Lab 9 - Size Exclusion Chromatography
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
chromatography
powerful analytical technique that separates mixtures into individual
components
Preparatory chromatography
isolation or purification of target molecules
analytical chromatography
identify and quantify components of mixtures
stationary phase
solid phase, liquid adsorbed on a solid surface
mobile phase
liquid or gas phase
effective separation depends on mixture characteristics such as...
absorption (l-s), partition (l-s), affinity towards one protein vs others, differences in mw
liquid chromatography
liquid = mobile phase, thermally unstable, non-volatile sample
gas chromatography
gas = mobile (He, N2), mixtures of volatile liquids & solid material, highly sensitive yet simple, small molecules
Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC)
silica gel that is immobilized on a glass slide
paper chromatography
Stationary phase is a thick filter paper and water drops settled in its pores,
mobile phase is the appropriate fluid
column chromatography
Stationary phase is a column on which the sample to be separated is loaded
and then washed with mobile phase
Ion exchange chromatography
Uses electrostatic interactions between charged protein groups, and solid support
material (matrix), matrix has ion load opposite of protein to be separated,
(+) ion-exchange matrix = anion exchange
(-) matrix = cation exchange
Affinity chromatography
The specific protein which makes a complex with the ligand attached to a solid
support (matrix), and retained in the column, while free proteins leave the column.
Usually an antigen-antibody interaction!
• The bound protein leaves the column by means of changing its ionic strength
through alteration of pH or addition of a salt solution
Gel permeation/Gel filtration/size exclusion
Uses matrix to separate macromolecules based on their differences in molecular
sizes.
• Matrix is made from dextran, agarose, or polyacrylamide
• Stationary phase is a column and consists of inert molecules with small pores
column chromatography (mobile phase)
acts as a solvent – sample mixture can be introduced in the column.
acts as a developing agent – helps in the separation of components in the
sample to form bands.acts as an eluting agent – the components that are separated during the
experiment are removed from the column
ex: ethanol, acetone, water.
column chromatography (stationary phase)
solid material with good absorption
Shape and size of particle: Particles should have uniform shape and size
• Stability and inertness of particles: high mechanical stability and chemically
inert.
• It should be colorless, inexpensive and readily available.
• Should allow free flow of mobile phase
• It should be suitable for the separation of mixtures of various compounds.
SEC separates molecules based on…
largest to smallest molecular weight (big to small)
gel - porous beads
diff size molecules are included/excluded from pores in matrix
large molecules
eluted FIRST in void, do not enter pores
small molecules
elute slower, s=s
factors affecting separation
flow rate, sample volume, column length, pore size, exclusion limit
exclusion limit
determined by pore diameter. proteins bigger than EL eluted tgt in single peak
large molecules are eluted in..
void volume (V0) (matrix)
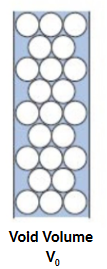
small molecules are eluted in..
total volume (Vt) (all)
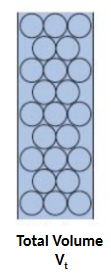
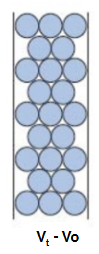
what is elution volume (Ve)
solutes within the separation range of matrix that are fractionally excluded with a characteristic (Vt-Vo)
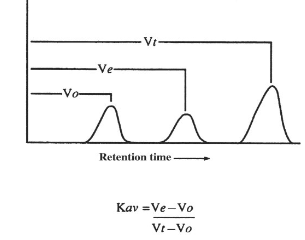
Kav
partition coefficient. specifies retention of molecules
gel permeation chromatography (GPC)
SEC when organic solvents are used
gel filtration
SEC with aqueous solvents
SEC protein mixture separation steps
apply protein mix into column → add buffer (so it can travel thru column) → collect eluted sample into diff tubes → identify proteins
hemoglobin
red-brown
mw = 65k daltons
eluted first
large (excluded)
Vitamin B12
pink
mw = 1,350 D
small (fractionated)
penetrates bead pores
eluted last
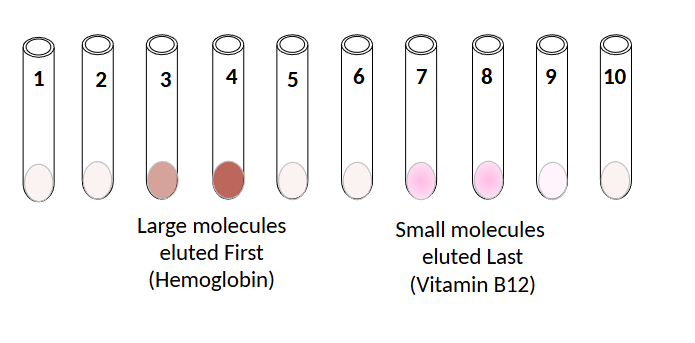
expected outcome