OCR Gateway GCSE Biology: B1
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Define Magnification
The degree to which the size of an object is larger than the real object
Define Resolution
The ability to distinguish two points as seperate entities
How do you work out magnification of an object?
Magnification of object = image size/ real size
How do you work out magnification of the microscope?
Magnification of microscope = magnification of eyepiece lens x magnification of objective lens
Describe the order of viewing specimen on a light microscope
-Place specimen on a slide
-Put a stain on specimen to highlight subcellular structures/ if the specimen is colourless
-Place cover slip on top
-Place this on stage of microscope
-Turn the lamp on so it shines constant light on the slide for specimen to be viewed
-Objective lens (closest to specimen) magnifies the image which is then further magnified by eyepiece lens
What are advantages of light microscopes?
Relatively cheap
Can be used in the field
Does not require specialist training
Can look at living specimens
What are advantages of electron microscopes?
Creates 3D images
Significantly higher resolution than light microscope
Higher magnification
What are the subcellular structures in an animal cell and how do they work?
Nucleus- Contains genetic info which codes for a particular protein
Cytoplasm- Liquid substance in which chemical reactions occur
Mitochondria- Where cellular respiration occurs, contains enzymes for cellular respiration
Ribosomes- Site for protein synthesis
Cell membrane- Contains receptor molecules to identify and selectively control what enters and leaves cell
What are subcellular structures in plant cells and how do they work?
Chloroplasts- Where photosynthesis takes place to provide food for the plant. Contains chlorophyll which harvests light needed for photosynthesis
Permanent vacuole- Contains cell sap. Improves cell's rigidity
Cell wall- Made from cellulose. Provides strength to cell
Nucleus- Contains genetic info which codes for a particular protein
Cytoplasm- Liquid substance in which chemical reactions occur
Mitochondria- Where cellular respiration occurs, contains enzymes for cellular respiration
Ribosomes- Site for protein synthesis
Cell membrane- Contains receptor molecules to identify and selectively control what enters and leaves cell
What are 3 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Do not have nucleus or mitochondria
Genetic information floats in the cytoplasm as a circular strand of DNA
Peptidoglycan cell wall instead of cellulose
Describe DNA structure
Double helix made from 2 strands twisted around each other
Polymer
2 rows of nucleotide monomers (2 polymers) joined together in double helix by complimentary base pairings
Describe nucleotide structure
2 rows of nucleotides joined together in double helix by complimentary base pairings
What are the type of bases and their pairings?
Complimentary base pairings
Adenine- Thymine
Guanine- Cytosine
Describe transcription
1. DNA is unzipped
2. mRNA read the DNA and mRNA nucleotides match to their complimentary base pairings on the unzipped DNA strand.
-Thymine is replaced with Uracil on mRNA
3. The mRNA creates a new strand which is now a template of the original DNA
Describe translation
1. mRNA leaves the nucleus and attaches onto the ribosomes
2. The mRNA is read in codons as each codon codes for an amino acid
3. tRNA brings the amino acid to the corresponding codon
4. Once all amino acids are brought, they form peptide bonds between them and fold to create a protein
16. What are enzymes?
Biological catalysts which increase the rate of reactions without being used up in them
Describe enzyme structure
Each enzyme has a unique and substrate specific active site to bond to a particular substrate
Describe the lock and key hypothesis
Shape of active site is complimentary to shape of substrate so when they bond it forms an enzyme-substrate complex
Once bound, the reaction takes place and products are released from surface of enzyme
Which 4 factors affect rate of reactions?
Temperature
pH
Substrate concentration
Enzyme concentration
How do you find out the rate of reaction?
change in concentration/ time
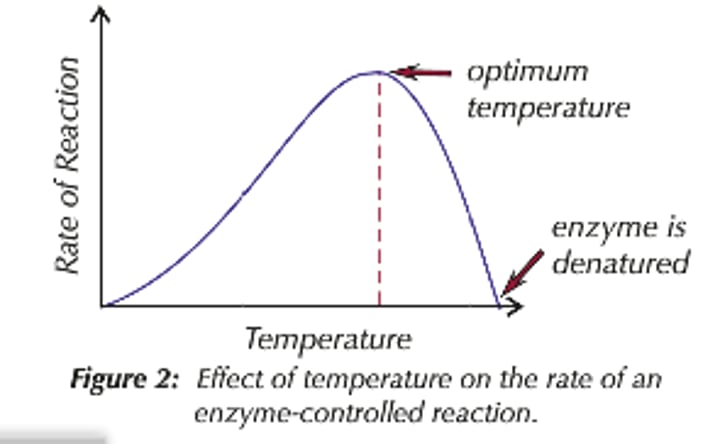
Outline temperature's effect on reaction rate and it's graph
Optimum temp is body temperature (37 degrees C)
Rate if reaction increases as temperature increases until the optimum temperature.
After it reaches it's optimum temperature, it rapidly decreases until the reaction stops.
This is due to the bonds in the structure of the enzyme breaking which changes the shape of the active site as it is too hot.
If the shape of the active sight is changed, the substrate can no longer fit in.
The enzyme is denatured and can no longer work.
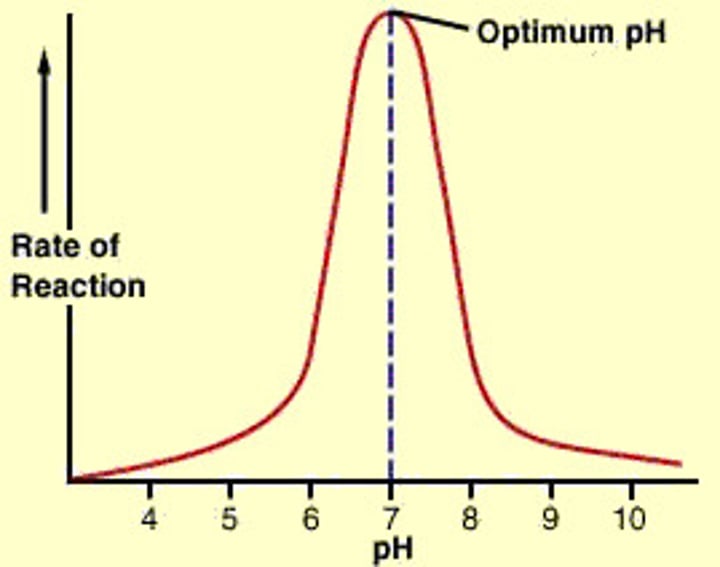
Outline pH's effect on reaction rate and it's graph
Optimum pH for most enzymes is 7 but some that are produced in acidic conditions such as stomach have lower pHs
If pH is too high or low, forces that hold amino chains that make up enzyme protein will be affected.
This will change the shape of the active site, the substrate can no longer fit in.
The enzyme is denatured and can no longer work.
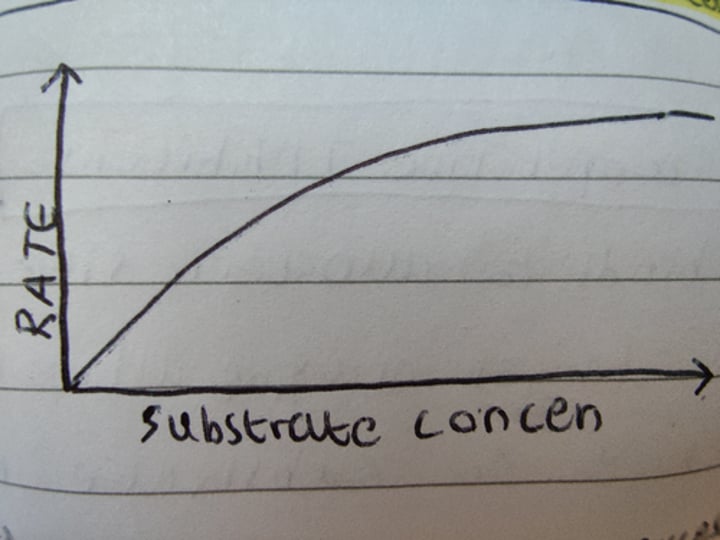
Outline substrate concentration's effect on reaction rate and it's graph
A higher concentration generally means an increased rate of reaction as enzyme is more likely to collide and therefore react with substrate.
However, after a while increasing the substrate concentration has no effect as the active sites of all enzymes present are full
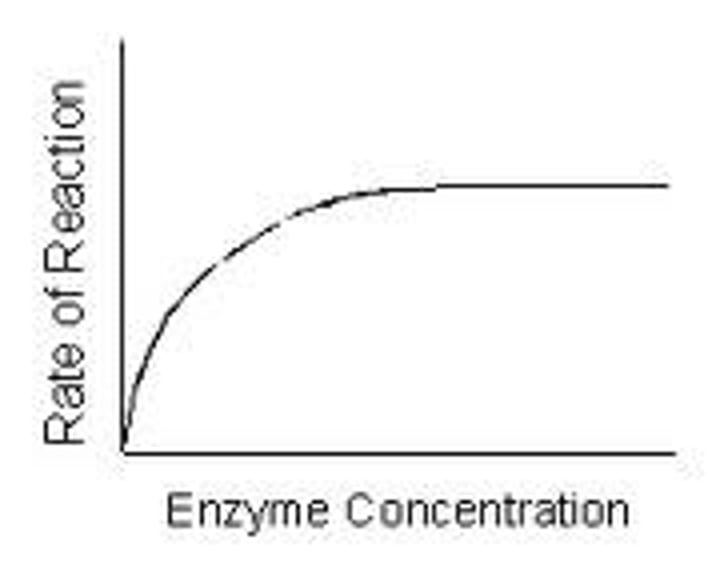
Outline enzyme concentration's effect on reaction rate and it's graph
A higher concentration generally means an increased rate of reaction as enzyme is more likely to collide and therefore react with substrate.
After a while, this stops as there are not enough/ no more substrate molecules to react with all of the enzymes
What is the purpose of respiration?
To produce energy in the form of ATP from larger molecules (like sugars)
What type of reaction is respiration?
Exothermic
What is the symbol equation for aerobic respiration?
Aerobic: C6H12O
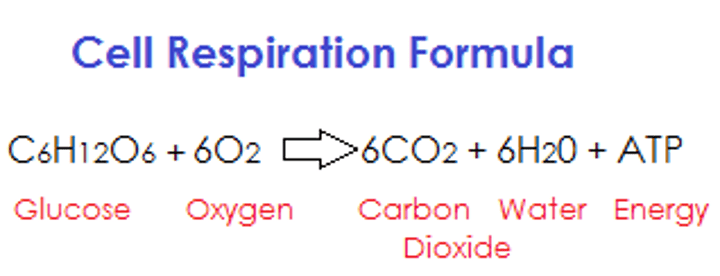
What is the symbol equation for anaerobic respiration?
In plant an yeast cells(bottom equation) it is called fermentation which is used to make bread and alcoholic drinks
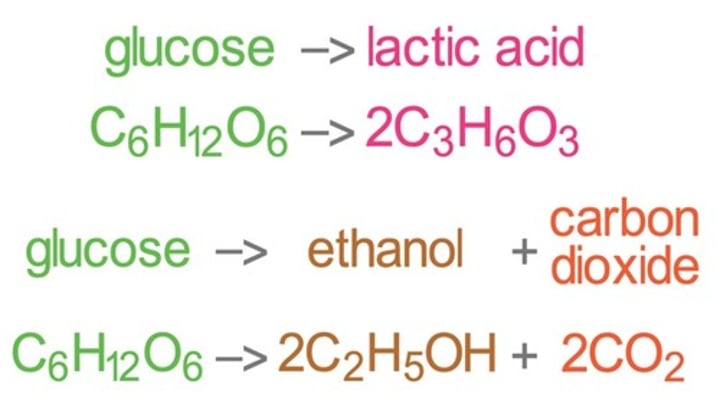
Compare aerobic respiration and anaerobic
Aerobic:
Uses oxygen
Yeilds most energy
Occurs in mitochondria
Produce ATP
Anaerobic:
Occurs when there is not enough oxygen
Last resort
Produce ATP
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
In the mitochondria
What is produced in plant + yeast anaerobic respiration and what is this called?
Ethanol and carbon dioxide and energy
What is produced in animal anaerobic respiration?
Lactic acid and energy
What is oxygen debt?
Extra oxygen needed to break down lactic acid formed in anaerobic respiration
What happens if there is too much lactic acid?
Can cause muscle fatigue and soreness
Name 2 polymers
Carbohydrates,
Proteins
Give an example of carbohydrates polymer
Carbohydrates:
-Starch which is broken down into maltose by amalyse enzymes
How are the two polymers broken down?
Carbohydrates are broken down by carbohydrase enzymes Protein is broken down by protease enzymes in stomach and small intestine
What are lipids broken down by?
Lipase enzymes
What are lipids broken down into?
Glycerol and 2 fatty acids
What emulsifies fat (makes large fat into small droplets) in the liver and why?
Bile made in liver emulsifies fat so that it is easier for lipase enzymes to work on lipids
What is photosynthesis?
Process of making glucose from sunlight in leaves of the plant.
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
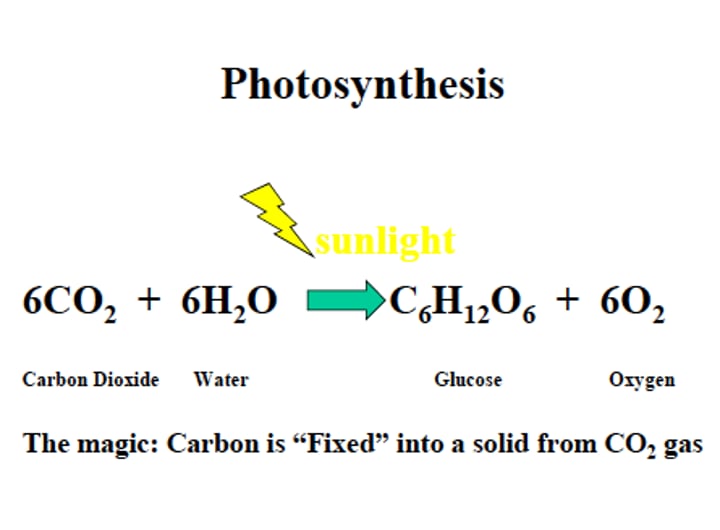
What type of reaction is photosynthesis?
Endothermic - energy is transferred from the environment to the chloroplasts by light
Where does photosynthesis take place?
In the chloroplasts
Outline the steps of an experiment to calculate rate of photosynthesis

What is the effect of temperature on photosynthesis and how does this link to its graph?
With an increase in temperature, the rate of photosynthesis increases
However, as reaction is controlled by enzymes this trend only continues up to a certain temperature before the enzymes begin to denature and rate of reaction decreases.
What is the effect of light intensity on photosynthesis and how does this link to its graph?
The higher the light intensity, the rate of photosynthesis increases because there is more light available to drive the reactions of photosynthesis.
However, if the light intensity is increased above a certain threshold, the rate of photosynthesis will not increase because another factor (such as temperature) is limiting the rate of the reaction.
Outline the steps of an experiment for light intensity

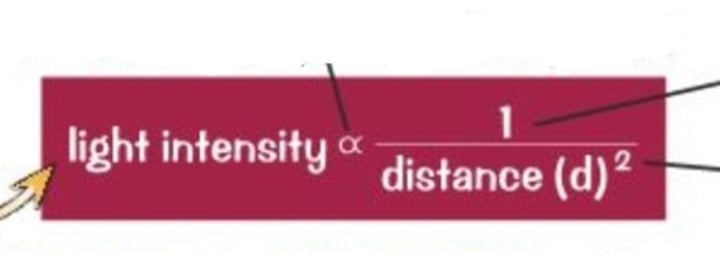
What is the inverse square law
As the distance between the light source and plant increases, the light intensity decreases.
What is the effect of carbon dioxide on photosynthesis and how does this link to its graph?
As carbon dioxide concentration increases, the rate of reaction increases as carbon dioxide is also needed to make glucose.
Define rate limiting factor
An environmental condition which restricts increase in rate of photosynthesis.
How can a rate limiting factor be spotted on a graph?
This can be seen in a graph levelling off
How can farmers use information about rate limiting factors?
To enhance conditions in a greenhouse for greater rate of photosynthesis which will increase growth leading to increased profits