PSYC 308: Midterm 2
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
in what aspects are emotions central to social psychology?
stories we tell
relationships
well-being and happiness
moral judgements
social identities
emotions
brief, specific responses, psychological and physiological, to challenges or opportunities that are important to individual’s life goals
arise because of construals (called appraisals)
created by many complex and automatic processes
cause shifts in physiology and involve expressive behaviour
appraisals
interpretations of events in terms of things like how pleasant, novel, fair, threatening event is and if you, others, or situation caused the event in the first place
how are emotions different from moods?
emotions are brief (secs to mins) vs. hours to days
emotions are specific to certain events vs. more general/unfocused
5 components of emotion
fast and automatic construal
physiological response
expressive behaviour
subjective (internal) feeling
action tendency
why do we have emotions?
help us interpret our surrounding circumstances - prioritize events and influence how much weight assigned to them/reasoning
guide our actions that advance our goals
enable us to respond effectively to specific challenges especially those with other people to strengthen relationships with people
empathy
understanding (cognitive) and experiencing (emotional) the feelings of another person
5 components of empathy
fast and automatic construal
physiological response (oxytocin - social bonding hormone)
expressive behaviour - mirroring of facial expressions
subjective (internal) feeling - sharing of the feeling
action tendency (social bonding, caring)
evolutionary basis of empathy
mammalian parental care
discrete view of emotion (universal emotion)
limited number of core basic emotions—sadness, anger, fear, disgust, happiness, surprise
accuracy rates of identifying them were 70-90% across cultures
the Foray tribe in Africa who had no exposure to Western culture had accuracy rates of 68-92% (Ekman and Friesen, 1971)
other emotions with evidence of universality
amusement, desire, interest, love, pride, some self-conscious emotions, awe, pain
constructivist approach to emotion
culture affects how we feel about events, what we do about our feelings, how we express/describe our feelings
emotions derive from language/knowledge structures of cultures
influenced by values, roles, institutions, socialization practices that vary across cultures
guilt vs shame
specific attribution (person) vs. global attribution (behaviour)
not likely triggered by awareness or loss of social status vs. is
elicits social damage repair (approach) vs. elicits social withdrawal (avoidance)
circumplex model of emotion
any emotion can be described using an unpleasantness/pleasantness dimension (valence) and a high arousal/low arousal dimension (activation).
positive valence/high arousal = elated, excited
positive valence/low arousal = happy, serene
negative valence/high arousal = furious, embarrassed
negative valence/low arousal = sad, melancholic
how are emotions evolutionary adaptive?
Darwin proposed human emotions derive from motivations that were evolutionary advantageous for primates
fear = danger avoidance
empathy = care for offspring
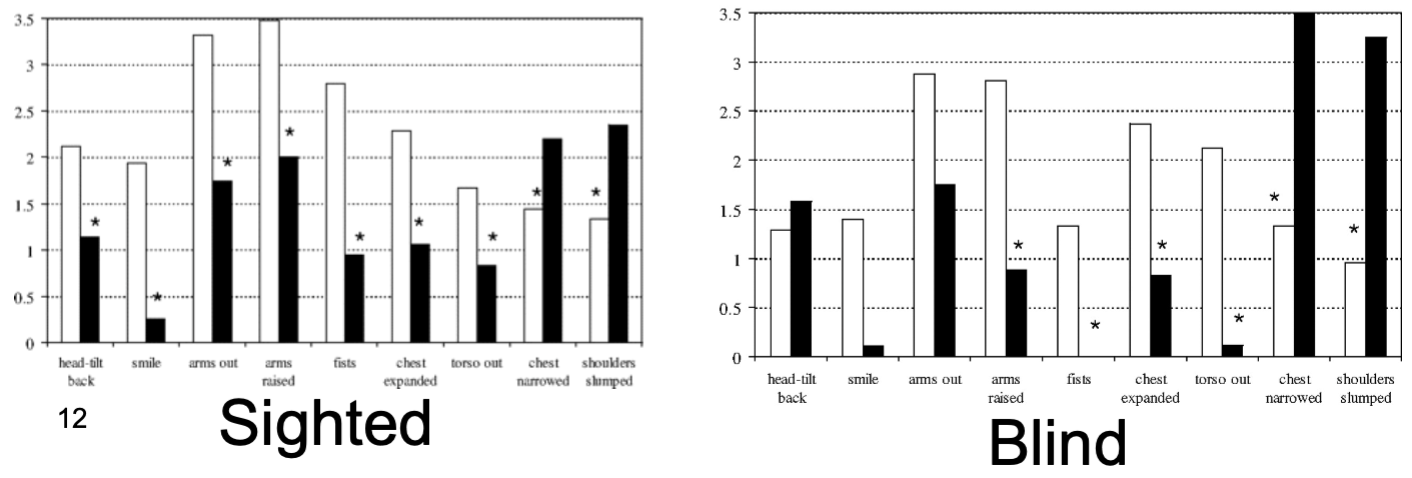
We share some basic emotional expressions with our primate relatives
blind individuals still show expressions similar to sighted people
what emotions do chimps share with humans?
threat displays (anger, sadness), happiness (smile, laughing), compassion, embarrassment
adaptive importance of embarrassment
signals remorse for social transgressions, prompting forgiveness and reconciliation after an individual has violated a social norm
results in people trusting you more
is pride a evolutionary based emotion? (Tracy and Matsumoto)
evidence of innately prepared emotional displays of pride - congenitally blind athletes show similar emotional displays as sighted athletes
emotional accents
culture-specific emotional expressions
open mouth or closed mouth smiling
biting your tongue as a display of embarrassment in India
focal and ideal emotions
emotions with cultural importance
feeling prideful when achieving something in North America
shame and embarrassment experienced more in collectivistic cultures
focal emotions
relatively common in everyday lives of members of a culture and that are experienced and expressed with greater frequency and intensity
shame and embarrassment are focal in more interdependent cultures
ideal emotions
emotions that are valued in a particular culture
affect valuation theory: emotions that promote important cultural ideal, play prominent role in social lives of individuals
display rules
when/how to express emotions
have to be sad at a funeral
cultural meaning
same situation may have different cultural meanings, eliciting different emotions
turning 21 in the US vs. Europe
cultures of honour (insult or bemusement
reappraise emotions
rethink the reasons they are feeling the way they do
accepting emotions
understand emotions are fleeting and causes typically change
suppressing emotions
minimizing outward signs of emotions
more common in interdependent cultures
emotional intelligence (Mayer, Salovey, Caruso, 2008)
overlap of emotional literacy, self-awareness, regulating emotions
emotional literacy
knowing emotional vocabulary and identifying emotions
self-awareness
getting to know internal states, motivations, preferences, emotions
cultivating a non-judgemental approach to our inner world
moment-to-moment awareness of inner states
regulating emotions
impulse control and self-regulation: resisting temptations, not getting overwhelmed
goal pursuit: perseverance when appropriate, recovering from setbacks
calibrating emotions to a given situation: feeling pain of another in distress, etc.
social functional theories of emotion
each emotion is associated with a unique motivational function for the individual and the social environment
shifting our construal of social context
emotion and the orbitofrontal cortex
damage to it causes loss of ability to rely on emotion to act in ways that fit the current situation
shows how important emotions are to healthy social relationships - shows a commitment to others, motivate how we act towards others
oxytocin and emotion
fosters emotions that strengthen commitment in long-term familial relationships and friendships
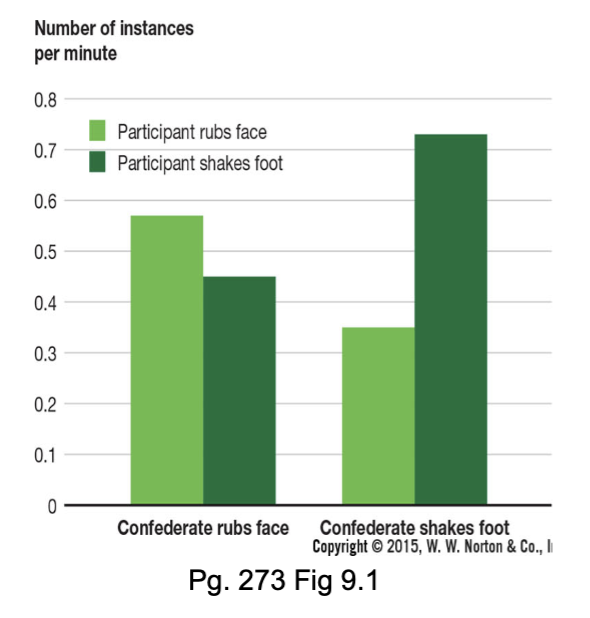
emotional mimicry
copying others’ emotional expressions
helps us collaborate more effectively with others
emotion and touch
Hertenstein et al., 2006 found that brief tactile contact could reliably communicate love, sympathy, gratitude
touch can also promote better collaboration
emotion and group membership
help us identify with groups and help us find our place within them
negotiate status through emotion expressions
pride and anger can signal desire to gain power/status
envy depicts dissatisfaction with someone’s group role
emotions influencing perception
we perceive events in ways that are consistent with how we are feeling
can influence broader judgements (if our circumstances are fair or safe)
anger can cause us to perceive others as hostile
emotions influence reasoning
positive emotions can prompt people to think creatively and with flexibility
broaden-and-build hypothesis
whereas negative emotions focus our attention on the narrow details of what we are perceiving, positive emotions broaden our patterns of thinking
culture variations in happiness
Americans: personal achievement
East Asians: maintaining harmonious interactions and fulfilling duties and societal expectations
Latino cultures: warm, affectionate interactions
measurement of happiness
life satisfaction and emotional well-being
benefits of happiness
enables better work, better personal relationships, better physical health
ways to improve happiness
writing down what you’re grateful for
appreciate the people you love
do something that makes you laugh
go for a walk somewhere
donate to charity
sit quietly and focus on feelings
write about life goals
use money to buy a experience
get off devices
affective forecasting
predicting future emotions - number of biases that affect it
immune neglect, overestimating long term life dissatisfaction, focalism
immune neglect
tendency to ignore our ability to respond productively to stress and other potential sources of unhappiness
focalism
focus too much on central elements of significant events and fail to consider how other aspects of our lives will influence how happy we are
ex. trying to break up with a toxic boyfriend
remembrance of past pleasures
peak moment of pleasure during an event and feelings at the end of the event strongly influence how we remember it
length of event has little impact (duration neglect)
pursuit of happiness
found in being with other people - avoid isolation
money will bring (some) happiness - only when it achieves base economic stability
practicing gratitude
better to give than to receive (sharing, charity, volunteering)
buying experiences over items
cultivating experiences that lead to awe
importance of emotional intelligence
associated with higher life and relationship satisfaction
more success in leadership positions
improves learning environments and academic achievement among kids
higher self-control as a child leading to better health and less financial difficulties as an adult
how does loneliness affect health?
more harmful than smoking 15 cigarettes daily, excessive drinking, obesity
how is attachment foundational to social relationships
experiencing of early bonding to caregivers provides template for adult relationships
securely attachment to parents predicts positive outcomes in adulthood
however early bonding experiences are not destiny
passionate love
intense longing, ecstasy/despair
intense but brief - intensity quickly plateaus
like a drug, burning fire
companionate love
feelings of intimacy, care, connection
slow growing but long lasting - intensity grows over time
vines growing and intertwining
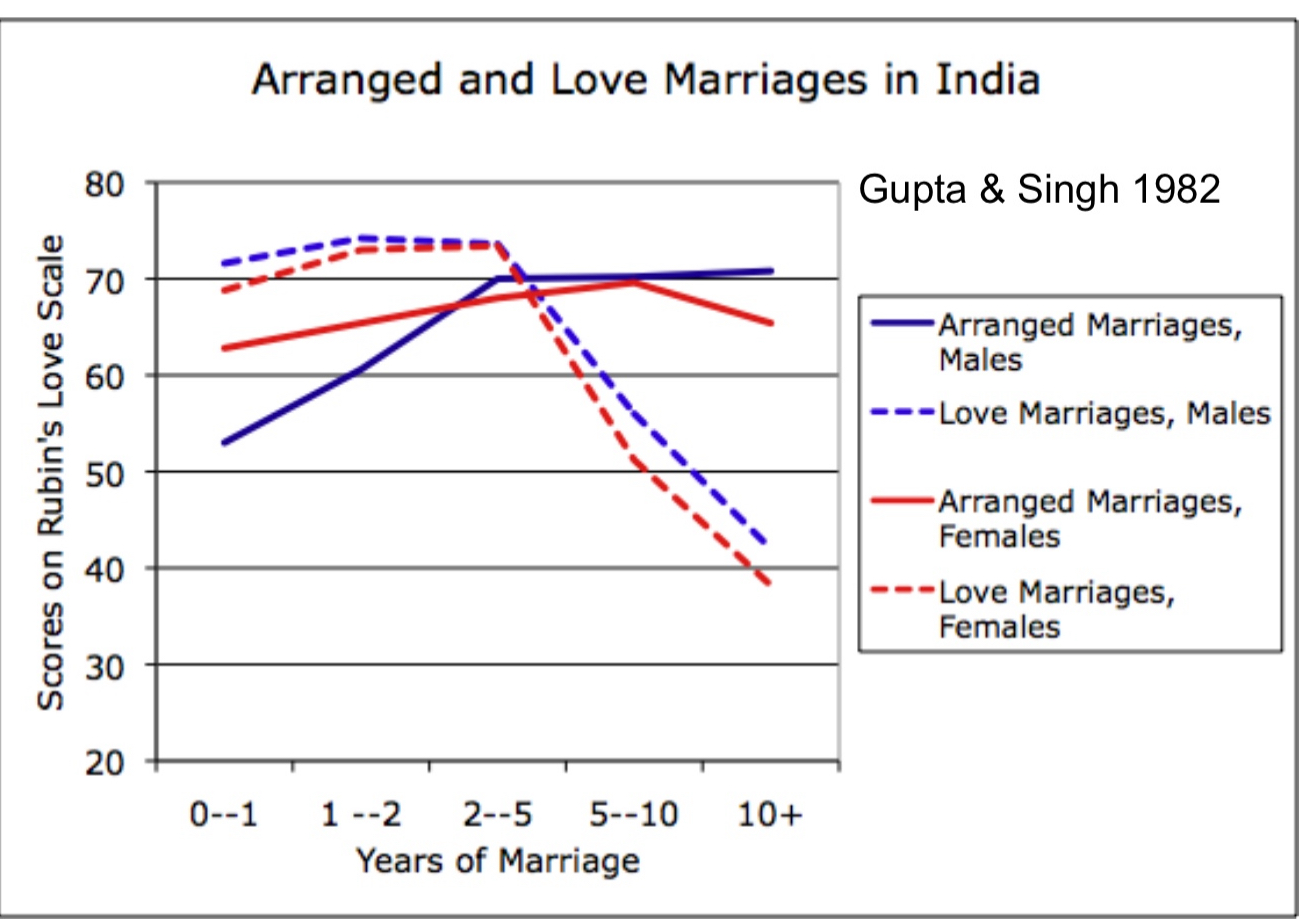
love and marriage across cultures (Levine et al., 1995)
49% of participants from India said they would marry a person if they didn’t love them but they had all the other qualities they desired
vs. <10% US, UK, JP, HK
~40% of participants from all those countries said it was ok to leave a relationship if love disappeared
romantic love
exists everywhere, but marriages based on it are not universal (arranged marriages are common)
are arranged marriages satisfying?
most end up becoming loving relationships even if they start out without love
studies show they are at lease as happy as love marriages
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
physiological
safety
belonging and love
esteem
self-actualization
shift in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
marriage has went from necessity/survival to meeting intimacy and self-expressive needs
causes more marriages to fail from this high standard
few marriages that succeed are as fulfilling as they used to be
4 horsemen of the apocalypse
criticism
contempt
defensiveness
stonewalling
criticism
attack on your partner at the core of their character
contempt
treat others with disrespect, mock them with sarcasm, ridicule, call them names, and mimic or use body language such as eye-rolling or scoffing
defensiveness
When we feel unjustly accused, we fish for excuses and play the innocent victim so that our partner will back off.
stonewalling
occurs when the listener withdraws from the interaction, shuts down, and simply stops responding to their partner
importance of relationships
humans have a biological need to be in a relationship
increase likelihood of passing on one’s genes, improves survival
monkeys even prefer cloth mothers than wire mothers with food
communal relationships
individuals feel a special responsibility for one another and often expect relationship to be long term
more common among East Asian and Latin American countries
exchange relationship
trade based and often short term - feel no special responsibility for one another’s well-being
concerned with equity and reciprocity
more common among European and North American countries
social exchange theory
humans, wanting to maximize own satisfaction, seek out rewards in interactions with others and are willing to pay certain costs to obtain those rewards
prefer when rewards exceed the costs
comparison level and comparison level for alternatives standards
comparison level
expectations people have about what they should get out of a relationship
comparison level for alternatives
outcomes people think they can get out of alternative relationships
think they can do better
equity theory
helps us understand how the combo of too many rewards and too few costs in a relationship can be unattractive - people are motivated to pursue fairness
universal features of relationships
caregiving between mother and child
wrestling between siblings
flirtation by young people
affection between romantic partners
dominance displays
grieving loss of loved ones
propinquity
physical proximity encourages liking, friendships, romance
disrupted by social media
explanations of propinquity effects
availability encourages interactions
anticipating interactions produces warm feelings
mere exposure effect
functional distance
influence of layout of a physical space that encourages contact between people
significant importance
mere exposure effect
repeated exposure breeds familiarity, encourages liking
does not need conscious reflection
oldest trick in advertising
familiarity is the key to exposure therapy
novelty seeking
familiarity is much more powerful - we just don’t noticed familiarity choices
similarity
breeds attraction
engaged couples study: the presence of the four horsemen in couples predicts divorce
bogus stranger studies: if shown a description of a random person, you are more likely to like them if they are like you
weaker in more collectivistic cultures
similar in social class, educational level, religious background
why is similarity important?
leads to consensual validation
assume they have other positive qualities
enables more rewarding interactions
opposites attract
some exceptions to the similarity preference
sexual attraction (masculine-feminine attraction)
some personality traits (dominant/submissive, talkative/quiet, nurturing/needy)
attachment theory
our early attachments with out parents and other primary caregivers shape our relationships for the rest of our lives
establishing a sense of security early in life is important for the rest of life (determinant on parents’ availability and responsiveness)
strange situation (Mary Ainsworth)
classified attachment of infants based on how they reacted when parents left the room
secure: comfortable exploring a novel environment - had caregivers who quickly comforted them
anxious: distressed in novel environment - less comforted by contact with caregiver
avoidant: caregivers frequently rejected them and children were less inclined to seek comfort
adult attachment
carries over from infancy - dimensional instead of rigid
can be changed
anxiety dimension of attachment
amount of fear a person feels about rejection abandonment within close relationships
avoidance dimension of attachment
degree to which a person is comfortable with intimacy and dependence
why does similarity encourage attraction?
social validation (egocentrism)
smooth social interactions
we expect similar others to like us
similar others have qualities we like -
physical attractiveness
one of the most powerful determinant of interpersonal attraction
variability in what individuals find attractive
variability in how attractive people are over time
how attractive you are perceived to be depends heavily on how you act
attractive people
more popular as friends
better liked as potential romantic partners
favoured more academically and professionally
halo effect
common belief that people who are appealing to look at have a host of positive qualities beyond their physical appearance
independent cultures: more dominant/assertive
interdependent cultures: more generous, sensitive, empathetic
reproductive fitness
capacity to pass one’s genes on to subsequent generations
prefer people who’s traits signify health
prefer symmetrical faces
investment in offspring
women invest more in offspring than men so they should be more selective with their mates
men want more partners to increase their genes
what are men and women attracted to?
men: younger women, cues associated with youth
women: material resources, ambition industriousness, social status, physical strength
investment model of commitment
why some romantic partners remain committed to their relationships - satisfaction, no alternative partners, magnitude of investments
related to the degree to which people see partners as being understanding, validating, responsive (perceived partner responsiveness)
predictors of relationship dissatisfaction
neuroticism, low self-esteem, high sensitivity to rejection, lower SES, marrying younger, 4 horsemen of the apocalypse, blaming
creating stronger romantic bonds
healthy conversation, capitalize on the good, being playful, pursuing growth, intimacy, rewards in relationship, laughter, finding the good
social influence
Ways people change another’s attitudes, beliefs, feelings, behaviour that result from comments, actions, presence of others
neither good or bad but can get ugly fast (war crimes, copycat suicides)
homophily
tendency for people to associate disproportionately with people like them
why do people participate in rituals
Hype and applause, crowd approval
Cultural significance
Approval by friends and family
Actions perceived as exiting rather than painful because of ritual standing
conformity
social influence in response to real or imagined pressure from others to change to align with others
automatic mimicry and chameleon effect, informational social influence, normative social influence
seen as a bad thing but is important for a society to function well
chameleon effect (automatic mimcry)
non conscious mimicry of expressions, mannerisms, movements, other behaviours of those with whom one is interacting
Mirror neurons in frontal cortex: base of synchrony in social animals and empathic skills - perception regions overlap with action regions
mimicking others facilitates smooth interaction and social connection