Intro to Anatomy & Physiology
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Hierarchy of Life Sciences
Cells>tissues>organs>organ systems>organism
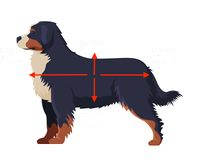
Left Arrow
Anterior (cranial)
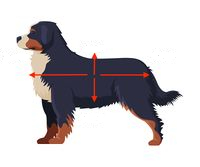
Right Arrow
Posterior (caudal)
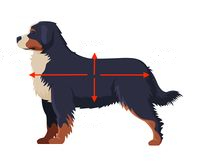
Up Arrow
Dorsal
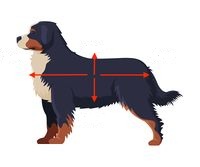
Down Arrow
Ventral
Functions of epithelial tissue
Protection, absorption, secretion, sensory
Function of connective tissue
Support, binding of organs, transport of substances, immunity
Function of muscle tissue
Movement
Function of nervous tissue
Conduction/control of nerve impulses, coordination of bodily functions
Description of the structure of simple squamous epithelial tissue
Single layer, flat cells
Description of the structure of simple cuboidal epithelial cells
Single layer, cube-shaped cells
Description of the structure of Simple columnar epithelial cells
Single layer, tall rectangular cells
Description of the structure of pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells
Single layer of cells of varying heights (looks to be stratified due to variation in heights but is not), tall rectangular cells
Description of the structure of stratified squamous epithelial cells
Multiple layers, flat cells
Description of the structure of stratified cuboidal epithelial cells
Multiple layers, cube-shaped cells
Description of the structure of stratified columnar epithelial cells
Multiple layers, tall rectangular cells
Description of the structure of transitional epithelial tissue
Cells shape can change depending on degree of stretch
Endocrine Glands Overview
Glands without ducts, empyt secretory products directly into the bloodstream
Practical Importance of Endocrine Glands
They regulate major bodily functions (growth, mood, reproduction, metabolism, etc.), they help maintain homeostasis
Exorcrine Glands Overview
Glands with ducts, empty their secretory products on an epithelial surface by means of ducts
Practical Importance of Exocrine Glands
Key for digestion (release enzymes), protection (sweat glands), lubrication (salivary glands), nutrition (mammary glands), defense (some animals can release sticky/toxic secretions)
Elastic Tissue
Kinked fibers that tend to regain their original shape
Collagenous Tissue
Coiled extracellular proteins
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Arranged in parallel bundles (cords/bands), high tensile strength
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Arranged in a thick mat, fibers run in all directions
Areolar Connective Tissue
Protective cushioning, flexible
Reticular Connective Tissue
Fine reticular fibrils made by fibroblasts, net-like scaffolding for other cells
Adipose Tissue
Forms when adipocytes store fat within the cytoplasm of a cell, as more fat gets deposited, the nucleus gets pushed to one side of the cell
What form of adipose tissue is commonly found in adult animals?
Seam fat - helps connect muscle to other structures
Cartilage Overview
Firmer than fibrous tissue but not as hard as bone, cartilage cells are called chondrocytes
Hyaline Cartilage
Glass-like covering over bones with joints
Elastic Cartilage
Mixture of cartilage substance and elastic fiber (eg. ear)
Fibrous Cartilage
Intervertebral disks between bodies of adjacent vertebrae
Primary Functions of Bone
Structural/organizational support, protects organs, stores minerals, bone marrow produces red blood cells
Skeletal Muscle
Striated, tubular, multinucleated fibers. Voluntary control. Typically attached to the skeleton.
Smooth Muscle
Non-striated, spindle shaped, single-nucleated. Involuntary control
Cardiac Muscle
Striated, branched, singe-nucleated fibers. Involuntary control
Nervous Tissue
Responsible for coordinating and controlling most of the body’s activities
Pleural Cavity
Potential space within the thorax between the lungs and the chest wall
What are potential spaces?
Anatomical regions where two adjacent membranes/structures press together with no gap. Membranes are lubricated by a think film of liquid allowing them to flide smoothly over each other.
Pericardial Cavity
Potential space between the parietal and visceral layers of the pericardium (sac around the heart)
Peritoneal Cavity
Potential space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum in the abdomen
Subdural Space
Potential space between the dura mater and arachnoid mater in the skull and spinal column
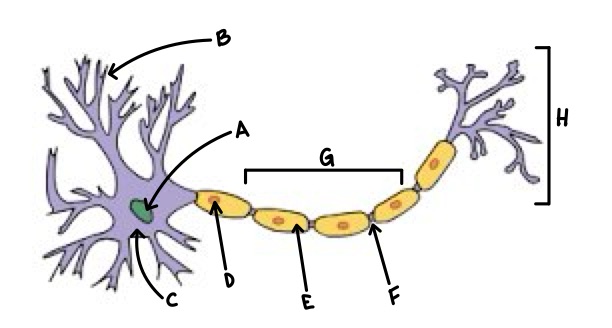
A
Nucleus
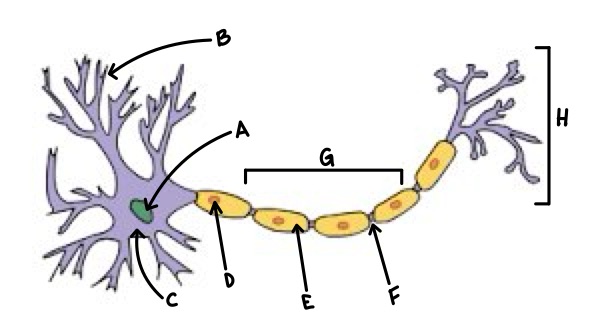
B
Dendrite
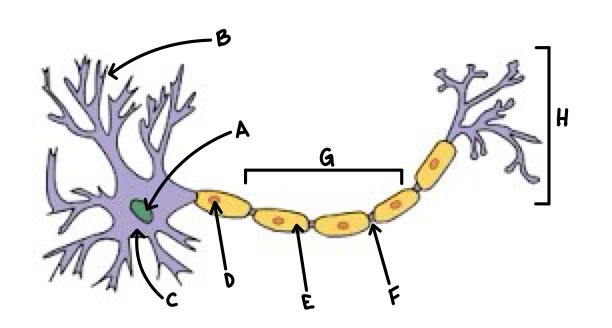
C
Soma
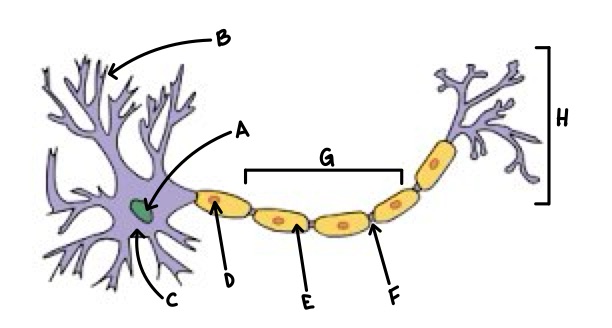
D
Schwann Cell
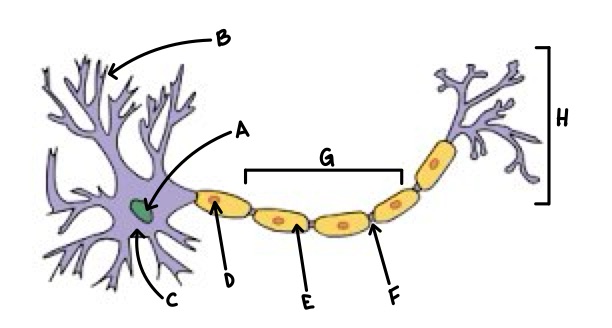
E
Myelin
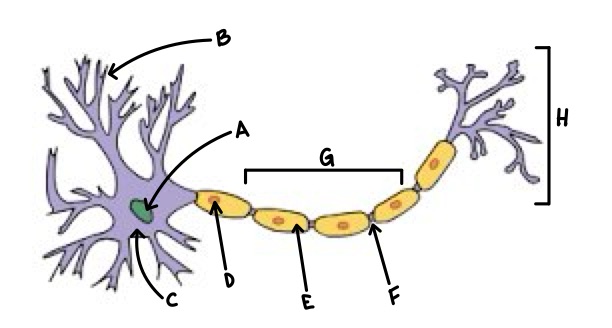
F
Node of Ranvier
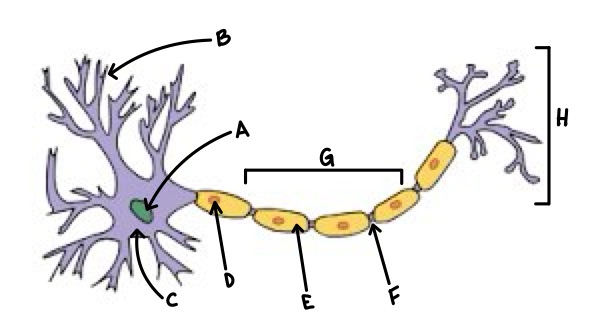
G
Axon
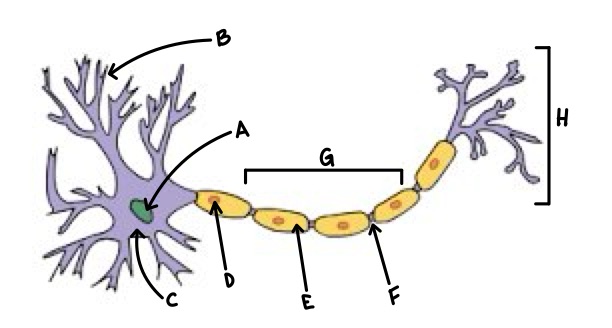
H
Axon Terminal