Unit 8: (8.11) Sewage Treatment
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Sewage
The water and human wastes that are washed down sinks, toilets, and showers

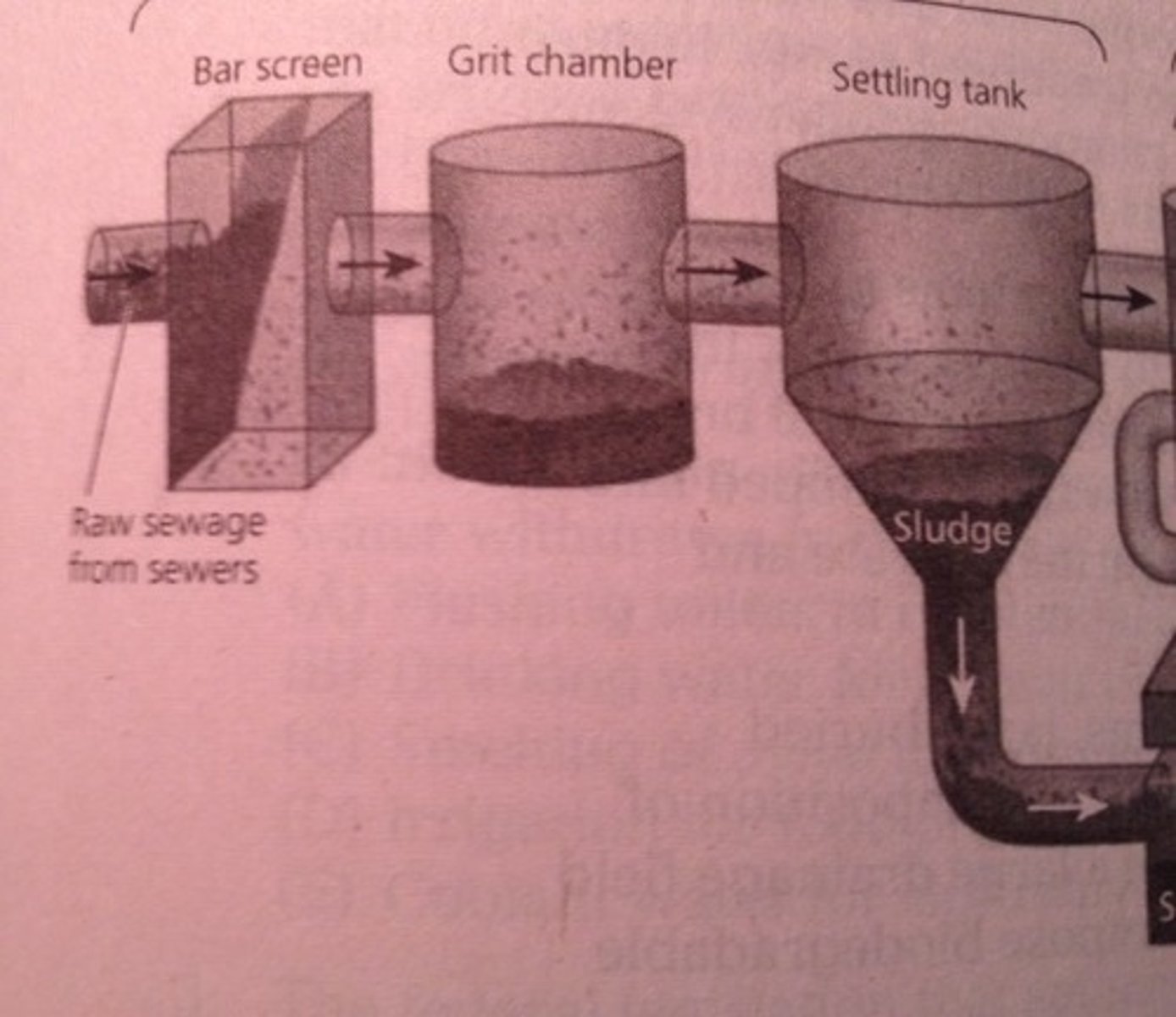
primary sewage treatment
a physical process that uses screens and a grit tank to remove large floating objects and to allow solids such as sand and rock to settle out
secondary sewage treatment
A biological process in which aerobic bacteria decompose oxygen-demanding organic wastes. Requires an aeration tank to add oxygen that the bacteria need to decompose organic matter
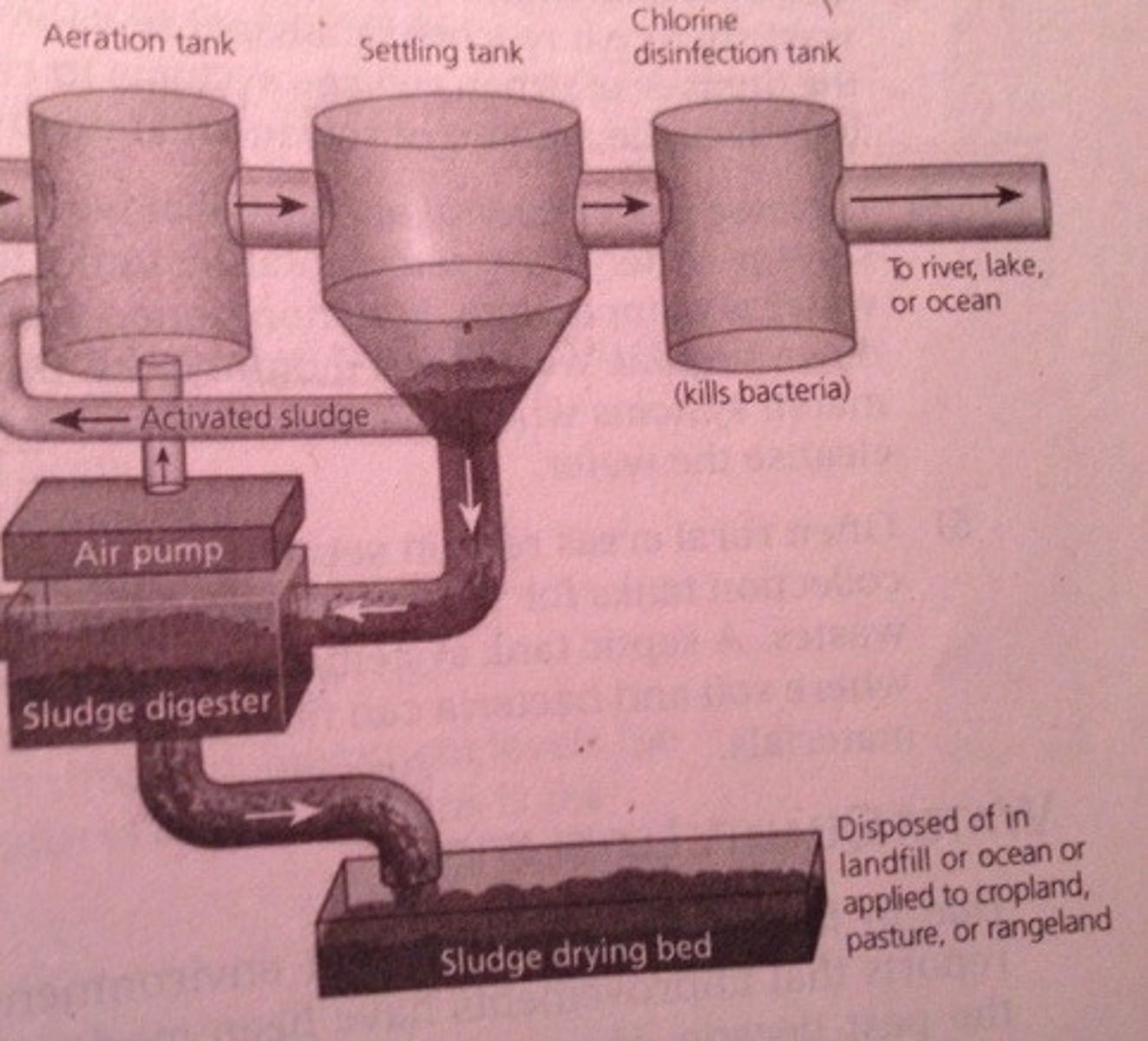
tertiary sewage treatment
specialized chemical filtration step that removes most remaining chemical pollutants like nitrogen and phosphorous. Cannot remove all POPs
Disinfectant
Use of chlorine, UV light, ozone to kill bacterial and viral pathogens (although not all viruses) in wastewater, before it is discharged as effluent
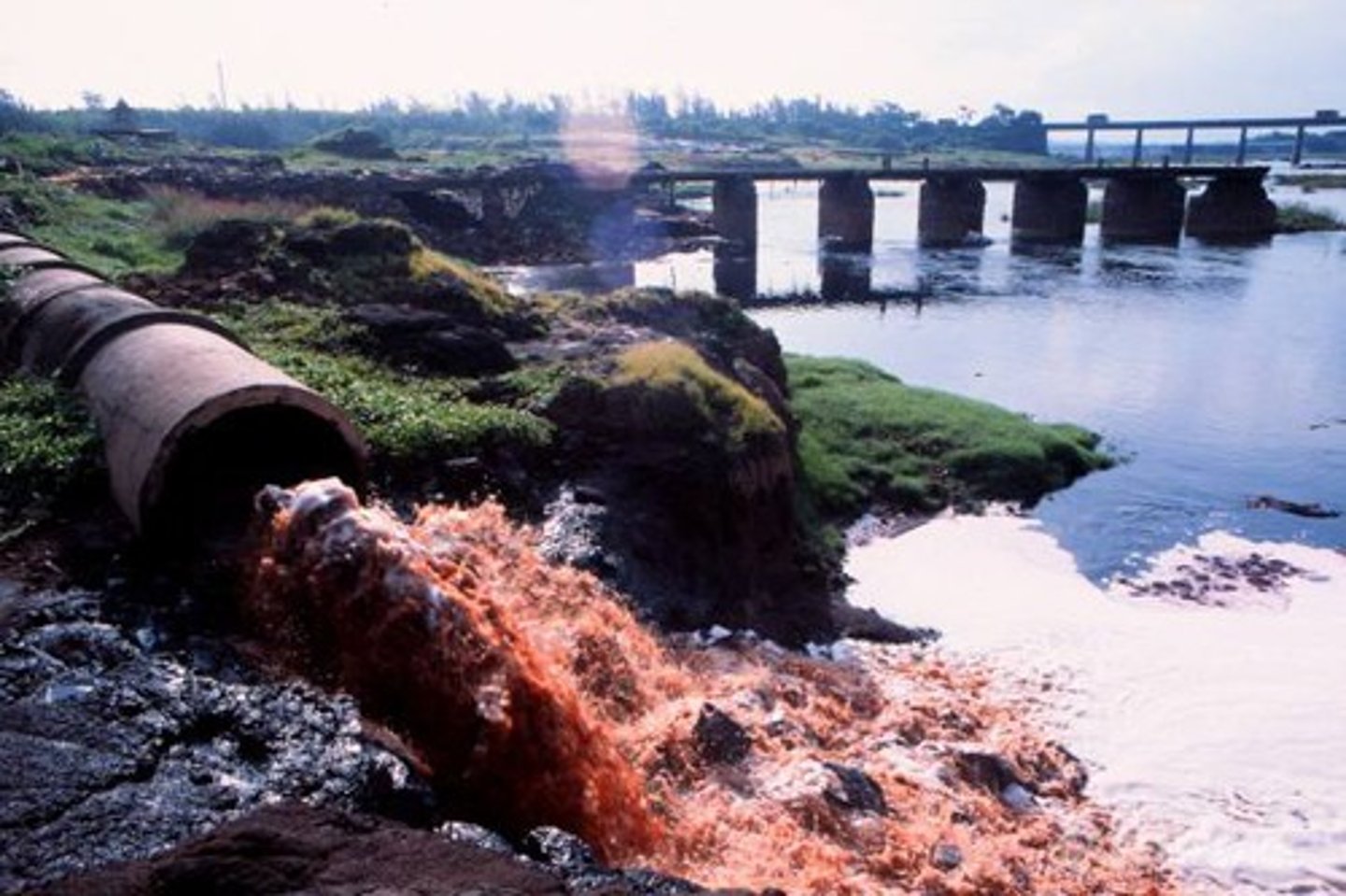
effluent
liquid waste or sewage discharged into a river or the sea after being treated

grit chamber
A step of primary treatment that allows grit (sand, rocks, silt)o settle at the bottom of the tank
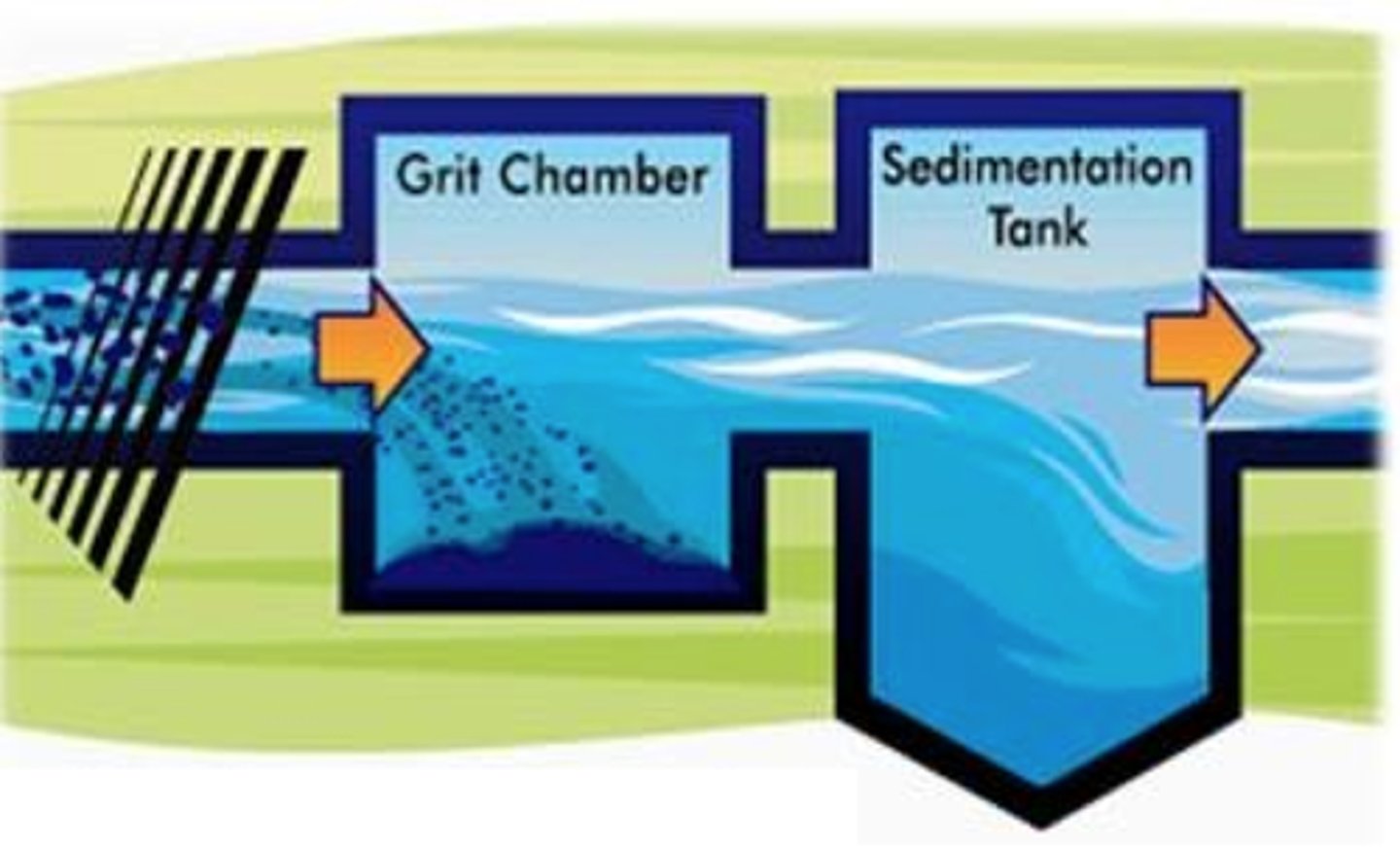
settling chamber
A chamber used in both primary and secondary treatment that allows solid, inorganic waste to settle into a sludge at the bottom of the tank
Sludge
the inorganic, solid waste that remain after the secondary treatment of sewage. Collected and exposed to more bacteria to kill pathogens, dried, and then taken to landfills, dumped in the ocean, or used as fertilizer

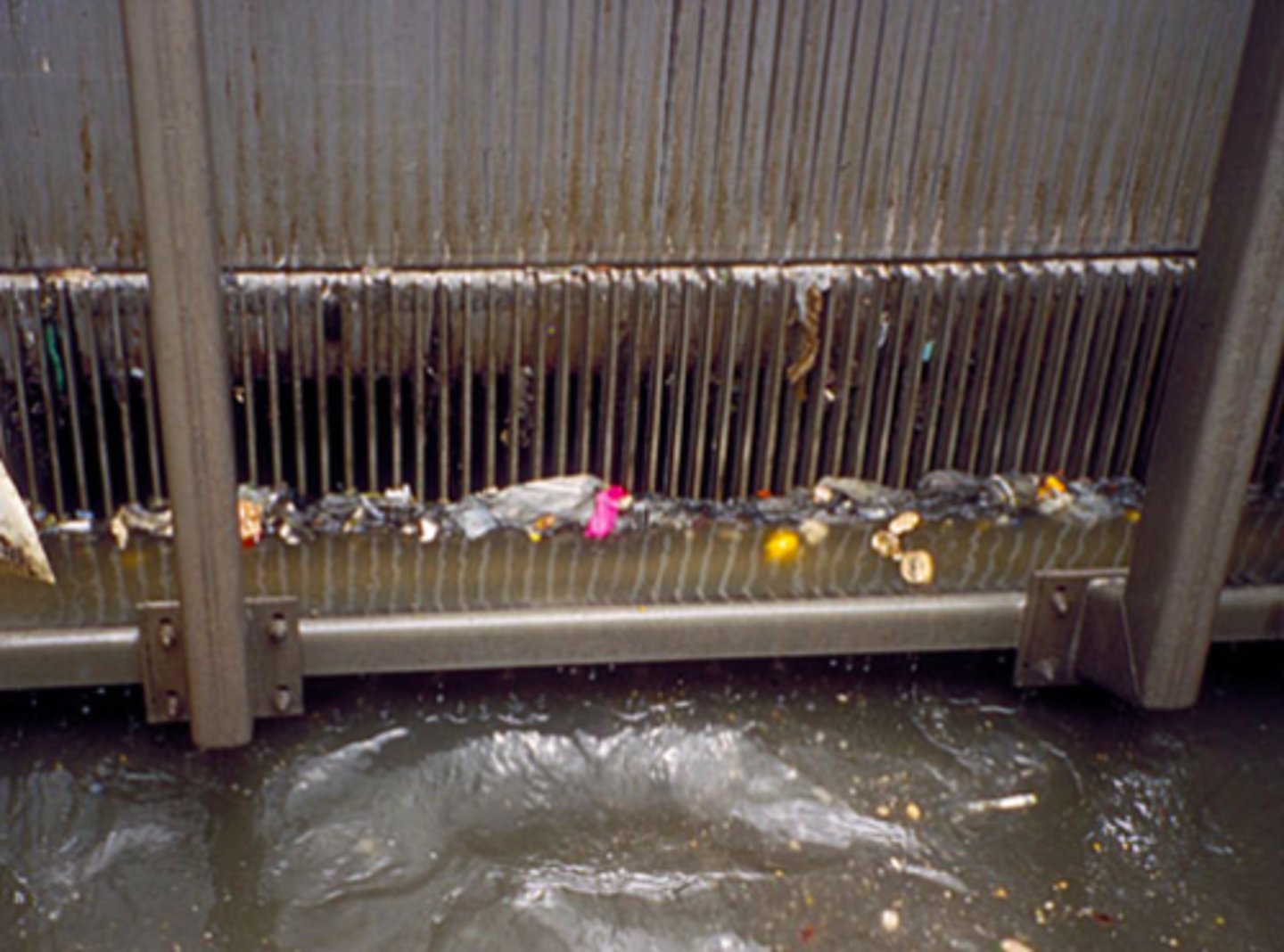
bar screen
A physical, metal filter that traps large debris in sewage like paper, plastic, or other garbage
