate care during seizure
keep airway patent → turn head to one side, place pillow under one shoulder/back if possible
call for assistance, do not leave bedside
padded side rails raised and safely locked
observe and record convulsion activity
after care for seizure
do not leave pt unattended until they are fully alert
observe for post convulsion coma, incontinence
use suction as needed
administer O2 & Mg sulphate/anticonvulsant med
insert in-dwelling urinary catheter and monitor hourly output
monitor BP, fetal and uterine status
expedite lab work as ordered to monitor kidney & liver function, coagulation system, med levels
provide hygiene and quiet environment
support pt and family; keep informed
be prepared to assist with birth as needed
gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)
elevated glucose levels that are first recognized during pregnancy
increased risk of developing glucose intolerance later in life
increased incidence of adverse maternal and fetal outcomes
risk factors of GDM
> 35 yo
high-risk group (African, Arab, Asian, Latin-American, Indigenous, or South Asian)
using corticosteroid medication
pregestational diabetes
obesity
GDM in previous pregnancy
given birth to a baby that weighed more than 4 kg
a parent, brother, or sister with T2 diabetes
PCOS or acanthosis nigricans (darkened patches of skin) associated insulin resistance
screening for GDM
screen for pre-existing diabetes before 12 weeks gestation
universal screening between 24-28 weeks is recommended in Canada + Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
multiple risk factors -> should screen in 1st trimester
interventions
interventions for GDM
antepartum - good blood glucose control, diet, exercise, monitor BG, pharmacological therapy (insulin, glyburide, metformin), fetal surveillance
intrapartum - macrosomia, birth injuries d/t shoulder, newborn hypoglycemia
postpartum - women with GDM, test again 6-12 weeks postpartum
Rh incompatibility / alloimmunization
isoimmunization: when abt 0.1mL of Rh+ fetal blood mixes with maternal Rh-
RBCs from fetus invade mom circulation -> create Rh antibodies & anti-Rh agglutinin
first baby not affect, but for the ones after
cause severe hemolysis & anemia in fetus
Rh incompatibility / alloimmunization prevention
good hx of past pregnancies to assess for incompatibility potential
determine mom's blood type & Rh factor; routine Rh antibody screen
Rh [D] immune globulin (RhoGAM) is given (at 28 weeks of pregnancy & within 72 hours postpartum)
hyperemesis gravidarum
prolonged vomiting that causes severe dehydration, weight loss, electrolyte imbalance, nutritional deficiencies, and ketonuria
between 4 and 8 weeks of pregnancy, resolves by 20 weeks
require hospitalization - fetal complication (LBW, SGA, preterm), maternal (vit k deficiency, thiamine)
hyperemesis gravidarum nursing care
assessment (VS, signs of dehydration, deep stick test for ketones)
clear liquids, slowly introducing small, frequent, bland meals that are high in protein/carbs but low in fat
avoid odours, tastes, other activities that can trigger nausea (eg. stuffy room, visually stimulating lights, strong perfume, etc.)
calm, compassionate, sympathetic care
support for pt and family
initiating and monitoring IV therapy
hyperemesis gravidarum meds
pyridoxine (vit B6) ; B complex
diphenhydramine
metoclopramide - accelerates gastric emptying
antiemetic and meds to control heartburn or reflux (antacids, histamine blockers, PPIs)
ondansetron if above medication are not effective (last resort)
biochemical assessment during pregnancy
-Coombs' test
-amniocentesis
-chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
screening tool for Rh incompatibility
amniotic fluid for genetic testing - for genetic concerns, fetal maturity, fetal hemolytic disease
test chromosomal abnormalities and other genetic disorders - removal of small tissue specimen from fetal portion of placenta
amniocentesis has the potential for maternal and fetal complications, such as...
maternal complications
-leakage of amniotic fluid
-hemorrhage, fetomateral hemorrhage
-infection
-paternal Rh isoimmunization
-placental abruption
-damage to intestines or bladder
-amniotic fluid embolism
fetal complications
-death
-hemorrhage
-infection (amnionitis)
-injury from needle
3rd trimester assessment of fetal well-being
determine whether intrauterine environment continues to be supportive to fetus
determines timing of childbirth for pts at risk for uteroplacental insufficiency
-fetal movement counting
-nonstress test (NST)
-contraction stress test (CST)
-biophysical profile (BPP)
-ultrasound tests
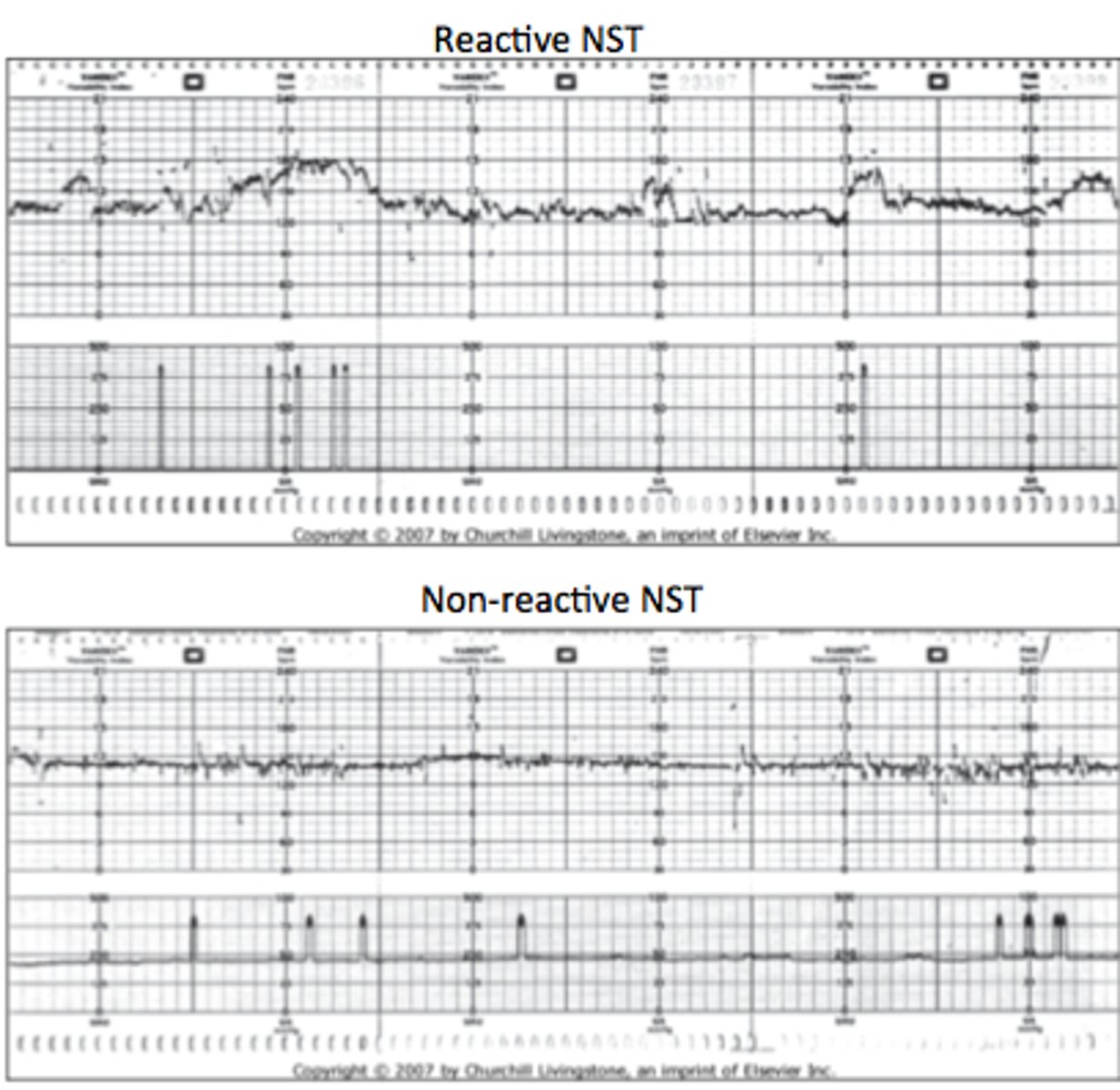
non-stress test (NST)
measure fetal HR in response to movement of fetus (electronic fetal monitor)
HR of healthy fetus should increase when fetus moves
reactive (normal) - at least 2 FHR accelerations lasting at least 15 secs & rising at least 15 beats/minute above established baseline HR
nonreactive - lacks sufficient FHR accelerations over a 40 min period
biophysical profile (BPP) & indications
for women at increased risk of problems that could lead to complications or pregnancy loss
non-invasive test using ultrasound and fetal heart monitoring
low score on BPP might indicate further testing is needed; early or immediate delivery might be recommended
-pregnancy has gone past 40 weeks gestation
-multiple gestation pregnancy
-previous stillbirth
-polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios
-GDM
-preeclampsia or other hypertensive disorder in pregnancy
-IUGR
5 components of the biophysical profile
1. fetal breathing movements (1+ episodes of rhythmic fetal breathing movements of 30+ secs within 30 minutes)
2. fetal movement (3+ discrete body or limb movements within 30 minutes)
3. fetal tone (1+ episodes of extension of a fetal extremity with return to flexion, or opening or closing of a hand)
4. amniotic fluid volume (one pocket of amniotic fluid exceeding 2 cm considered evidence of adequate amt)
5. NST
**each component given a score of 2; high = normal, low = complications
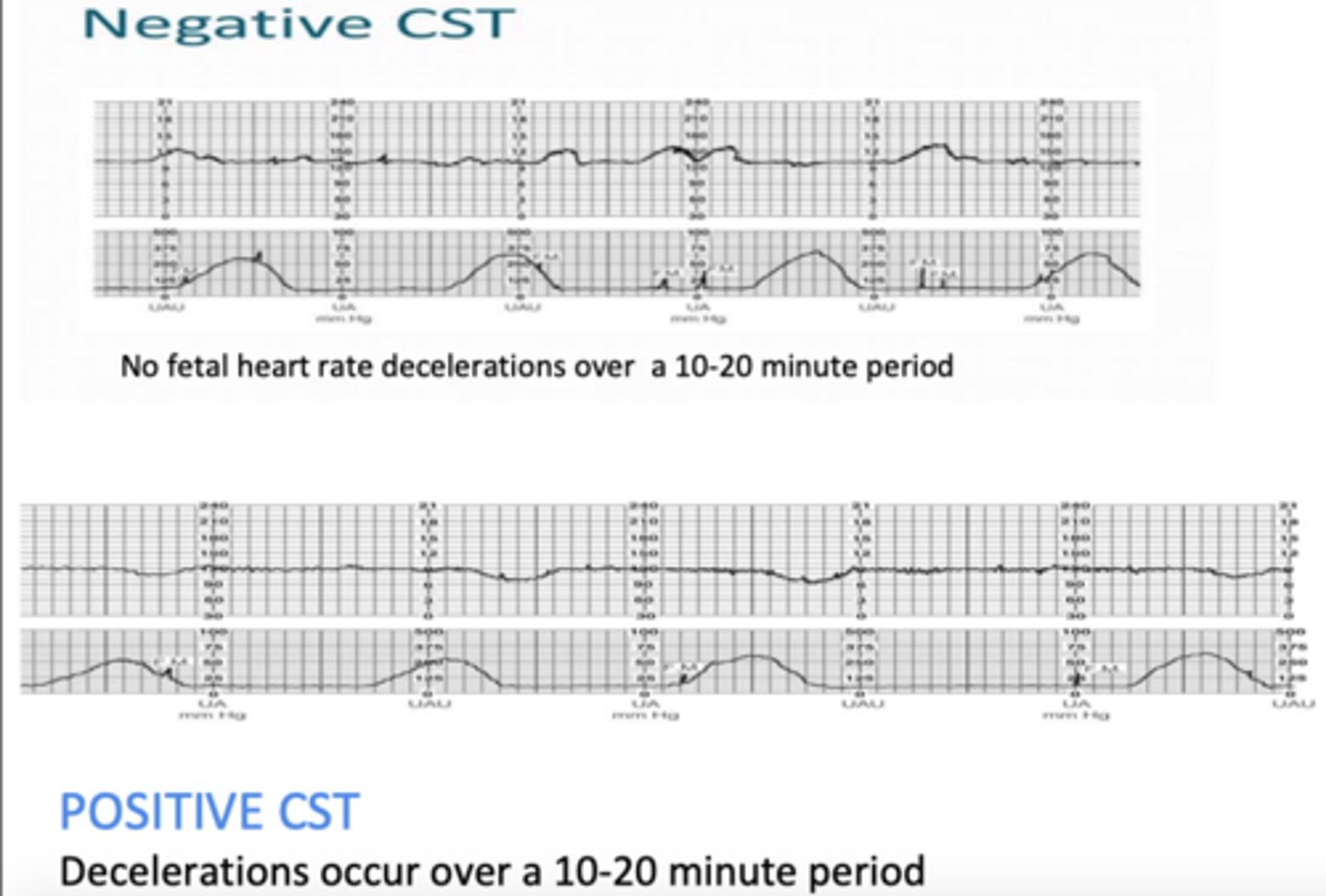
contraction stress test (CST)
measure response of fetus (FHR) after uterus is stimulated to contract
ensure that during labour, fetus can handle contractions and get O2 needed from placenta
nipple- or oxytocin-stimulated contraction test
negative test: FHR does not show deceleration or late decelerations (GOOD)
positive test: FHR is showing decelerations and late decelerations (BAD)
amniotic fluid volume: oligohydramnios vs polyhydramnios
oligohydramnios (< 300 mL of amniotic fluid, associated with fetal renal abnormalitie)
polyhydramnios (> 2 L of amniotic fluid, associated with GI and other malformations)