Nose, Mouth, Pharynx, Larynx
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Pharynx made of _____, ____, ____ (top to bottom)
Nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
Nasal cavity and nasopharynx composed of ________ epithelium
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar with goblet cells
Oropharynx and laryngopharynx made of _________ epithelium
Non-keratinized stratified squamous
Aspiration = ___
Food/fluid enters the breathing tube
Esophagus is _____ to the laryngopharynx and the larynx and trachea are _______ to the laryngopharynx
inferior, anterior
The _______ connects the __________ to everything below
Nasal and oral cavity
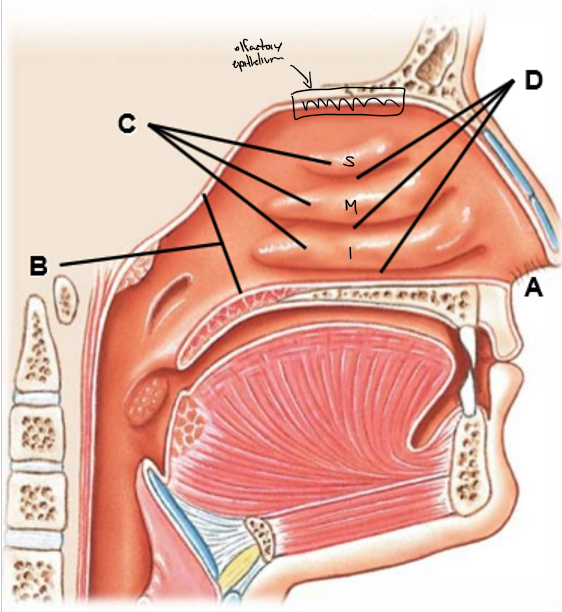
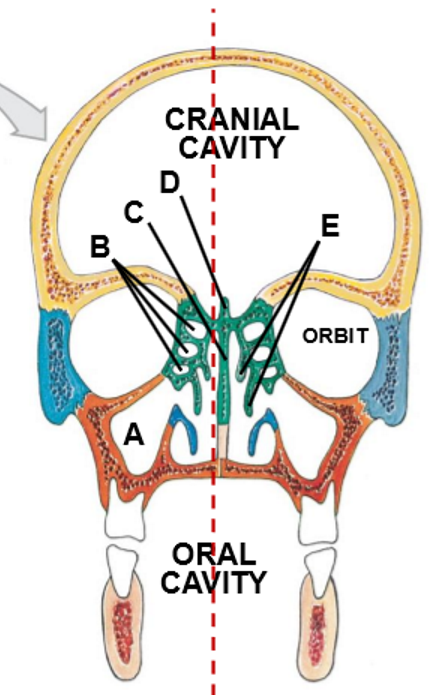
A-D
A: Nares (nostrils)
B: Choanae (posterior nares)
C: Superior, middle, inferior nasal conchae
D: Meatus
The ______ open into nasopharynx
choanae
Medial wall formed by ______
Nasal septum
Lateral walls include _________ with intervening ______-
Nasal conchae, meatuses
Functions of the nose (3)
Conduct air into the respiratory tract
Condition (warm, filter, hydrate) inspired air
Sense odourant molecules in inspired air
_________ are found at the roof of the ___ bone
olfactory epithelium, ethmoid
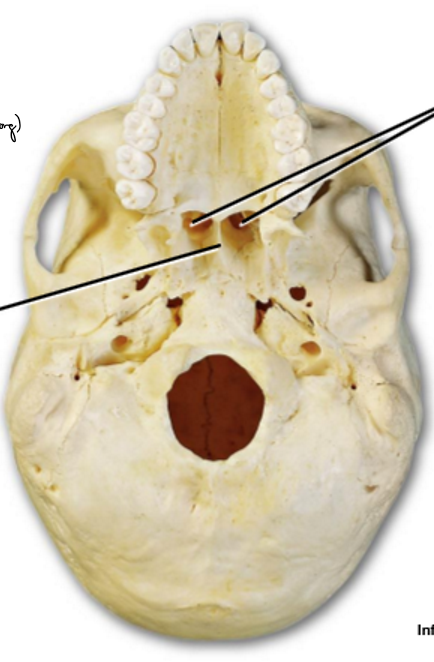
Choanae
Nasal septum
The _____ closes the nasopharynx when eating
soft palate
The superior and middle nasal conchae are made by the _____, and ______, also separating the _______ and _____
ethmoid, cribiform plate, cranial, nasal
The superior, middle, and inferior meatus open up to the _____
air sinuses
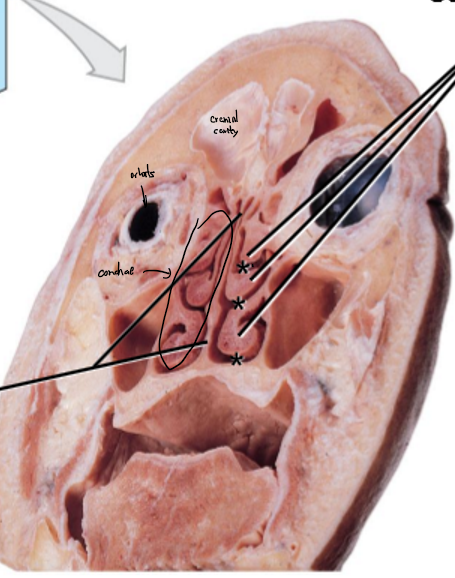
Nasal septum
Superior, middle, inferior nasal conchae
Superior, middle, inferior meatuses
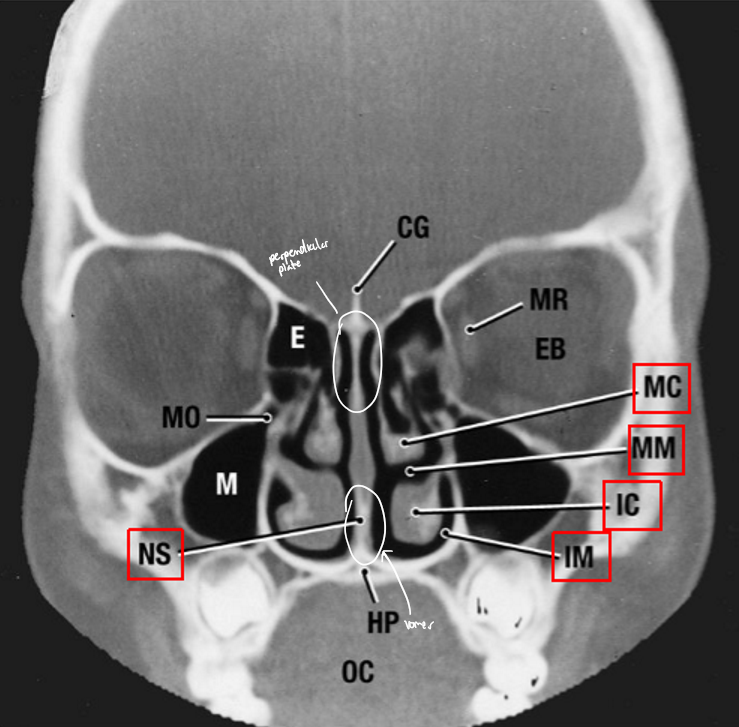
CG: Crista galli
NS: Nasal septum
EB: Eyeball
MR: Medial rectus
E: Ethmoid air cell
M: Maxillary sinus
HP: Hard palate
OC: Oral cavity
MC: Middle concha
MM: Middle meatus
IC: Inferior concha
IM: Inferior meatus
The ______ is not part of the ethmoid
inferior concha
A-D, colours from top to bottom
A: Maxillary air sinus
B: Ethmoid air cells
C: Perpendicular plate
D: Crista galli
E: Superior/middle nasal concha
Beige: Frontal bone
Turquoise: Zygoma
Red: Maxillary bone
Green: Ethmoid bone
Beige: Vomer
Blue: Inferior nasal concha
Superior and middle nasal concha are overlayed with ____
respiratory epithelium
Crista galli is a continuation of the _____ into cranial cavity
perpendicular plate
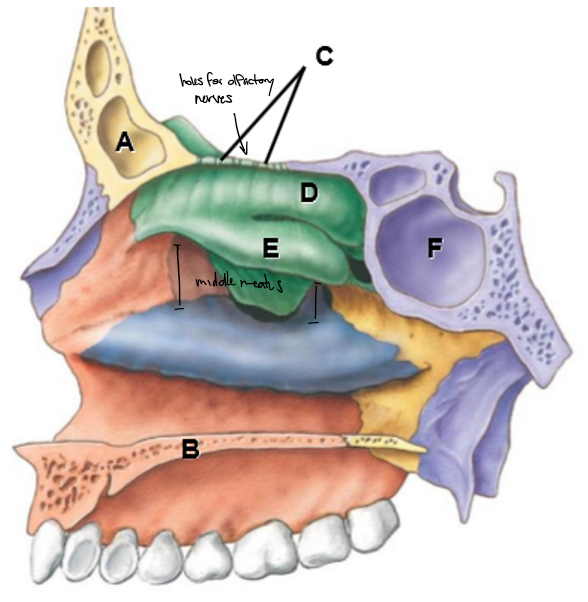
A-F
A: Frontal sinus/bone
B: Hard palate/maxillary
C: Cribiform plate
D: Superior nasal concha
E: Middle nasal concha
Blue: Inferior nasal concha
Purple: Sphenoid bone
F: Sphenoid air sinus
Yellow: Palatine bone
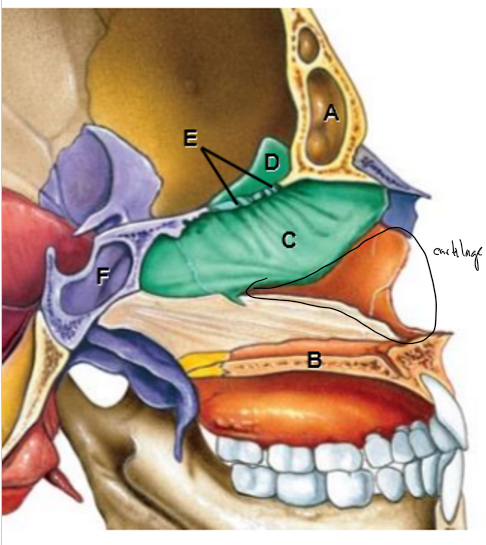
A-F
A: Frontal sinus/bone
B: Hard palate/maxillary bone
C: Perpendicular bone
D: Crista galli
E: Cribiform plate
Beige: Vomer
F: Sphenoid air sinus/bone
Yellow: Palatine bone completed by septal cartilage
Paranasal sinuses are ____, ______ spaces which open into the _____
air-filled, mucus-membrane lined, nasal cavity
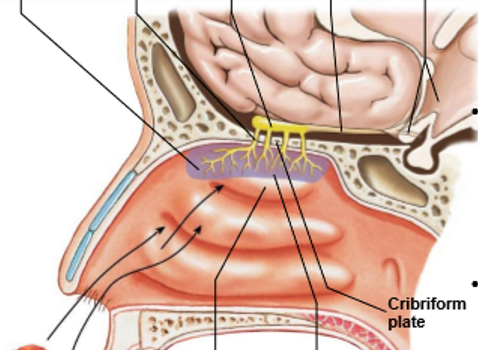
Top and bottom, left to right
Olfactory epithelium
Olfactory nerve fibres
Olfactory bulb
Olfactory tract
Primary olfactory cortex
Superior nasal concha
Olfactory epithelium
Cribiform plate
_____ brings odorants into contact with _____
Turbulence, olfactory epithelium
Axons from olfactory epithelium pass through the _____ as ______ to synapse on neurons in ________
Cribiform plate, CN I (olfactory nerve), olfactory bulbs
Secondary sensory neurons project to the ______, ______, _____
primary olfactory cortex, hypothalamus, limbic system
CNS interpretation of smell based on _________
Pattern of receptor activation
Olfactory organs are _______, ______
Neuroepithelium, underlying CT
Odorants dissolve in _____
mucus
Specific receptor binding of odorant causes _______
depolarization
>__ primary smells; different _______ on different neurons
50, receptor populations
_______ and _______ decrease with age
receptor #, sensitivity
___________ divide to replace worn out olfactory receptor cells
Regenerative basal cell
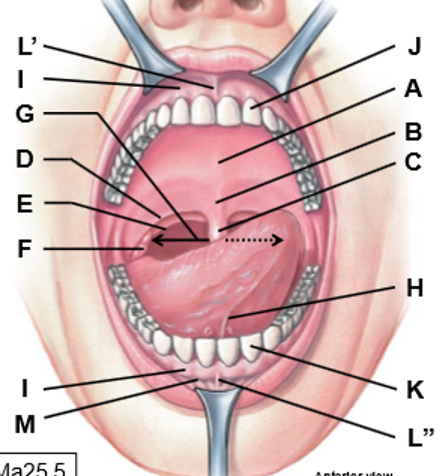
A-M
A: hard palate
B: Soft palate
C: Uvula
D: Palatoglossal arch (between palate and tongue)
E: Palatopharyngeal arch (soft palate and pharynx)
F: Palatine tonsils
G: Fauces
H: Lingual frenulum
I: Gingivae
J: Maxillary teeth
K: Mandibular teeth
L: Superior/inferior labial frenulum
M: Oral vestibule
Function of oral cavity
Analysis
Mechanical processing
Lubrication
Limited digestion
Oral mucosa made of ______ and _____-
Stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium, lamina propria
Lateral walls: cheeks containing _______
Buccinator muscles
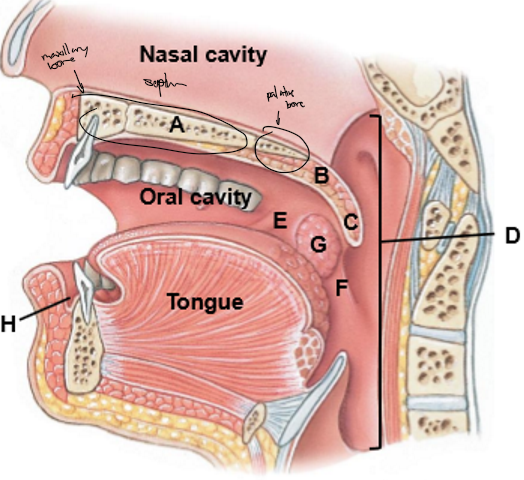
A-H
A: Hard palate
B: Soft palate
C: Uvula
D: Pharynx
E: Palatoglossal arch
F: Palatopharyngeal arch
G: Palatine tonsils
H: Oral vestibule
Roof: Hard and soft palate
Floor: Tongue
Ant: Lips with orbicularis oris
Post: Palatoglossal folds
Orbicularis oris allows lips to ___
pucker
Intrinsic tongue muscles are entirely within the ____, no ______
tongue, bony attachments
Intrinsic muscles are ____, separated by the _______
Bilateral, fibrous septum of tongue
Intrinsic muscles are ______, _____ and _____, change _________
longitudinal, vertical, transverse, shape of the tongue
Motor innevervation of tongue: ___
CN XII
Touch innervation of tongue
Ant 2/3: CN V (mandibular division)
Post 1/3: CN IX
Taste innervation of tongue
Ant 2/3: CN VII
Post 1/3: CN IX
Extrinsic muscles pass to tongue from ______, ()
Bony attachments, position the tongue
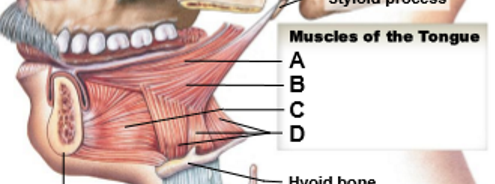
A-D
A: Palatoglossus (palate)
B: Styloglossus (styloid)
C: Genioglossus (chin)
D: Hyoglossus (hyoid)
Motor innervation of extrinsic muscles via _____ except _____ which is _____
CN XII, palatoglossus, CN X
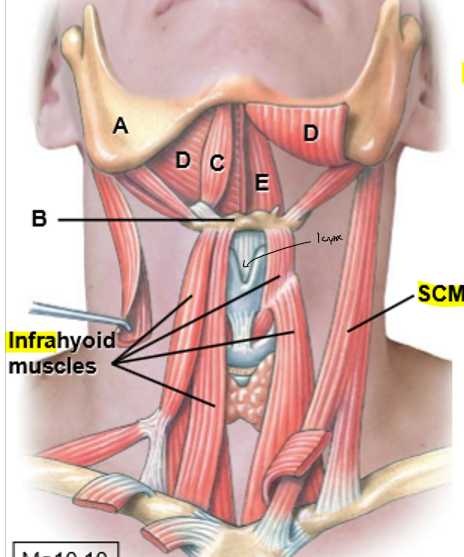
A-E
A: Mandible
B: Hyoid bone
Suprahyoid muscles
C: Anterior belly of digastric
D: Mylohyoid
E: Geniohyoid
Salivary glands are __________, each enclosed by a dense _______
3 paired exocrine glands, fibrous CT capsule
Serous cells (secretory portion) secretes _____ and _____
Proteins, glycoproteins
Mucous cells secrete _______
Glycoproteins
_________ cells of secretory portion are contractile, lie between _____ and ______ to move secretions into ______
Myoepithelial, secretory cells, basement membrane, ductal system
Ducts carry secretions of glands to surface of ____
Oral mucosa
Ducts are _______; _____ in basolateral membrane → ___, _____
highly branched, Na+-ATPase, Na+, H20 conservation
Most saliva produced by ________
submandibular gland
Salivary glands produce, secrete _____ made of ____, ____, ____, ____, ____
saliva
water
ions
enzymes
metabolites
glycoproteins
_____ are anterior to ears; duct opens into _______ by ________
Parotid gland, oral vestibule, 2nd maxillary molar
Submandibular glands inferior to _____, ducts open into ______, lateral to ____
floor of oral cavity, lateral to lingual frenulum
Sublingual glands inferior to ____, numerous ducts open into ________, lateral to that of the ______
tongue, floor of oral cavity, submandibular gland
TMJ lies between the ______ and _______
Mandibular fossa, mandibular condyle
Articular disc of fibrocartilage subdivides TMJ _____
Joint space
The TMJ is a loose capsule, therefore it is ______ and ______
Highly mobile, easily dislocated
TMJ allows ______ movements (), and ______ movements ()
hinge (elevation, depression), gliding (protraction, retraction, lateral grinding)
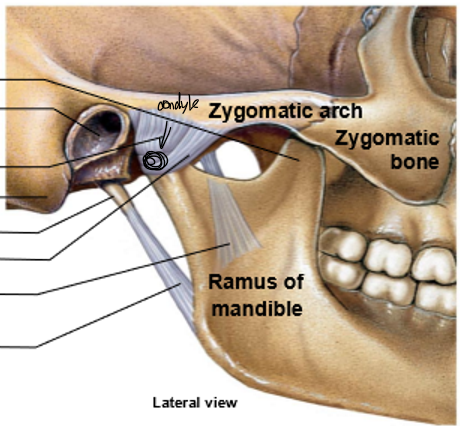
Top to bottom
Coronoid process
External acoustic meatus
Articular capsule
Mastoid process
Styloid process
Lateral ligament
Sphenomandibular ligament
Stylomandibular ligament
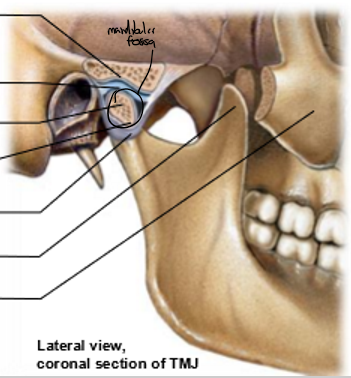
Top to bottom
Articular surface of mandibular fossa
Articular disc
Condylar process
Neck of mandible
Articular capsule
Coronoid process
Zygomatic bone
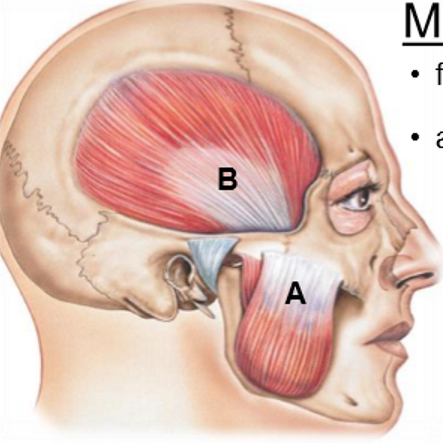
A: Masseter
B: Temporalis
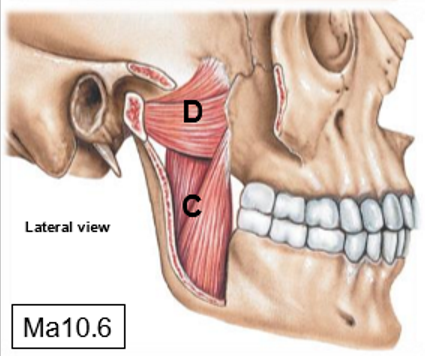
C: Medial pterygoid
D: Lateral pterygoid
Masseter is the ____ and responsible for __
largest, elevation
Temporalis responsible for ____ and ____
Elevation, retraction
Medial pterygoid responsible for ______
Elevation, side to side movement of mandible
Lateral pterygoid responsible for __________
Protrusion, side to side movement of mandible
Somatic motor control of the muscles of mastication via __________
Mandibular division of CN V
The pharynx extends from the ______ to the ______
base of skull, upper esophageal sphincter
The pharynx _______ reflexively in ________
contracts, swallowing
Sensory innervation of pharynx by ______ and motor innervation largely by _______-
CN IX, CN X
Damage to CN X can cause _____
dysphagia
Nasopharynx opens into _____, ends at _____
Nasal cavity, soft palate
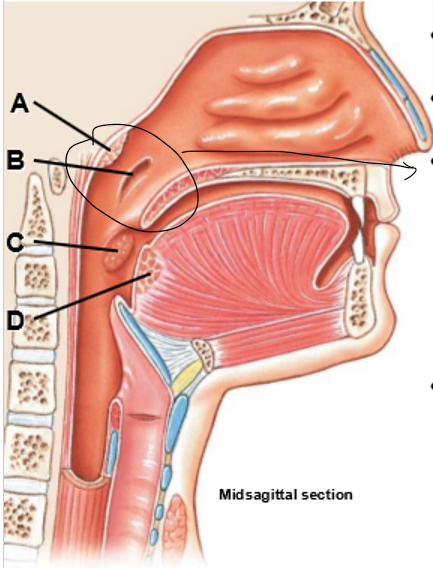
A-D
A: Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids)
B: Opening of pharyngotympanic tube
C: Palatine tonsils
D: Lingual tonsil
Oropharynx opens into _____, ends at _____
nasal cavity, soft palate
Laryngopharynx opens into ____ and _____
Larynx, esophagus
All pharyngeal muscles are innervated by the _____, except the ______, ()
CN X, stylopharyngeus, CN IX
Three circular pharyngeal muscles
Superior, middle, inferior constrictor
Three pharyngeal longitudinal muscles
Stylopharyngeus
Palatopharyngeus
Salpingopharyngeus
Stylopharyngeus attaches to ______
styloid process
Palatopharyngeus attaches to _____
Soft palate
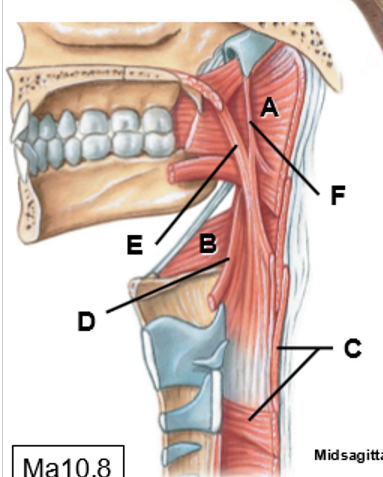
A-F
A-C: Superior, middle, inferior pharyngeal constrictor
D: Stylopharyngeus
E: Palatopharyngeus
F: Salpingopharyngeus
3 phases of swallowing
Buccal phase
Pharyngeal phase
Esophageal phase
Buccal phase is _____ ()
voluntary (decision to gulp)
Pharyngeal phase is _____, triggered by ______
involuntary, bolus touching back of oropharynx
Bolus is propelled through pharynx ______ by ___________
reflexively, coordinated contraction of pharyngeal muscles
Contraction of _____ isolates _____- from ______
Palatal muscles, oropharynx, nasopharynx
In esophageal phase, _____________ of esophageal muscles _________
Peristaltic contraction, propels bolus to stomach
3 main functions of the larynx
Conducts air into the trachea
Guards the trachea against entry of liquids and solids
Produces sounds
Opening into the larynx is called the ____
glottis
Glottis is guarded by the _______
epiglottis
Inferiorly, the larynx opens into the ____
trachea