CH 11: The Gastrointestinal System
1/265
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
266 Terms
BE
barium enema
NGT
nasogastric tube
NPO
nothing by mouth
PEG
percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
PEJ
percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy
BM
bowel movement
N&V
nausea and vomiting
CCE
cholecystectomy
EGD
esophagogastroduodenoscopy
ERCP
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
EUS
endoscopic ultrasound
FOBT
fecal occult blood test
LFT
liver function test
GI
gastrointestinal
UGI
upper gastrointestinal
GERD
gastroesophageal reflux disease
HAV
hepatitis A virus
HBV
Hepatitis B
HCV
Hepatitis C
IBD
inflammatory bowel disease
IBS
irritable bowel syndrome
PUD
peptic ulcer disease
RLQ
right lower quadrant
RUQ
right upper quadrant
LLQ
left lower quadrant
LUQ
left upper quadrant
What does the gastrointestinal system do?
breaks down food for absorption and distribution to the rest of the body
-first step is digestion
what are the three types of food feul?
protein, fat, carbohydrates
Gastrointestinal system is broken into the
1. Gastrointestinal (GI) tract
- divided into upper and lower tracts
2. Accessory organs
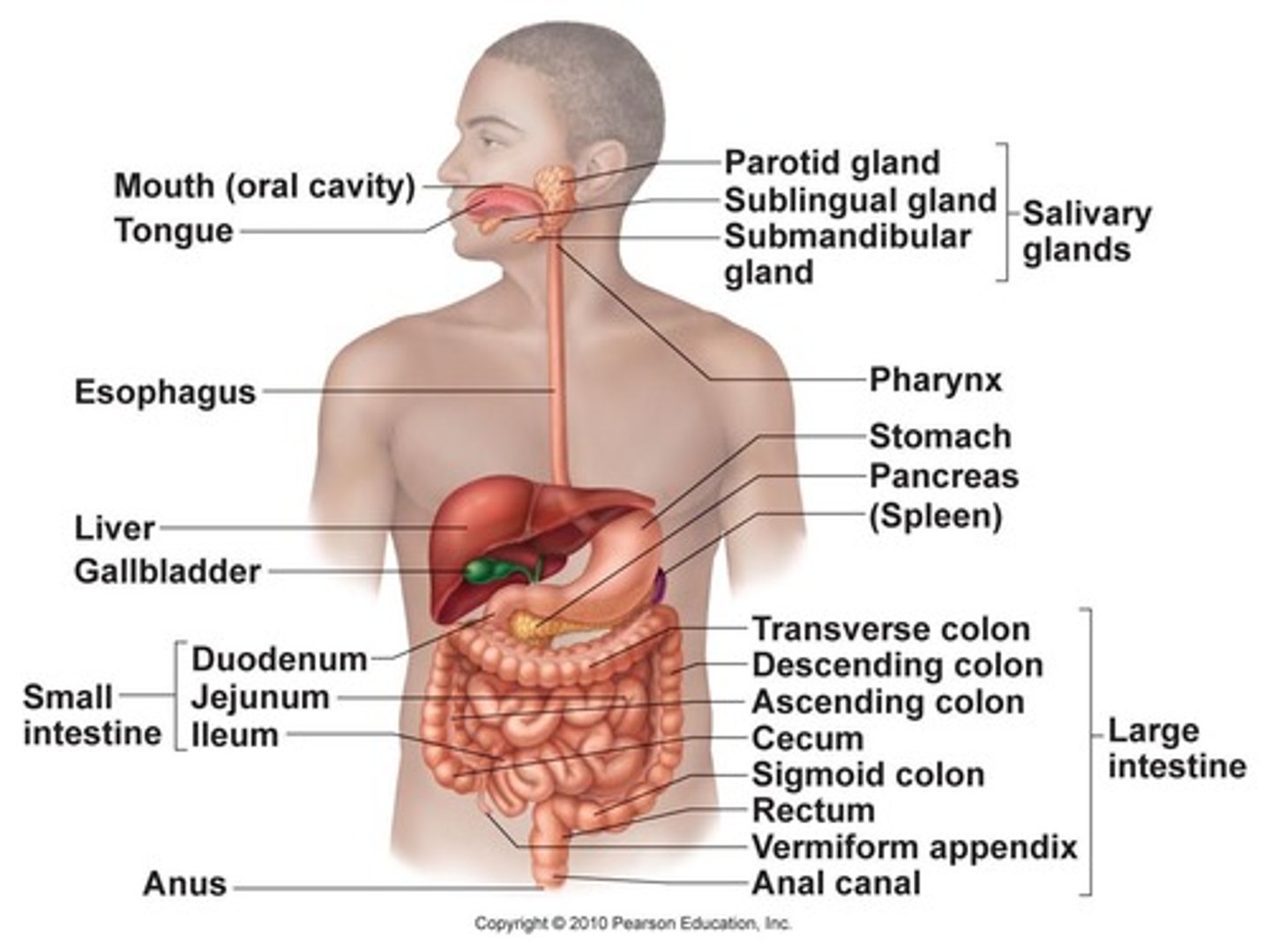
gastrointestinal tract
1.mouth
2.pharynx
3.esophagus
4. stomach
5. small intestine
6.large intestine
Accessory structures
1. Teeth
2. Tongue
3. Salivary Glands
4. Liver
5. Gallbladder
6. Pancreas
or/o, stomat/o
mouth
dent/o, odont/o
teeth
gingiv/o
gums, gingiva
chyme
mixture of enzymes and partially-digested food
gloss/o, lingu/o
tongue
esophag/o
esophagus
gastr/o
stomach, belly
Lower GI tract
small intestine, large intestine, colon, rectum
small intestine consists of
1. Duodenum- most of the chem breakdown happens here
2. Jejunum
3. Ileum
large intestine consists of
cecum, colon(ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid) , rectum
main function- absorb remaining water
enter/o
intestines (usually the small intestine)
duoden/o
duodenum (first part of small intestine)
jejun/o
jejunum (second part of small intestine)
ile/o
ileum (third part of small intestine)
col/o,colon/o
colon, large intestine
sigmoid/o
sigmoid
rect/o
rectum, straight
an/o
anus
proct/o
rectum
supporting structures/digestive organs
liver-produces bile
--bile is stored in the gallbladder and secreted into the small intestine
pancreas
--enzymes to break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates
sial/o
saliva, salivary
bil/i, chol/e
bile, gall
GI organs have three primary functions:
digestion, absorption, elimination
-surrounded by peritoneum
peritoneum
a multilayered membrane that protects and holds the organs in place within the abdominal cavity
abdomin/o, celi/o, lapar/o
abdomen
cyst/o
bladder, sac
doch/o
duct
hepat/o, hepatic/o
liver
pancreat/o
pancreas
peritone/o
peritoneum
GI problems can be categorized into problems of
-infection or inflammation
-change in function
-GI tract structure
Infections are common
-lead to organ inflammation
-viral or bacterial
-signs and symp lead practitioner to area of gi tract affected
-pain common
-inflam. can be caused by inherited disorders, stress, or reaction to med
change in function
-food flows in wrong directions
-food flows without being properly digested or absorbed
change in structure
overgrowth, stones
aerodontalgia
ER-oh-dawn-TAL-jah
tooth pain caused by exposure to air
aphagia
-ah FAY jee ah-
inability to eat
dentalgia
den-TAL-jah
tooth pain
dyspepsia (dis-PEP-see-ah)
indigestion
esophagalgia
eh-SAWF-ah-GAL-jah
pain in the esophagus
eupepsia
yoo-PEP-see-ah
good digestion
gastralgia (gas-TRAL-jee-ah)
pain in the stomach
gastrodynia (gas-troh-DIN-ee-ah)
stomach pain
gingivalgia
JIN-jih-VAL-jah
gum pain
gingivostomatitis
(JIN-jih-voh-STOH-mah-TAI-tis)
inflammation of the mouth and gums
hematemesis
(HEM-at-EM-eh-sis)
vomiting blood
hemat / emesis
blood / vomiting
hyperemesis
(HAI-per-EM-eh-sis)
excessive vomiting
hyper / emesis
over / vomiting
odontalgia
(OH-dawn-TAL-jah)
tooth pain
odontodynia
(oh-DAWN-toh-DIH-nee-ah)
tooth pain
stomatitis
inflammation of the mouth
stomatodynia
(stoh-MAT-oh-DAI-nee-ah)
mouth pain
constipation
difficulty in passing stools
diarrhea
passing of fluid or unformed feces
dysentery (DIS-en-TER-ee)
another name for diarrhea
enterodynia
(EN-ter-oh-DIH-nee-ah)
pain in the intestines
hemorrhoid
(HEM-oh-ROID)
inflammation of the veins surrounding the anus
rectalgia
rek-TAL-jah
rectal pain
cholecystalgia
KOH-lay-sis-TAL-jah
pain in the gallbladder
jaundice
yellowing of skin, tissue, and fluids caused by increased levels of bilirubin in the blood
icterus
another name for jaundice
sialorrhea
SAI-ah-loh-REE-ah
excessive salivation
gastromalacia
GAS-troh-mah-LAY-shah
softening of the stomach
gastroparesis
GAS-troh-par-EE-sis
partial paralysis of the stomach
gingivitis
JIN-jih-VAI-tis
inflammation of the gums
gingivoglossitis
JIN-jih-voh-glaw-SAI-tis
inflammation of the gums and tongue
glossoplegia
GLAW-soh-PLEE-jah
paralysis of the tongue
odontoclasis
(OH-dawn-TAWK-lah-sis)
breaking of a tooth
stomatogastric (stoh-MAH-toh-GAS-trik)
pertaining to the mouth and stomach
stomatosis
(STOH-mah-TOH-sis)
mouth condition
anophony
an-AW-foh-nee
sound from the anus