A Level Bio 1.4 Protein & Enzymes
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pls rate it 5 stars if you find it helpful :P
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
A student investigated starch digestion by mixing starch with a solution of the enzyme used to digest starch. The student did a biochemical test for protein when starch digestion was completed.
The student’s test for protein was positive. Explain why. (2)
(Positive because) enzymes are protein (1)
(because) enzymes not used up (in reactions) (1)
A scientist investigated the hydrolysis of the protein casein.
The scientist:
• mixed a solution of a protease enzyme with a solution of casein
• then measured the casein concentration in the mixture at intervals
• controlled all relevant variables appropriately.
For this investigation, identify:
the independent variable and the dependant variable (2)
(independant) Time (of measurement/test/sample taken) (1)
(Dependant) Casein concentration (1)
Describe the primary structure of all proteins (2)
Sequence/order of amino acids (1)
(Joined by) peptide bonds (1)
Complete the passage with the appropriate terms
ATP synthase comprises several polypeptides, so is said to have a _______________ structure. It catalyses the synthesis of an ATP molecule by a _______________ reaction; this involves the _______________ of a water molecule. The ATP synthase in the figure above is in a mitochondrion so would catalyse reactions during _______________.
1) Quaternary
2) Condensation
3) Release/loss/formation
4) (Aerobic) respiration
All correct = 2 marks, 2–3 correct = 1 mark,
As shown in the figure above, ATP synthase has two functions.
• It catalyses the synthesis of ATP.
• It allows the movement of H+ ions.
Suggest how the shape of the ATP synthase allows it to have these two
functions.
Explain your answers.(4)
(Catalyses the synthesis of ATP)
Active site complementary to ADP + Pi (1)
Enzyme-substrate complex forms (1)
(Allows the movement of H+ ions)
Channel (in membrane/protein/enzyme) (1)
Allows facilitated diffusion of H+
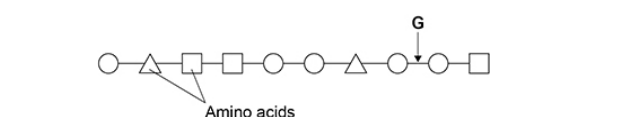
The diagram shows the primary structure of part of a polypeptide. Each shape represents an amino acid. Identical amino acids have the same shape.
Name the type of peptidase which will hydrolyse the bond labelled G in the diagram above. (1)
Endo(peptidase) (1)
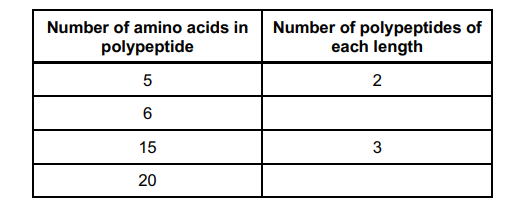
A scientist used an enzyme to digest a polypeptide containing 101 amino acids.
The digestion produced a range of smaller polypeptides.
The scientist determined the number of amino acids in each of the polypeptides
produced. He also counted the number of polypeptides of each length.
The table below shows some of the scientist’s results.
Use the information in the table above to calculate the number of
polypeptides:
6 amino acids in length ______________________________________
20 amino acids in length ______________________________________ (2)
(6 amino acids in length) 1 (1)
(20 amino acids in length) 2 (1)
Describe the induced-fit model of enzyme action and how an enzyme acts as a catalyst. (3)
Substrate binds to the active site/enzyme (1)
Active site changes shape (slightly) so it is complementary to substrate (1)
Reduces activation energy (1)
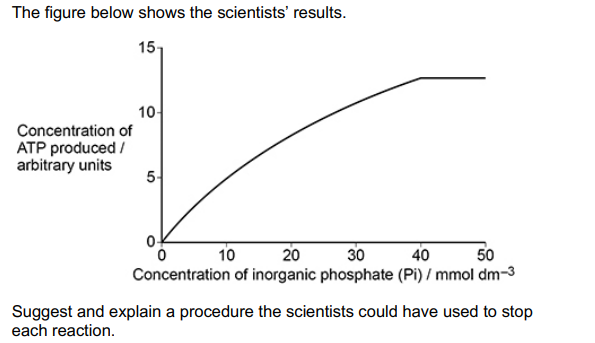
The scientists investigated the effect of concentration of inorganic phosphate (Pi) on ATP synthase activity.
After 2 minutes, they stopped each reaction and then measured the concentration of ATP.
Suggest and explain a procedure the scientists could have used to stop each reaction (2)
Boil (1)
Denatures the enzyme/ATP synthase (1)
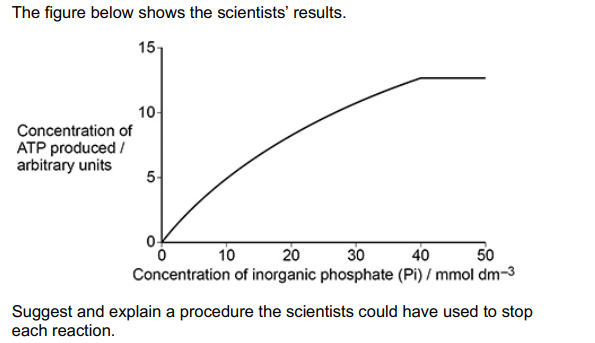
Explain the change in ATP concentration with increasing inorganic phosphate concentration. (2)
(With) increasing Pi concentration, more enzyme-substrate complexes are formed (1)
At or above 40 (mmol dm-3) enzyme concentration is a limiting factor (1)
When bread becomes stale, the structure of some of the starch is changed.
This changed starch is called retrograded starch.
Scientists have suggested retrograded starch is a competitive inhibitor of amylase in the small intestine.
Assuming the scientists are correct, suggest how eating stale bread could help to reduce weight gain. (3)
Less hydrolysis of starch (1)
to maltose (1)
(so ) less absorption (of glucose) (1)
Describe how the structure of a protein depends on the amino acids it contains.(5)
Structure is determined by (relative) position of amino acid/R group (1)
Primary structure is sequence/order of amino acids (1)
Secondary structure formed by hydrogen bonding (between amino acids) (1)
Tertiary structure formed by interactions (between R groups) (1)
Quaternary structure contains >1 polypeptide chain (1)
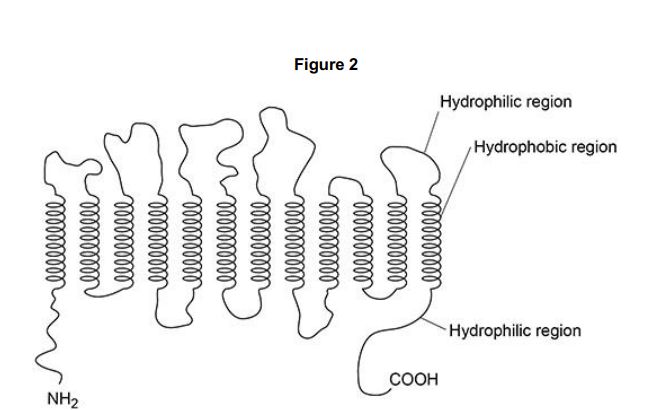
Figure 2 shows the SGLT1 polypeptide with NH2 at one end and COOH at the other end. Describe how amino acids join to form a polypeptide so there is always NH2 at one end and COOH at the other end. (2)
One amine/NH2 group joins to a carboxyl/COOH group to form a peptide bond (1)
(so in chain ) there is a free anime group at one end and a free carboxyl group at the other (1)
Explain how the active site of an enzyme causes a high rate of reaction. (3)
Lowers activation energy (1)
Induced fit causes active site (of enzyme) to change shape (1)
(so) enzyme-substrate complex causes bonds to form/break (1)
Describe a biochemical test to confirm the presence of protein in a solution. (2)
Add biuret (reagent (1)
(positive result) lilac (1)
Describe how a quaternary protein is formed from its monomers. Do not include the process of translation in your answer. (5)
Amino acids joined by peptide bond(s) (1)
(by) condensation reaction(s) (1)
Secondary structure is formed by hydrogen bonding (1)
Tertiary structure formed by interactions (between R groups) (1)
Quaternary structure contains >1 polypeptides (1)
A non-competitive inhibitor decreases the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction. Explain how (3)
The non-competitive inhibitor binds to the allosteric site (1)
Changes the enzyme’s active site (1)
No/fewer enzyme-substrate complexes (1)
Describe the structure of DNA and the structure of a chromosome (6)
Polymer of nucleotides (1)
(Nucleotide) consists of deoxyribose, phosphate and an organic/nitrogenous base (1)
Phosphodiester bonds (between nucleotides) (1)
DNA double helix held by H bonds (1)
(Hydrogen bonds/pairing) between adenine, thymine and cytosine, guanine (1)
(During mitosis/when visible) chromosome consists of two chromatids joined at a centromere (1)
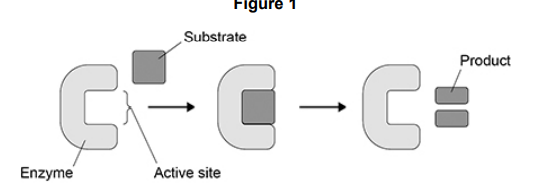
Many proteins are enzymes.
In 1894, a scientist suggested the lock and key model of enzyme action.
Figure 1 shows the lock and key model.
Describe one similarity and one difference between the induced-fit model of enzyme action and the lock and key model of enzyme action (2)
Similarity - substrate binds to active site (1)
Difference-(Initially) active site not complementary to substrate with induced-fit, but is complementary in lock and key (1)
State how enzymes help reactions to proceed quickly at lower temperatures. Do not write about active sites in your answer. (1)
Lower/reduce activation energy (needed to start a reaction) (1)
Explain how two enzymes with different amino acid sequences can catalyse the same reaction.(2)
(Both) active sites have similar/identical tertiary structures (1)
(So) form enzyme-substrate complexes (with the same substrate) (1)
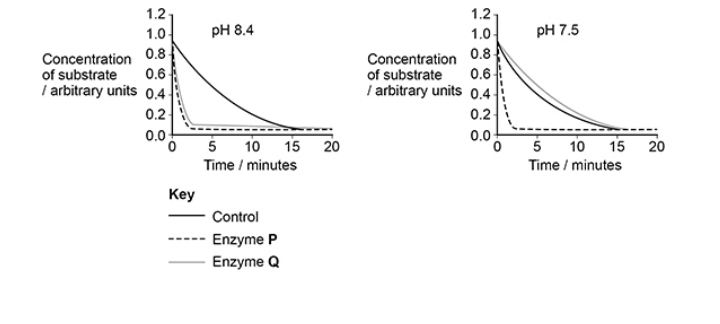
Scientists investigated the effect of pH 8.4 and pH 7.5 on the activity of enzymes P and Q. The figure below shows their results.
Describe what the scientists should place in the control tubes in this investigation. (3)
Same volume of (each) buffer/pH solution (1)
Same concentration/mass of substrate (at start) (1)
Same concentration/mass of denatured enzyme (1)
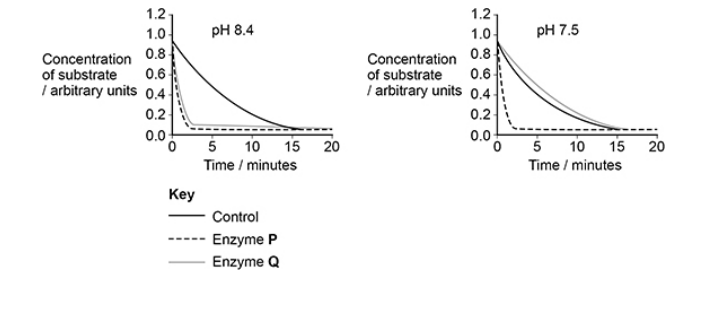
Give three conclusions you can make from the figure above(3)
Both/P and Q (are) active at pH 8.4 (1)
Reaction occurs without enzyme(s) (1)
Q is denatured/not active at pH 7.5 (1)
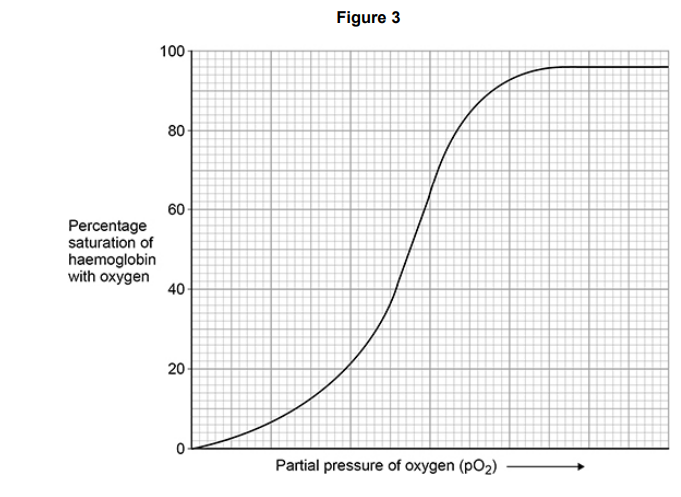
When a substance called BPG binds to haemoglobin, it reduces the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen.
Figure 3 shows an oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve for haemoglobin in normal conditions.
Suggest and explain when it would be an advantage to a human for BPG to bind to haemoglobin.(2)
(Allowing) more oxygen for respiration (1)
During exercise(1)

The action of the enzyme catalase is shown below.
A student investigated the effect of hydrogen peroxide concentration on the rate
of this reaction. He used catalase from potato tissue.
The student:
• put five potato chips in a flask
• added 20 cm3 of 0.5 mol dm–3 hydrogen peroxide solution to the flask
• measured the time in seconds for production of 10 cm3 of oxygen gas
• repeated this procedure with four different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide solution.
Suggest a change the student could make to his procedure so that 10 cm3 of oxygen would be produced in less than 6 seconds. (1)
Cut up/use discs/homogenise/increase surface area (of potato chips) (1)
A dipeptide consists of two amino acids joined by a peptide bond.
Dipeptides may differ in the type of amino acids they contain.
Describe two other ways in which all dipeptides are similar and one way in
which they might differ. (3)
(similarities)
Amine/NH2 (group at end) (1)
Carboxyl/COOH (group at end) (1)
(Difference)
Variable/different R group(s) (1)
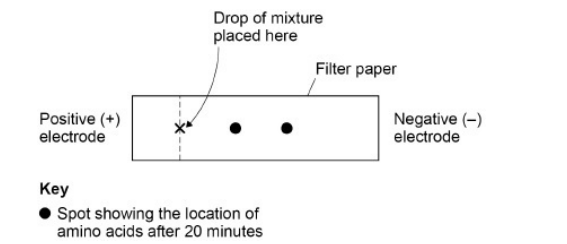
A solution contained a mixture of three different amino acids. A scientist passed an electric current through the solution to separate the amino acids.
She placed a drop of the mixture at one end of a piece of filter paper, attached an electrode to each end of the paper and switched on the current. She switched off the current after 20 minutes and stained the paper to show spots of the amino acids at new positions.
Her results are shown in the diagram.
Explain what the positions of the spots in the diagram show about these amino acids. (3)
Moved to negative (electrode) because positive(ly charged) (1)
(Spots move) different distances/rates because (amino acids) different charge/mass (1)
Two spots (not three) because (amino acids) have same charge/mass (1)
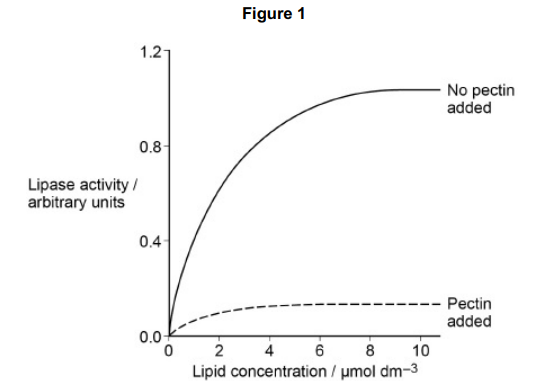
The scientist concluded that pectin is a non-competitive inhibitor of the lipase enzyme.
Use Figure 1 to explain why the scientist concluded that pectin is a noncompetitive inhibitor. (1)
(With inhibitor) increase substrate/lipid (concentration) does not increase/affect/change rate of reaction (1)
The secondary structure of a polypeptide is produced by bonds between amino acids. Describe how (2)
Hydrogen bonds (1)
Between NH (group of one amino acid) and C=O (group) (1)
Two proteins have the same number and type of amino acids but different tertiary structures. Explain why. (2)
Different sequence of amino acids (1)
Forms ionic / hydrogen / disulfide bonds in different places (1)
Formation of an enzyme-substrate complex increases the rate of reaction. Explain how. (2)
Reduces activation energy (1)
Due to bending bonds (1)
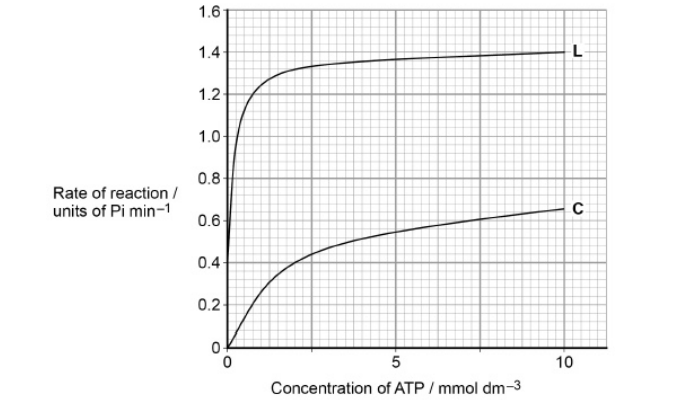
Another scientist investigated an enzyme that catalyses the following reaction.
ATP → ADP + Pi
The scientists set up two experiments, C and L.
Experiment C used
• the enzyme
• different concentrations of ATP.
Experiment L used
• the enzyme
• different concentrations of ATP
• a sugar called lyxose.
The scientists measured the rate of reaction in each experiment. Their results
are shown in the graph.
Lyxose binds to the enzyme.
Suggest a reason for the difference in the results shown in the graph with and without lyxose. (3)
(Binding) alters the tertiary structure of the enzyme (1)
(This causes) active site to change (shape) (1)
(So) More (successful) E-S complexes form (per minute) (1)
In humans, the enzyme maltase breaks down maltose to glucose.
This takes place at normal body temperature.
Explain why maltase:
• only breaks down maltose
• allows this reaction to take place at normal body temperature (5)
Tertiary structure / 3D shape of enzyme (means)
Active site complementary to maltose / substrate (1)
Description of induced fit (1)
Enzyme is a catalyst / lowers activation energy / energy required for reaction (1)
By forming enzyme-substrate complex (1)
What type of protein is collagen and how many polypeptide chains does it have? (2)
Fibrous protein (1)
3 polypeptide chains (1)
What type of protein is insulin and how many polypeptide chains does it have? (2)
globular protein (1)
2 polypeptide chains (1)
What type of protein is haemoglobin and how many polypeptide chains does it have?
Globular protein (1)
4 polypeptide chains (1)
Aspirin is a useful drug. One of its uses is to reduce fever and inflammation. Aspirin does this by preventing cells from producing substances known as prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are produced by an enzyme-controlled pathway. Aspirin works by inhibiting one of the enzymes in this pathway. Aspirin attaches permanently to a chemical group on one of the monomers that make up the active site of this enzyme.
The enzyme involved in the pathway leading to the production of prostoglandins is also involved in the pathway leading to the production of thromboxane. This is a substance that promotes blood clotting. A small daily dose of aspirin may reduce the risk of myocardial infarction.
Aspirin only affects one of the enzymes in this pathway, use lines 5-7 to explain why aspirin doesn't affect the other enzymes. (2)
Affects one monomer (1)
Not found in all active sites (1)
Aspirin is a useful drug. One of its uses is to reduce fever and inflammation. Aspirin does this by preventing cells from producing substances known as prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are produced by an enzyme-controlled pathway. Aspirin works by inhibiting one of the enzymes in this pathway. Aspirin attaches permanently to a chemical group on one of the monomers that make up the active site of this enzyme.
The enzyme involved in the pathway leading to the production of prostoglandins is also involved in the pathway leading to the production of thromboxane. This is a substance that promotes blood clotting. A small daily dose of aspirin may reduce the risk of myocardial infarction.
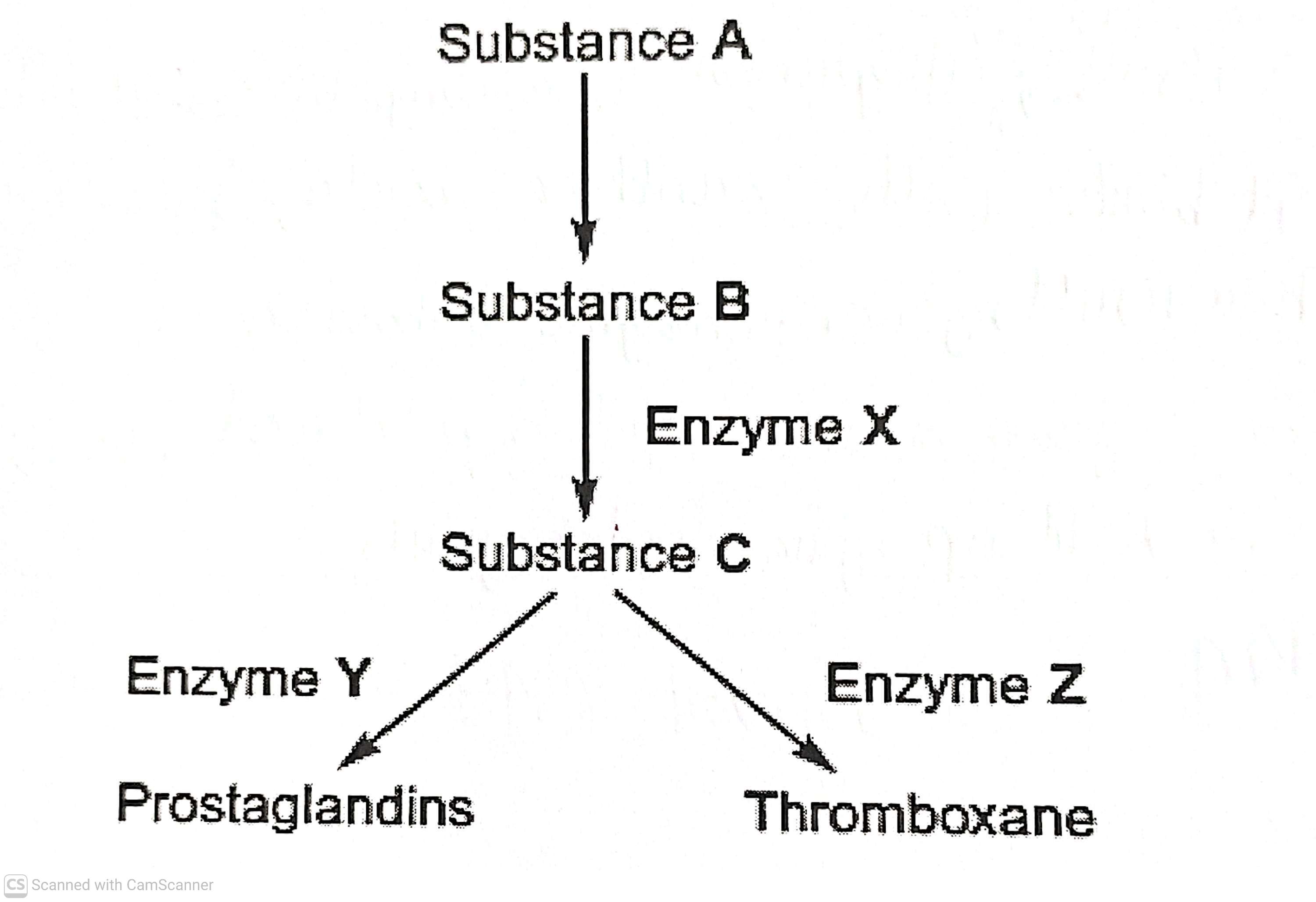
The diagram shows the pathways by which prostaglandins and thromboxane are formed
Which enzyme, X, Y or Z is inhibited by aspirin? Explain the evidence from the passage that supports your answer(2)
Enzyme X (1)
Enzyme in both pathway (1)
Describe how proteins are digested in the human gut. (4)
Hydrolysis of peptide bonds (1)
Endopeptidases break polypeptides into smaller peptide chains (1)
Exopeptidases remove terminal amino acids (1)
Dipeptidases hydrolyse / break down dipeptides into amino acids. (1)
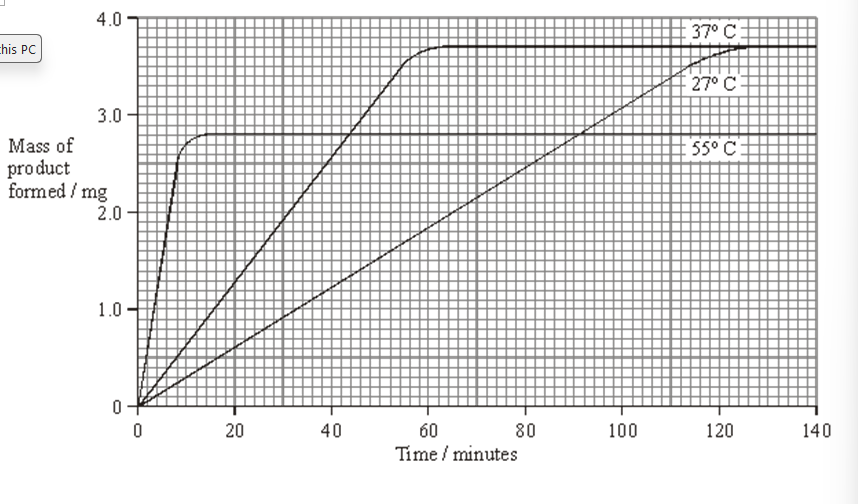
Use your knowledge of enzymes to explain
the shape of the curve for 55 °C after 20 minutes. (3)
High temperature causes enzyme to denature (1)
shape of active site changes (1)
substrate no longer binds to active site (1)
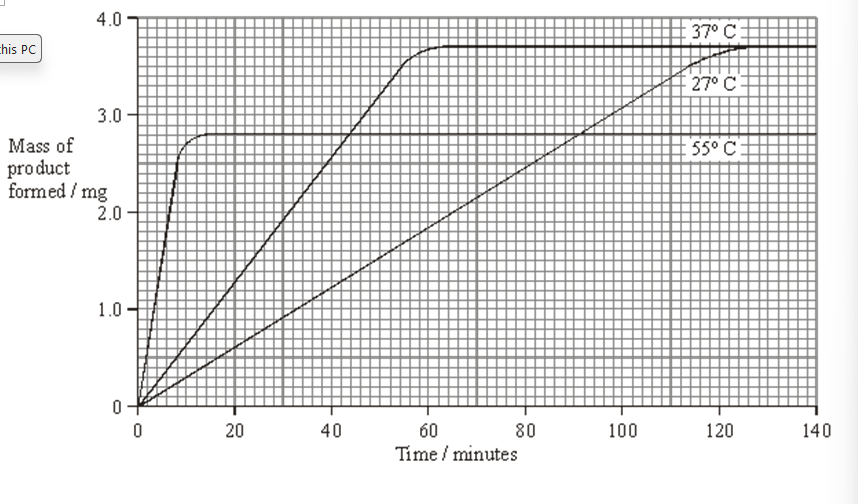
Explain why the curves for 27 °C and 37 °C level out at the same value. (2)
The reaction is complete (1)
same amount of products are formed as same initial substrate concentration (1)