Chapter 10 - Hydration, Dehydration, Alcohols
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
hydration reaction
the reaction of an alkene with water to form an alcohol
the product contains an OH group (hydroxyl group) bonded to a carbon atom
2 or more atoms become bonded to original alkene and double bond becomes single bond
hydroxyl group
OH group connected to a carbon
alcohol
product of hydration reaction, contains hydroxyl group bonded directly to a hydrocarbon chain
Hydration reaction of alkenes
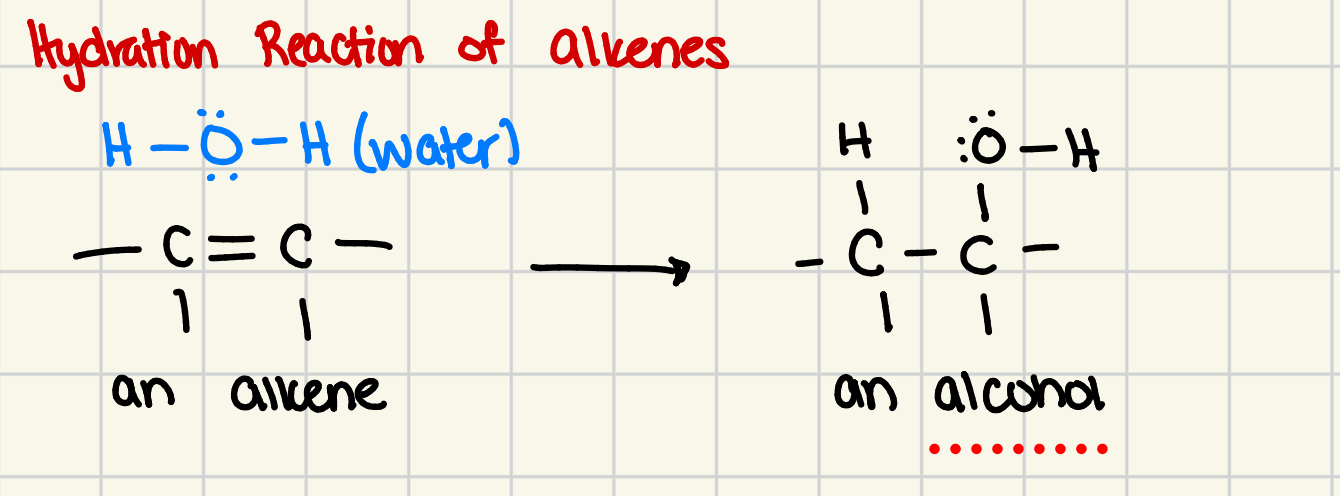
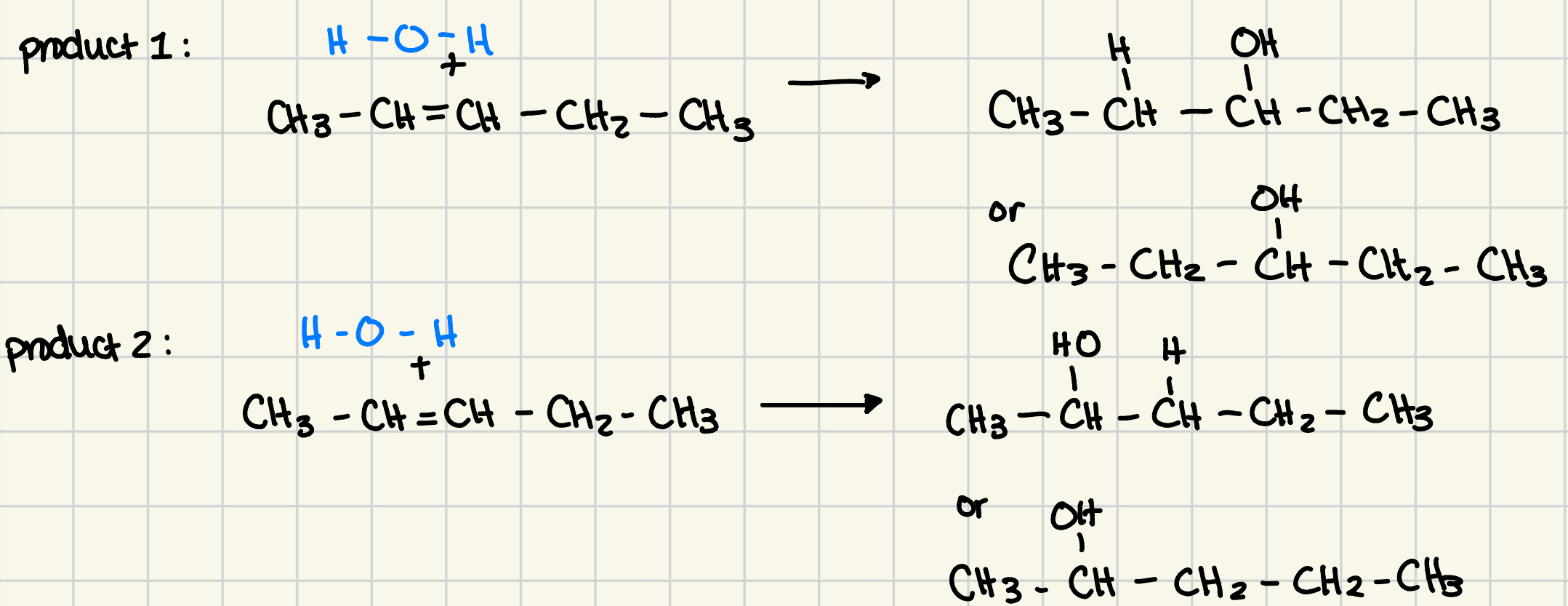
many alkenes produce 2 hydration reactions
the hydroxyl group can be bonded to either side of original alkene group (the double bond)
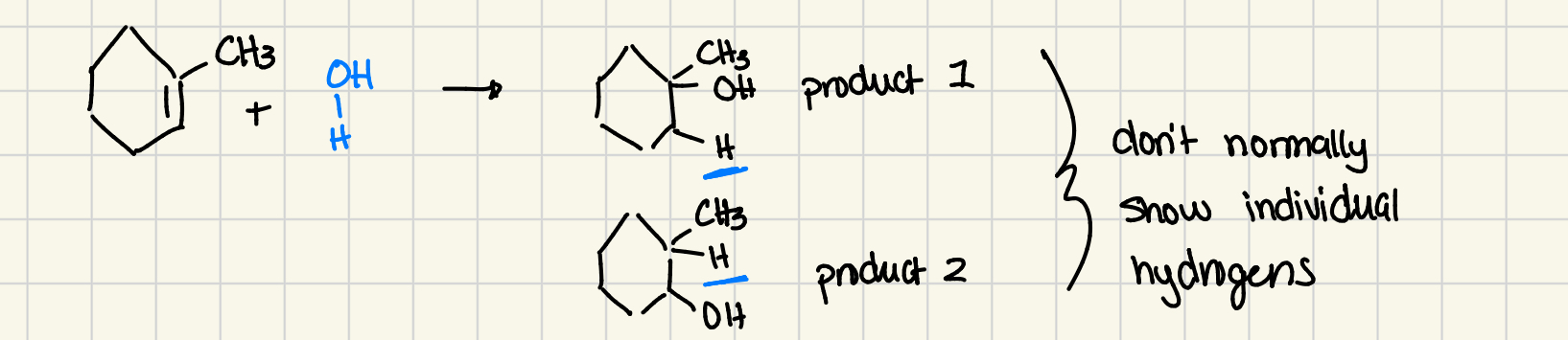
cycloalkenes can be hydrated
can react with water to form alcohol
double bond becomes single bond, H and OH become attached to the ring
symmetrical alkenes
able to produce only 1 hydration product
if 2 sides of the alkene are identical, we obtain the same alcohol regardless
enzyme
a protein that catalyzes a chemical reaction; holds the water molecule in place so it can only react with the alkene grp in the correct way
roles of enzymes
speeds up reactions
ensure that correct product is formed whenever 2 or more products are possible, can ensure the H and OH are placed in correct orientation
using IUPAC to name alcohol
name the hydrocarbon framework
identify the functional grp by modifying the ending of the alkane name
add a number to tell where the functional grp is located
step 2
to identify the alcohol grp, we replace the “-e” at the end of the alkane name with '“-ol”
2 simplest alcohols are
methanol
ethanol
step 3
have more than one possible location for our alcohol group
add the # before rest of name to tell us which carbon atom is bonded to functional grp
cyclic alcohol
ring of carbon atoms attached to a hydroyxl grp
naming cyclic alcohols
change the end of the name of the corresponding hydrocarbon from “-e” to “-ol”
do not use #’s
drawing the structure of an alcohol
draw hydrocarbon
“-ol” ending tells us molecules has a hydroxyl grp, then count where the hydroxyl grp is
then add enough hydrogen atoms to achieve all four bonds
alcohols commonly used trivial names
(names usually contain name of alkyl group followed by alcohol)
methyl alcohol (methanol)
ethyl alcohol (ethanol)
isopropoyl alcohol (2 - propanol)
propertites of alcohol
polar O-H bond allows alcohols to form hydrogen bonds
hydrogen atom from one alcohol grp is attracted to the oxygen atom of a second alcohol grp
boiling point of alcohol is higher than corresponding alkane
alcohols are more soluble in water than hydrocarbons are
alcohol boiling points
BP is higher than corresponding alkane because they have stronger attractions due to their hydrogen bonds
solubility of alcohols
more soluble in water than hydrocarbons
depends on size of carbon chain
hydroxyl grp is
hydrophillic
hydrocarbon portion is
hydrophobic
if the hydrophobic region is small
ability of hydroxyl group to form hydrogen bond dominates
high solubility
if the hydrophobic region is large
its properties dominate and compound behaves more like an alkane
low solubility
dehydration reaction
a reaction where an alcohol breaks down into an alkene and a molecule of water
reverses hydration reaction
hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl grp must be attached to neighboring carbon atoms, removing these allows the 2 carbon atoms to form an additional bond (double bond)
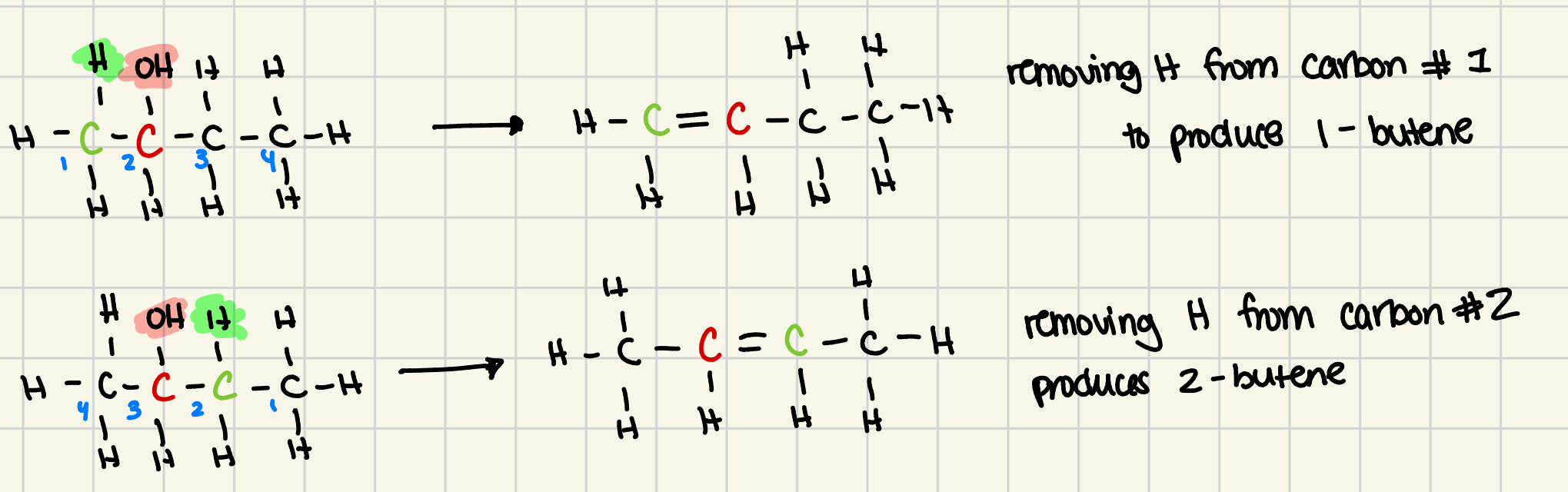
dehydration example (1-propanol)
remove OH from carbon #1
then have to remove hydrogen from neighboring carbon #2
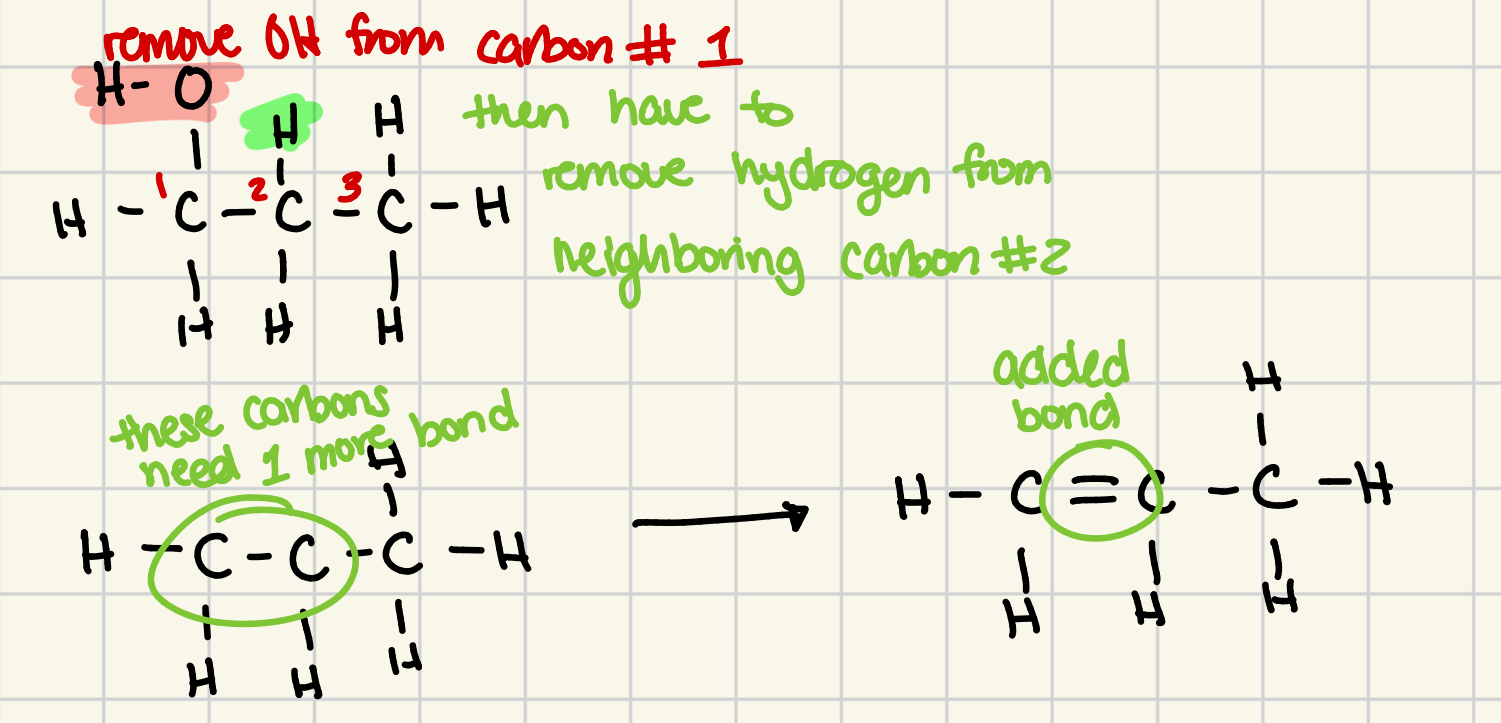
dehydration reactions form more than one product
if an alcohol has more than one carbon atom next to the functional grp, it can usually yield more than one dehydration product
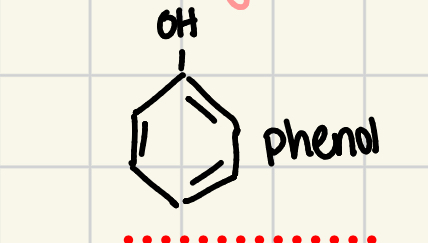
phenol
organic compound that contains a benzene ring bonded to a hydroxyl group (also called carbolic acid)
hydroxyl grp can form hydrogen bonds so have high BP and dissolve well in water
can occur in more complex molecules
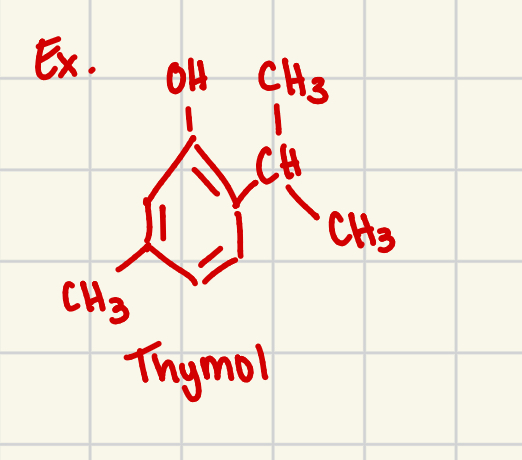
phenol is a functional grp
can occur in more complex molecules
ex. thymol
thiols
an organic compound that contains a SH group bonded to an alkyl group
oxygen atom of hydroxyl group is replaced by sulfur
cannot form hydrogen bonds, so low BP and less soluble in water
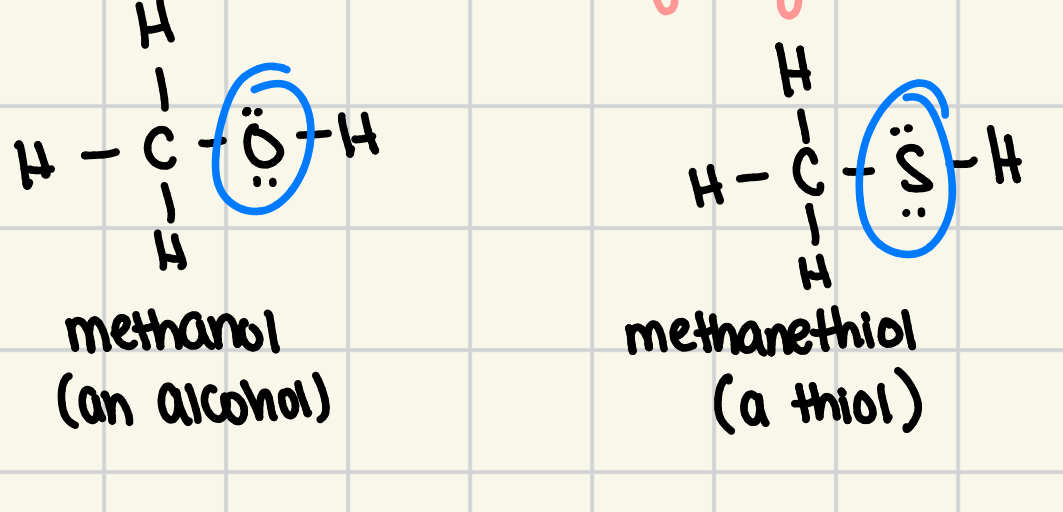
thiols cannot form
hydrogen bonds… so they have low BP and are less soluble in water
increasing solubility of an alcohol
by adding more hydroxyl groups
water solubility increases as we add hydrophilic groups to a carbon framework
solubility of any organic compound depends on
# of hydrophilic groups
locations of those groups
structure and size of carbon skeleton
solubility trends (general statements)
compounds with hydrogen bonding group (hydrophilic grp) dissolves better than compounds that cannot form hydrogen bonds, regardless of sizes of molecules
if 2 compounds have same hydrophilic grp, the molecule with the SMALLER carbon framework is more soluble
if 2 compounds have the same carbon framework, the molecule with MORE hydrophilic groups is the more soluble
the hydroxyl grp in alcohols are not
acidic or basic
how to recognize a true hydroxide ion in the formula of a compound
metallic element
metallic element
compounds that contain hydroxide ions also contain a metallic element, which forms a positively charged ion when dissolved in water
ex. KOH, Ca(OH)2 , Al(OH) 3
chiral
an object that cannot be superimposed on its mirror image
(has left and right versions that don’t match ex. hands)
superimposed
you can put one thing on top of another and they match perfectly
achiral
identical to and superimposable on its mirror image (nose)
many chemical compounds are chiral
alcohols can have 2 possible forms that are mirror images of each other
entatiomers
mirror image forms of a compound that are not superimposable
type of stereoisomer where compound has the same atoms, connected the same way, are mirror images but cannot be stacked exactly ontop of each other
how can we recognize chiral molecules (chiral carbon molecules)
if a molecule contains a carbon atom that is bonded to FOUR DIFFERENT groups of atoms

example of not chiral molecule
1st and 3rd carbon their 3 grps are identical to each other
2nd carbon is not chiral because 2 bonded grps are identical
