BIOLOGY FLASHCARDS FOR TOP MARKS ABOUT EVERYTHING
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
184 Terms
What is an example of a free living nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
Azotobacter
What is an example of a mutualistic nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
Rhizobium
What is an example of nitrifying bacteria that converts ammonium ions to nitrite?
Nitrosomonas
What is an example of a nitrifying bacteria that converts nitrite to nitrate?
Nitrobacter
What is selection pressure?
Selection pressure is an external factor in an environment that influences an organism's reproductive success, favoring individuals with certain traits while disadvantaging others
What is the equation to caculate cell divison?
N=N0*2n Where N is original number of cells and n is number of cell divisions that have occurred.
What is selection pressure?
A selection pressure is an environmental factor that influences an organism's ability to survive and reproduce, driving natural selection
What moves deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs?
Pulmonary artery
What brings oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs?
Pulmonary vein
Where do arteries take blood and where do veins take blood?
Veins take blood towards the heart and arteries take blood away from the heart.
Where does the aorta take blood?
Oxygenated blood from the left ventricle in the heart to the rest of the body.
Where does the vena cava take blood?
Deoxygenated blood from the rest of the body towards the right atrium in the heart.
Where does renal vein carry blood to?
Deoxygenated blood towards the right atrium in the heart from the kidneys.
Where does renal artery carry blood to?
Oxygenated blood from the left ventricle towards the kidneys.
What is partial pressure?
The partial pressure of oxygen is a measure of oxygen concentration. Partial pressure is measured in kilopascal (kPa). The greater the concentration of dissolved oxygen in a cell, the greater the partial pressure. Haemoglobin has different affinities for oxygen depending on its partial pressure.
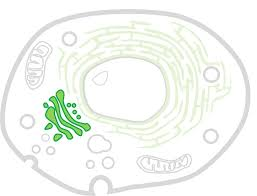
What is this called and what is its function?
The golgi body and it processes, packages and modifies proteins and lipids to be transported to their final destination in or outside of the cell.
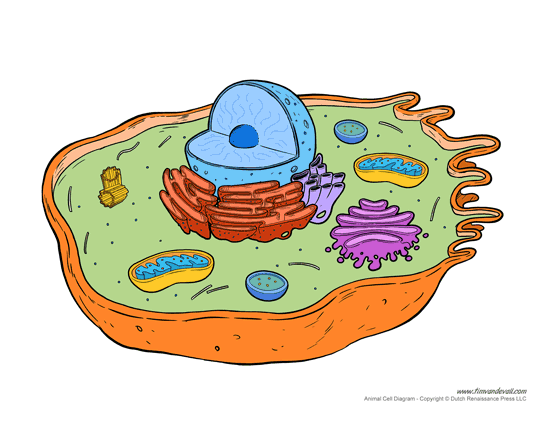
What is this red organelle called and what is its function?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum and it is embedded with ribosomes to allow it to carry out protein synthesis such as modification and folding. While specifically it receives new proteins synthesized by its attached ribosomes, further folds them into their correct 3D shapes, and modifies them by adding carbohydrates (glycosylation) to create glycoproteins.
What elements are present in triglycerides, cellulose and antibodies?
Triglycerides/ C,H,O
Cellulose/ C,H,O
Antibodies/ C,H,O,N,S
How to test for lipids in a sample?
Firstly add ethanol to a sample and shake well.
Then add in equal parts water and a positive result will have a white milky emulsion form.
How to test for reducing sugars?
Add benedict’s reagent, heat in a water bath for 80 degrees celsius for 5 minutes.
A positive result is indicated by the solution turning brick red (can be blue,green,yellow or orange depending on concentration).
How to test for non-reducing sugars?
Add benedict’s reagent and heat in a water bath at 80 degrees celsius for 5 minutes. If result remains blue continue to next steps.
Add dilute hydrochloric acid (HCI) and heat to hydrolyse glycosidic bonds.
Neutralise with sodium hydrogen carbonate which is alkaline.
Repeat the Benedict’s test and a positive result will show a change in colour from blue to brick red.
How to test for starch?
Add iodine solution to the sample
A positive result is indicated by a change in colour from orange-brown to black
How to test for proteins?
Add biuret reagent which contains sodium hydroxide and copper sulphate to sample.
Positive result indicating by change in colour from light blue to purple.
Describe the processes involved with transcription?
Firstly, RNA polymerase breaks the hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs separating the DNA strands and exposing the bases.
Next, RNA polymerase adds RNA nucleotides to complementary bases on one strand of DNA called the template strand.
After the nucleotides are added by RNA polymerase, the DNA helix behind is reattached.
RNA polymerase continues along the strand forming phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides until the pre-mRNA is completed
The pre-mRNA strand and RNA polymerase detach, leaving behind the original DNA helix and a complete strand of mRNA.
What is the speed of an action potential travelling down the axon called?
The speed of conductance
What are the two main purposes of the refractory period?
To ensure that action potentials are unidirectional and only travel away from the receptor.
To ensure action potentials are discrete and separate as they travel along the axon of neurons.
How sensitive are rod and cone cells to light?
Rod cells are very sensitive to light and cone cells and cone cells are less sensitive to light, requiring bright light.
What type of vision do cone and rod cells provide?
Rod cells provide black and white vision and cone cells provide colour vision (red,green,blue cones)
How does visual acuity differ between rod cells and cone cells?
Visual acuity is lower in rod cells providing poor detail, whilst con cells have high acuity providing fine detail.
What is visual acuity?
Visual acuity is a measure of how clearly and sharply you can see details
How are rod cells and cone cells distributed in the eye?
Rod cells are mainly found in the peripheral retina ; absent from the fovea. Meanwhile cone cells are highly concentrated in the fovea; fewer in the peripheral retina.
What photopigments are in rod and cone cells?
Rod cells have rhodopsin and cone cells have iodopsins (three types, each sensitive to different wavelengths)
How many neural connections do rod and cone cells have?
Rod cells have high convergence- many rods connect to one bipolar neuron. Meanwhile cone cells have low convergence- often one cone to one bipolar neuron.
Number of cone and rod cells in the retina?
There are 120 million rod cells in the human retina and about 6 million conce cells.
What does the eye’s structure consist of?
The eye's structure involves three layers: the outer fibrous (sclera, cornea), middle vascular (choroid, ciliary body, iris), and inner neural (retina with rods/cones, optic nerve) layers
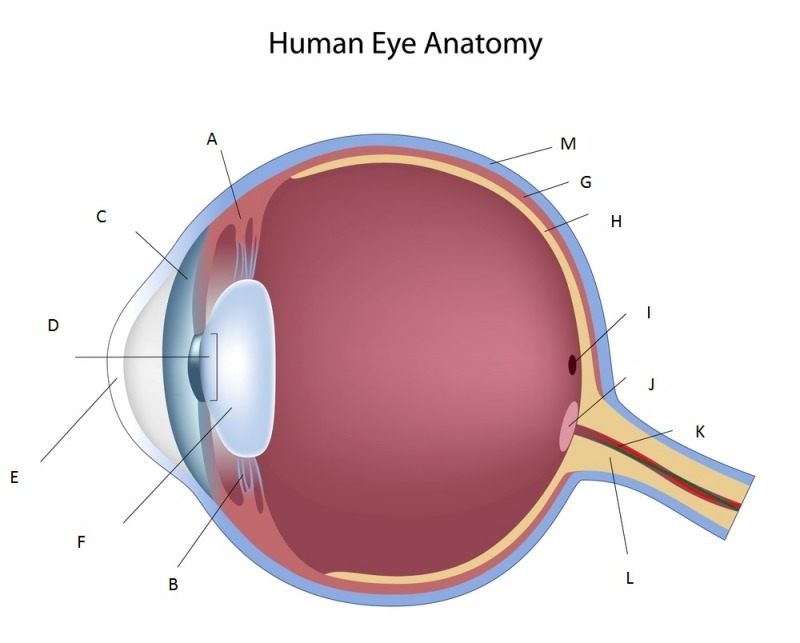
Label these features
Define resting potential and threshold potential
Resting potential: Membrane potential at rest (~–70 mV).
Threshold potential: The critical level (~–55 mV) the membrane must reach for an action potential to occur.
Define depolarization
The neuron membrane becomes less negative than the resting potential (towards 0 mV).
Voltage-gated Na⁺ channels open and Na⁺ ions diffuse into the cell down a concentration gradient.
Associated with the rising phase of an action potential.
Define repolarization
The membrane potential returns toward the resting potential after depolarisation.
Caused by K⁺ ions diffusing out of the cell through voltage-gated K⁺ channels.
Associated with the falling phase of an action potential.
Define hyperpolarization
The membrane potential becomes more negative than the resting potential.
Happens when K⁺ channels remain open too long or Cl⁻ enters.
Occurs during the after-hyperpolarization phase, contributing to the refractory period.
Describe the process of a synapse
Firstly an action potential arrives at the presynaptic neuron and causes the voltage gated calcium
What enzyme breaks down acetylcholine?
Acetylcholinesterase
Which part of the brain is the cardiovascular centre located?
The medulla oblongata.
What neuron connects the brain to the adrenal gland?
The neuron that connects the brain (via the spinal cord) to the adrenal gland is a preganglionic sympathetic neuron
What does stimulating the preganglionic sympathetic neuron do?
Leads to rapid and mass secretion of hormones triggering the fight or flight response
What neuron connects cardiovascular center of brain to sinoatrial node?
The neurons that connect the cardiovascular center in the brain (medulla oblongata) to the sinoatrial (SA) node are the parasympathetic neurons (via the vagus nerve) and sympathetic neurons (via the cardiac accelerator nerves).
Effects of stimulating the parasympathetic neurons (via the vagus nerve) and sympathetic neurons (via the cardiac accelerator nerves).
Stimulating the vagus nerve decreases the heart rate (bradycardia). Acetylcholine binds to muscarinic receptors on the SAN, making the membrane potential more negative (hyperpolarizing it) and reducing the frequency of electrical impulses generated by the SAN, thus slowing the heart rhythm.
Describe how an impulse reaches the base of the ventricles of the heart from the sinoatrial node.
It spreads through the atria / right atrium / through cardiac muscle;
to the atrioventricular node;
then through conduction fibres / bundle of His
What gradient do sodium ions move down to enter post synaptic neuron?
Electrochemical gradient
How many receptor sites does each sodium channel have?
Three receptor sites for neurotransmitters which cause them to open
What is the sequence of events called occuring between the pre and post synaptic neuron?
Synaptic transmission
What do mitochodnria do in the pre-synaptic neuron?
Enable the movement of acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles which fuse with the membrane and release the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft.
What enzyme breaks down acetylcholine?
Acetylcholinesterase
What reaction does acetylcholinesterase uses to break down acetylcholine?
Hydrolysis
Why is hydrolysing acetylcholine important?
It allows for discrete action potentials to occur which are seperate.
How do choline, ethanoic acid enter the cell and how does acetylcholine enter the vesicle?
Choline enters the cell via facilitated diffusion as it is charged.
Ethanoic acid enter the cell via simple diffusion as it is not charged.
Acetylcholine enters the vesicle carrying it by active transport
What does the synaptic knob have a lot of?
Mitochondria so ATP can be provided to the cells allowing active transport of acetylcholine into vesicles to occur quickly and reduce time between synaptic transmissions.
How is acetylcholine formed?
Ethanoic acid and choline are combined by an enzyme to form the neurotransmitter.
Describe the 8 stages of a cholinergic synapse?
1: An action potential arrives at the presynaptic neurone and causes the presynaptic membrane to become depolarised
2: Voltage-gated calcium channels open. Calcium ions diffuse into the synaptic knob, which causes synaptic vesicles to move down the synaptic knob.
3: Synaptic vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane, which leads to acetylcholine being released into the synaptic cleft.
4: Acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft, where it binds to receptor sites on sodium channels, causing them to open.
5: Sodium ions diffuse into the postsynaptic neurone, which leads to an action potential inside the postsynaptic neurone.
6: Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine into choline and ethanoic acid.
7: Choline and ethanoic acid are taken back into the presynaptic neurone, where they're recombined to form acetylcholine.
8: Acetylcholine is transported into synaptic vesicles using ATP.
What does acetylcholine bind to on the post synaptic neuron?
Receptor sites
What is the difference between cholinergic synapses and neurotransmitter junctions?
Neurotransmitter junctions are between a muscle cell and a motor neuron (synaptic knob/pre-synaptic), a range of neurotransmitters are used so refer to them as neurotransmitters.
Meanwhile cholinergic synapses use acetylcholine so refer to the neurotransmitter as this, between two neurons.
How many neurotransmitter molecules does the voltage gated sodium ion channel bind to?
2
What are neurotransmitters that lead to an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron called and what is the neuron called once this occurs.
Excitatory neurotransmitter and an excitatory synapse.
What are neurotransmitters that prevent an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron forming called and what is the synapse called.
Inhibitory neurotransmitter and its an inhibitory synapse.
What happens in an inhibitory syanpse?
The same start but then the inhibitory neurotransmitter binds to the voltage gated chloride ion channels on the postsynaptic neuron causing them to open. After that chloride ions move into the postsynaptic neuron making it more negative and hyperpolarization takes place preventing an action potential occurring.
Are neuromuscular junctions what does a synapse cause and is it inhibitory or excitatory neurotransmitters?
Muscle contraction occurs and the neurotransmitters are always excitatory.
Are cholinergic synapses excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitters?
Can be either. (Christ is King)
What are the five steps when investigating the effect of a named drug on synaptic transmission?
1. Identify the main target structure.
2. Recall the role of the target structure.
3. Recall steps that follow after target structure.
4. Identify the effect of the drug on the target structure.
5. Identify the effect of the drug on the whole synaptic transmission.
Where and what is the pacinian corpuscle located?
Deep under the animals skin and made up of tissue layers and a sensory neuron.
What do pacinian corpuscles respond to?
Mechanical pressure, shaking hands with someone for example
How does an action potential occur for pacinian corpuscles.
First, the membrane of the sensory neuron contains stretch-mediated sodium ion channels.
When the pressure compresses layers in the Pacinian corpuscle, these ion channels open.
An influx of sodium ions causes the inside of the neuron to become depolarised. This is called a generator potential.
When many of these potentials build up, the threshold value is reached, triggering an action potential. This action potential is sent to the central nervous system.
What is the layer of tissue at the back of the human eye that detects light from the environment?
The retina.
What is the centre of the retina called?
The fovea
What nerve do sensory neurons in the eye connect to?
Optic nerves
What do optic nerves do?
Carry impulses from the sensory neurons to the brain.
Which light receptor cell in the human retina relies on many generator potentials to trigger a single action potential?
Rod cells. This happens because many rod cells are connected to a single sensory neuron so these cells trigger many generator potential in order to reach the action potential threshold and cause an action potential.
What are rod cells sensitive to and what do they interpret?
They are sensitive to low light intensities, interpret all colours in shades of black and white and percieve images in less detail than cone cells do.
What three colours are associated with cone cells and why?
Green, red and blue. This is because these optical pigments allow these colours to be interpreted by cone cells.
What is resting potential?
When potential difference across a neuron is not stimulated and no action potential is occurring.
How is resting potential maintained across a neurone?
One way is the sodium potassium pump which actively transports 3 sodium ions out of the neuron and 2 potassium ions into the membrane against their concentration gradients using ATP. This makes the outside of the neuron more positive and the inside nerone less so.
The other factor is how there is many open potassium leak channels, allowing K+ to diffuse out, down its concentration gradient, further increasing negativity inside.
Sodium (Na+): Most sodium channels are closed, so Na+ leaks back in very slowly, preventing the cell from losing its negative charge and a lower quantity than potassium ions.
These establish a steady electrochemical gradient, keeping the inside of the neuron relatively negative compared to the outside.
Why would an antibiotic that combines potassium ions into large complexes impact potential difference inside the membrane?
•As the concentration of valinomycin increases, the membrane becomes depolarised/membrane potential becomes less negative/more positive.
At low concentrations, not enough valinomycin to combine all K+ ions together.
•Na+ K+ pump (maintains resting potential);
At high concentrations of valinomycin, K+ ion complexes too large to pass through Na+ K+ pump.
(Leads to) more Na+ inside the cell and more K+ outside the cell (increasing membrane potential).
Why would a antibiotic that inhibits ATP synthase impact respiration?
Oligomycin prevents production of ATP, in oxidative phosphorylation.
Leads to less energy being released/inhibits respiration;
Explain how the loss of mitochondrial cristae impacts ATP production in neurons and suggest how this may impair memory function in Alzheimer’s patients?
The loss of mitochondrial cristae results in less oxidative phosphorylation so less ATP is produced. This means that there will be less ATP available for the sodium potassium pump which may impact memory function.
Why does less mitochondrial cristae impact ATP production?
It increases the surface area available for the processes of oxidative phosphorylation and the electron transport chain which is the main driver of ATP production.
What is the refractory period and what is its purpose?
The period after an action potential;
• (When) the voltage-gated sodium channels are closed;
(So) movement of sodium ions into the axon is prevented;
(So) an additional action potential is prevented;
• Ensures discrete impulses;
What factors affect the speed of conductance of a nerve impulse along the axon?
Myelination - insulated axon; this is because less action potentials need to be triggered across the same axon length due to the process of saltatory conduction where action potentials can only occur at nodes of ranvier as schwann cells insulate the axon so the nerve impulse jumps node of ranvier to node of ranvier.
Diameter of the axon. This is because a larger diameter means a larger surface area for diffusion which leads to reduced electrical resistance, increasing the speed of conductance.
Temperature, this is because colder conditions means ions have less kinetic energy and warmer temperatures do the opposite which impacts speed of conductance.
Why is it important for acetylcholine to be broken down?
To prevent voltage gated sodium channels on the postsynaptic membrane permanently staying open.
This is called depolarization
What do rod cells have that increases sensitivity to light and what is its function?
Rod cells have rhodopsin and this allows for the eye to see more clearly in darkness/low light and when more red cells are present pigment of rhodopsin is higher.
What is the difference in relaying synapses in rod and cone cells?
Single cone cells form synapses with a single bipolar cell but multiple rod cells form synapses with one bipolar cell.
What is a bipolar cell in the eye?
Bipolar cells are crucial interneurons in the retina, acting as messengers that transmit visual signals from photoreceptors (rods and cones) to retinal ganglion cells, forming the primary pathway for vision.
What is the eye pathway in receiving light?
Light enters the cornea, being controlled by the iris and focused onto the lens in the retina. Then photoreceptors in the eye (rod and cone cells) convert light to nerve impulses. These impulses travel via bipolar cells to the optic nerve which transmits them to the brain for processing.
What is tropism?
Where part of a plant has a directional growth response to a stimulus.
What is it called when a plant moves towards and away from a stimulus?
Positive tropism where a plant moves towards a stimulus
Negative tropism where a plant moves away from a stimulus.
What is tropism where the stimulus is light called?
Phototropism.
What is tropism where gravity is the stimulus called?
Geotropism or gravitropism.
What are the things that dictate how a plant responds to a stimulus?
Plant growth factors
Which plant growth factor regulates phototropism and geotropism?
IAA a type of auxin
Where is IAA synthesised?
Where plants are actively growing so usually at the tip of roots and tip of shoots.
How does IAA move?
IAA moves from the tip of the root and the tip of the shoot towards the other areas of the plant where it dictates how the plant responds to stimulus and the form of tropism it exhibits.
What does IAA do?
It controls how quickly a cell grows in length as it either stimulates cell elongation or inhibits it.