INDG 2455 - Social Organization and Kinship
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
"Indigenous social organization is based on complex kinship systems that extend beyond immediate family, forming networks of obligation, shared responsibility, and mutual support. These systems define roles, ensure fair resource distribution, promote social cohesion, and connect individuals not only to each other but also to the land, culture, and spirituality. Kinship systems establish an individual's responsibilities, rights, and proper relationships within the community, influencing everything from marriage and ceremony to day-to-day interactions and land ownership. " (from google)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Kinship terminological term for: Mother =
= M
Kinship terminological term for: Father =
= F
Kinship terminological term for: Sister =
= Z
Kinship terminological term for: Brother =
= B
Kinship terminological term for: Uncle =
= FB (Fathers Brother) OR MB (Mothers Brother)
Kinship terminological term for: Aunt =
= MZ (Mothers Sister) OR FZ (Fathers Sister)
Kinship terminological term for: Grandma =
= MM (Mothers mother) OR FM (Fathers Mother)
Kinship terminological term for: Grandpa =
= FF (Fathers father) OR MF (Mothers Father)
Kinship terminological term for: Nephew or Niece =
= BS (brothers son) OR BD (brothers daughter) OR (sons, son) OR SD (sons daughter) OR ZS (sisters son) OR ZD (sisters daughter) OR DS (daughters son) OR DD (daughters, daughter)
Kinship terminological term for: Cousins =
= FZS or FSD OR FBZ OR MBD OR MBZ OR MZS OR MZS
Emic
perspective within a system (insider perspective) a perspective from within a system. How does someone living in that system understand their ways of life
Etic
perspective outside of a system (outside perspective) perspective from without a system. How does someone outside of a culture understand and how do they take a comparative approach?
Kinship terminological term for: Daughter =
= D (daughter)
Kinship terminological term for: Son =
= S (son)
Kinship terminological term for: EGO
You (represented by triangle) ego is line 0, +1 goes up, -1 goes down
Phonetic
Soundsystems in different languages = biological aspects to what sounds are selected.
Looking for universals, kinship.
Filiation
line of descent. Can have different meanings depending on the society. Father mother is directly related to filiation, genes (western culture.)
Genetrix/Genitor:
Biological link through DNA(biological parents.)
Mater/Pater: social roles (eg. adoption, step parent)
Unilineal
patrilineal and matrilineal (in the minority as of now) systems.
Economic systems - agriculture, hunting/gathering, pastoralism and horticulture.
Primogeniture:
the first born male (usually) inherits the farm, daughter marries off the farm to a different one.
Uterine
matrilineal descent
Agnatic/agnation
another word for patrilineal descent
Cognate/cognatic
related to both lines of descent.
Ambilineal
Tracing decent through both (same as cognatic)
Descent
wider view of the line, relation between ego and another member, but not relationship. (relationship between family)
Corporate group:
to talk about a group that acts as a single cultural entity.
can allow for access to land. Eg. Blackfoot has access to territory because of their ethnic group.
Can be determined by descent, usually unilineal as ambilineal can cause conflict.
Exogamy
need to marry outside of the group
Edogamy
need to marry outside the group
What is Clanship related too (on exam)
Lineage only used when you can trace your line
Clan is deeper in time, cant trace ancestry to them
Age of the system
What is polgamy (on exam)
Multiple partners
Polgamy (many women)
Polyandry (many male)
what is a Dowry?
Males gift to female family
what is bride wealth ?
Wife's family to husband's family
What she brings with her
Why did couples form?
Pair-bonding
Forming links with other groups (alliances)
Historically marriages happened for society or benefit of the kingroup
what is Networking?
make connections and strengthen your trade, retaining power, keeping influence, connections can help you in certain cases.
what is Kindred?
a network of relatives, taken from a particular group of siblings. Networks of relatives are usually similar. These networks are used in many different cultures. (always die off and are recreated with each generation)
what is Successions?
pass the role down to the next generation (monarchy) (passes to the oldest son)
KEY TERMS * Descent & Filiation
Descent: family line, grandparents, parents, children
Filiation: direct parent to child
Asscendants
Ascendants: great grandparents, then grandparents +1, +2
Descendants
Descendants: children, grandchildren - 1, -2
Family groups in western society
Family groups
Nuclear (direct relation, M,F, Z, S) (Conjugal) mother and children make a family
Stem (
Extended ( all related, great grand parents, cousins, aunts, uncles, etc)
lineage and clan
direct links through the age of systems
define affines:
relations you get through marriage
cognates
relations you get through descents
polygamy
multiple partners
polyandry
several male partners
polyandry
several female partners
what is a dowry?
gifts from the grooms family to the brides family
what is bride wealth?
brides family to the grooms family
what is bride service?
working for the wife family for a period
Weber - Ideal types and protoypes
Ideal notions of how things should be or look like. Eg. traditional marriage models vs. how marriage actually is.
Assumptions based on social ideas. Eg. the thought that all nurses are women. All surgeons are men, etc.
Categorization: How these prototypes fit into categories and what are the borders?
if there is no legal marriage, no love, no living together, no children, is that actually a marriage?
Classificatory systems:
Gender is distinguished (aunt vs uncle, mother vs father). Different from descriptive because it lumps in its own categories. F=FB. All systems that distinguish cross cousins are classificatory systems. Eg. all men in gen -1 are fathers.
In English, Dene, Blackfoot and Cree systems.
Descriptive:
If they distinguish between F is not = to FB it is descriptive. Father, uncle, etc. Distinct terms.
Generational:
Eg. In Hawaiian systems, ego is not distinguished by certain terms. F=FB=MB. Distinguishes the generations but the terms are only distinguished by gender but not specific terms.
lineage:
Eg. the Eskimo system that distinguishes parents, siblings and their children as cousins. Patrilineal system, Father and his brother is different from maternal uncle as they are in their own patriline. This system is concerned with lines of lineage. The English system cares about filiation rather than terms.
What are ‘Complex Systems’ in Kinship?
they are called this because you can’t easily predict what is going to happen
What are Elementary Systems in Kinship?
Are kinship systems defined by positive rules of alliance. which dictate whom one must marry and are contrasted with ‘complex’
what are Phratries?
situations where you have clans in the society but these clans may be related to other clans that aren't near, so if we have groups of clans or people who associate with each other we call these clans “phratries”. (fraternities of clans is another way to look at it)
what does ‘moieties’ mean
Marriage groups - marriage out groups - can’t marry within your moieties
bilateral cross cousins
is a person who is a cross cousin on both the maternal and paternal sides of a family. This happens when a man and woman from different families marry their siblings, and their children then become bilateral cross cousins to each other.
define ‘patrimoiety’
a kinship group that divides a society into two halves, with membership inherited through the father’s male line.
define matrimonial
a kinship group that divides a society into two halves with membership through the mothers line
define generational moieties
a system of social classification that divides an entire society into two groups based in a person’s generational level. In this system, adjacent generations belong to opposite moieties, while alternate generations (grandparents, grandchildren) belong to the same moiety.
CASE STUDY: Kariyarra
“Mamanmaru ‘Fathers People’; Balumaru ‘Other peoples’
Paterillenal line
These type of systems don't need to be exact bilateral cross cousin, it just needs to be someone we can apply this kinship term to successfully
Marriage rule - if you are a manumaru male you need to marry a balumaru female and visversa
A system that has 2 types of moieties (patrimoieties and generational moieties)
They have to marry within their generation ! no older, no younger, and someone from the outside of their group
Creates alliances between groups, small populations, they want a way to prevent warfare so they created this alliance system in their society - 750 people total (2 people every 5 miles or something like that) !
Women move between groups and locations, men tend to stay. Also referred to as “sister exchange”
Alliance provides long term survival ! (Connor kept stressing this idea)
How does complexity emerge in kinship?
If you have a patrimoieties you also have matrimoietiies
Why do people get married?
Can be lots of reasons, social systems were lots of reasons explain why marriage patterns are the way they are
These are called “Complex Systems” : called complex systems because you can't easily predict what is going to happen
Alliance theory of kinship
Meant to cement people together
Building a larger social structure to increase your chances of survival
Maintaining social, economic, and political ties between family groups
Symmetric alliance systems
Characteristics: In a two-group system, Group A gives women to Group B, and Group B simultaneously gives women to Group A (e.g., through sister exchange). In this setup, a group acts as both wife-givers and wife-takers in relation to the same other group across generations.
Marriage Rule: This system is typically associated with a rule of prescriptive or recurrent marriage that mandates marriage with a bilateral cross-cousin (the child of one's father's sister and mother's brother).
Asymmetric exchange systems
is a marriage alliance structure where there is a one-way flow of women between different descent groups across generations, establishing a hierarchical relationship between "wife-givers" and "wife-takers”.
Wife's cross cousin most of the time *
1-4 groups
Generalized exchange system
Open ended system !
These systems occur in more diverse and larger areas - it promotes bringing more people into your system
Many groups = 8-16
Migration and kinship
looking for better opportunity - the country people go to is mostly influenced by family members being in that country.
Social Network Technique
examining peoples social networks (family networks vs kinship networks vs friend networks, etc) Finding connections between relations with others.
what is Generation Moieties
Tracking the moiety membership across generations. To understand group membership of individuals. Moieties based on generation. For example, within a Moiety there are many groups however a child and parent will not be in a generation together. Grandfather = Ego, Father = Son. for distinctions which allow for marriage
what is restricted exchange?
A restriction to who you can marry through a cultural value. Can be about partner exchange, but also divide into wife-givers and wife-takers. Eg. societies with moieties.
generalized exchange
systems where there are little to no restrictions to who you marry (Canadian society for example)
elementary systems
simple systems with controlled stated marriage rules
complex systems
there aren’t any prescriptive marriage rules; es, anyone can marry.
negative marriage rules
you can’t do something (marrying your sibling). Only in complex marriage systems
positive marriage rules
marriage rules that tell what you can do in a marriage and who you can marry
indirect exchange
multiples clans exchanging, usually three or more exchanged in cycles. groups always cycle through spouses
direct exchange
harder to scale up as it gets more complicated. the problem with it is that there needs to be an equal number of men to women in each generation. specific groups give to other specific groups. eg A always gives to B and B always gives to C and C always gives to A sort of thing.
English system is Eskimoian system
descent is tied into most and if any all systems. many African groups still use unilineal descent
What is a potlatch system?
exchange of spouses but also valued items (engraved copper plates) at a large celebration for social prestige. The more you give away the better.
what is an delayed exchange ?
sub-type of direct exchange, exchange direction changes with each generation.
Case Study: China: The Moso
Kingdom of women
Family name is passed on from the mother
Father and husband leave to go to their own homes at sunrise.
Dried pig is wealth - the more you have the more rich you are.
Walking marriages - men walking home from their spouses house at sunrise.
Leader of the household - “Dape”
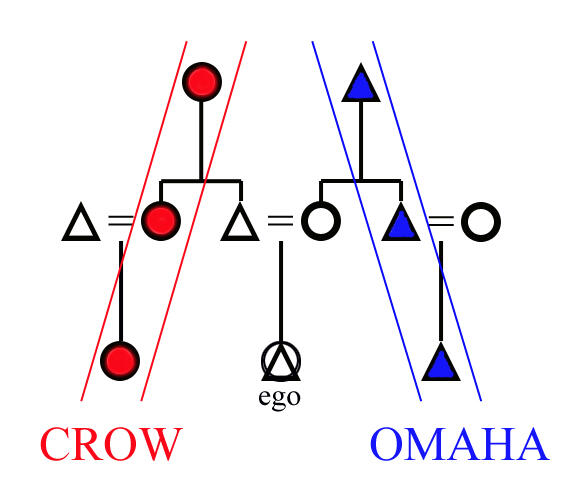
Crow and omaha kinship systems:
Crow: a matrilineal clan system (Ashammaliaxxiia) where lineage and status trace through the mother. distinguishing relatives by sex and generation on the mother's side but grouping father's kin by sex only
Omaha: a patrilineal system where descent is traced through the father, but with distinct rules for mother's side (maternal) and father's side (paternal) relatives, merging generations on the mother's side while distinguishing them on the father's, grouping mother's brother (MB) and his sons together, and defining marriage rules that avoid certain kin (like father's sister's family)