Exercise 27 - Heart Structure and Function Part A and B
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
heart
a double pump that simultaneously pumps blood to body cells through the systemic circulation and to the lungs through the pulmonary circulation
arteries
blood vessels that carry blood from the heart
veins
blood vessels that carry blood to the heart
human heart
has four chambers and is divided into right and left sides
atrium (atria)
upper chamber of the heart
ventricle
lower chamber of the heart
auricles
pouch like extensions of the atria
heart
size of a fist and shaped like a cone
heart
lies on its side in the thoracic cage within the meidastinum
mediastinum
an area bounded by the lungs laterally, the sternum and ribs anteriorly, and the diaphragm inferiorly
two-thirds of the heart
lies to the left of the thoracic midline
right ventricle
forms most of the anterior surface of the heart
left ventricle
also observed on the anterior surface of the heart
apex of the heart
inferior pointed end of the left ventricle and is located in the 5th intercostal space
inferior surface of the heart
lies on the diaphragm and is attached to the diaphragm by dense fibrous connective tissue
atria and the left ventricle
observed on the posterior surface of the heart
right and left atria
form the base of the heart
base of the heart
faces the right shoulder while the apex points to the left hip
coronary blood vessels and adipose tissue
found in the sulci or grooves that externally mark the boundaries between the four heart chambers
coronary sulcus
a deep groove that externally shows the separation of the atria and the ventricles
anterior interventricular sulcus and posterior interventricular sulcus
shallow grooves that depict the surface boundaries between the two ventricles
auricle of right atrium
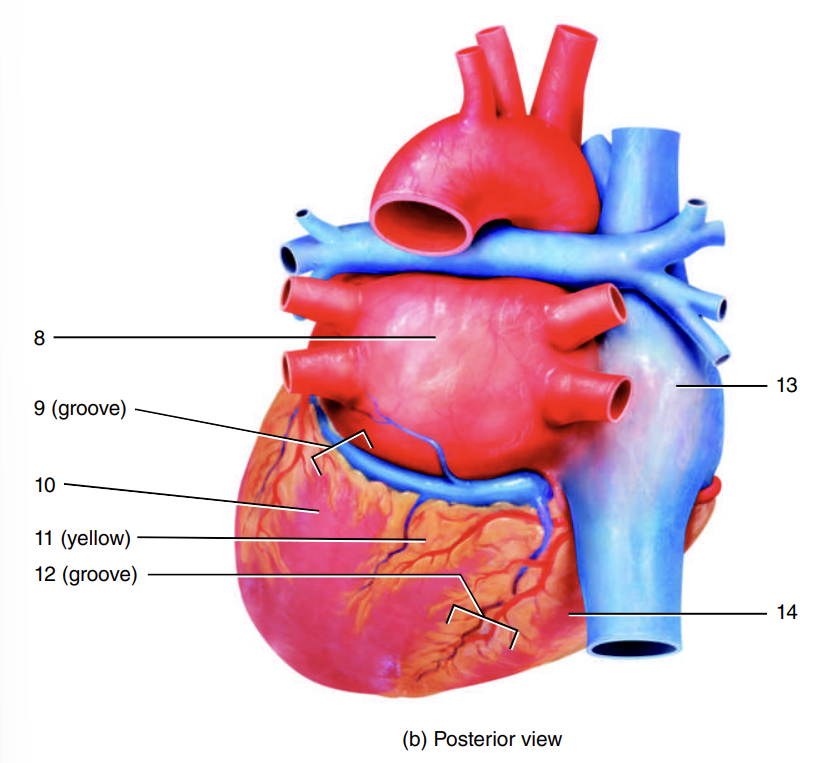
1
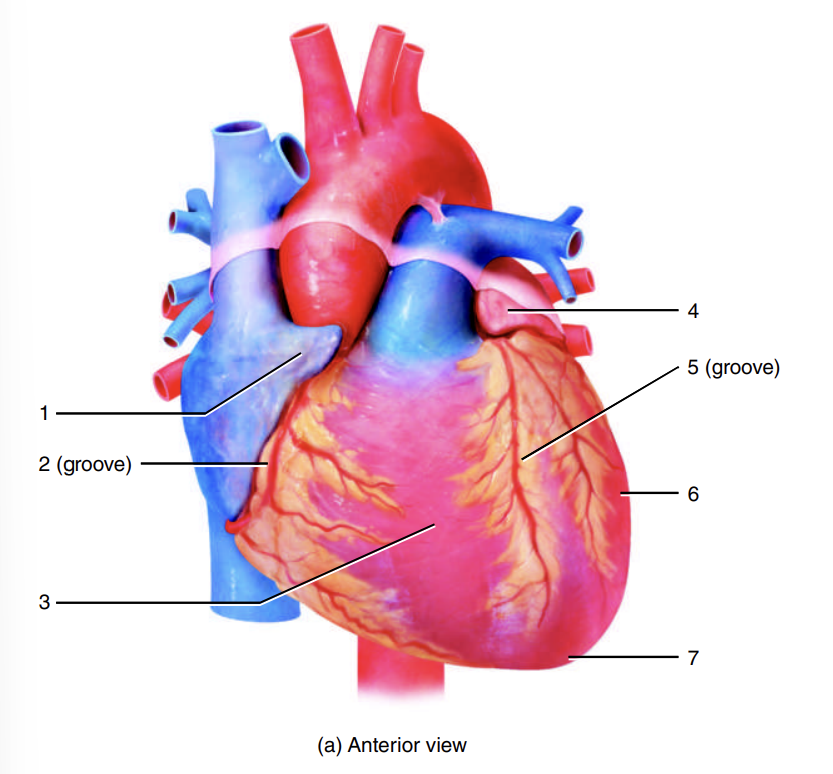
coronary sulcus
2
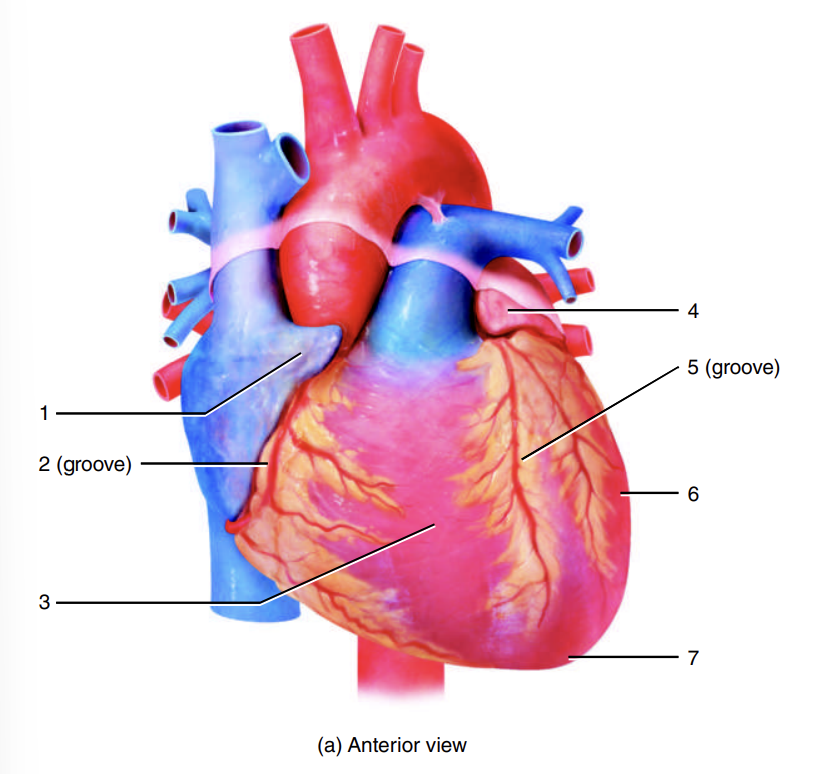
right ventricle
3
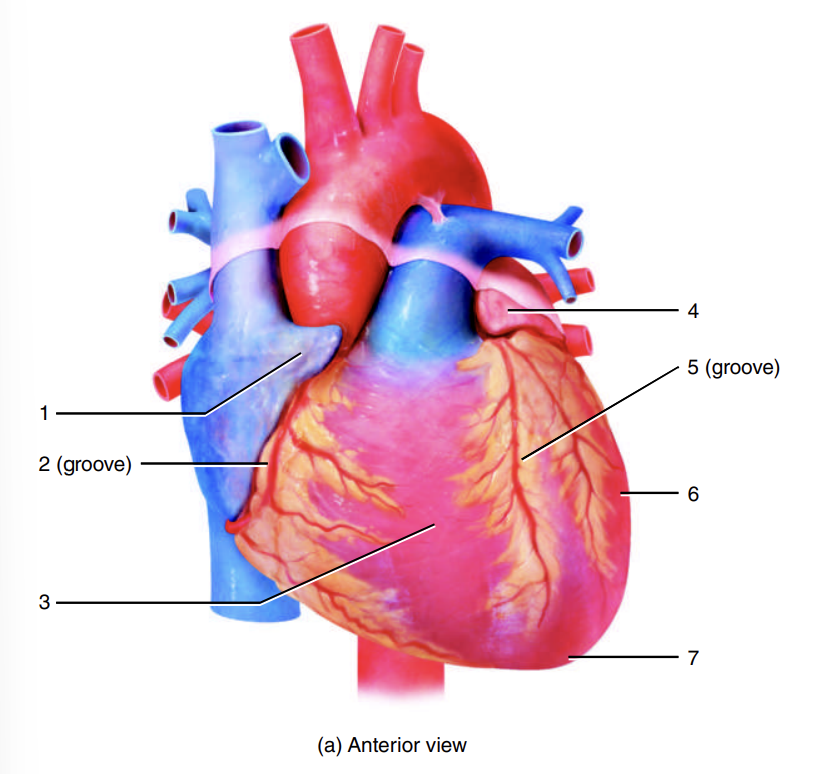
auricle of left atrium
4
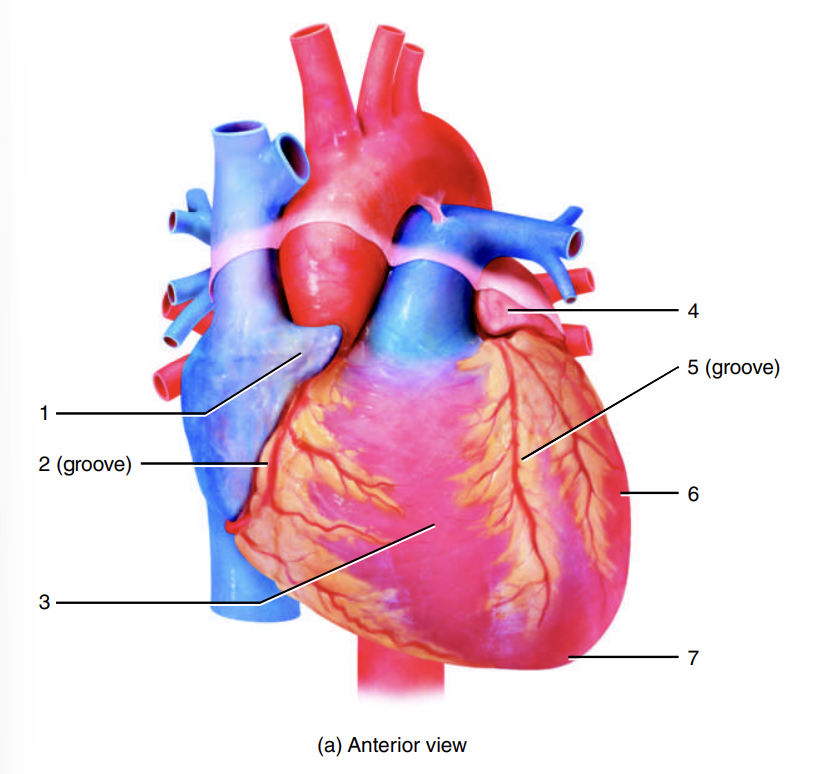
anterior interventricular sulcus
5
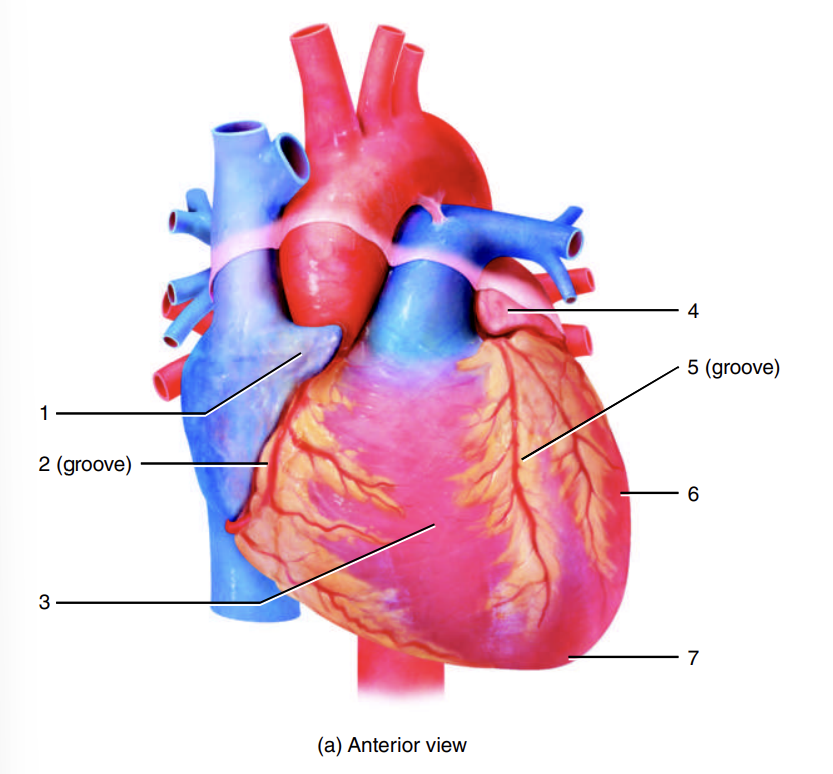
left ventricle
6
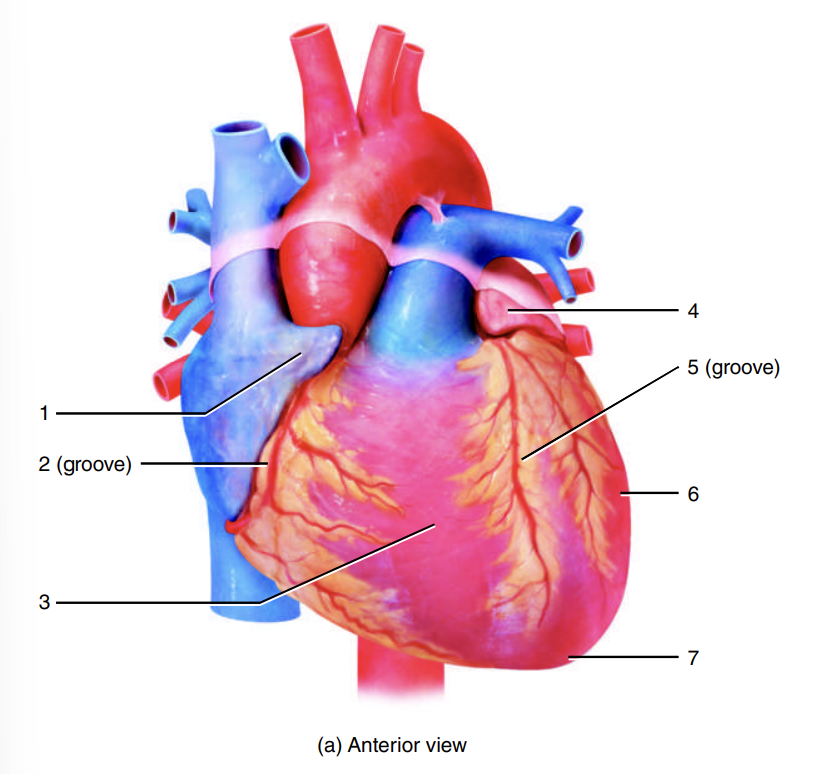
apex of heart
7
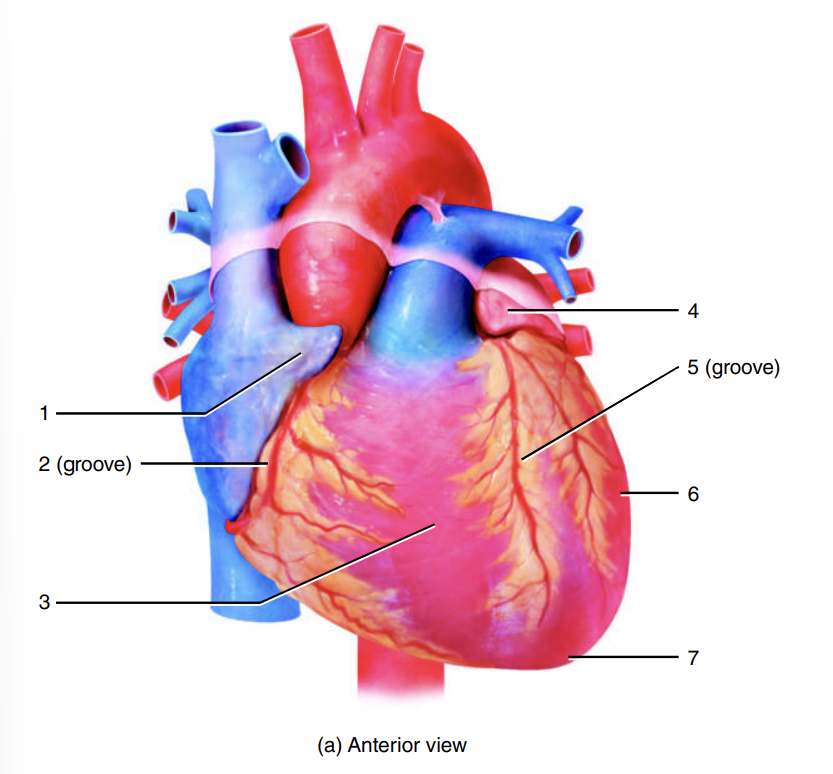
left atrium
8
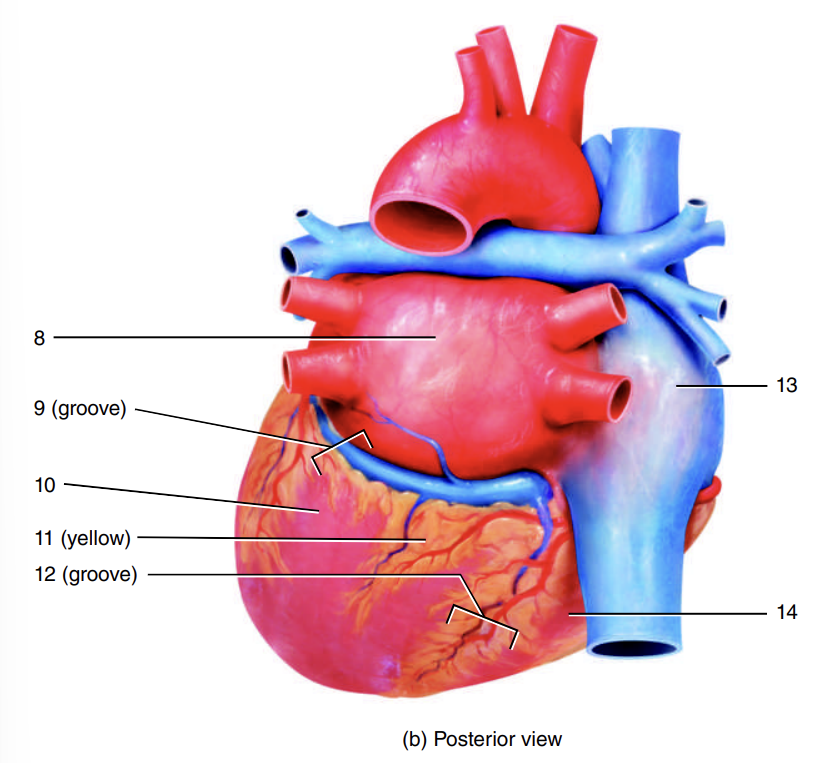
coronary sulcus
9
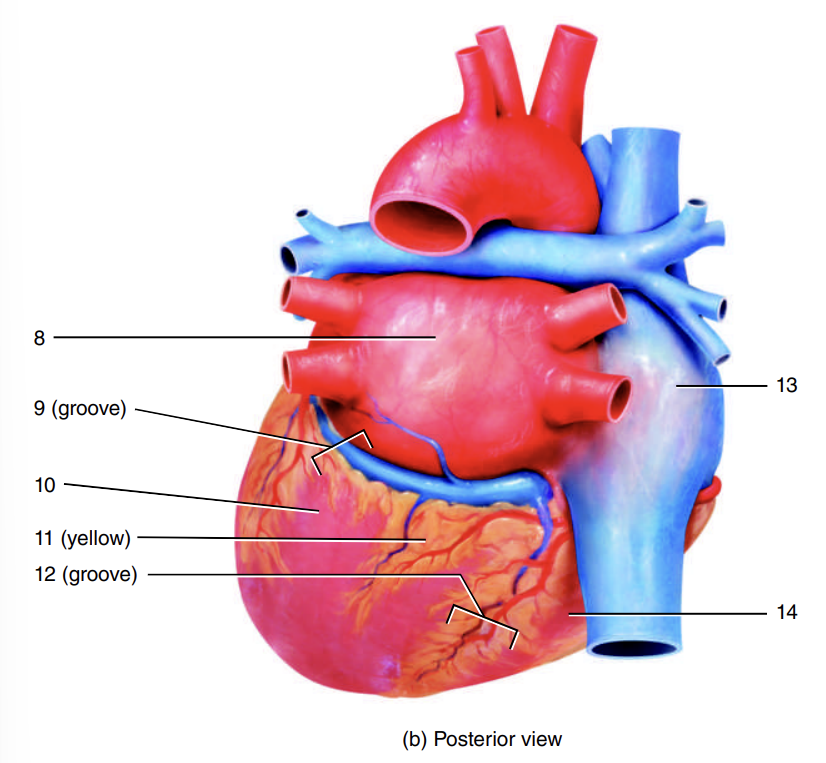
left ventricle
10
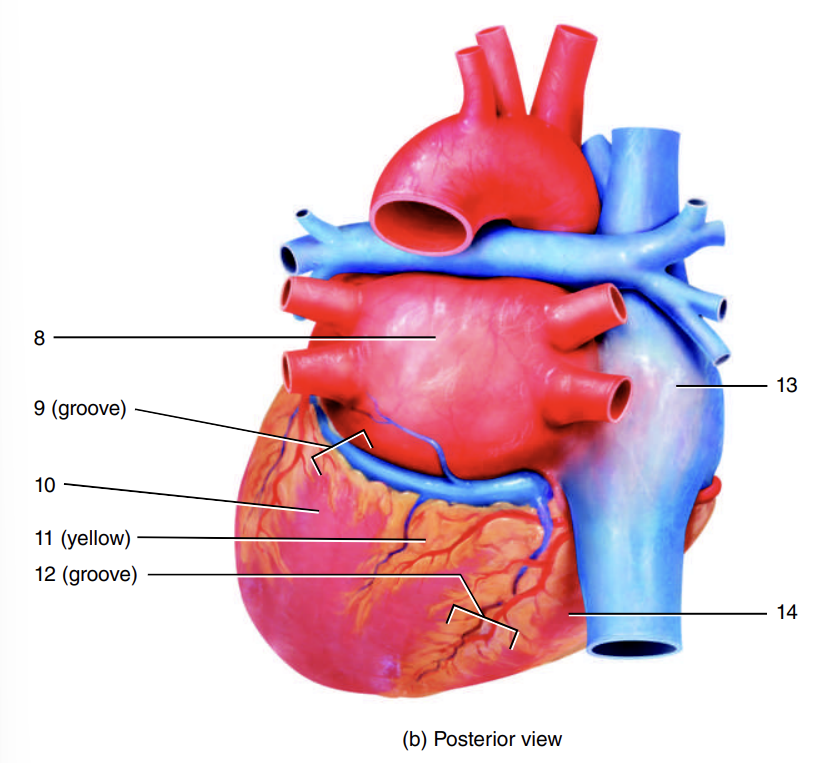
adipose tissue
11
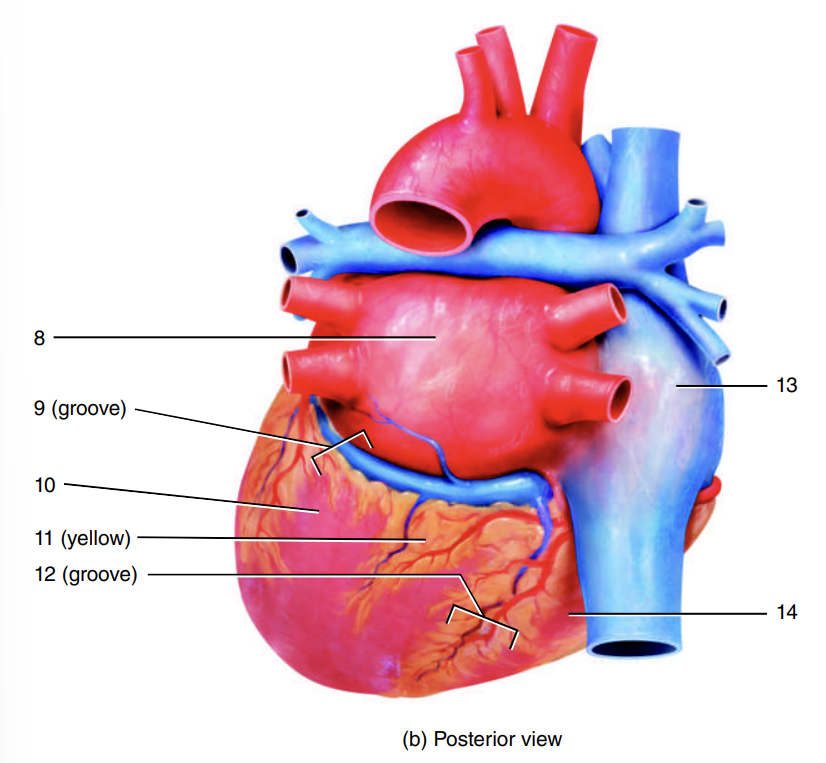
posterior interventricular sulcus
12
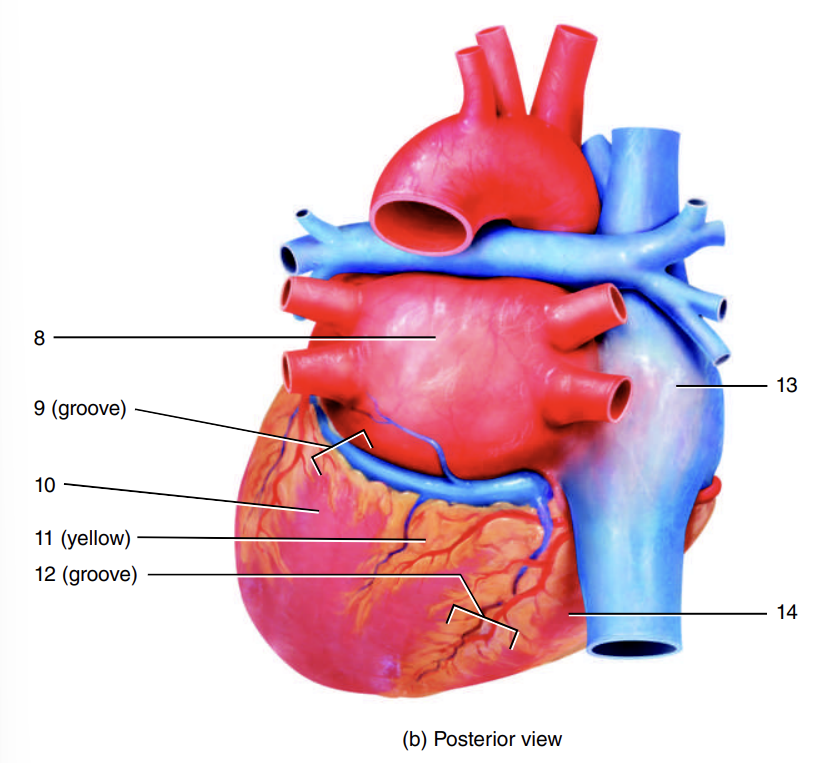
right atrium
13
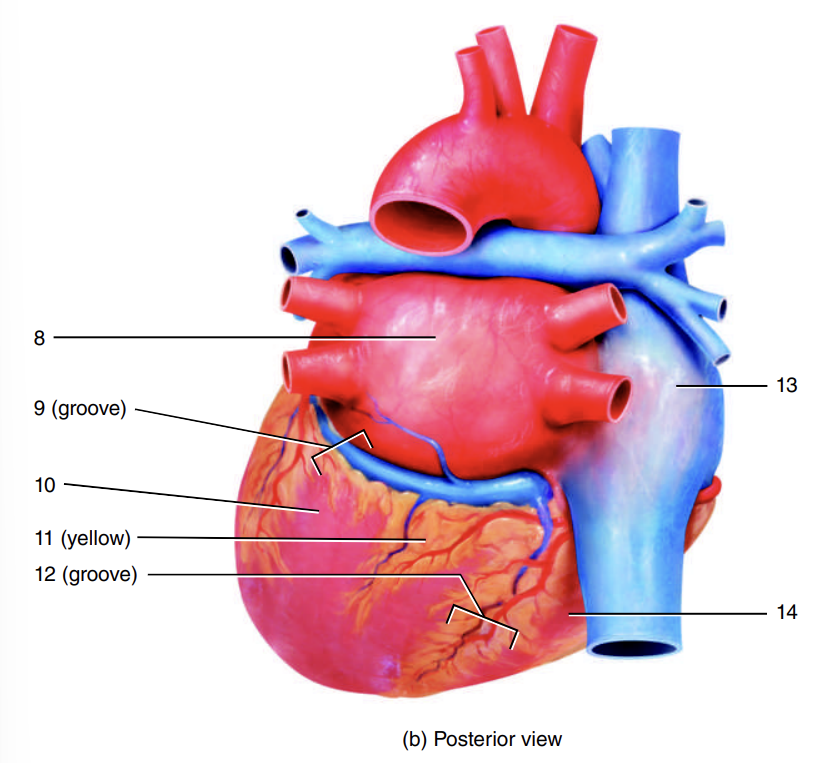
right ventricle
14
great vessels of the heart
either return blood to the atria (veins) or carry blood away from the ventricles (arteries)
superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, coronary sinus
return oxygen-poor blood to the right atrium
superior vena cava
returns blood from the head, neck, and ars
inferior vena cava
returns blood from the body inferior to the heart
coronary sinus
a smaller vein that returns blood from the coronary circulation
blood
leaves the right atrium to enter the right ventricle
pulmonary trunk
where a contraction of the right ventricle pumps blood
large artery
divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries
right and left pulmonary arteries
carry oxygen-poor blood to the lungs, where it then gets oxygenated
oxygen-rich blood
returns to the left atrium through two right and two pulmonary arteries
large aorta
distributes blood to the systemic circulation
fetal heart
contains a short, temporary vascular channel
ductus arteriosus
connects the pulmonary trunk and the aorta
placenta of the mother
where oxygen is obtained in fetal life
ligamentum arteriosum
what the ductus arteriosus changes into
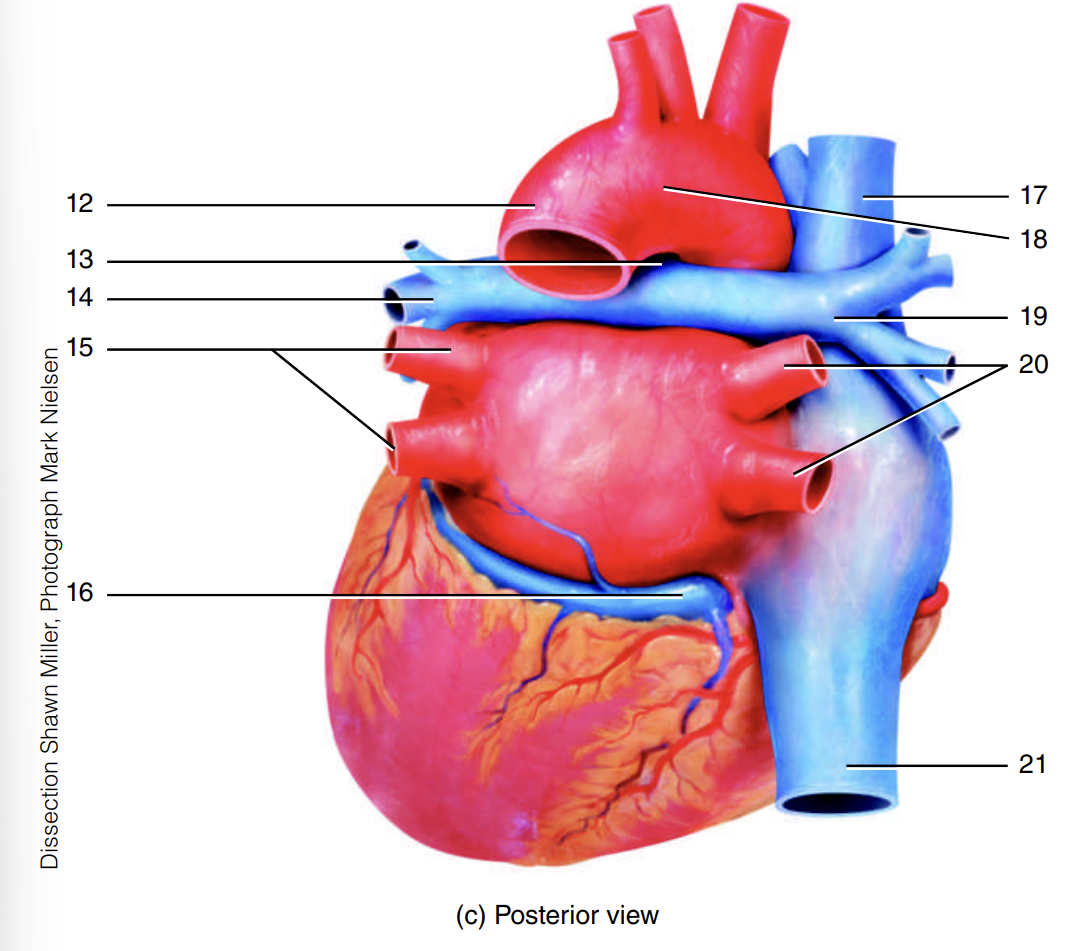
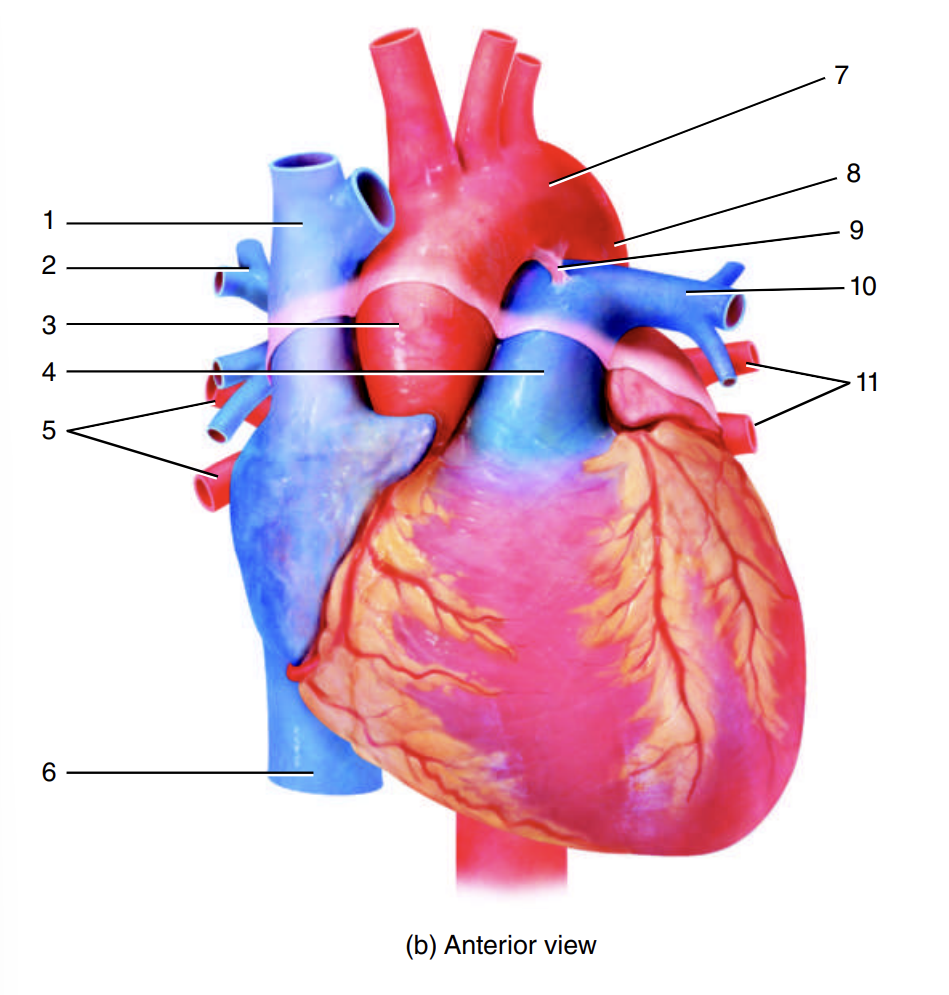
superior vena cava
1
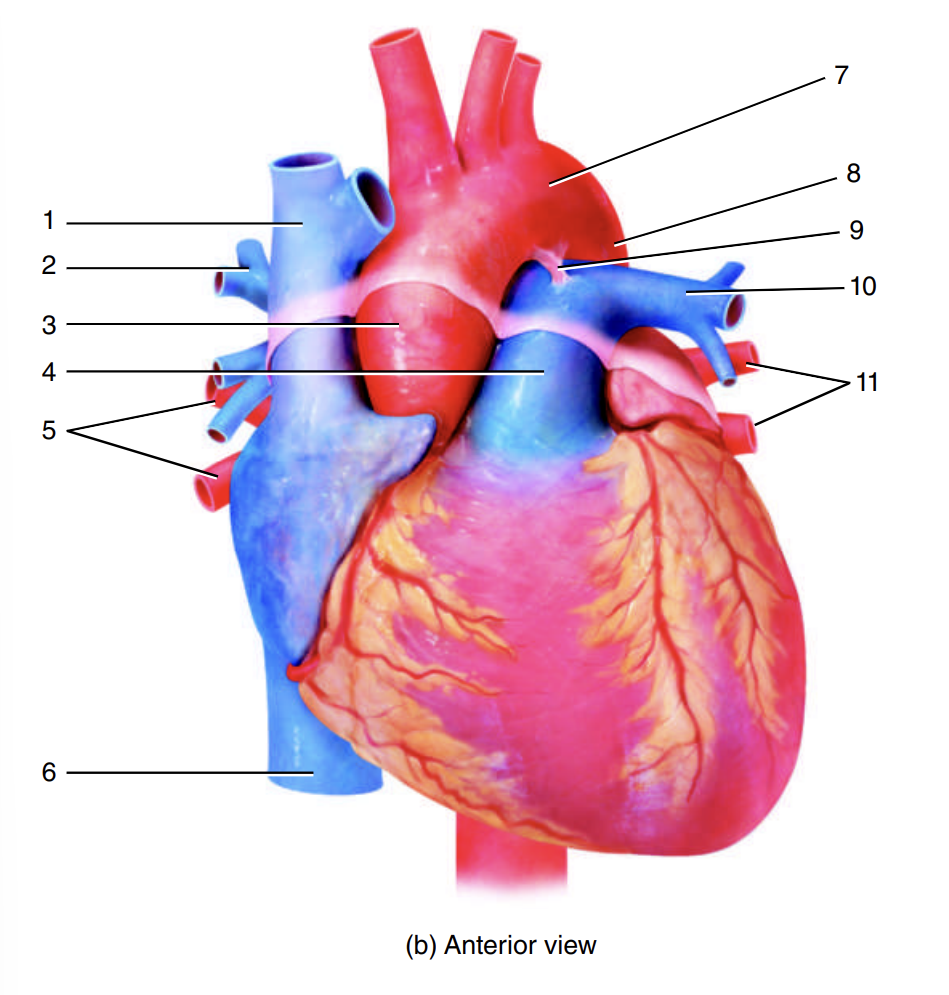
right pulmonary artery
2
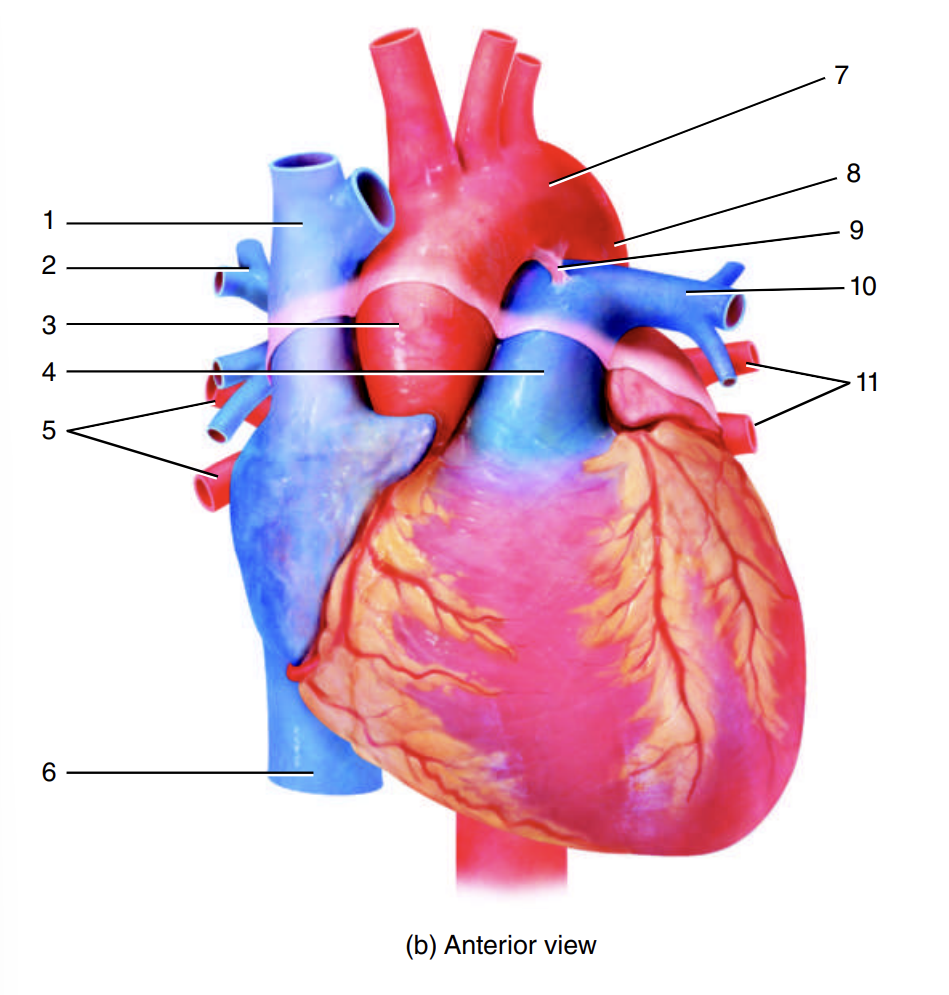
ascending aorta
3
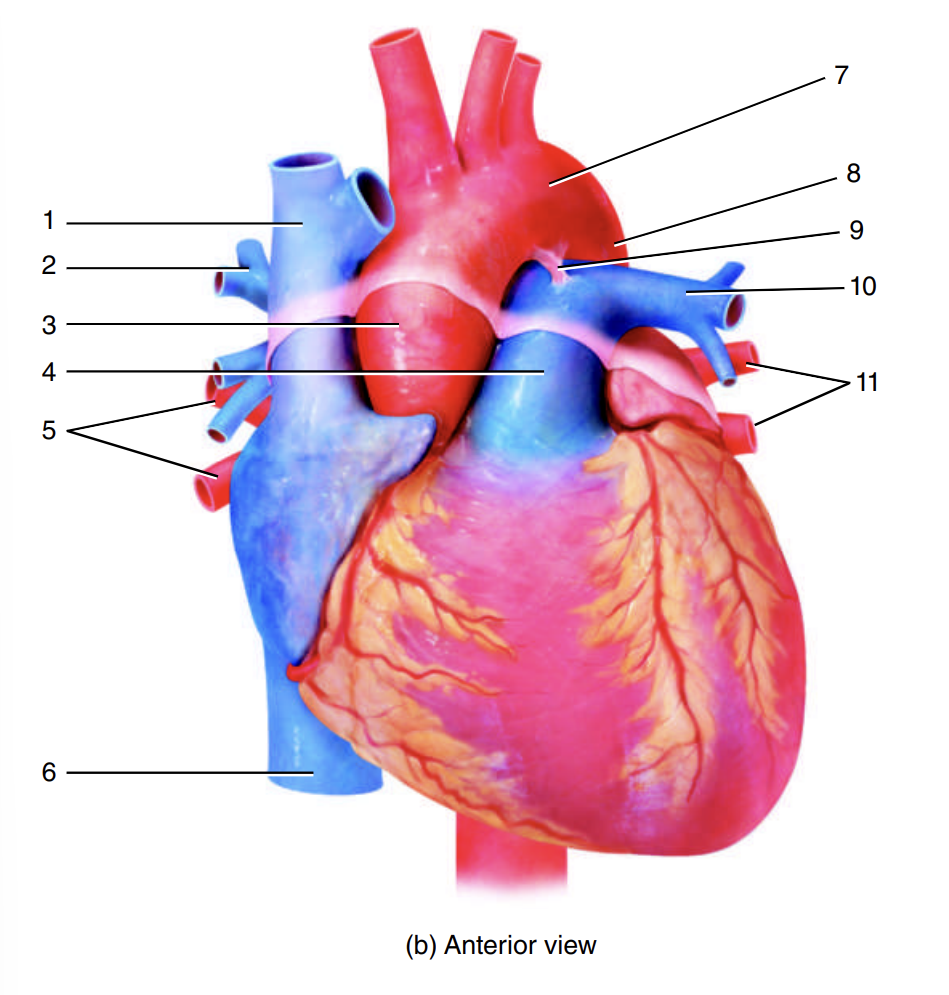
pulmonary trunk
4
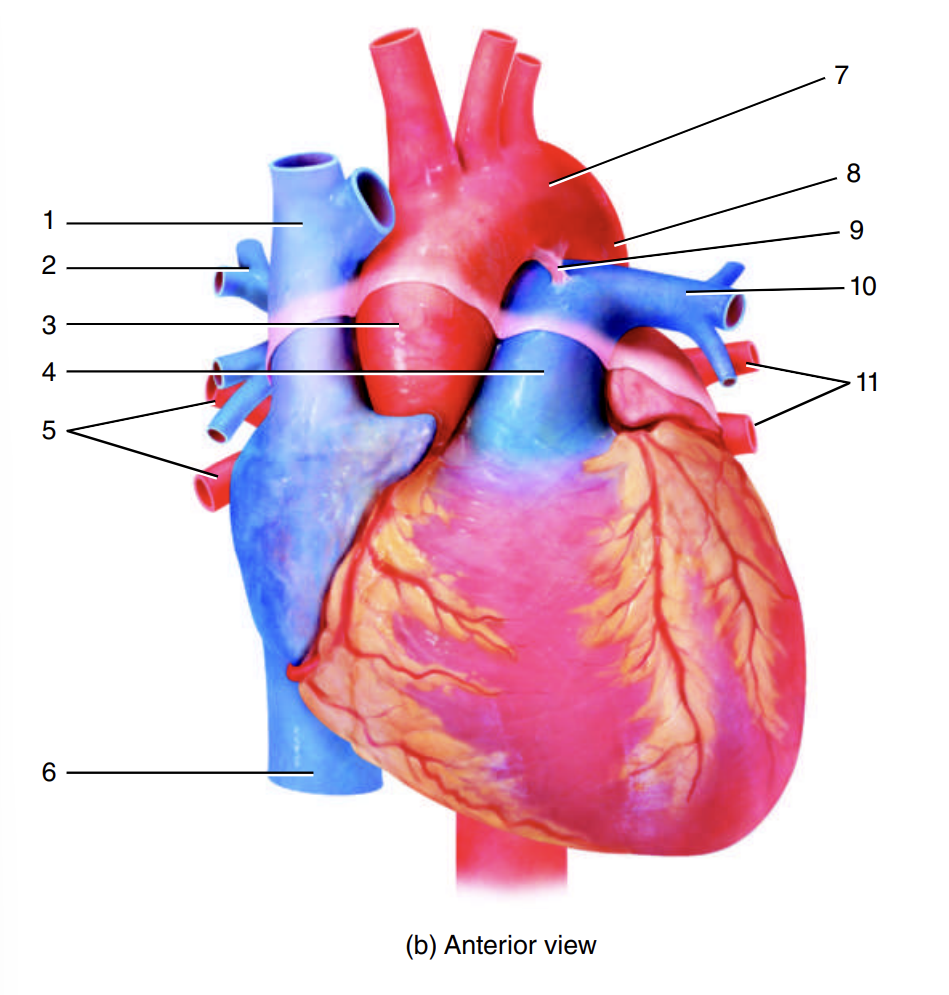
right pulmonary veins
5
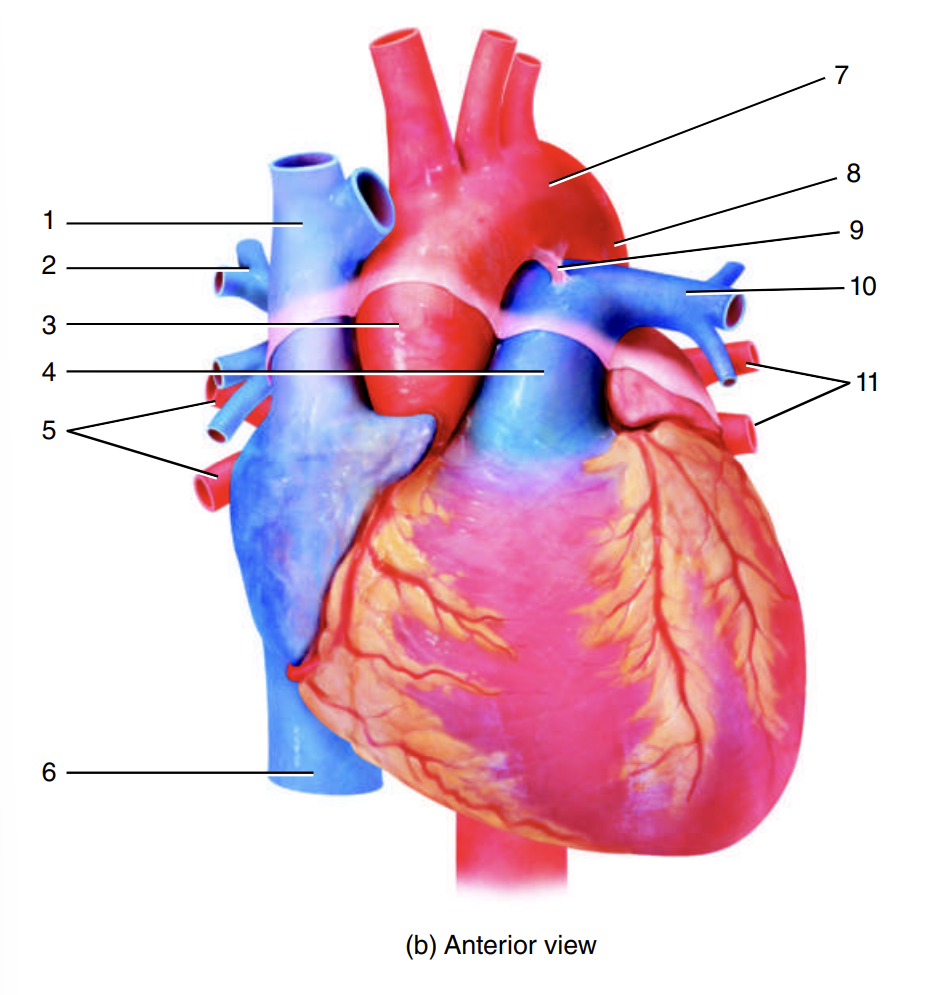
inferior vena cava
6
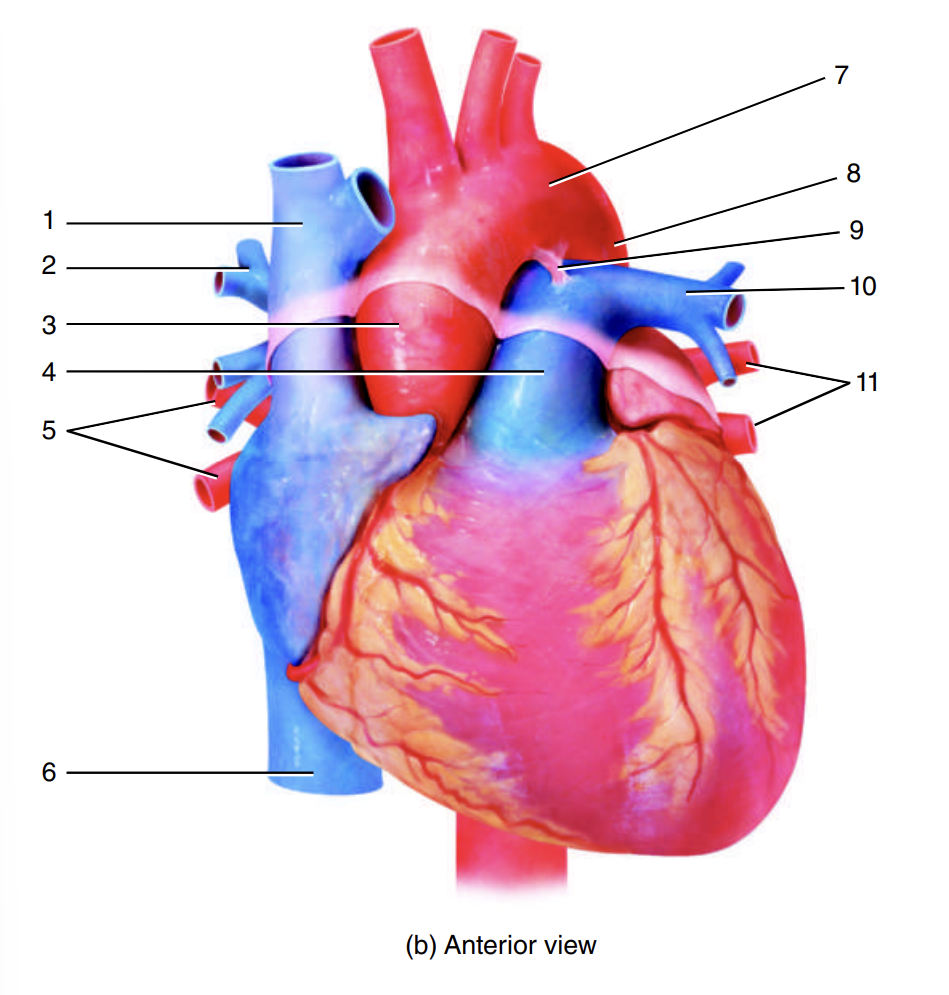
arch of the aorta
7
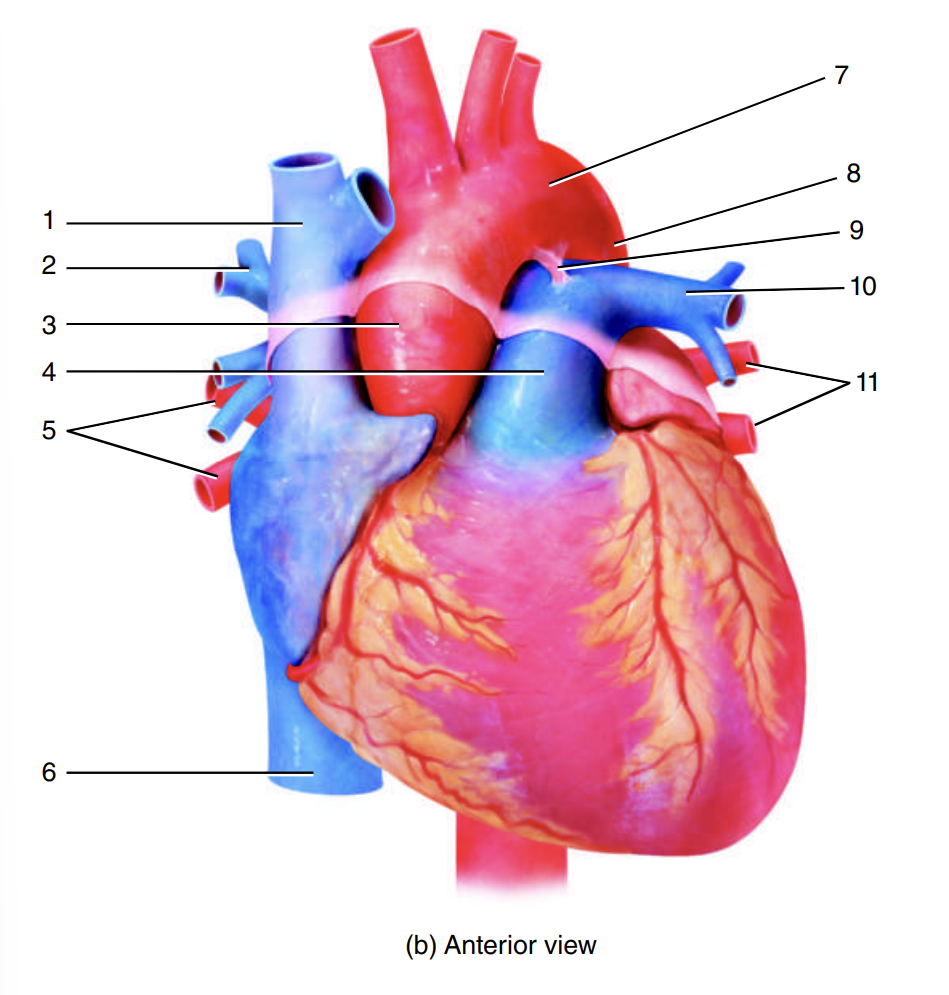
descending aorta
8
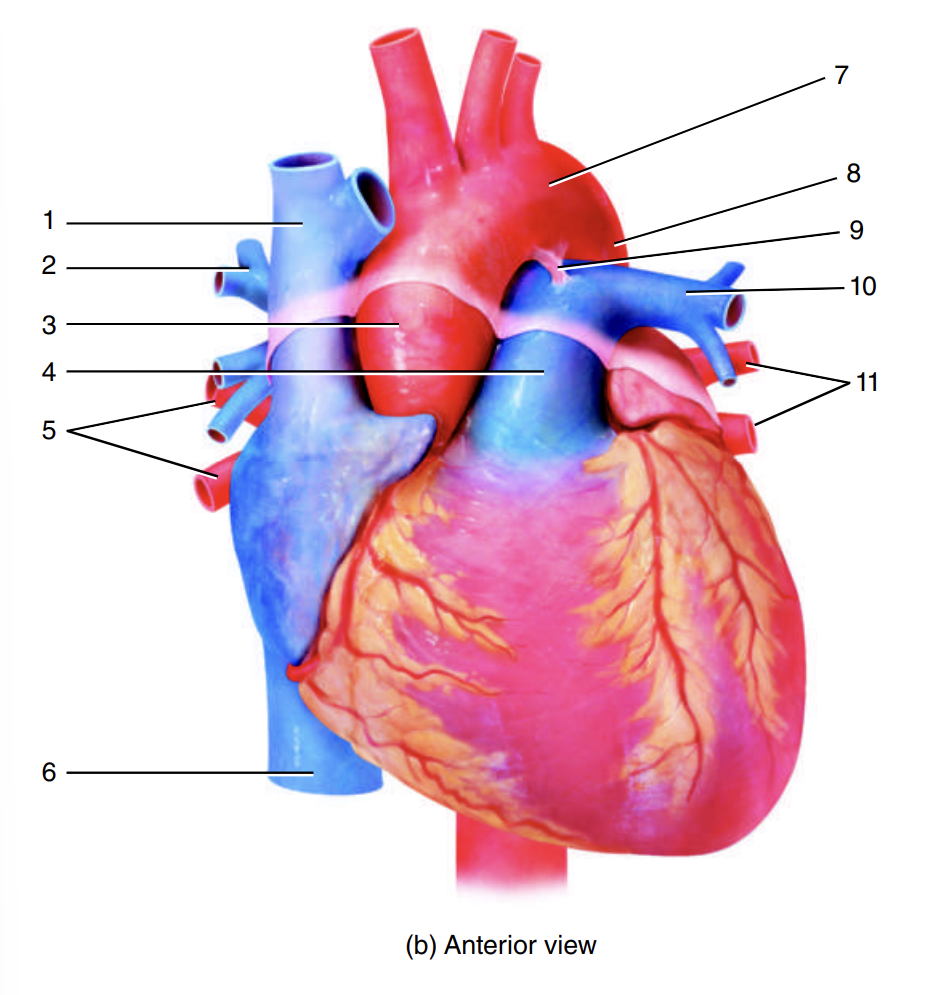
ligamentum arteriosum
9
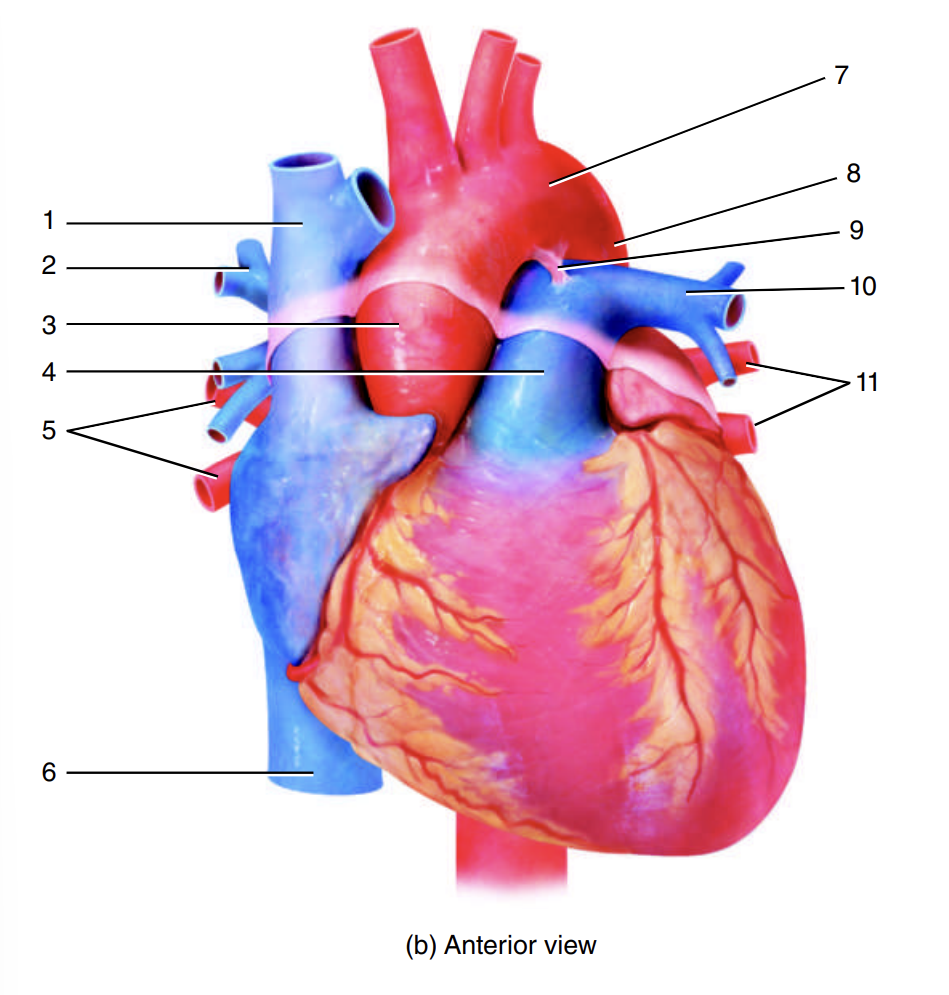
left pulmonary artery
10
left pulmonary veins
11
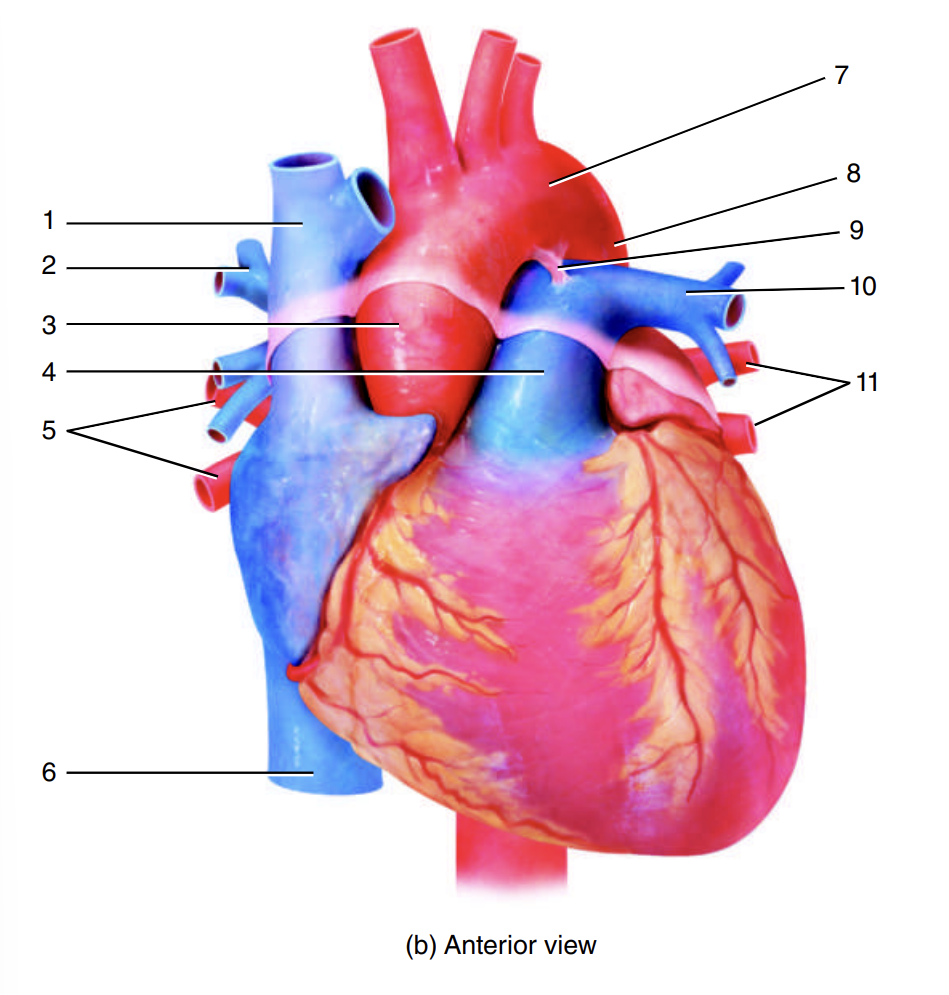
descending aorta
12
ligamentum arteriosum
13
left pulmonary artery
14
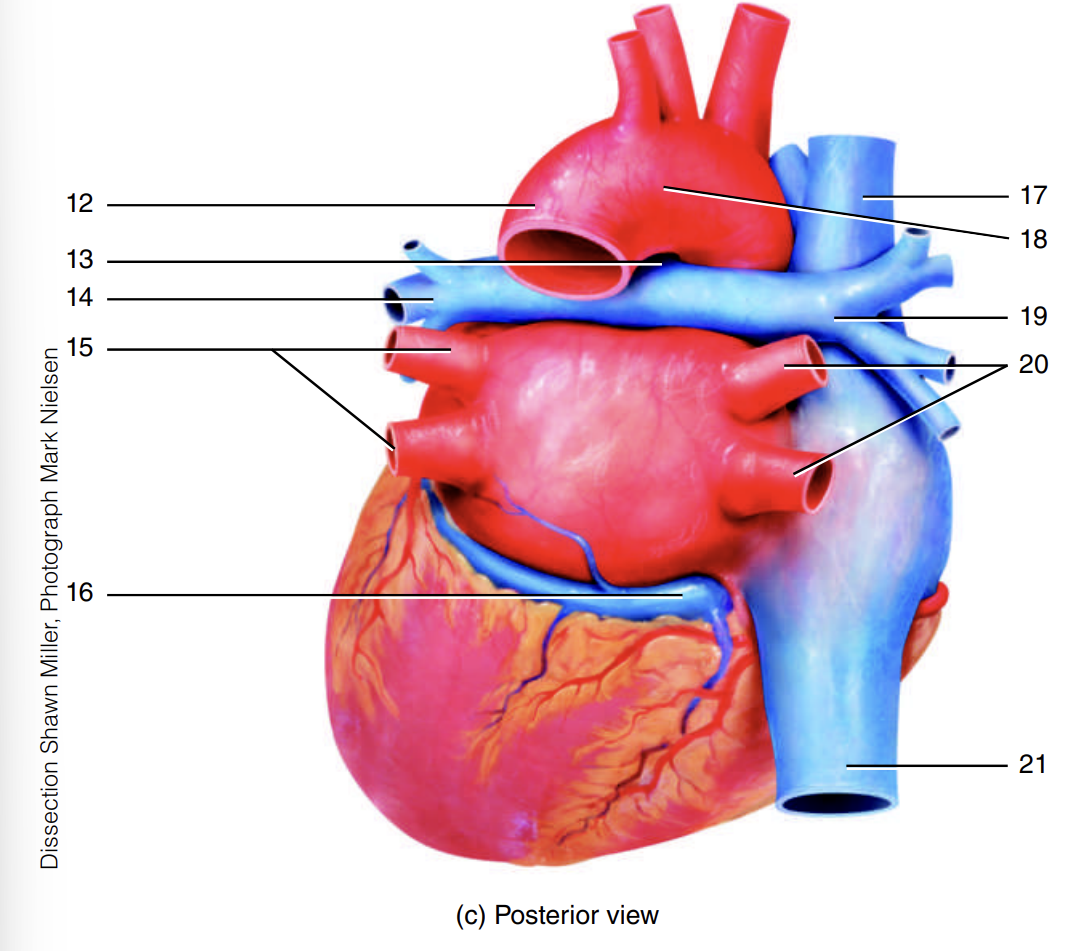
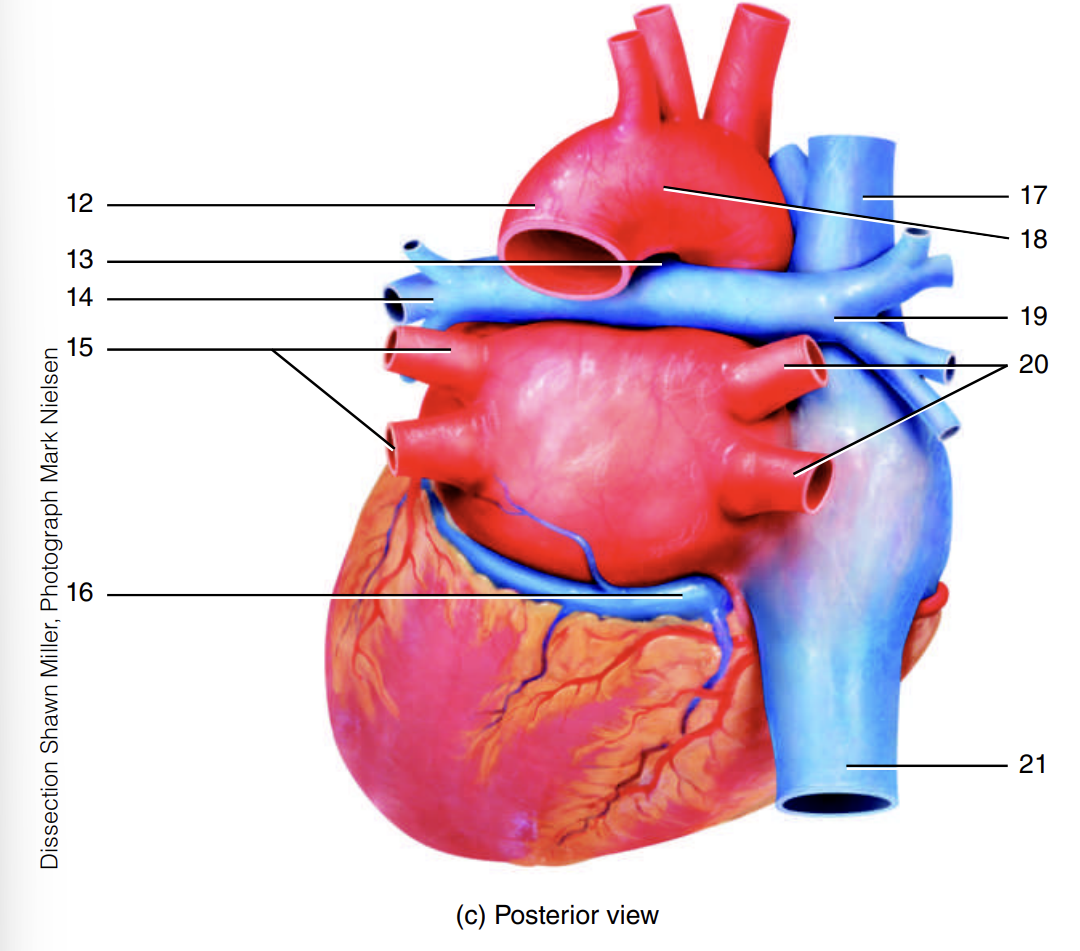
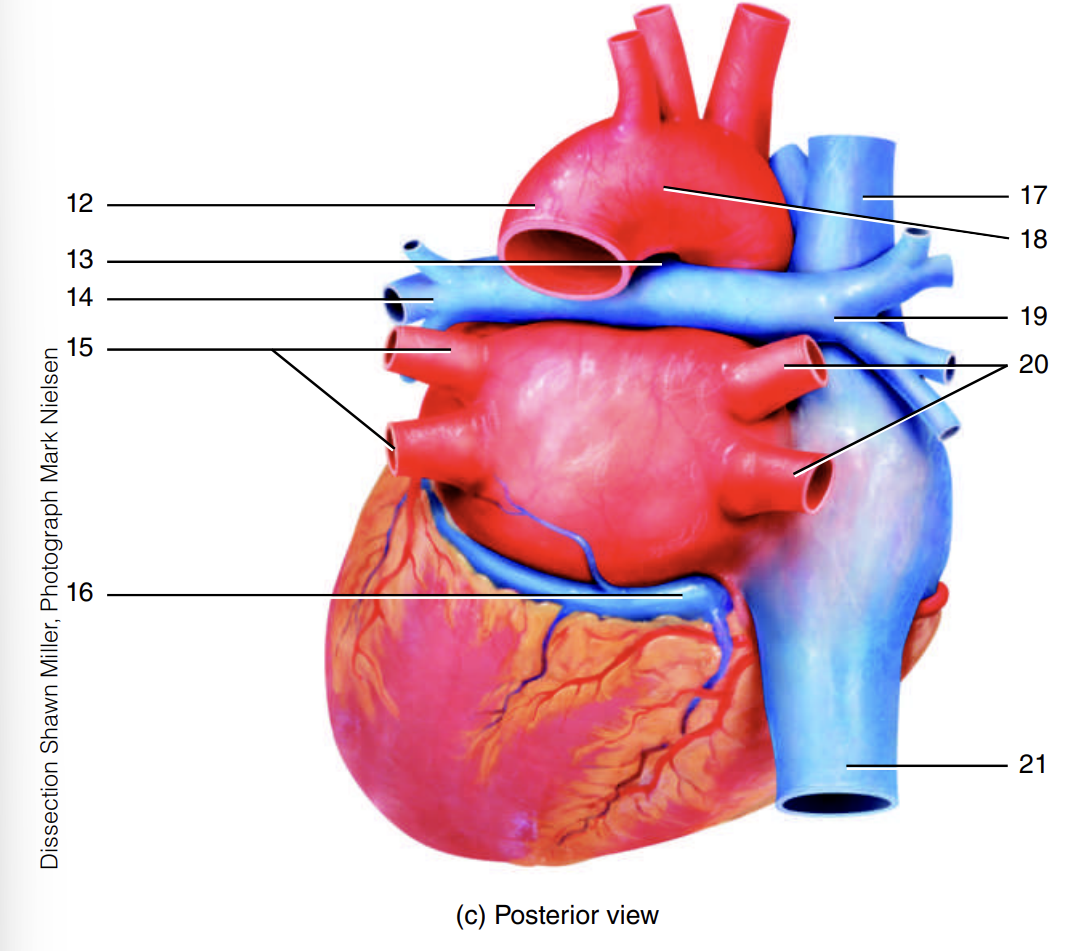
left pulmonary veins
15
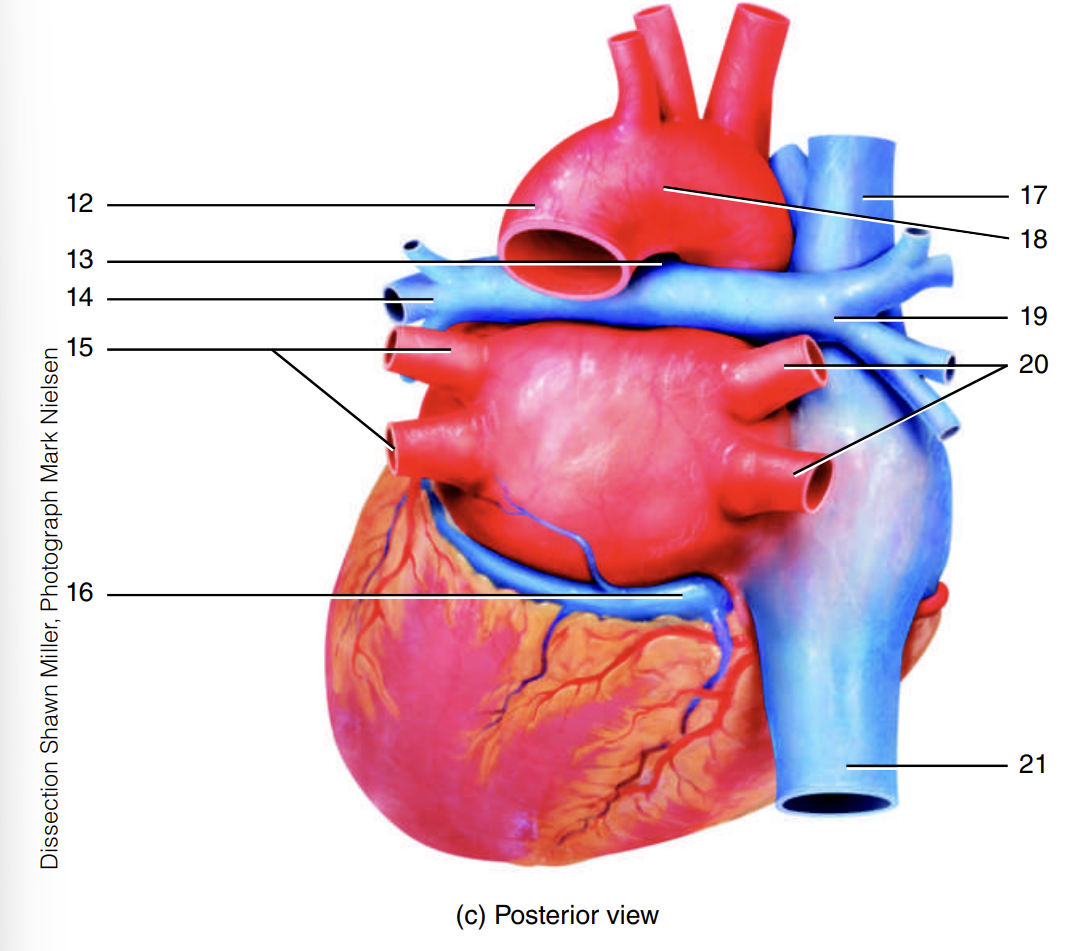
coronary sinus
16
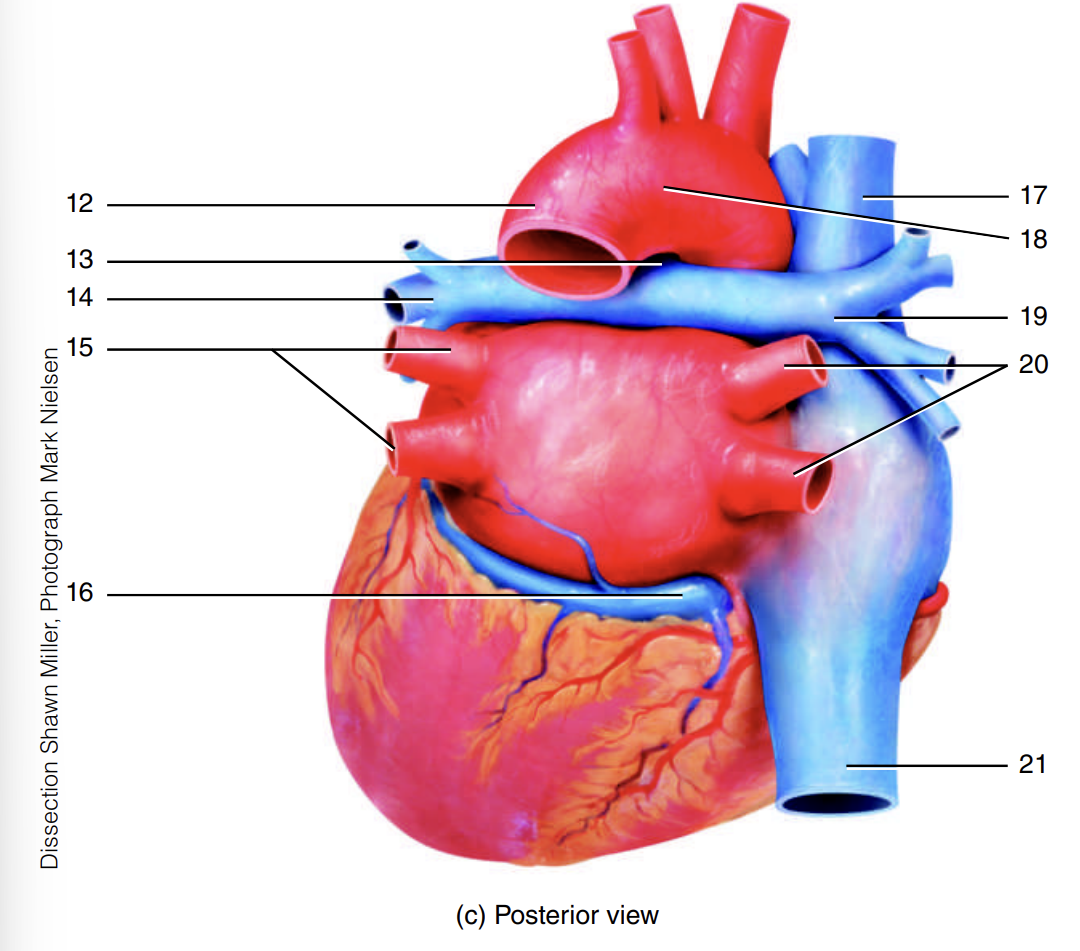
superior vena cava
17
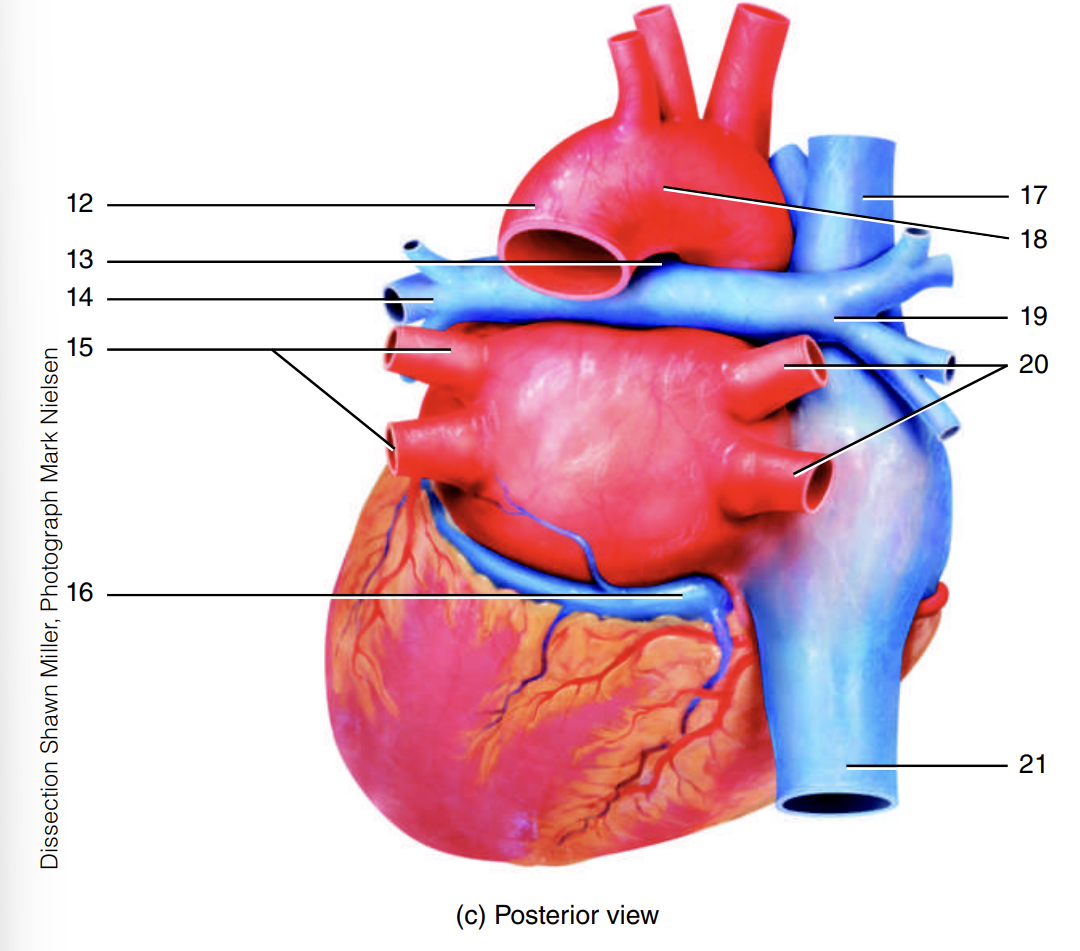
arch of the aorta
18
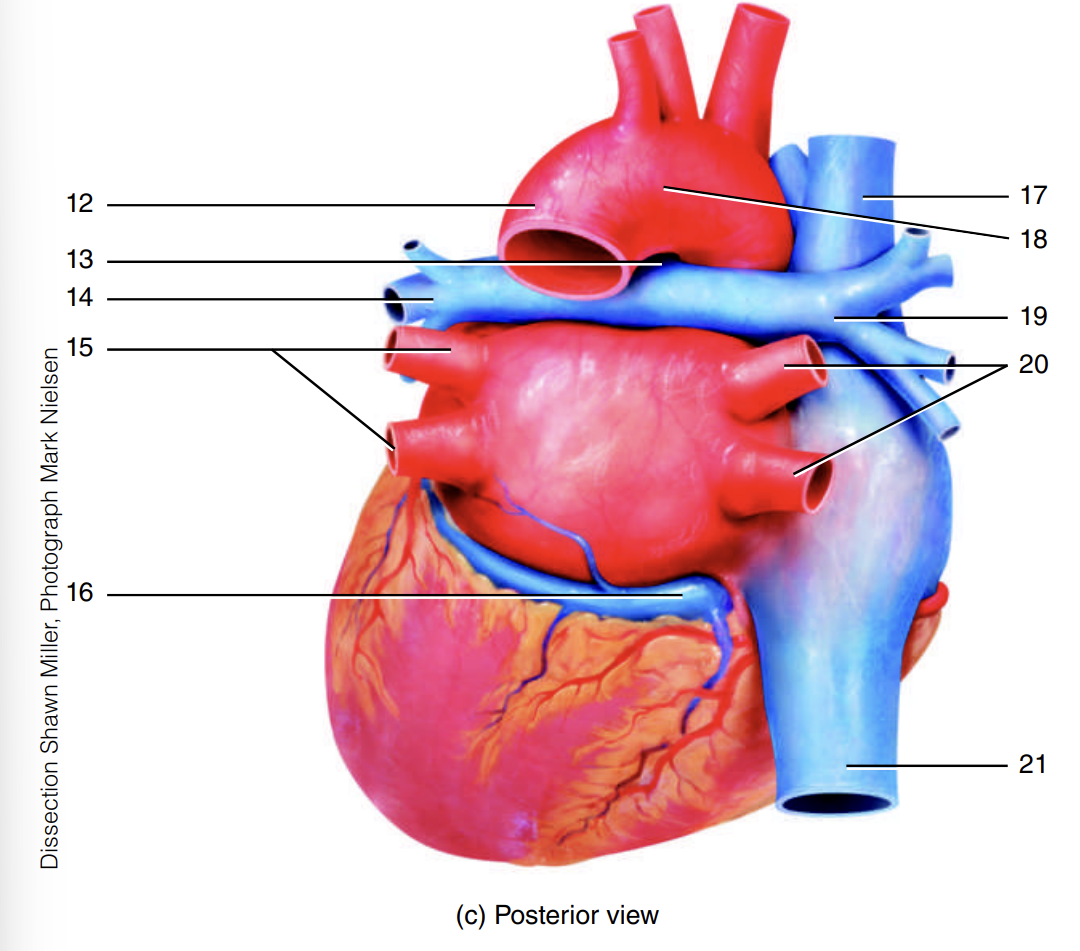
right pulmonary artery
19
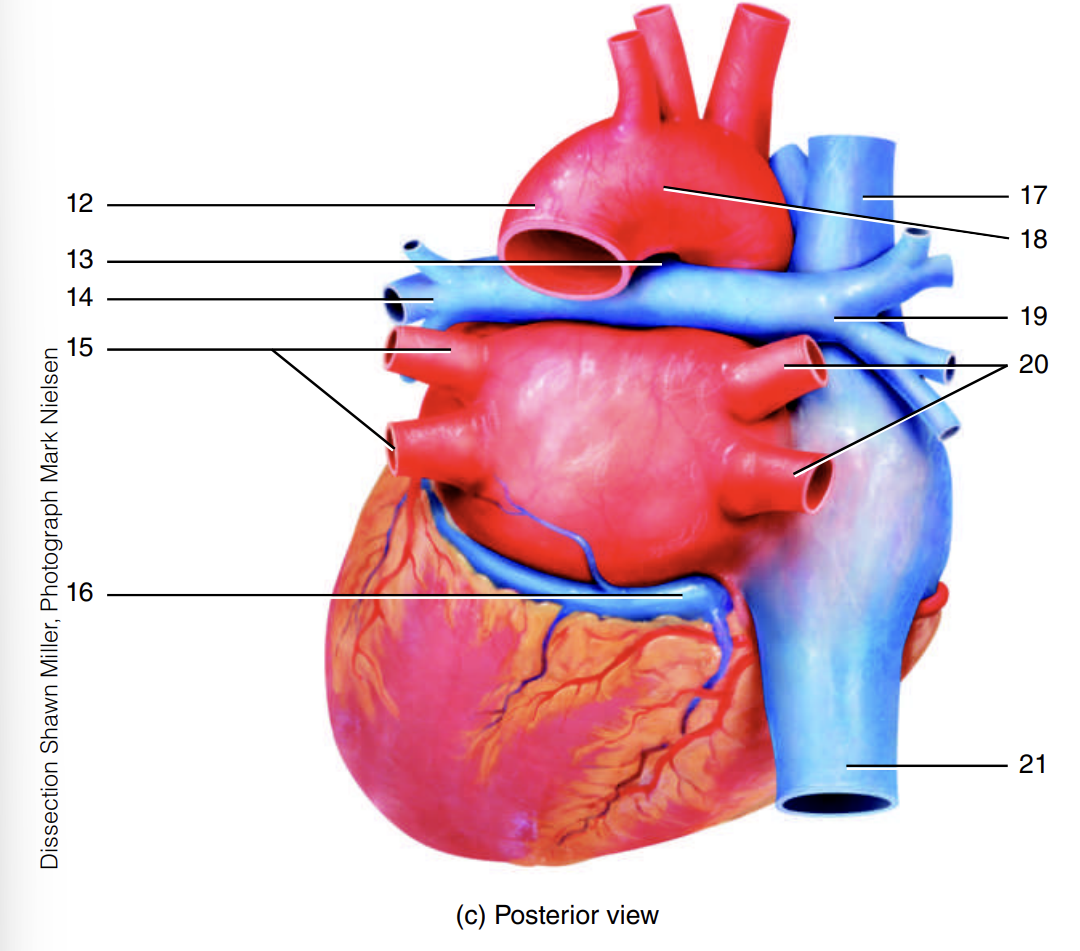
right pulmonary veins
20
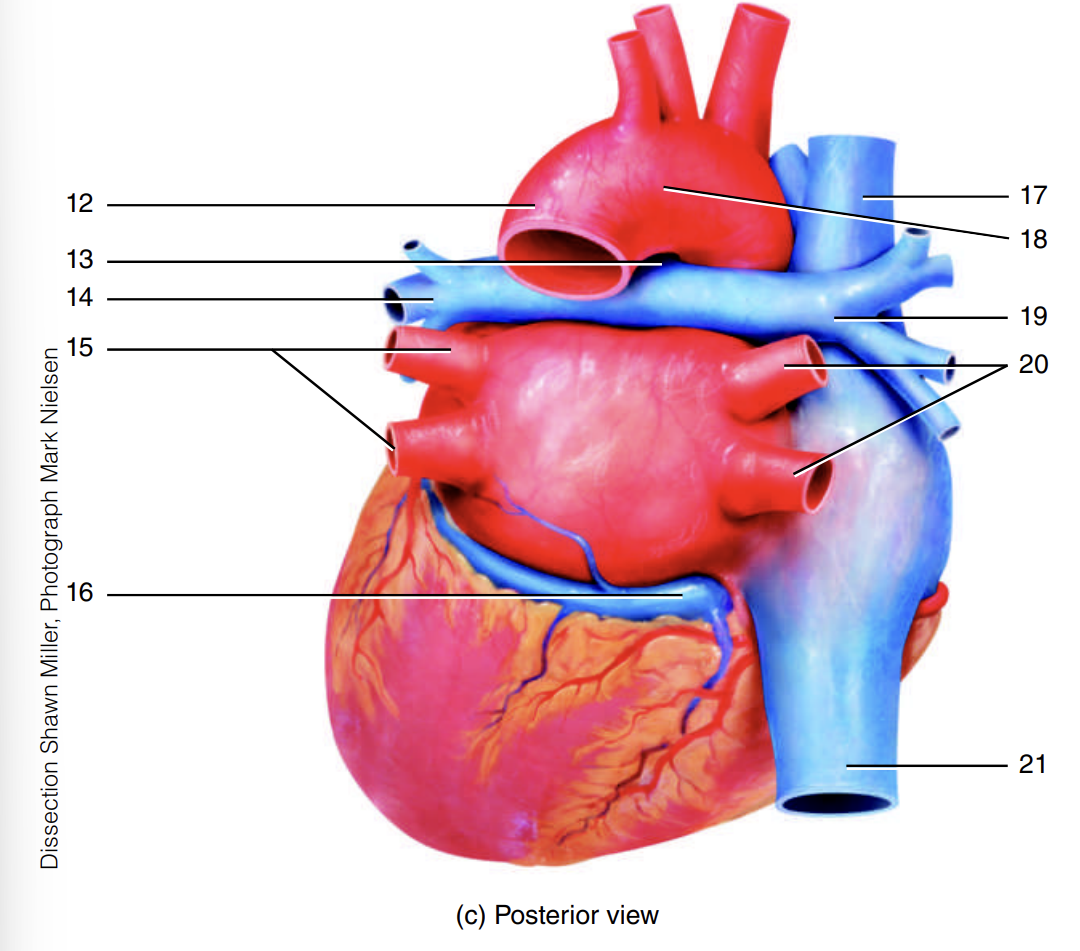
inferior vena cava
21