PT7711- Osteoarthritis and Total Shoulder Replacement (TSA/rTSA)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Synovial articular; degeneration; remodeling; osteophyte; inflammation
Osteoarthritis pathophysiology:
- Multi-factorial disease affecting the entire ____________________
- Cartilage ____________________, abnormal bone ___________________, _____________________ formation, and joint _____________________
- Mechanical and inflammatory processes involved
Commonly
Shoulder is most ______________________ affected joint in UE!
Trauma; older; females; rotator cuff; instability
Risk factors for osteoarthritis:
- ____________________ (20-50% more likely)
- Obesity
- _____________________ age
- ______________________ are more likely
- _____________________ pathology (4% of patients with massive tears develop OA)
- Chronic ____________________ (56% of participants that had GH instability followed longitudinally)
Hypermobility; hypomobility
Osteoarthritis progresses from ___________________ → ____________________.
Non-specific; night; stiffness; crepitus; ↓; ↓
Signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis:
- ____________________ pain pattern
- Pain pattern similar to many other should problems
- Progressive pain complaints
- Severe __________________ pain
- ______________________
- ______________________ with movement
- ____________________ ROM
- ____________________ RC strength
Compression/rotation; scour
Osteoarthritis patients will have positive _____________________. This will be painful and often show crepitus (__________________ test).
Distraction
______________________ should be less painful in patients with OA.
Imaging
___________________ can confirm OA. → More useful for younger patients who are presenting with OA-like symptoms, but you're unsure of diagosis.
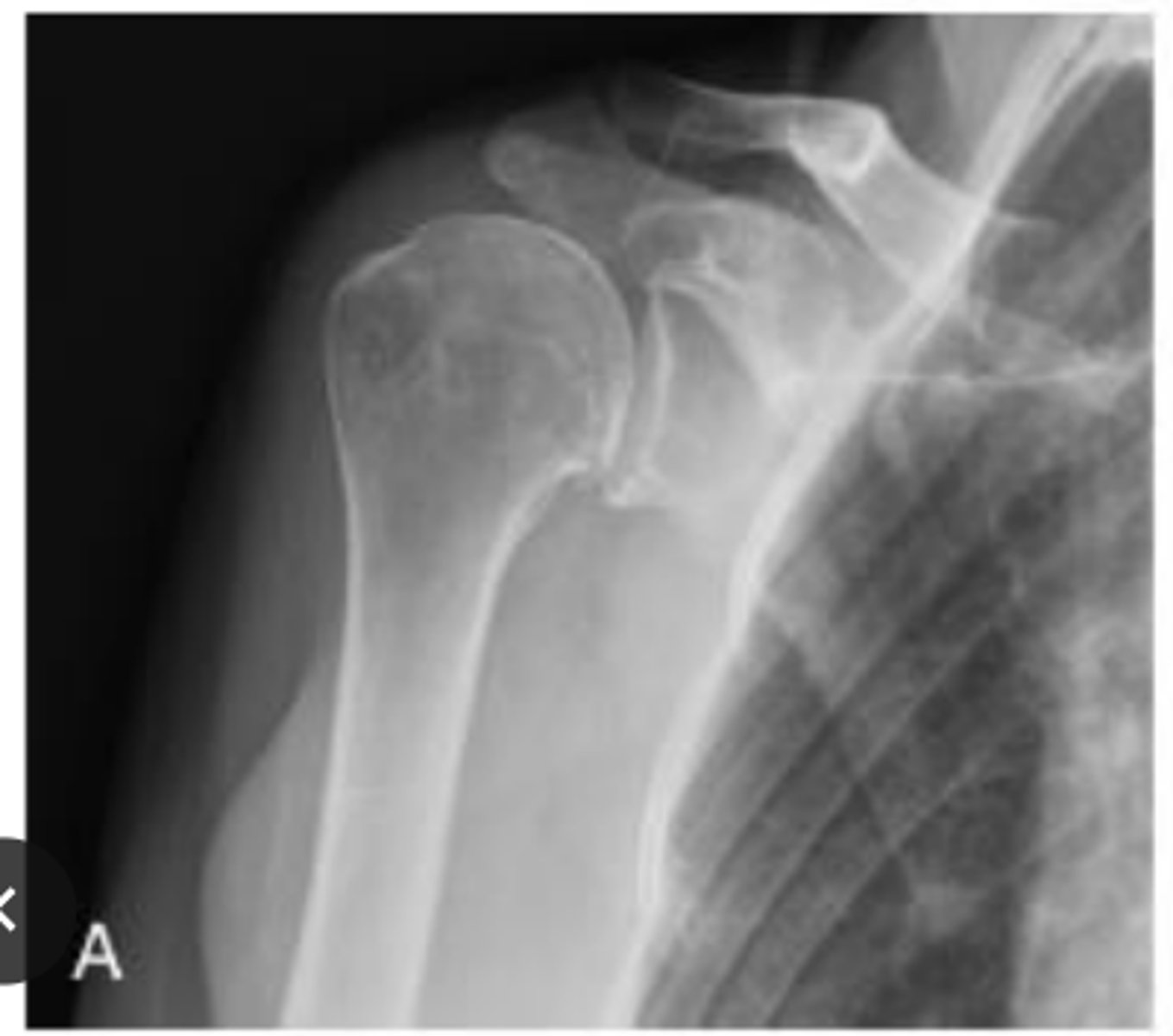
Normal shoulder
What does the image show?
Moderate osteoarthritis
What does the image show?
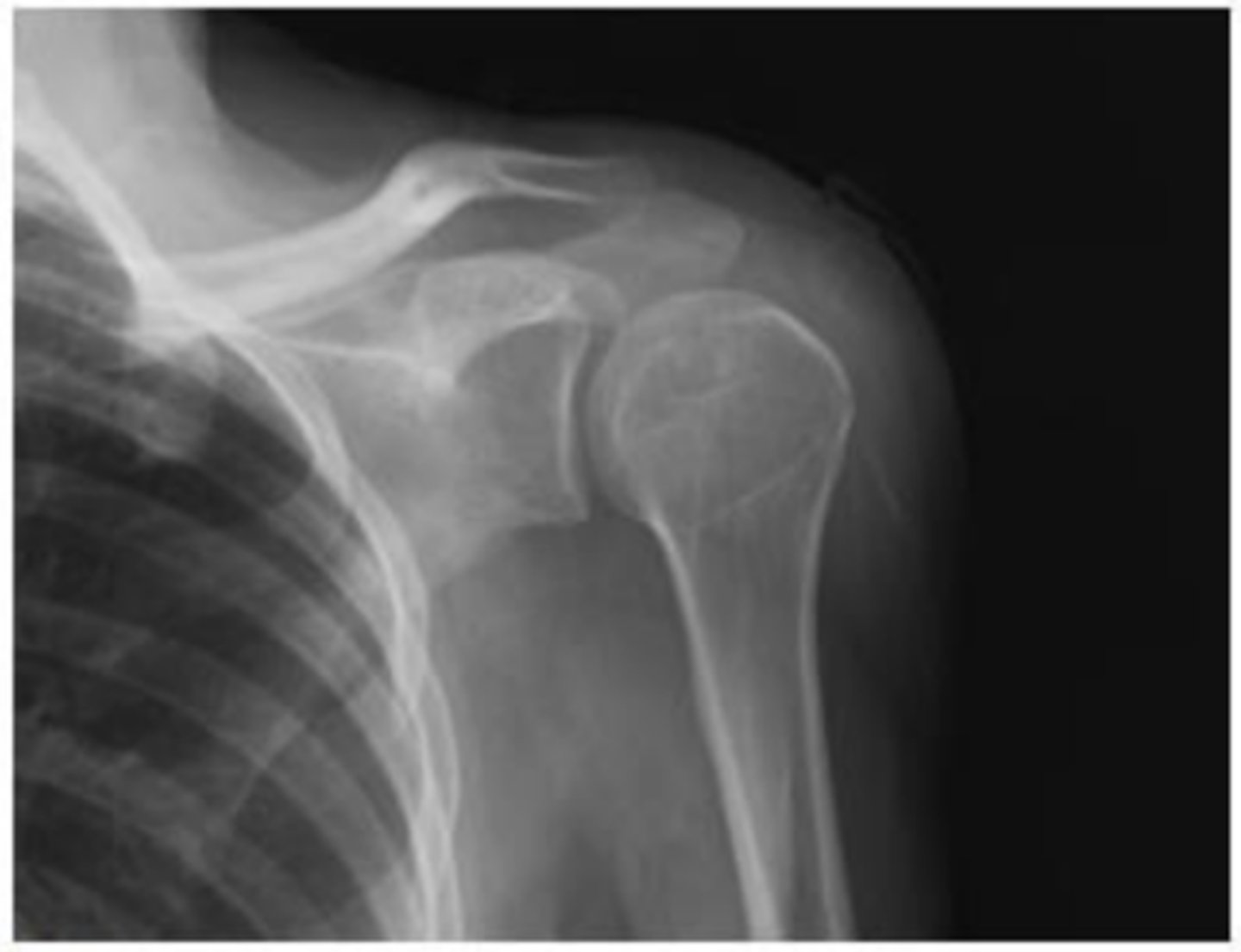
Sclerosis; ↓; spurring; osteophyte
What does the image show?
- Increased whitening of glenoid and humeral head (_________________)
- ________________ joint space
- Bone ___________________
- __________________ formation
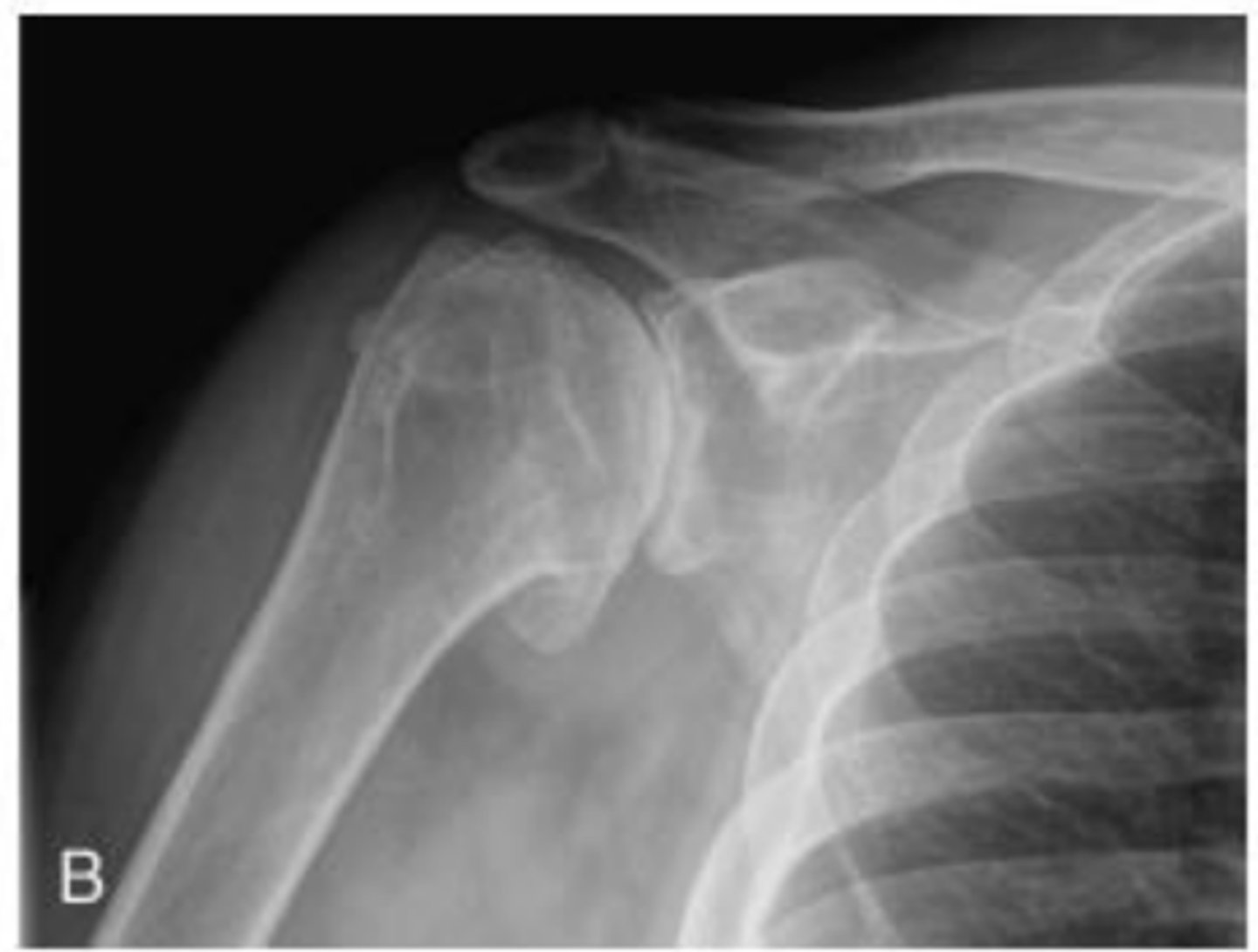
Rotator cuff arthropathy
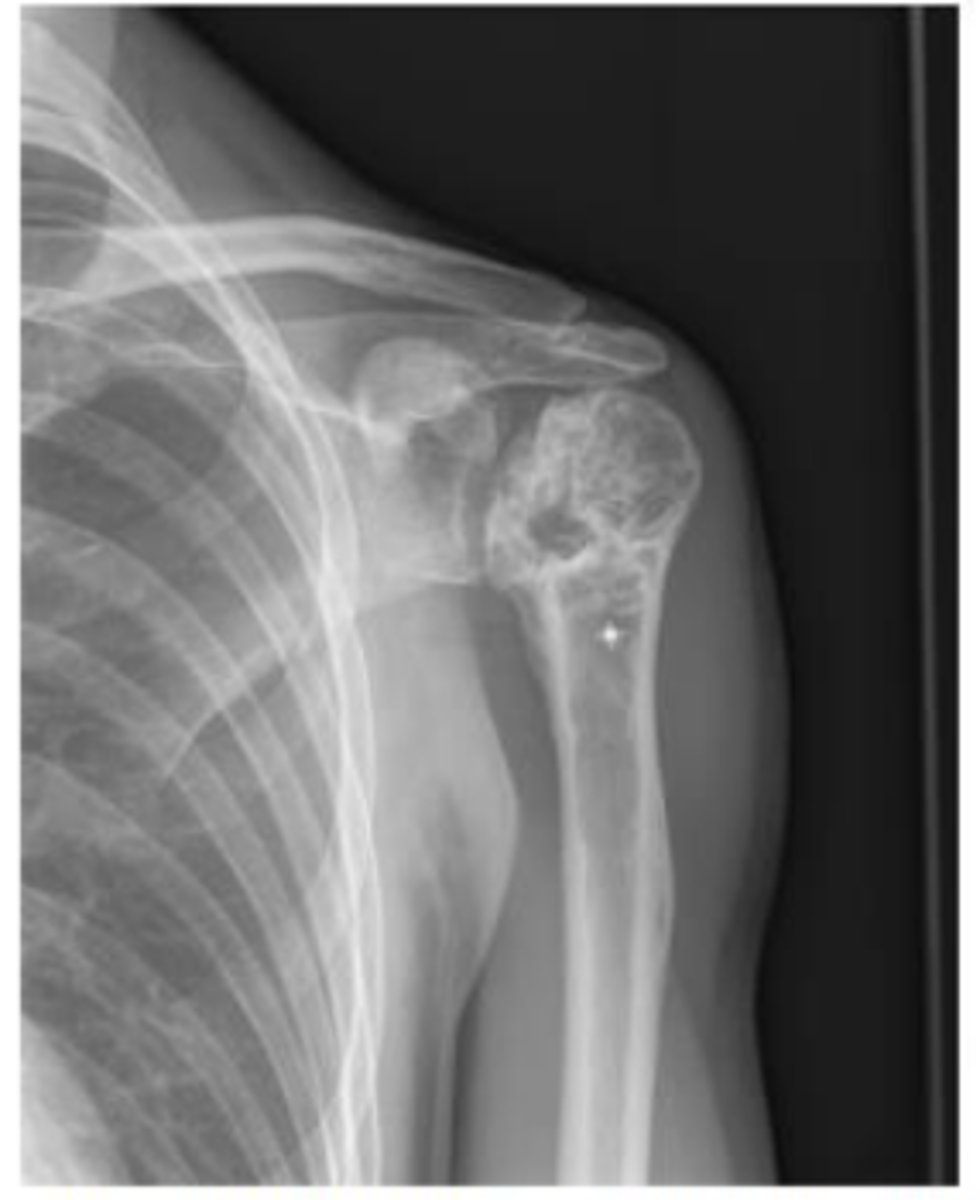
What does the image show?
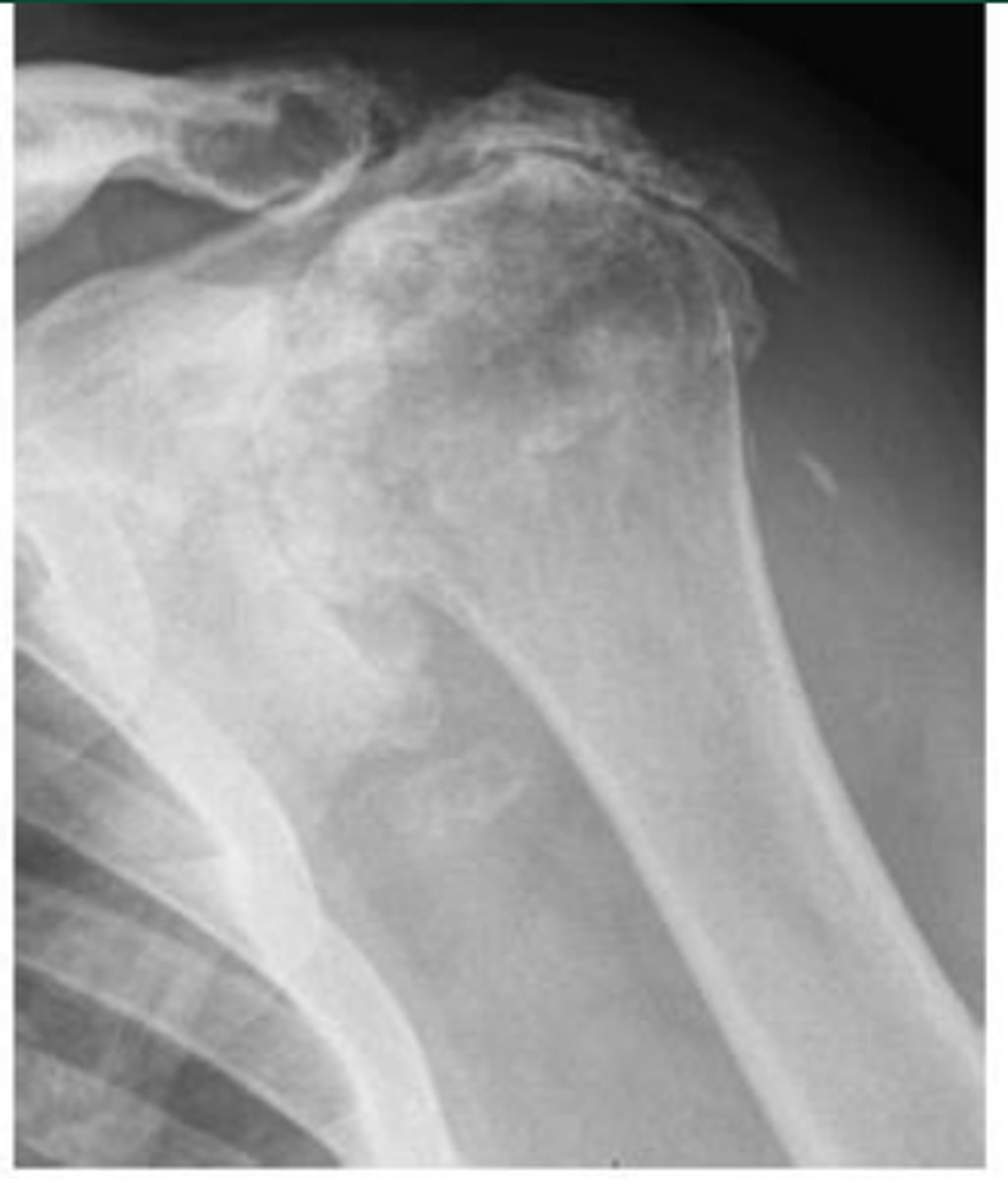
Avascular necrosis (collapse of humeral head and cyst formation within humerus)
What does the image show?
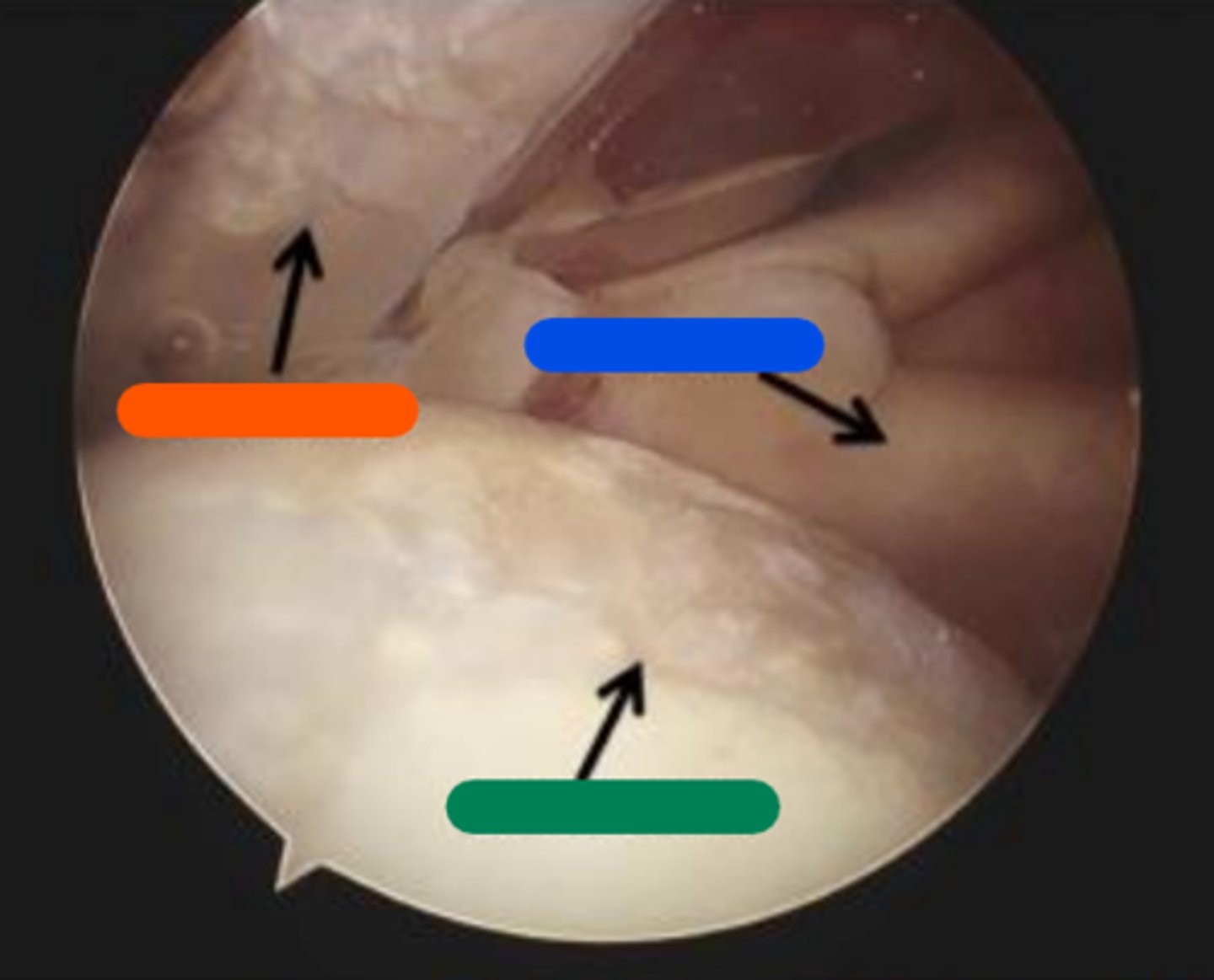
Supraspinatus
Orange in image.
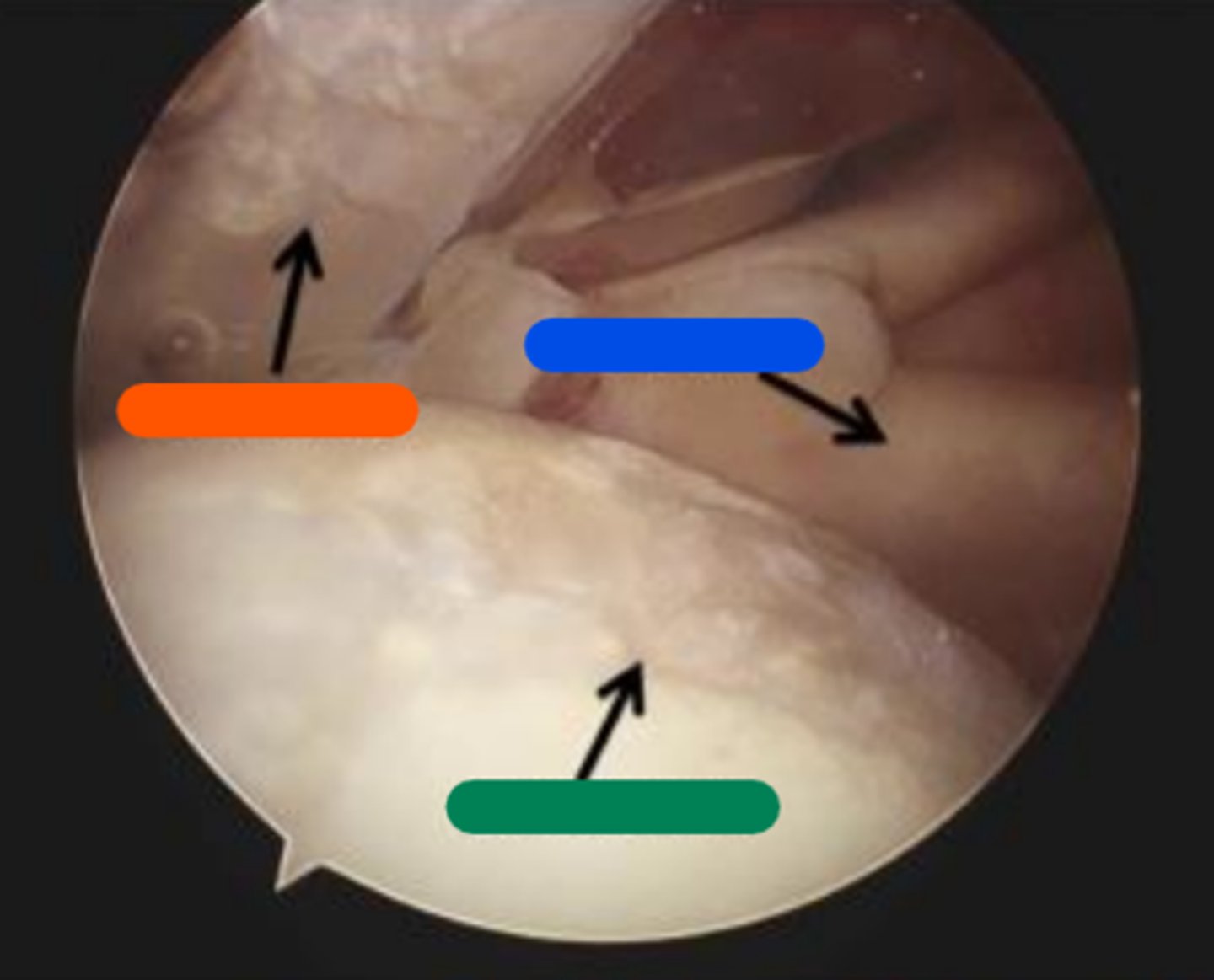
Subscapularis
Blue in image.
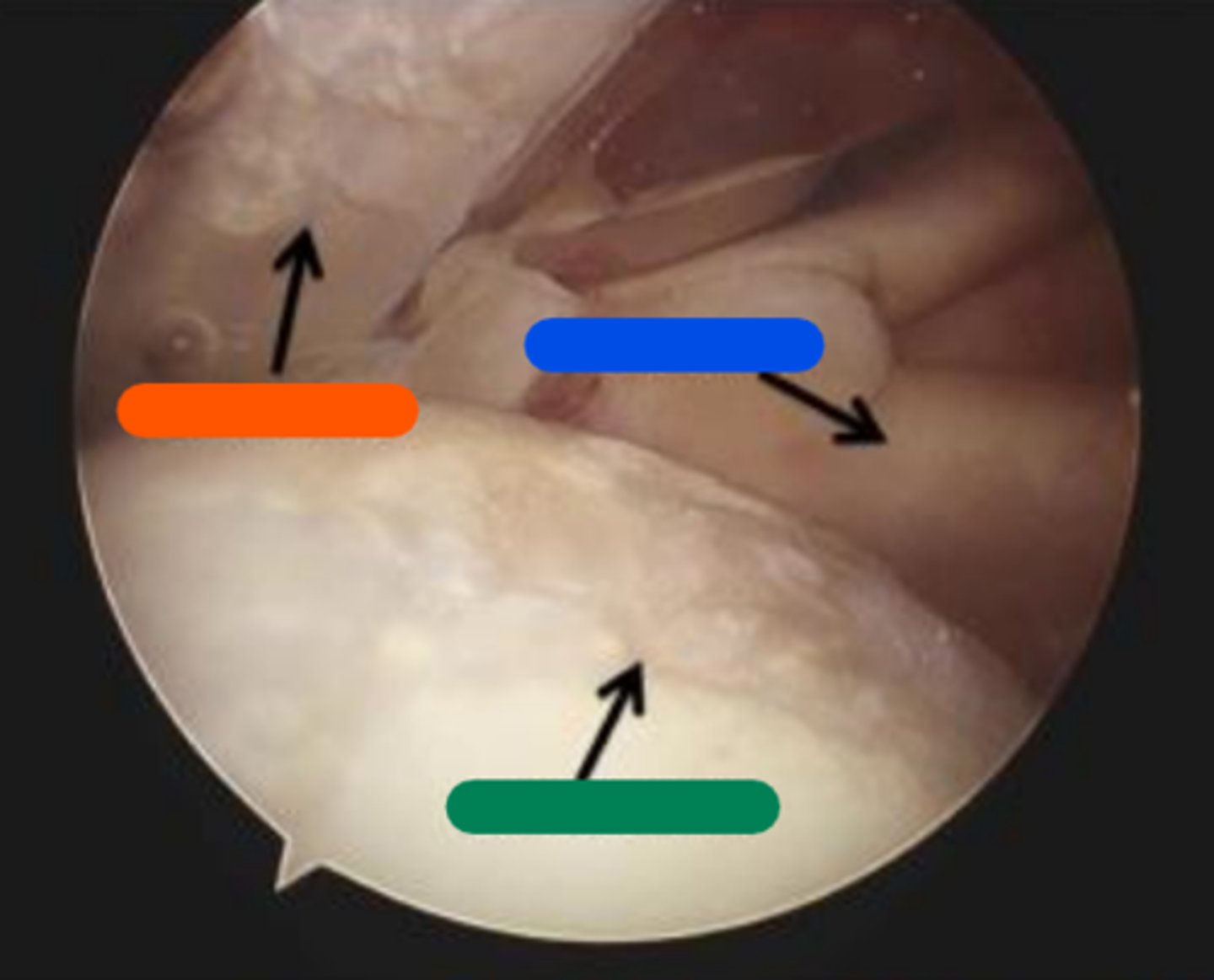
Chondral lesion
Green in image.
Modification; NSAIDs; corticosteroid; rotator interval
Non-operative treatment of osteoarthritis:
- Activity _____________________
- ___________________
- ___________________ injections
- Physical Therapy → Address impairments of decreased ROM and strength. Surgical release of ___________________ has shown improvements in motion and decreased pain.
Osteoarthritis; arthritis; fractures
Total shoulder replacement indications:
- ___________________ is #1 reason for TSA ("post-traumatic")
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Combination of severe ___________________ with massive RC tear
- Avascular necrosis (osteonecrosis)
- Failed previous total shoulder replacement
- Severe __________________
Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty
- Humeral head is concave, glenoid is convex.
- Reverse arthrokinematics.
- Appropriate for patients w/ RC weakness, allows deltoid to "take over".
Hemiarthroplasty
Refers to the resurfacing of only the glenoid or the humeral head.
Intact
TSA is most common to use with severe OA and an ____________________ rotator cuff.
6 weeks
Joint mobilization would be contraindicated for ___________________ after TSA surgery, but PROM to tolerance.
AROM; minimally
____________________ should be limited after surgery but, depending on the amount of muscle tht has been damaged, may be allowed in some directions _____________________.
ER; IR
Avoid excessive _________________ and active _________________ for about 4 weeks after TSA surgery (d/t surgical approach).
1; 4-6
Submax isometrics can be started as soon as week __________________ → Follow with isotonic strengthening about ________________ weeks within available ROM, try and encourage proper scapulohumeral rhythm.
120-140°; 120-140°; 45-60°; 45-70°
Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Expected Eventual Functional ROM:
- Flexion: ___________________
- Abduction: ___________________ (prefer scaption)
- ER: ____________________
- IR: _____________________
Not getting back "normal range" but enough for ADLs.
Washing hair
______________________ is an example of a functional ADL that will be do-able for a patient at the end of TSA expected functional ROM.
Do not
Reverse shoulder arthroplasty is used for patients that ___________________ have an intact rotator cuff.
ER; abducted
Reverse shoulder arthroplasty has similar results and treatment progression as TSA, with the difference being do not force __________________, especially in an __________________ position.
Similar
Reverse shoulder arthroplaty has ____________________ functional ROM after surgery.
Anterior deltoid; pectoralis major; active IR
Anterior surgical approach goes through _____________________ and _____________________. With this approach, _____________________ is contraindicated as subscapularis is cut.
Posterior deltoid
Posterior surgical approach separates _____________________ and the surgeon tries not to cut the RC.
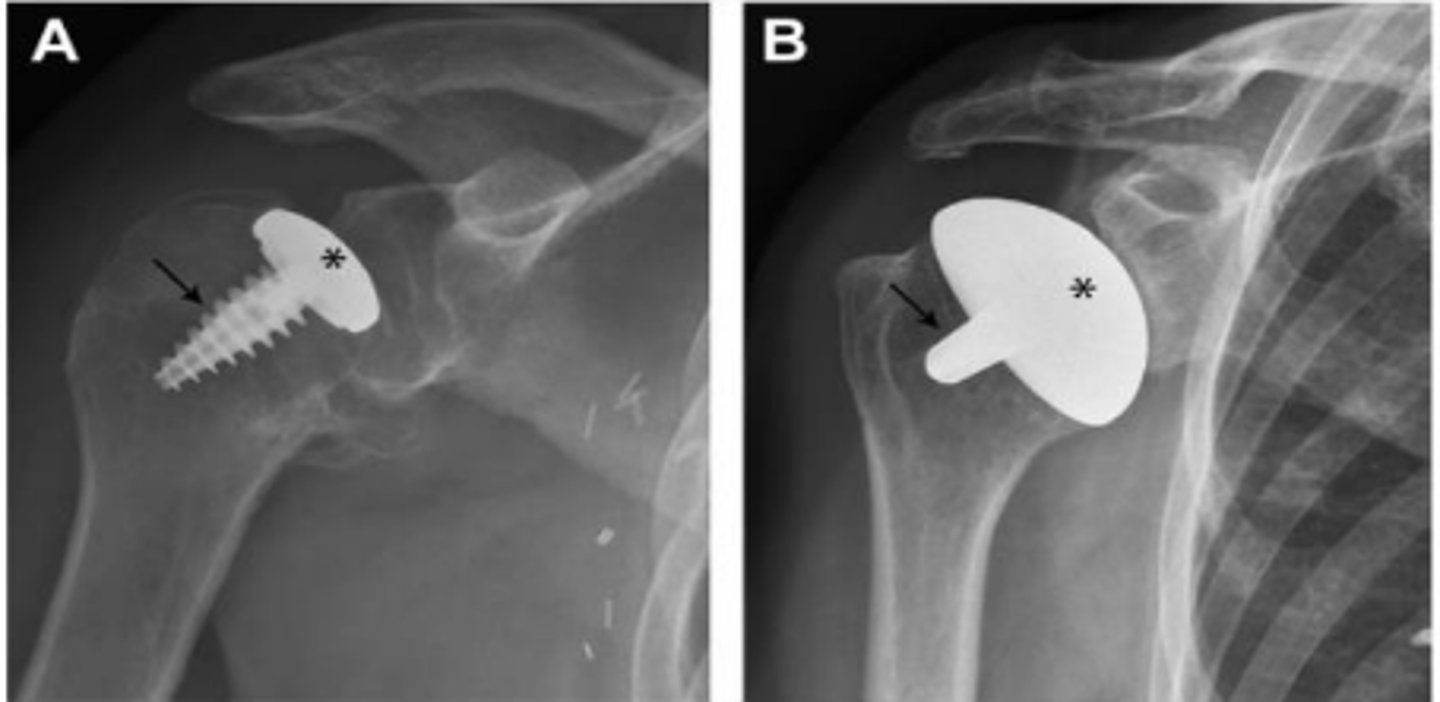
Hemiarthroplasty
What do the images show?
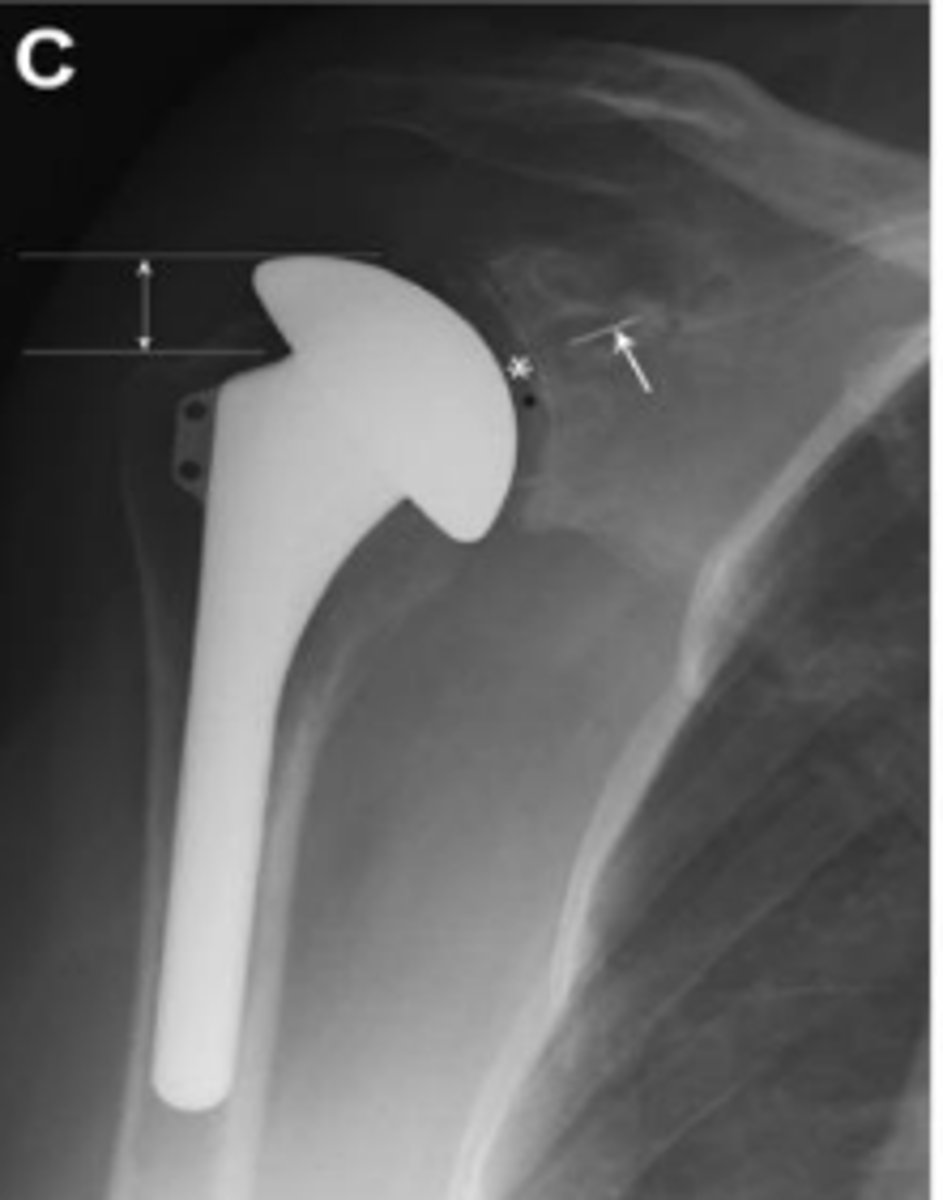
Total shoulder arthroplasty
What does the image show?
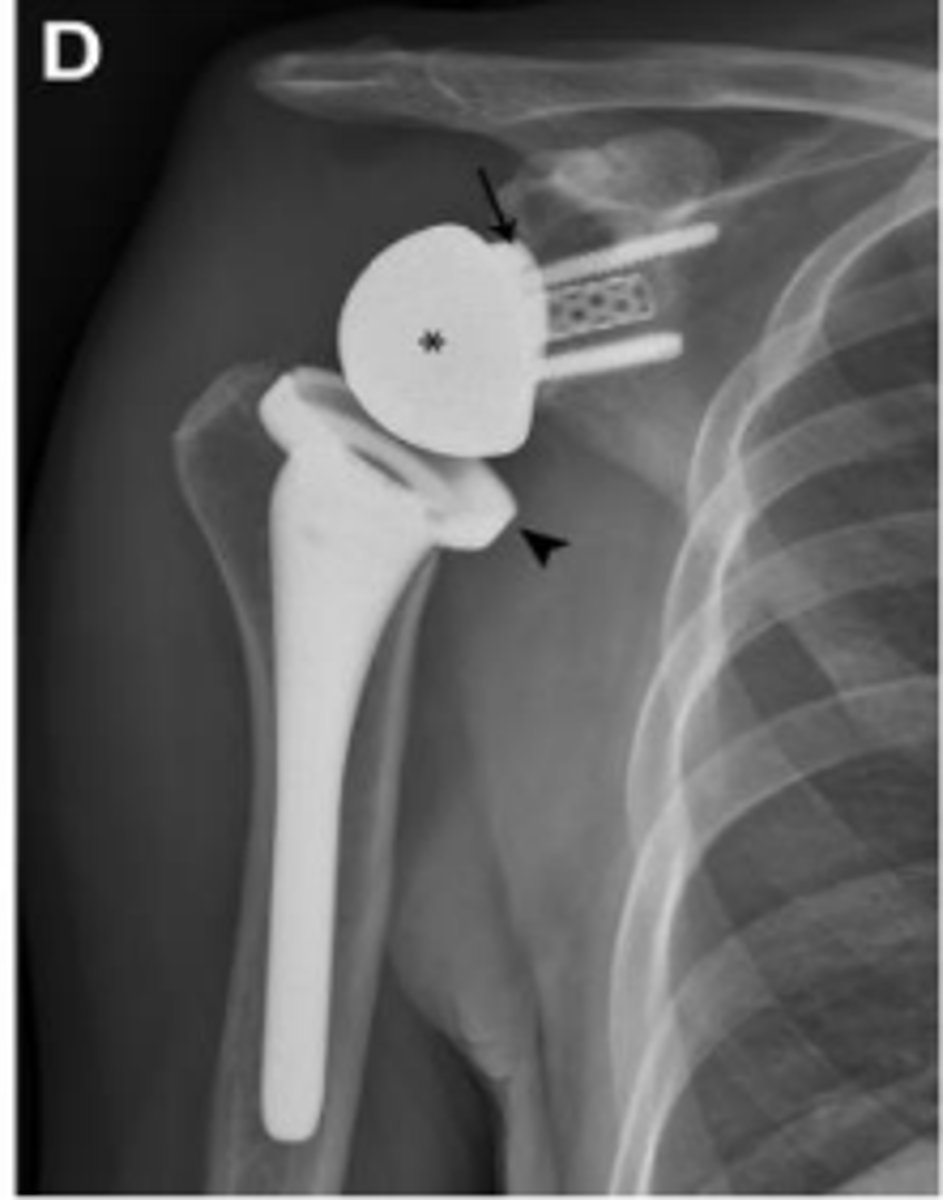
Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty
What does the image show?
14.7%; loosening; instability; fracture; subscapularis; supraspinatus/infraspinatus
Complications after TSA:
- Complication rate reported to be as high as ____________________ in 2005.
- Component ___________________ (39% of all complications)
- GH ___________________ (30% of all complications)
- Periprosthetic ____________________ (11% of all complications)
- RC tears (1st = __________________, 2nd = ___________________)
- Infection (0.7% of all complications)
- Nerve injury
- Deltoid muscle dysfunction
Inconsistency
Bullock, GS, et. al. found ___________________ present in rehab protocols.
6; PROM; scapular
Stage I: Maximal Protection Phase
- __________________ weeks
- Goals are to restore ________________, minimize pain, reduce swelling and muscle spasm.
- Gradually progressing the PROM as tolerated.
- Target at end of phase I → 120-140° elevation; not a lot of abduction is emphasized. 45° ER
- While some protocols are calling for initiating deltoid isometrics within the first few weeks, it is not commonly performed. ______________________ isometrics would likely be okay but again these should be submax if they occur.
6-12; AAROM; AROM; arm
Stage II: AROM and Early Strengthening
- _________________ weeks
- Here is when you would progress to more ___________________ and ___________________ activities; therefore you would be initiating more light strengthening with weight of ___________________ and adding to isometrics load.
12+; low; high; CKC
Stage III: Later Strengthening Phase
- ___________________ weeks
- Begins once patient can move periscapular and deltoid musculature properly with those target ROMs.
- Would be emphasizing strengthening with ________________ load, ________________ reps during this phase and progressing into higher load, lower reps by the end of the third month or so.
- Emphasize __________________ and ↑ load.
16+; 10-25 lbs; loosen
Stage IV: Continue Home Program
- _________________ weeks
- Never really exceeding ___________________ lifting restriction.
- Functional activities with the shoulder are acceptable and encouraged (i.e., golf, tennis, recreational shoulder use).
- Just avoid heavy lifting because this is more likely to _________________ the prosthesis.