CDC Echinococcosis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
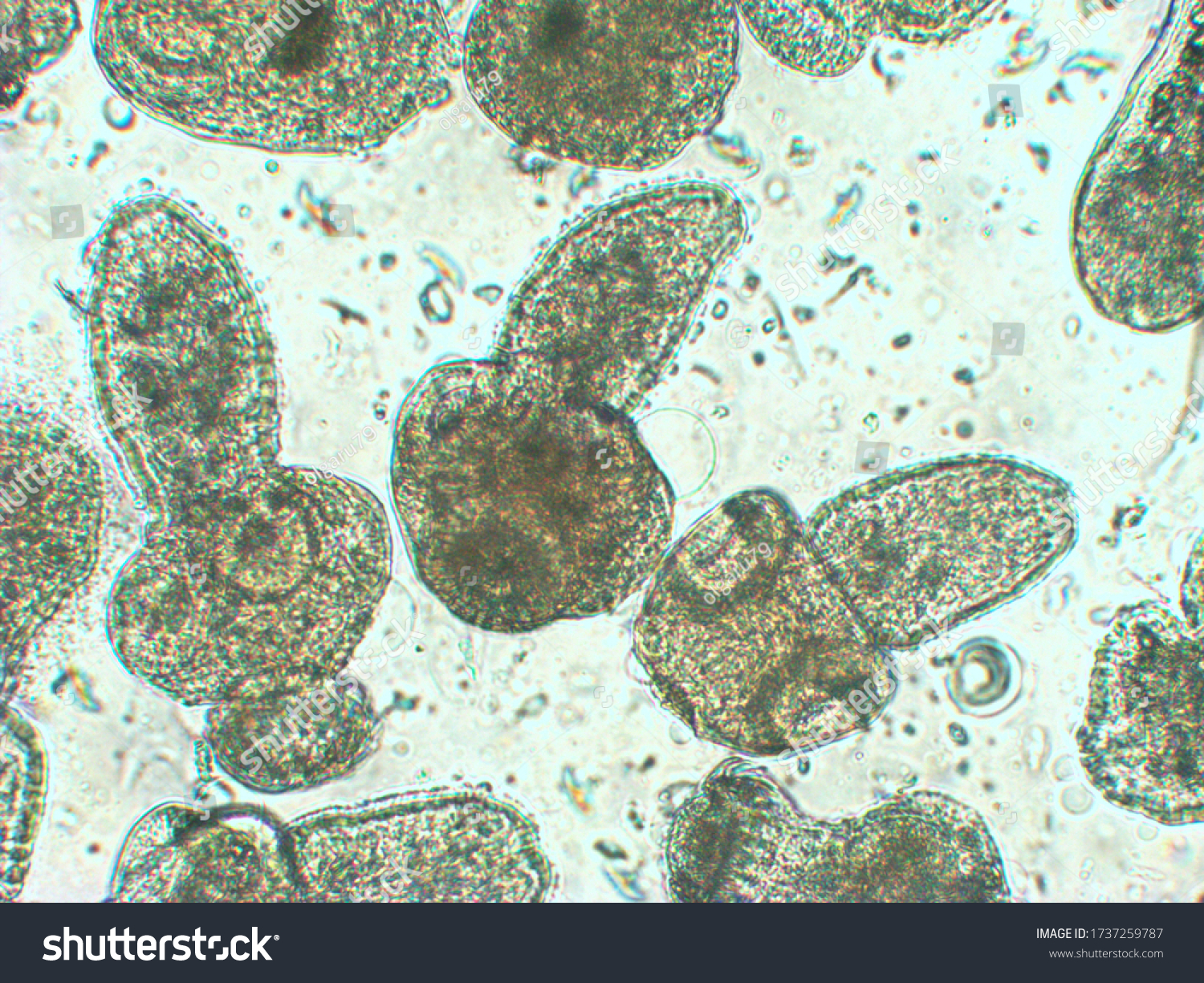
larval stages of cestodes
Human echinococcosis (hydatidosis, or hydatid disease) is caused by the _____________ (tapeworms) of the genus Echinococcus.
cystic echinococcosis
Echinococcus granulosus (sensu lato) causes ________ and is the form most frequently encountered.
alveolar echinococcosis
Another species, E. multilocularis, causes __, and is becoming increasingly more common.
Two exclusively New World species, E. vogeli and E. oligarthrus, are associated with “Neotropical echinococcosis”
polycystic form
E. vogeli causes a___________ .
unicystic form
whereas E. oligarthrus causes the extremely rare_.
genotypes of E. granulosus
Many __________have been identified that differ in their distribution, host range, and some morphological features these are often grouped into separate species in modern literature.
E. granulosus sensu stricto (G1–G3 genotypes), E. ortleppi (G5), and the E. canadensis
The known zoonotic genotypes within the E. granulosus sensu lato complex include the “classical”,,_______________group (usually considered G6, G7, G8, and G10). Research on the epidemiology and diversity of these genotypes is ongoing, and no consensus has been reached on appropriate nomenclature thus far
(2—7 mm long)
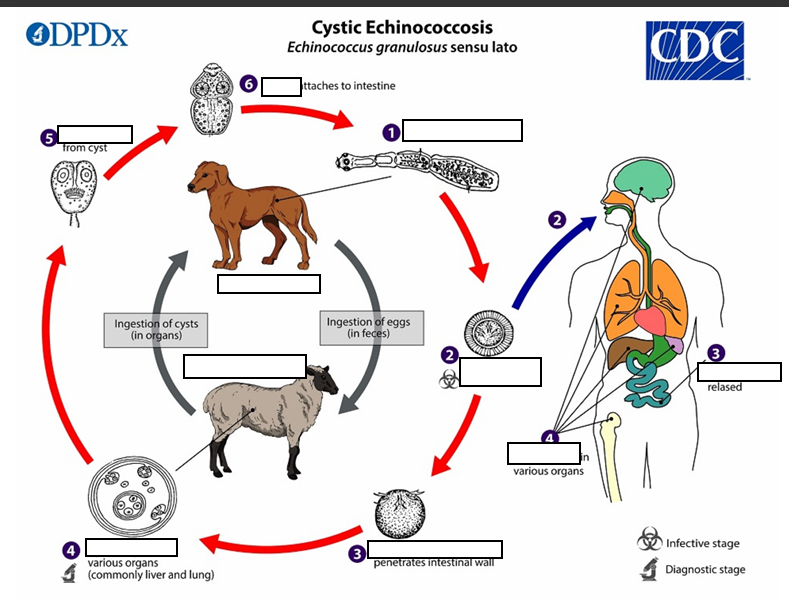
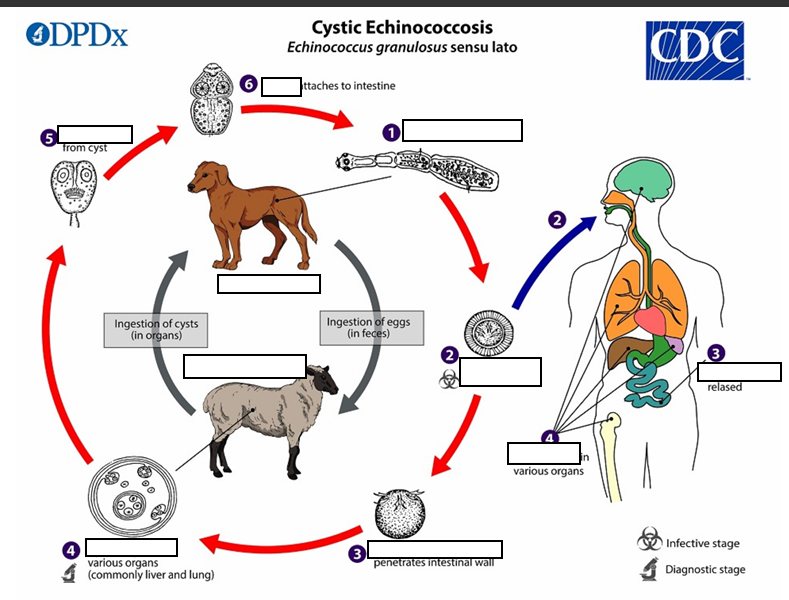
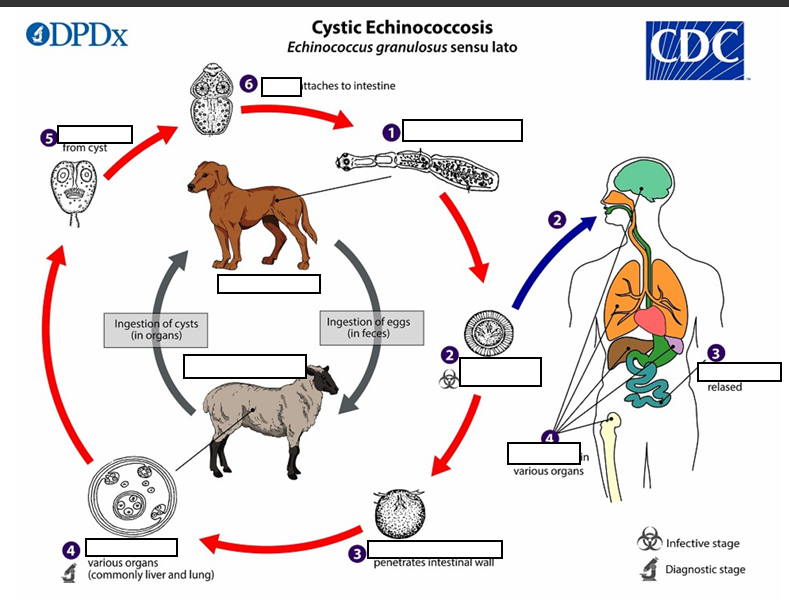
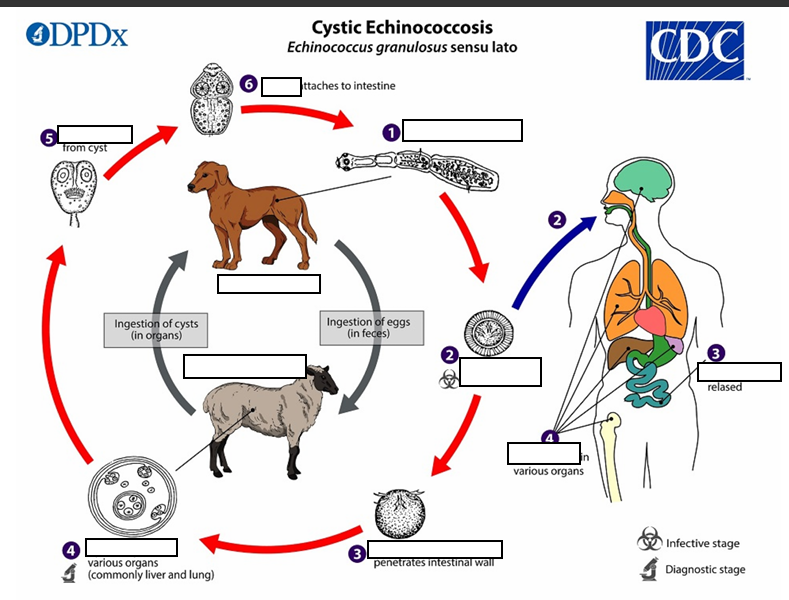
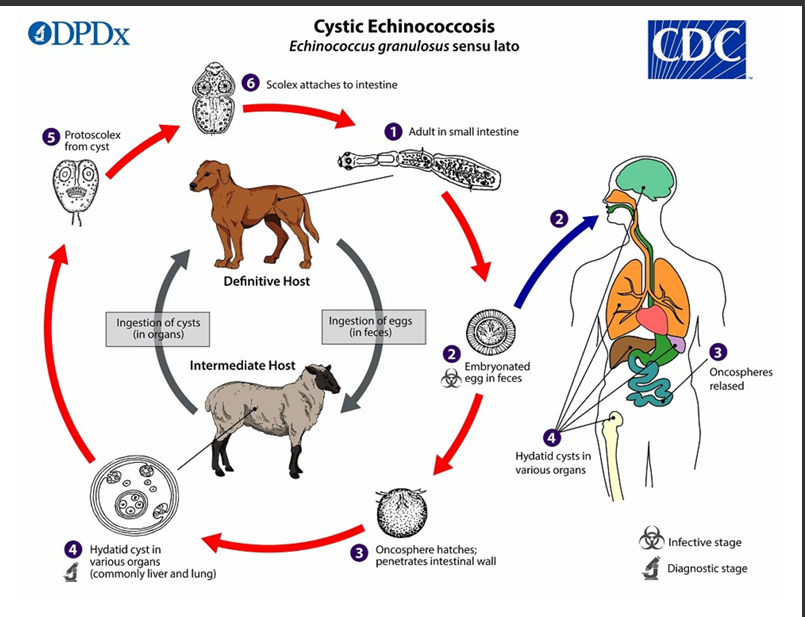
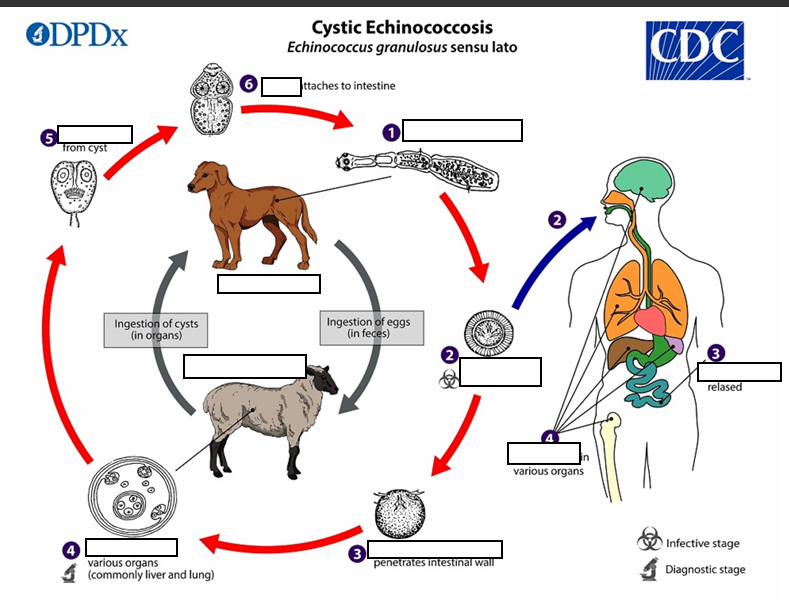
(1) The adult Echinococcus granulosus (sensu lato) __mm resides in the small intestine of the definitive host. Gravid proglottids release eggs
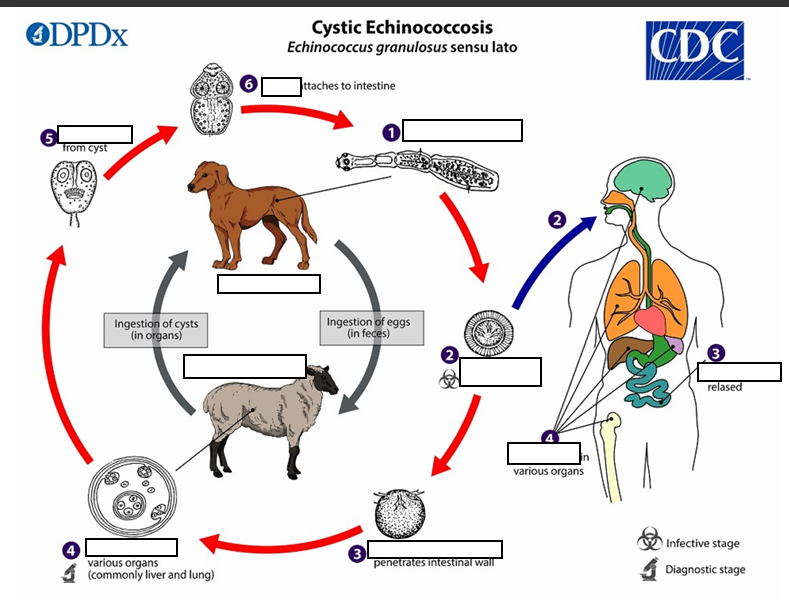
After ingestion by a suitable intermediate host
(2) that are passed in the feces, and are immediately infectious., eggs hatch in the small intestine and release six-hooked oncospheres
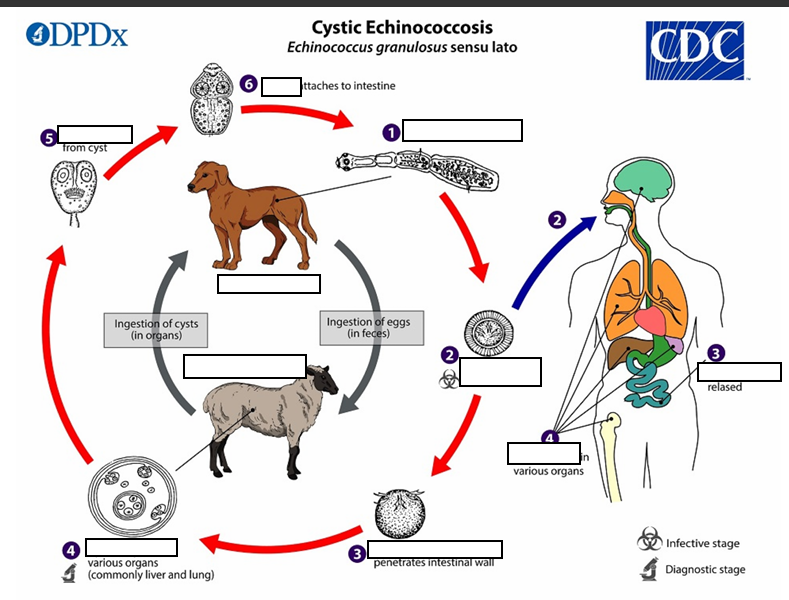
intestinal wall ,circulatory system into various organs
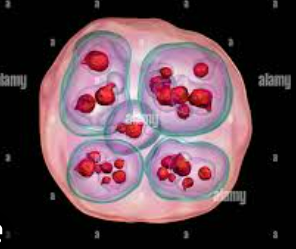
(3)six-hooked oncosphere penetrate the _____and migrate through the _______, especially the liver and lungs. In these organs, the oncosphere develops into a thick walled hydatid cyst
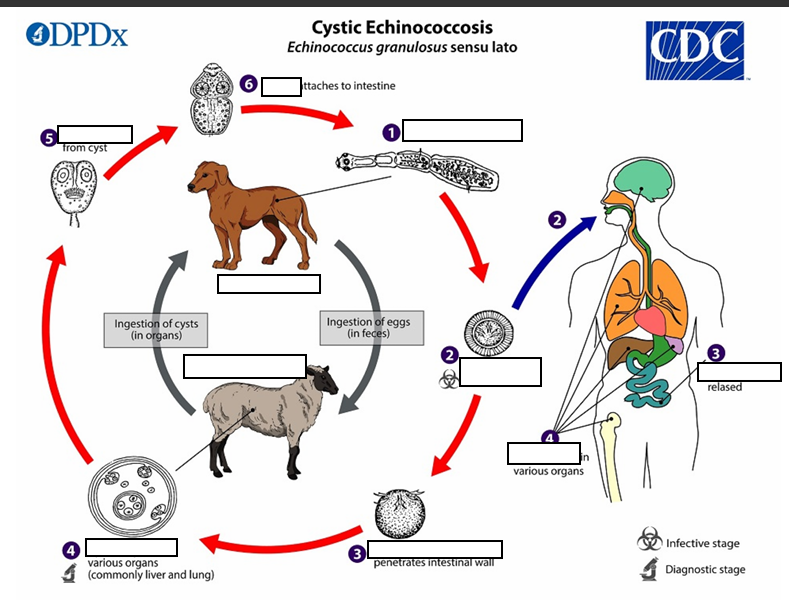
enlarges gradually, protoscolices
(4) _____________, producing __________ and daughter cysts that fill the cyst interior. The definitive host becomes infected by ingesting the cyst-containing organs of the infected intermediate host. After ingestion, the protoscolices evaginate, attach to the intestinal mucosa
cyst-containing organs
In stage 4 The definitive host becomes infected by ingesting the_______ of the infected intermediate host.
adult stages
After ingestion, the protoscolices evaginate, (5) attach to the intestinal mucosa (6) and develop into __32 to 80 days
aberrant (not conforming to an accepted or usual standard) intermediate hosts
{1} Humans are ___, and become infected by ingesting eggs in 32 to 80 days.
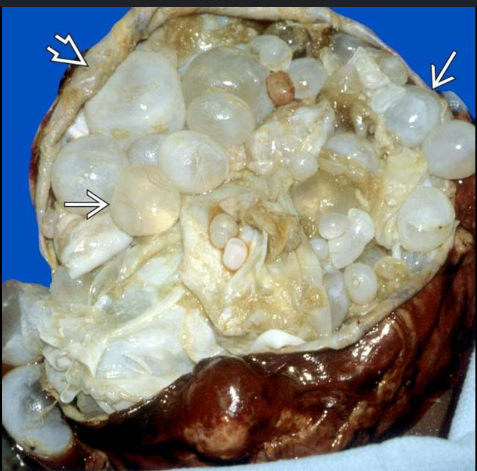
hydatid cysts
{2} Oncospheres are released in the intestine and ___________develop in a variety of organs
cysts rupture
{3} If ________, the liberated protoscolices may create secondary cysts in other sites within the body (secondary echinococcosis)
Life cycle of Cystic Echinococosis
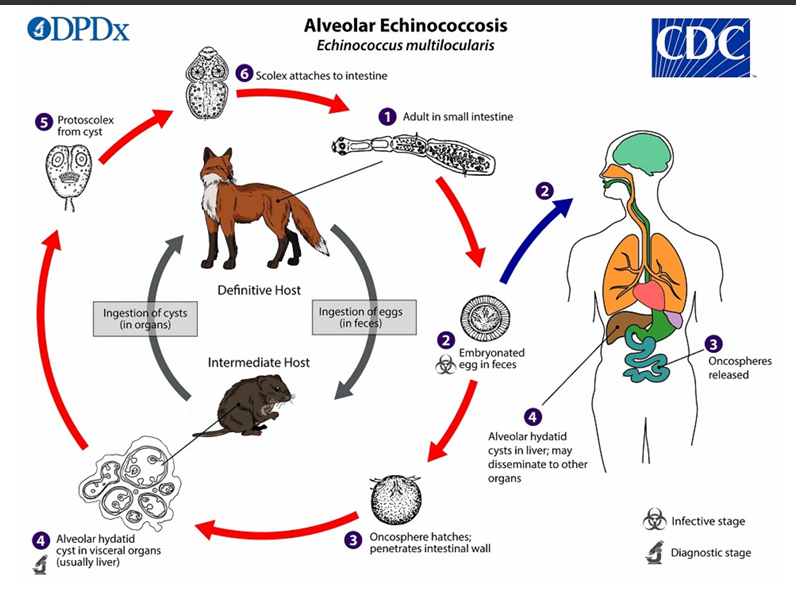
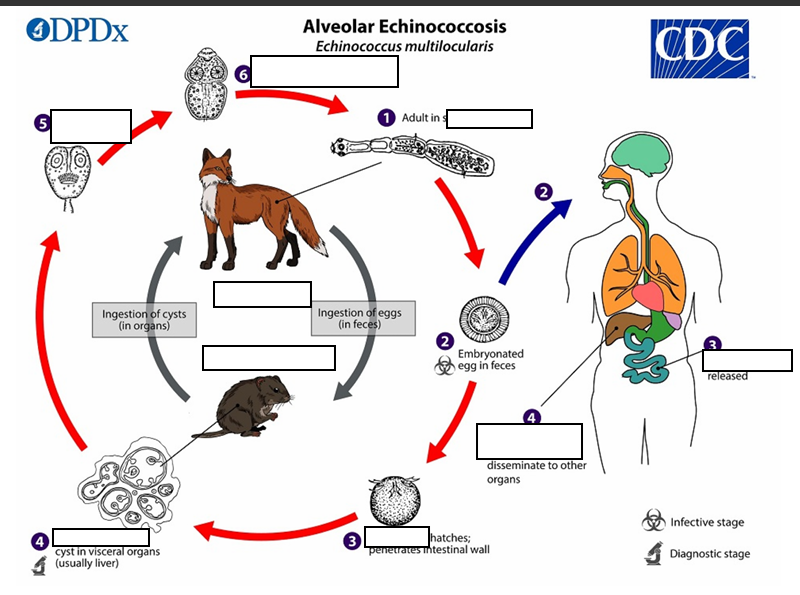
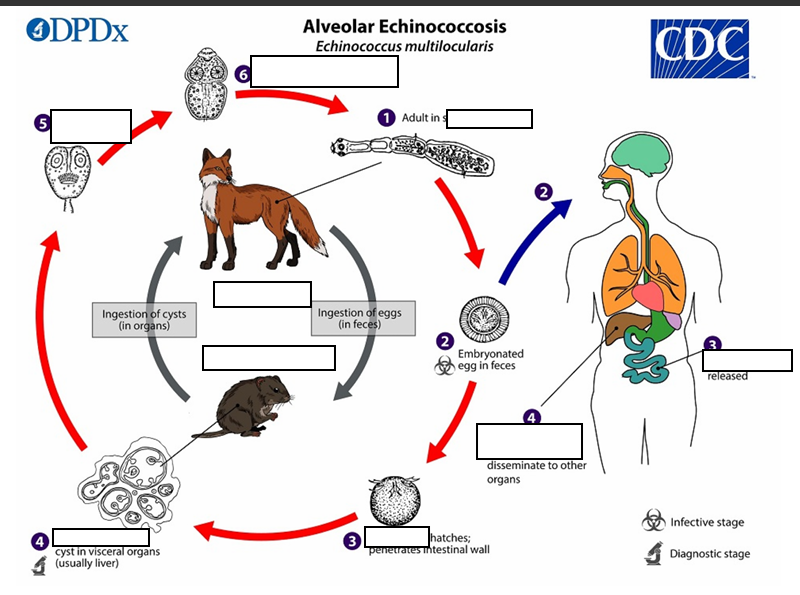
Life cycle of Alveolar Echinococosis
(1.2—4.5 mm long)
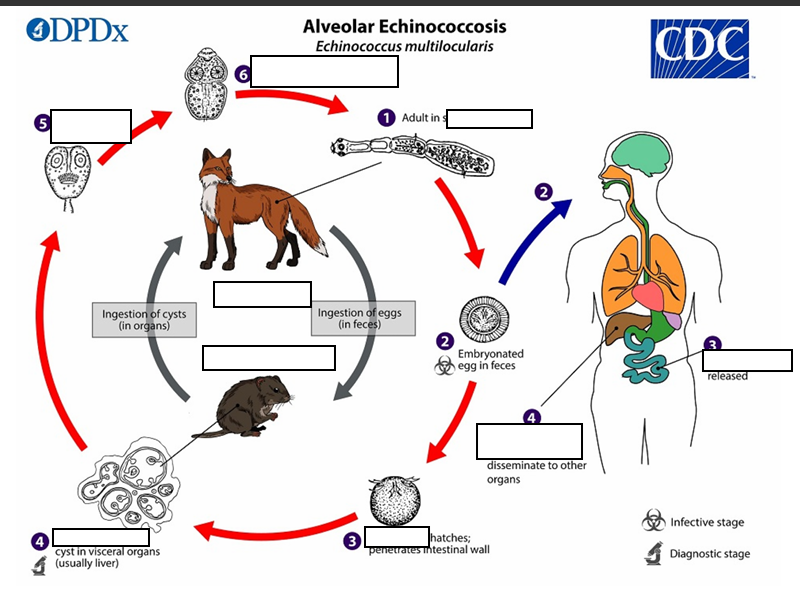
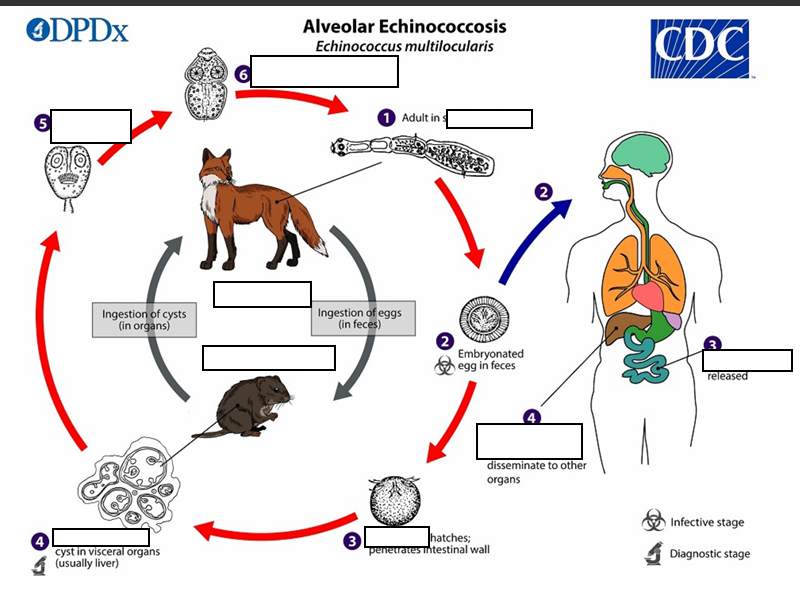
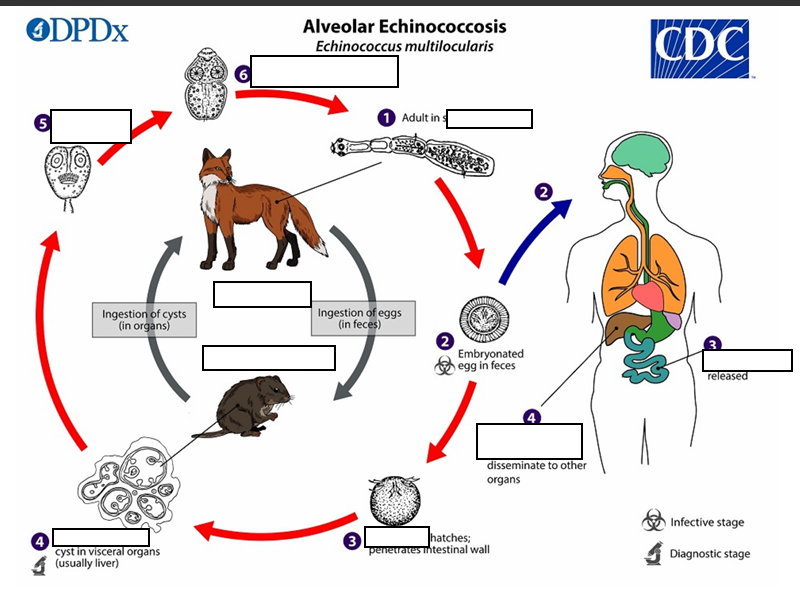
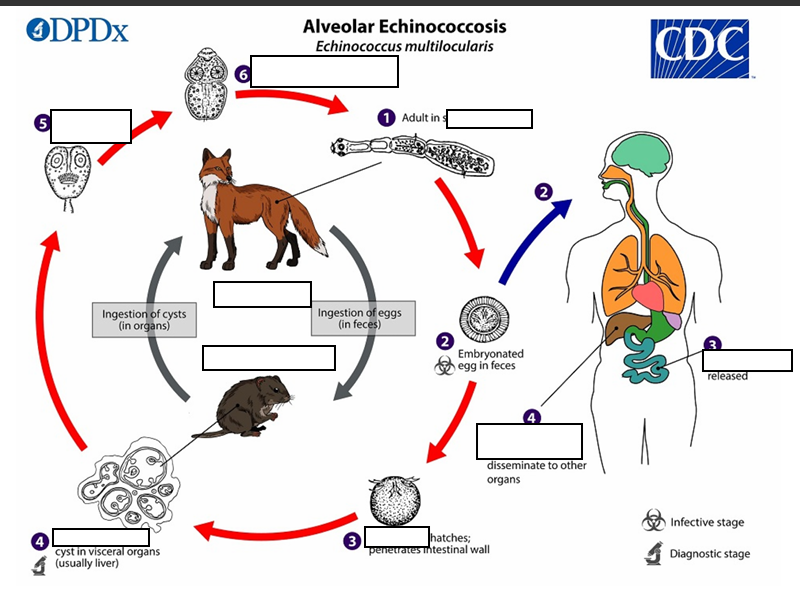
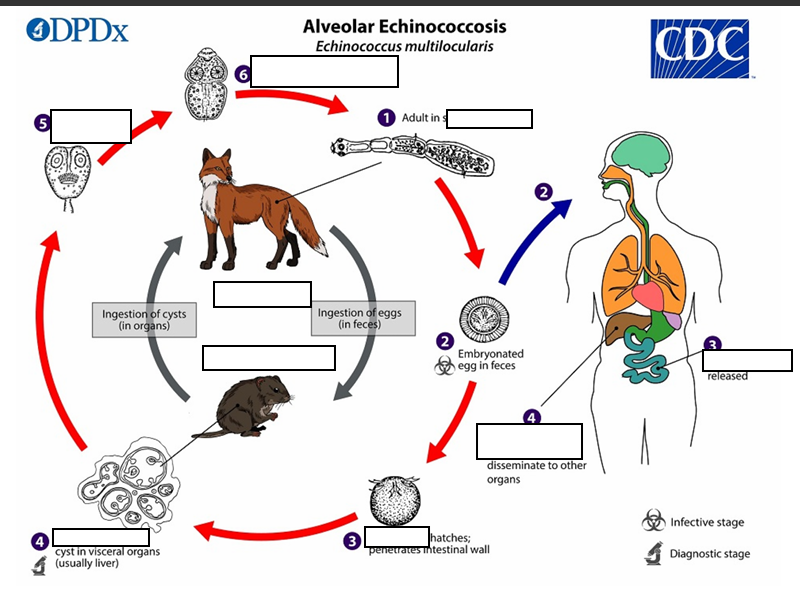
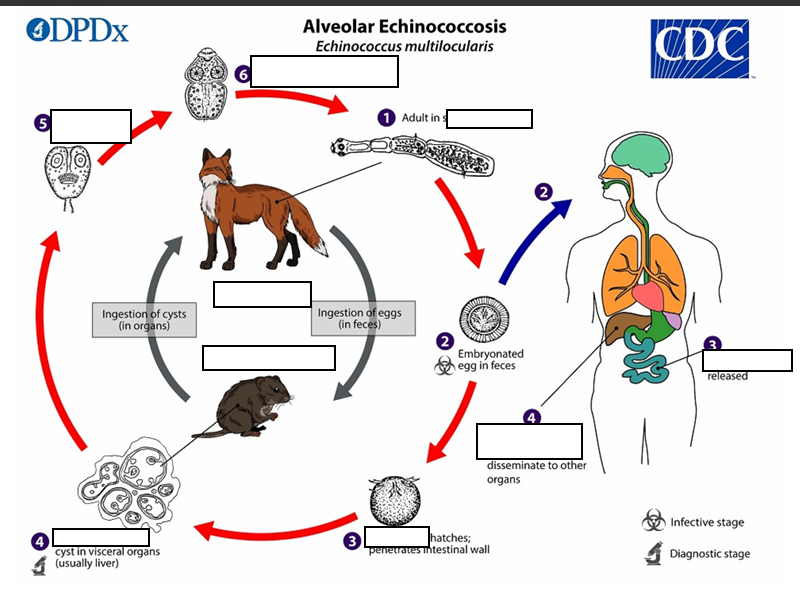
The adult Echinococcus multilocularis ___long
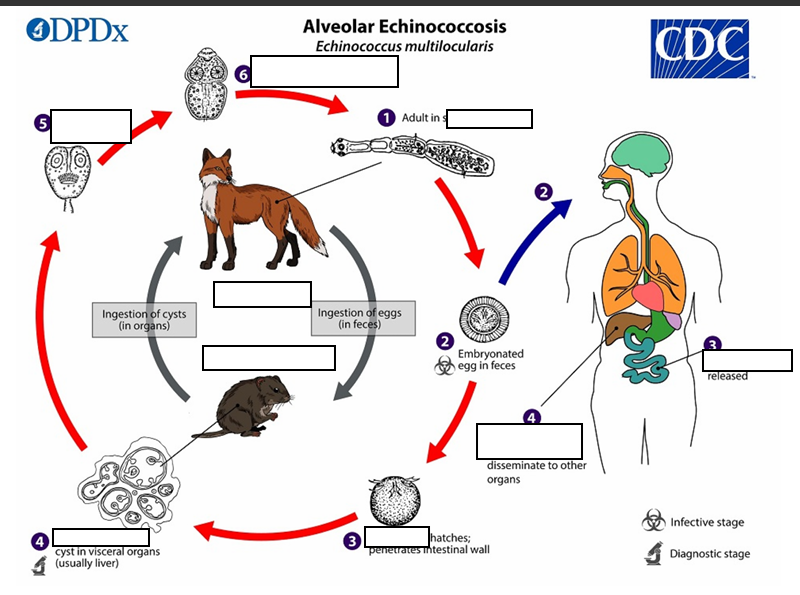
small intestine of the definitive host
(1) The adult Echinococcus multilocularis resides in the__________of the definitive host. Gravid proglottids release eggs
immediately infectious, six-hooked oncosphere
(2)Gravid proglottids release eggs that are passed in the feces, and are__________. After ingestion by a suitable intermediate host eggs hatch in the small intestine and releases a___________ ,
thin-walled (alveolar) hydatid cyst
(3)six-hooked oncosphere penetrates the intestinal wall and migrates through the circulatory system into various organs (primarily the liver for E. multilocularis). The oncosphere develops into a multi-chambered (“multilocular”), _______________________
ingesting the cyst-containing organ
(4) The oncosphere develops into a multi-chambered (“multilocular”), thin-walled (alveolar) hydatid cyst that proliferates (increase rapidly by number) by successive outward budding. Numerous protoscolices develop within these cysts.
The definitive host becomes infected by _________________s of the infected intermediate host. After ingestion, the protoscolices evaginate, attach to the intestinal mucosa
Budding
refers to a type of asexual reproduction where a new organism grows from an outgrowth (bud) on a parent, seen in yeast and hydra, or to plant propagation (grafting a single bud onto another plant)
intestinal mucosa (the innermost, highly folded lining of the gut)
(5) After ingestion, the protoscolices evaginate, attach to the _
(6) and develop into adult stages.
32 to 80 days,
Liver
(1) After ingestion the protoscolices evaginate, attach to the intestinal mucosa and develop into adult stages in ______ days. Humans are aberrant intermediate hosts, and become infected by ingesting eggs (2) Oncospheres (3) and are released in the intestine cysts develop within in the __________.
secondary echinococcosis.
(4) Metastasis or dissemination to other organs (e.g., lungs, brain, heart, bone) may occur if protoscolices are released from cysts, sometimes called “_"
ultrasonography
The diagnosis of echinococcosis relies mainly on findings by __________ and/or other imaging techniques supported by positive serologic tests. In seronegative patients with hepatic image findings compatible with echinococcosis, ultrasound guided fine needle biopsy may be useful for confirmation of diagnosis. During such procedures precautions must be taken to control allergic reactions or prevent secondary recurrence in the event of leakage of hydatid fluid or protoscolices
95% of alveolar cases
Most patients with alveolar disease have detectable antibodies. Immunoaffinity-purified E. multilocularis antigens (Em2) used in EIA allow the detection of positive antibody reactions in more than ______________.
Protoscolices
The larval stage of Echinococcus tapeworms