Extension 1 maths
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Polynomials
SKIP
What is a polynomial
A polynomial is a mathematical expression in which contains variables and numbers, where variables are raised to a whole number power and the terms are added, subtracted or multiplied
Not polynomials examples
Examples of non polynomials are
negative powers: 1/x
fractional powers
logs
powers of x
What is a leading term
A leading term is the highest number and power
Degrees of the sum and difference
If P(x) and Q(x) are polynomials with degrees n and m:
Case 1:n ≠ m: when you add or subtract, the degree stays the same
Case 2: n = m: the degree drops or disappears if they cancel
Identically equal polynomials
Polynomials are identically equal when P(x) and Q(x) are the same for all values of x
P(x) ≡ Q(x)
Tip when the polynomials are Identically equal
for questions asking for a, b c you can add polynomials by equating coeffcients
When you derive a polynomial is it even or odd? Why?
It becomes odd as P(x) is even in which an even polynomial has only even powers so when it is derived it becomes odd as every term in p′(x) has odd power ⇒ p′(x) is odd.
( works other way around if P(x) is odd)
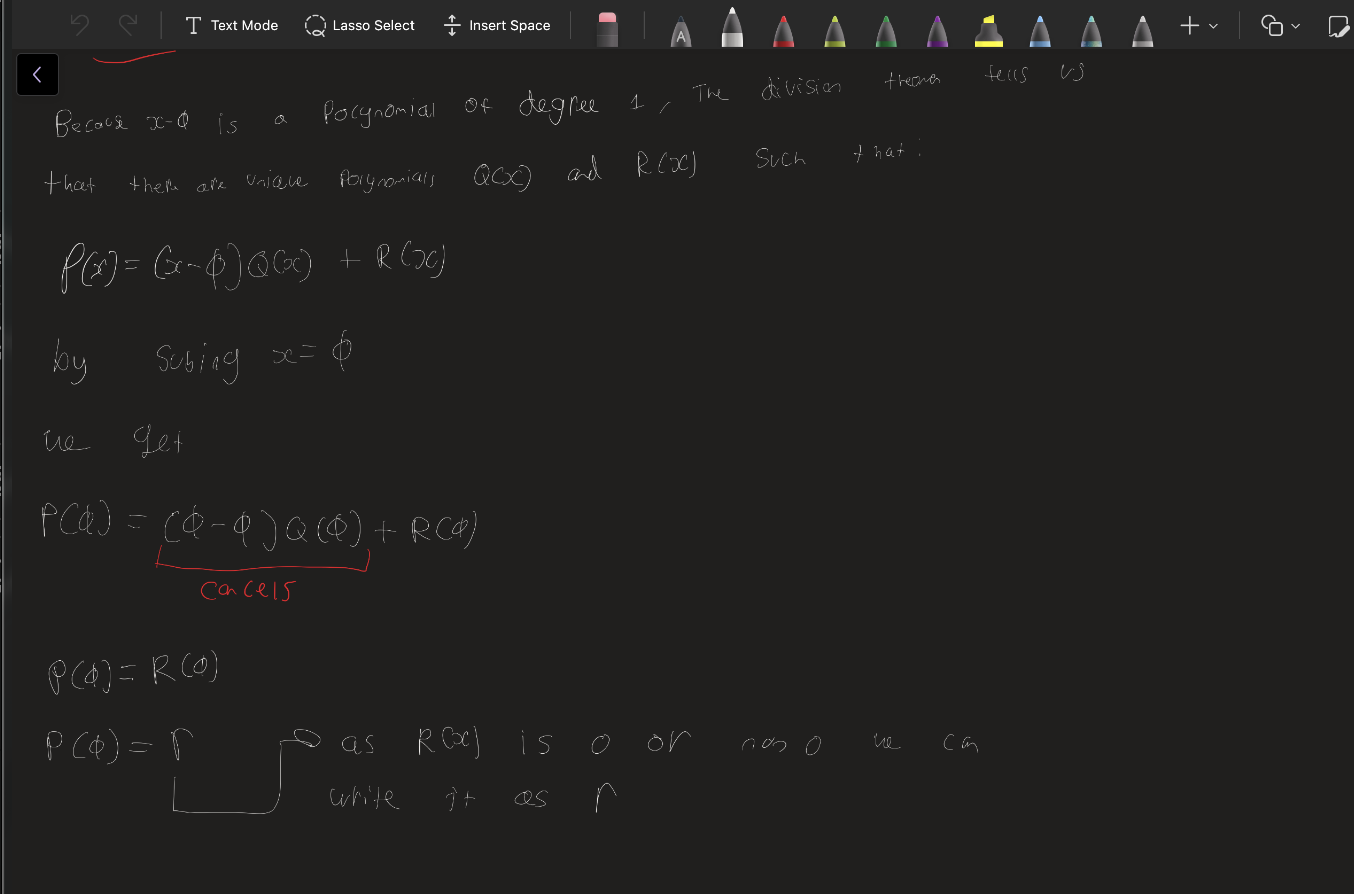
Division of polynomial formula
P(x)= D(x) ⋅ Q(x) + R(x)
Rational Form
P(x)/D(x)= Q(x)+ R(x)/D(x)
Tips when finding a and b to make it exactly divisible by x
Make set a and b as the remainder and equate coefficient so:
Set remainder = 0.
Equate coefficients of like powers.
Solve for a, b.
Remainder Theory
If you divide a polynomial by (x − Φ), the remainder is the value of the polynomial at x = Φ.
Suppose P(x) is a Polynomial and Φ is a constant
then R(x)= x-Φ = P(Φ)
Why does this work
What is the Factor Theorem
If a polynomial f(x) is divided by (x − a):
If the remainder is 0, then (x − a) is a factor of the polynomial.
If the remainder is not 0, then (x − a) is not a factor.
Proof for this theorem
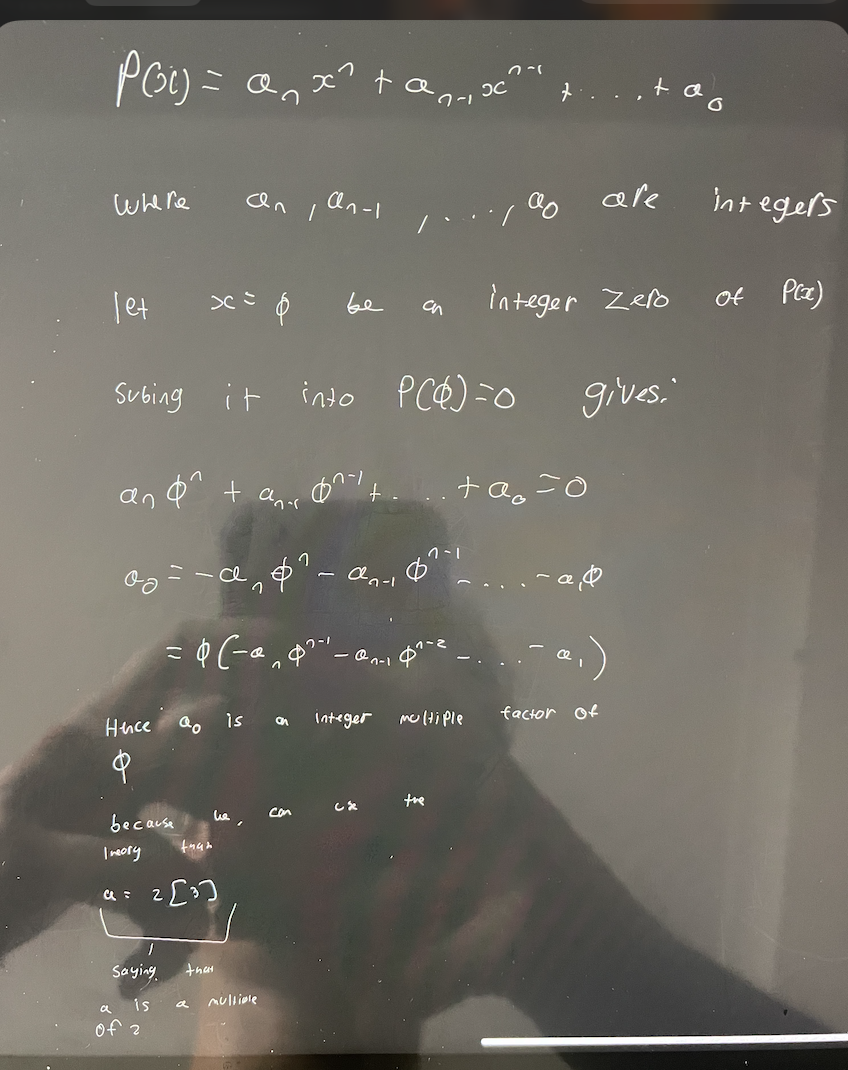
What are Distinct Zeroes
Distinct zeroes of a polynomial are the different values of x that make the polynomial equal to zero, counted only once each.
Suppose that Φ1,Φ2……Φn are zeroes of the polynomial P(X)
Then: (x-Φ1),(x-Φ2)…..(x-Φn) are factors of P(X)
The proof for this
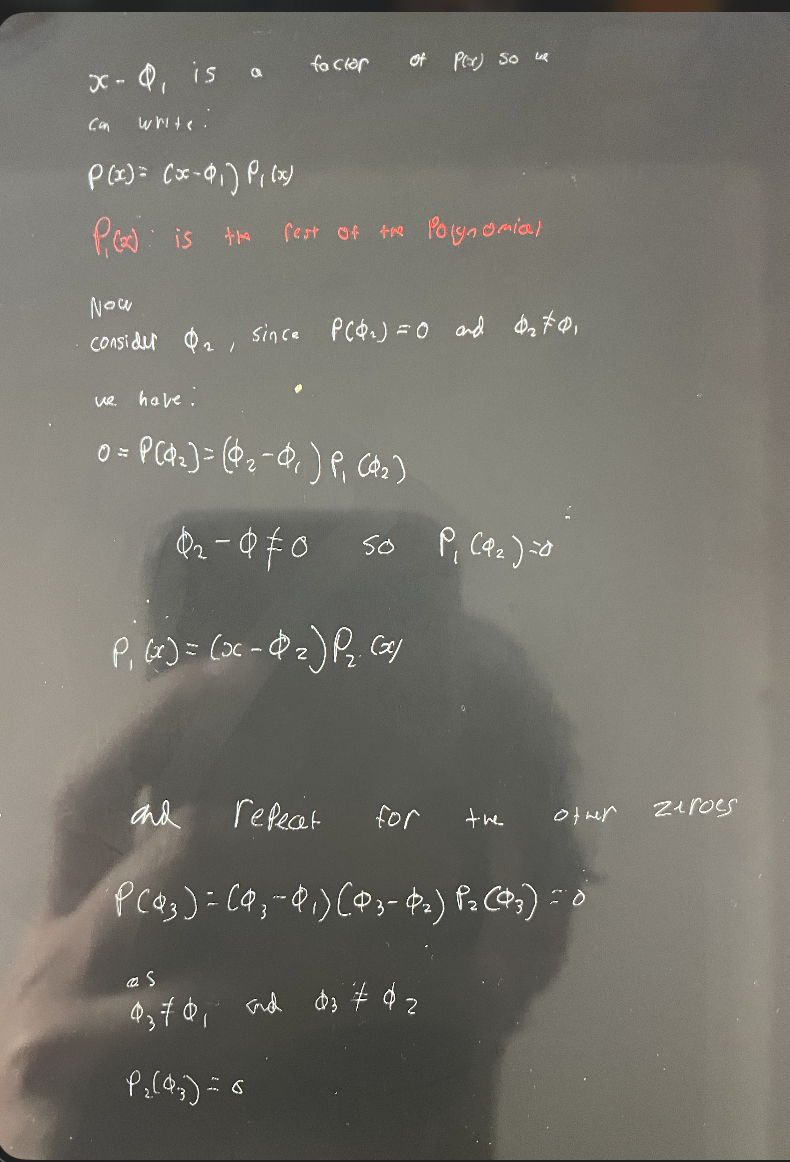
The vanishing Condition
Supposed P(x) has degree at most n and it is a zero at n+1 then P(X)≡ 0
Tip for this
If it says it has 3 zeroes sub in 0 to find a,b and c
if two polynomials have degrees m and n, where m>n then the maximum number of intersections is m
The reason why a cubic with 3 distinct zeroes must have 2 stationary points are because when we derive the polynomial it’ll give a quadratic hence having only 2 real roots.
Multiple roots
if Φ is a multiple root of P(x), then the graph y=P(x) has a stationary point at x=Φ
Another rule for multiple root is
When we have the polynomial in the form of (x-Φ)mQ(x), where Q(x) is not divisible by x-Φ from the factor theorem that Q(x) is only divisible by x-Φ when Q(Φ)=0
Behaviour at simple and mulitiple zeroes 1.
if x=Φ has even multiplicity then the curve is tangent to the x axis at x=Φ and does not cross the x axis so the point (Φ,0) is a turning point
if x=Φ has odd multiplicity at least 3 then the curve is tangent to the x axis at x=Φ but crosses the x axis at (Φ,0) making it a horizontal inflection
3.
if x=Φ is a simple zero then the curve croesses the x axis at x=Φ in which theres no stationary points there.
formula for absolute value of alpha + beta
sqr (alpha + beta)²
Further functions (nothing)
how to graph reciprocals
we find values of x when y = + - 1
then we find asyomtotes
then we graph
How to find maximum value of reciprocal
f’(x)
equal to zero
solve for x
imput to f(x)
how to do sums and products of function.
just add or times the values together but always keep checking where itll be headed as if f(x) is below G(x) when x=n then itll make it negative
How to sketch absolute value of y = f(x)
delete everything in the below x axis then replace it by duplicating it on the other side
everything above the x axis stays the same
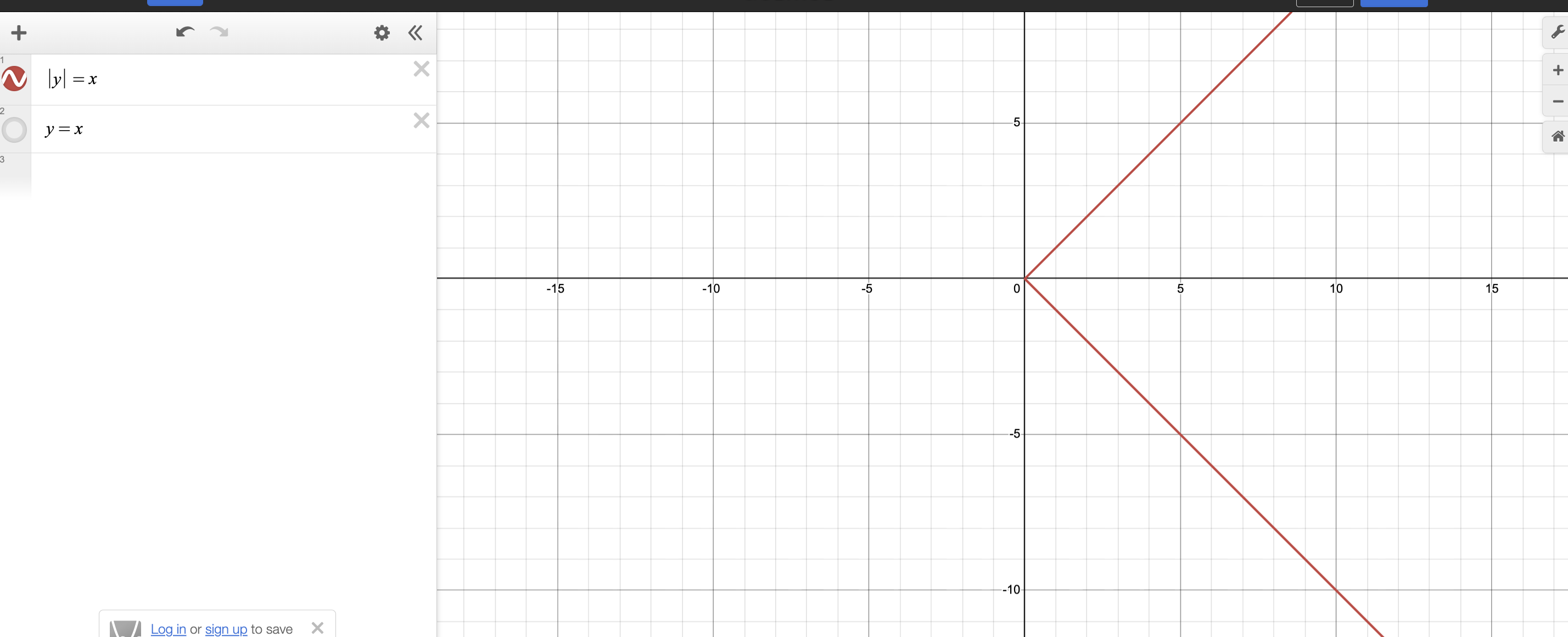
how to graph y= f( absolute value of x)
delete everything from the left and keep everyting to the right. then duplicate it to the left
y= absolute value of f(x)
just move everything thats below the x axis up above it
Tips to draw square root graph
f(x) < 1 it’ll be higher
f(X) > 1 it’ll be lower
How does inverse functions work and what happens to the domain and range
we reverse x and y so the domain becomes the range and the range becomes the domain
how to do trig parametrics
isolate cos and sin
sub sin² +cos² =1
solve
Further trig (nothing)
formula for cos(A+ - B)
CosACosB - + SinASinB
Formula for SIn(A + - B)
SinaCosB + - CosASinB
Formula for Tan (A + - B)
TanA + - TanB / 1 - + (tanA)(TanB)
formula for sin2A
2sinACosA
formula for cos2A
cos²A - Sin²A
Formula for Tan2A
2TanA/ 1 - tan²A
What does “t” equal to in the t formula
t = tan x/2
sinx using t formula
2t / 1 + t²
cosx using t formula
1 - t² / 1+ t²
tanx using t formula
2t / 1 -t²
SinAsinB formula
½ [cos(A-b) - Cos (A+b)
CosACosB
½ [ Cos(A-B) + Cos(A+b)]
SinACosB
½ [sin(A+B) + Sin(A-B) ]
CosASinB
½ [ Sin(A+B) - sin(A-B)
Combinatorics
The two formula for N!
N! = n times (n-1) times (n-2) …..
N! = n times (n-1)!
Formula for (n-r)!
(n-r) ( n-r-1)
Formula for (K+1)! - K!
K! [ (K+1) -1 ] = K times K!
Tips on when to use
arranging lines
queue
placed in first second third…..
formula for when “two people in a line must be together
(n-1)(x)
n = total number of people
x = number of ways the people inside the block can be arranged
note
2 people : 2! ( n-1)
3 people: 3! (n-2)
how to choose number of ways of choosing a completed section
multiply everything
eg
12 shirts
6 pants
= 12 times 6
how to do ordered selection with repetition
the number of r letter words formed from n distinct letters with repetition is equal to n^r
(dont use factorials)
eg
How many 4-letter words can be formed using the letters A, B and C
n = 3
r = 4
What is permuatation
is an arrangement of objects chosen from a set without repetition and replacement in which where order matters.
Formula for permuatation
n p r = n! / (n-r)!
n = total avalible
r = items chosen and arranged (how many were used)
eg
the permuation of 3 distinct letters take from 5 letter set
n = 5
r = 3
What does n p n equal to
n!
Question types of permuations
pins: if it doesnt say the amount then assume it’ll be 10
words with no repeating letters
block method for permuatation
(n-r+1) times r!
n total objects
r objects that must be together
when to us eblock method and when to not
Must be together” → block method
“Must NOT be together” → total arrangements − together arrangements
tips for ordered selections and grouping
order the groups then order the people in the group
cases should never overlap
always times each case by the amount of ways they can be arranged
if letters are together what to do
group them as one
ordered selection with identical elements
n! / r1! times r2! ….
use when there are multiple of the same letter/ variable
how to do seperated letters with identically element s
Total arrangements - S’s togethr
for S c S
arrangement together for identically elements: (n-r+1)!/ factorial of repeats
how to do questions like “how many n letter words can be formed using _____”
"1. make cases if theres 2’ns or 3 n’s
2. times
combination formula and meaning
it is the set order of objects where order doesnt matter
formula is n C r= n!/ (n-r)! times r!
variation of this
(n r)
n c r = n c n-r
next 10 slides are for circles. note: n= total and k = number of objects that must be together
No restrictions
(n-1)!
two people must sit apart
(n-1)! - [(n-2)! times 2!]
boys and girls alternating
(b-1)! times g!
arrange boys in a circle
arrange girls in the gaps
solve
opposite from each other
(n-2)!
two of the same boys next to each other
2(n-1)!
all boys together
(n-k)! times k!
k = amount of boys
Rules for pigeonhole principle and the meaning
r = 0 : one pigeonhole with Q pigeons
r > 0 : one pigeon hole with Q+1 pigeons
If more objects than containers, at least one container holds multiple objects.
How to solve pigeon hole questions
identify n
identify k
use n/k
n = number of items
k = places they can go
binomial expansion
its just
(x+y)^n = n c o times x^n + n c 1 times x^n-1 times y
Further calc (nothing)
formula
Q = Ae^kt
Dq/Dt = KQ
what are the variables meaning
A= is the inital value
k = growth constant
another way of expressing Dq/Dt and what is A here
k( Q-b)
in which
Q= B +Ae^kt
A = the value of Q-B at t=0
Yr 12 Trig (nothing here)
What does cos² x and sin² x equal to
½ + ½ cos2x
½ - ½ cos2x
Tips when doing trig equations
get all the angles the same
get all the trig functions the same
What is a homogeneous equation
IT is called a homogenous equaion in sinx and cosx if the sum of the indices of sinx and cosx in each term are the same. So pretty much
A homogeneous equation is an equation where every term has the same degree.
Simply:
If you multiply all variables by a number, the whole equation scales consistently.
How to solve a homogenous equation
divide through a suitable power of cosx to produce a equation of tanx
Steps in solving
use formulas (compound, t etc etc)
reduce to variables (if needed)
look for similarities to move to the same side
determine if its homogenous
divide sides by cosx
solve
Auxiliary angle method
it says that any f(x) = asinx +bcosx can be rewritten in the forms of
y = Rsin (x- alpha)
y = Rsin( x + alpha)
y = Rcos( x - alpha)
y = Rcos( x + alpha)
What is R
R is equal to the square root of a² + b²
Steps to do this
set them to equal y or f(x)
equate coeffcients sinx and cosx
squaring them (for sin² +cos²=1) then add
solve R
find alpha
put equations together
Yr 12 stats
Bernoulli trials
is a single stage random experiment with two outcomes (success) and (failure) in which we asign them as
p =( changes depending on situtation but it is the success)
q = 1 - p = ½ (failure)
Binomial experiments
n stage experiments in which
each stage is a bernoulli trial
stages are independent'
random variable x is the number of success and order is irrelevant
Formula for this is
P( x success) = ncx times p^x times q^n-x
p (x success) = ncx times (1/2)^n ( for p=q)
probability of one specific order: P = p^x times q^n-x
(p + q) = 1^n = 1
TIp to understand this better. P(two are clubs) and P(at least one is a)
P(two are clubs) = 6 c 2
P(at least one is a ) = 1 - p(all are non )
How to do questions like P(2 girls and 3 boys) for 5 people
set x = 2 or 3
use formula '
done
as if you have success 2 girls then through inspection you have 3 boys